大三下每日打卡007
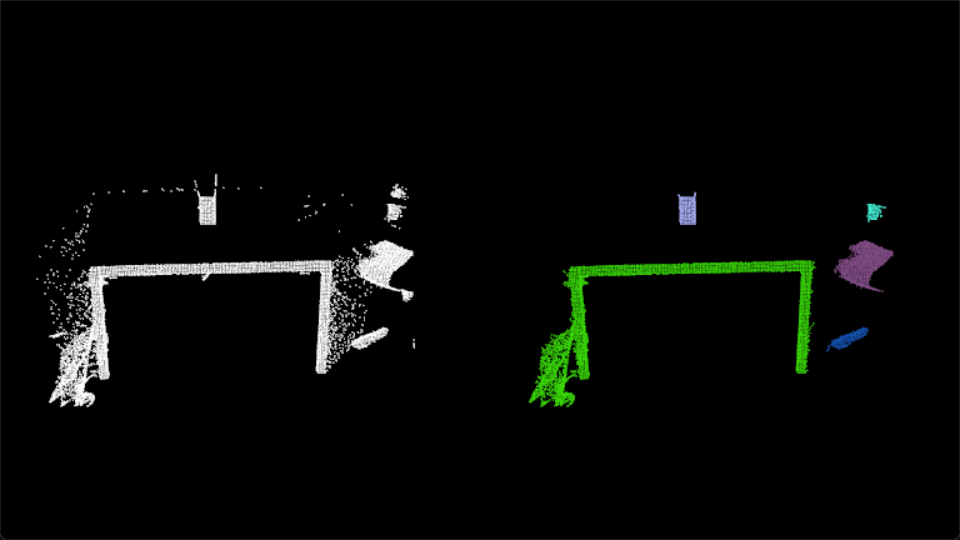
把pcl配置进visual studio2022了,非常麻烦,下面是我用欧式聚类算法得到的效果图
1. 安装 PCL 首先,确保您已经正确安装了 PCL。您可以通过以下几种方式进行安装: 通过 PCL 官网安装:下载并安装 PCL。 通过 vcpkg 安装:如果您熟悉 vcpkg,可以使用以下命令安装 PCL: bash 复制 编辑 vcpkg install pcl 2. 创建 Visual Studio 项目 打开 Visual Studio,点击 "Create a new project"。 选择 "Console App" 模板,确保选择 C++ 语言。 为项目命名并选择存储位置。 3. 配置项目以使用 PCL 库 a. 配置包含目录 右键点击项目,选择 "Properties"。 在 "Configuration Properties" 下,选择 "VC++ Directories"。 在 "Include Directories" 中,添加 PCL 的 include 目录路径。假设 PCL 安装路径为 C:\Program Files\PCL 1.11.1,则包含目录为: makefile 复制 编辑 C:\Program Files\PCL 1.11.1\include\pcl-1.11 b. 配置库目录 在 "Configuration Properties" 下,选择 "Linker" -> "General"。 在 "Additional Library Directories" 中,添加 PCL 的 lib 目录路径: vbnet 复制 编辑 C:\Program Files\PCL 1.11.1\lib c. 配置库文件 仍在 "Linker" 下,选择 "Input"。 在 "Additional Dependencies" 中添加 PCL 所需的库。例如,添加: vbnet 复制 编辑 pcl_common.lib pcl_io.lib pcl_filters.lib pcl_features.lib pcl_segmentation.lib pcl_visualization.lib pcl_kdtree.lib pcl_sample_consensus.lib freeglut.lib opengl32.lib 注意:不同的 PCL 版本和安装方式可能会有不同的库文件,确保添加与您的安装匹配的库。 d. 配置 OpenGL(可选) PCL 使用 OpenGL 进行可视化,因此您还需要配置 OpenGL 相关的库: 在 "Additional Dependencies" 中添加 freeglut.lib 和 opengl32.lib(这些库通常随 PCL 一起安装)。 4. 编写和添加代码 将您的代码(例如您提供的代码)添加到项目中。 右键点击项目,选择 "Add" -> "New Item" -> "C++ File (.cpp)"。 将您的代码粘贴到新创建的 .cpp 文件中。 如果需要,还可以添加 PCD 文件路径,确保文件可以被读取。 5. 编译并运行 点击 "Build" -> "Build Solution"(或按 Ctrl+Shift+B)来编译项目。 如果一切配置正确,您应该能够编译并运行代码。 6. 确保 PCD 文件存在 确保您代码中的 table_scene_lms400.pcd 文件存在,并且路径正确。可以将 PCD 文件放置在项目的同一目录下,或者使用完整的文件路径,如: cpp 复制 编辑 reader.read("C:\\path_to_pcd_file\\table_scene_lms400.pcd", *cloud); 小结 通过上述步骤,您可以在 Visual Studio 中手动配置项目以使用 PCL,而无需 CMake。只需确保正确配置包含目录、库目录和依赖项,您就能成功运行代码。如果遇到任何问题,随时告诉我,我会帮助您解决!
