BLOG作业-2
*/
一、前言:
(一)菜单计价程序-4,菜单计价程序-5
知识点:读写文件、字符串操作、条件语句、循环语句、函数、异常处理、时间操作等。题目的难度比较高,需要综合运用多种知识点进行解决,而且解决过程中需要考虑较多的细节和异常情况,需要进行充分的测试和调试。在处理菜单、订单和特色菜时,需要设计合适的数据类型和数据结构,便于后续的操作与处理。处理特色菜时需要注意辣度、酸度和甜度的范围,并进行四舍五入处理。对于口味度水平的计算,需要充分考虑代点菜情况,且需要按照要求输出。最后需按照输入的桌号从小到大输出每一桌的信息,并按照字母顺序依次输出每位客户需要支付的金额。需要注意的是,由于不同的四舍五入顺序可能会造成金额误差,因此需要按照特定步骤进行菜价的计算。
(二)期中考试
第一二三题------知识点:面向对象编程、类与对象、数据类型、输入输出操作、算数运算、精度控制、继承、多态和抽象类的使用、异常处理等。是比较简单的编程题,基本属于面向对象编程的基础练习。需要设计Circle和Rectangle两个类,实现计算圆的面积和矩形的面积。题目描述清晰明确,实现难度不高。需要注意输入数据的合法性,如果输入数据不合法需要输出相应的错误信息。在输出面积值时,需要保留两位小数。此外,需要注意输入时先输入图形类型选择,再输入对应的图形参数。
第四题------这道题要求对列表中的图形进行排序,重点考察的是comparable接口的使用和sort()方法的应用。还需注意输入格式和保留小数位数的问题。题目基础是继承、多态和抽象类,难度适中。需要注意,本题要求将Shape类实现Comparable接口,按图形面积进行排序。
二、设计与分析:
(1)菜单计价程序-4


(1)宏观分析
这道题是在菜单3的基础上,针对于异常情况处理的迭代版本,主要的测试样例都是各种各样的异常情况,故有以下分析:
针对异常情况,需要对输入数据进行严格的格式验证和处理,确保计算得到的结果准确无误。有以下几点:
1、需要对菜谱信息与订单信息进行区分,不处理不属于订单信息的菜谱信息。
2、需要对桌号所带时间数据进行有效性和合法性的判断,确保时间格式正确且在有效范围内。
3、需要对同一桌的点菜记录进行合并,以避免出现四舍五入的误差。
4、需要对删除操作进行重复校验,避免重复删除记录。
5、需要对代点菜的桌号进行验证,确保桌号存在且有效。
6、需要对菜谱信息中重复的菜品名进行去重,以最后一条记录为准。
7、需要对重复桌号信息进行时间段的判断,确保在同一时间段内的记录进行合并计算。
8、需要对重复桌号信息进行桌号时间有效性的判断,确保记录时间在有效时间段内,并进行合并计算。
9、需要对份额和份数进行范围的限制验证,避免数据超出范围。
10、需要对桌号进行范围和格式的限制验证,避免数据超出范围或格式不正确。
11、需要对菜品价格进行范围和格式的限制验证,避免数据超出范围或格式不正确。
12、需要对时间进行有效性和范围的限制验证,确保时间在有效范围内。
13、需要对记录数据进行格式的限制验证,避免数据格式不正确。
14、需要对点菜记录的序号进行排序,以保证顺序正确。
总之,本次作业增加了很多异常情况的处理,需要对数据进行多方面的验证和处理,确保计算出来的结果正确无误。