PATH=D:\tool\PCL 1.12.0\bin;D:\tool\PCL 1.12.0\3rdParty\VTK\bin;D:\tool\PCL 1.12.0\3rdParty\FLANN\bin;D:\tool\PCL 1.12.0\3rdParty\OpenNI2\Tools;D:\tool\PCL 1.12.0\3rdParty\Qhull\bin D:\tool\PCL 1.13.0\lib D:\tool\PCL 1.13.0\3rdParty\Boost\lib D:\tool\PCL 1.13.0\3rdParty\FLANN\lib D:\tool\PCL 1.13.0\3rdParty\OpenNI2\Lib D:\tool\PCL 1.13.0\3rdParty\Qhull\lib D:\tool\PCL 1.13.0\3rdParty\VTK\lib BOOST_USE_WINDOWS_H NOMINMAX _CRT_SECURE_NO_DEPRECATE D:\tool\PCL 1.13.0\include\pcl-1.13 D:\tool\PCL 1.13.0\3rdParty\Boost\include\boost-1_80 D:\tool\PCL 1.13.0\3rdParty\Eigen\eigen3 D:\tool\PCL 1.13.0\3rdParty\FLANN\include D:\tool\PCL 1.13.0\3rdParty\OpenNI2\Include D:\tool\PCL 1.13.0\3rdParty\Qhull\include D:\tool\PCL 1.13.0\3rdParty\VTK\include\vtk-9.2 #include <pcl/ModelCoefficients.h> #include <pcl/point_types.h> #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/filters/extract_indices.h> #include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h> #include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h> #include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree.h> #include <pcl/sample_consensus/method_types.h> #include <pcl/sample_consensus/model_types.h> #include <pcl/segmentation/sac_segmentation.h> #include <pcl/segmentation/extract_clusters.h> #include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h> bool isPushSpace = false; // 键盘事件 void keyboard_event_occurred(const pcl::visualization::KeyboardEvent& event, void* nothing) { if (event.getKeySym() == "space" && event.keyDown()) { isPushSpace = true; } } int main(int argc, char** argv) { // 从PCD文件中读取点云数据 pcl::PCDReader reader; pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>), cloud_f(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>); reader.read("C:\\Users\\huxiang\\Downloads\\table_scene_lms400.pcd", *cloud); std::cout << "PointCloud before filtering has: " << cloud->points.size() << " data points." << std::endl; pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("Cluster Extraction"); // 注册键盘事件 viewer.registerKeyboardCallback(&keyboard_event_occurred, (void*)NULL); int v1(1); int v2(2); viewer.createViewPort(0, 0, 0.5, 1, v1); viewer.createViewPort(0.5, 0, 1, 1, v2); // 创建滤波对象: 使用下采样,叶子的大小为 1cm pcl::VoxelGrid<pcl::PointXYZ> vg; pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>); vg.setInputCloud(cloud); vg.setLeafSize(0.01f, 0.01f, 0.01f); vg.filter(*cloud_filtered); std::cout << "PointCloud after filtering has: " << cloud_filtered->points.size() << " data points." << std::endl; viewer.addPointCloud(cloud, "cloud1", v1); viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_filtered, "cloud2", v2); // 渲染10秒再继续 viewer.spinOnce(10000); // 创建平面分割对象 pcl::SACSegmentation<pcl::PointXYZ> seg; pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers(new pcl::PointIndices); pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients(new pcl::ModelCoefficients); pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_plane(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>()); pcl::PCDWriter writer; seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true); seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE); seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC); seg.setMaxIterations(100); seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.02); // 把点云中所有的平面全部过滤掉,重复过滤,直到点云数量小于原来的0.3倍 int i = 0, nr_points = (int)cloud_filtered->points.size(); while (cloud_filtered->points.size() > 0.3 * nr_points) { // Segment the largest planar component from the remaining cloud seg.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered); seg.segment(*inliers, *coefficients); if (inliers->indices.size() == 0) { std::cout << "Could not estimate a planar model for the given dataset." << std::endl; break; } // Extract the planar inliers from the input cloud pcl::ExtractIndices<pcl::PointXYZ> extract; extract.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered); extract.setIndices(inliers); extract.setNegative(false); // Write the planar inliers to disk extract.filter(*cloud_plane); std::cout << "PointCloud representing the planar component: " << cloud_plane->points.size() << " data points." << std::endl; // Remove the planar inliers, extract the rest extract.setNegative(true); extract.filter(*cloud_f); // 更新显示点云 viewer.updatePointCloud(cloud_filtered, "cloud1"); viewer.updatePointCloud(cloud_f, "cloud2"); // 渲染3秒再继续 viewer.spinOnce(3000); cloud_filtered = cloud_f; } viewer.removePointCloud("cloud2", v2); // 创建KdTree对象作为搜索方法 pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>); tree->setInputCloud(cloud_filtered); std::vector<pcl::PointIndices> cluster_indices; pcl::EuclideanClusterExtraction<pcl::PointXYZ> ec; ec.setClusterTolerance(0.02); // 2cm ec.setMinClusterSize(100); ec.setMaxClusterSize(25000); ec.setSearchMethod(tree); ec.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered); // 聚类抽取结果保存在一个数组中,数组中每个元素代表抽取的一个组件点云的下标 ec.extract(cluster_indices); // 遍历抽取结果,将其显示并保存 int j = 0; for (std::vector<pcl::PointIndices>::const_iterator it = cluster_indices.begin(); it != cluster_indices.end(); ++it) { // 创建临时保存点云族的点云 pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_cluster(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>); // 通过下标,逐个填充 for (std::vector<int>::const_iterator pit = it->indices.begin(); pit != it->indices.end(); pit++) cloud_cluster->points.push_back(cloud_filtered->points[*pit]); // 设置点云属性 cloud_cluster->width = cloud_cluster->points.size(); cloud_cluster->height = 1; cloud_cluster->is_dense = true; std::cout << "当前聚类 " << j << " 包含的点云数量: " << cloud_cluster->points.size() << " data points." << std::endl; std::stringstream ss; ss << "cloud_cluster_" << j << ".pcd"; writer.write<pcl::PointXYZ>(ss.str(), *cloud_cluster, false); // 显示, 随机设置不同颜色,以区分不同的聚类 pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> cluster_color(cloud_cluster, rand() * 100 + j * 80, rand() * 50 + j * 90, rand() * 200 + j * 100); viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_cluster, cluster_color, ss.str(), v2); j++; } while (!viewer.wasStopped()) { viewer.spinOnce(); } return (0); } 欧式聚类算法(Euclidean Clustering)是一种将点云数据分割成不同聚类(簇)的算法。它是点云分割中的一种常用方法,旨在将距离比较近的点分为同一簇,从而识别出不同的物体或结构。这个算法主要适用于包含较小噪音和具有一定距离差异的点云数据。基本思想: (1)选择一个种子点(Seed Point)作为当前簇的起始点。 (2) 遍历所有未分类的点,计算它们与种子点的距离。如果距离小于设定的阈值,将其归为同一簇。 (3) 对于同一簇中的点,重复步骤2,将与当前簇内任一点距离小于阈值的点加入簇。 (4) 切换到下一个未分类的点,作为新的种子点,继续重复步骤2和3。 (5) 当所有点都被分类为某个簇,聚类过程结束。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号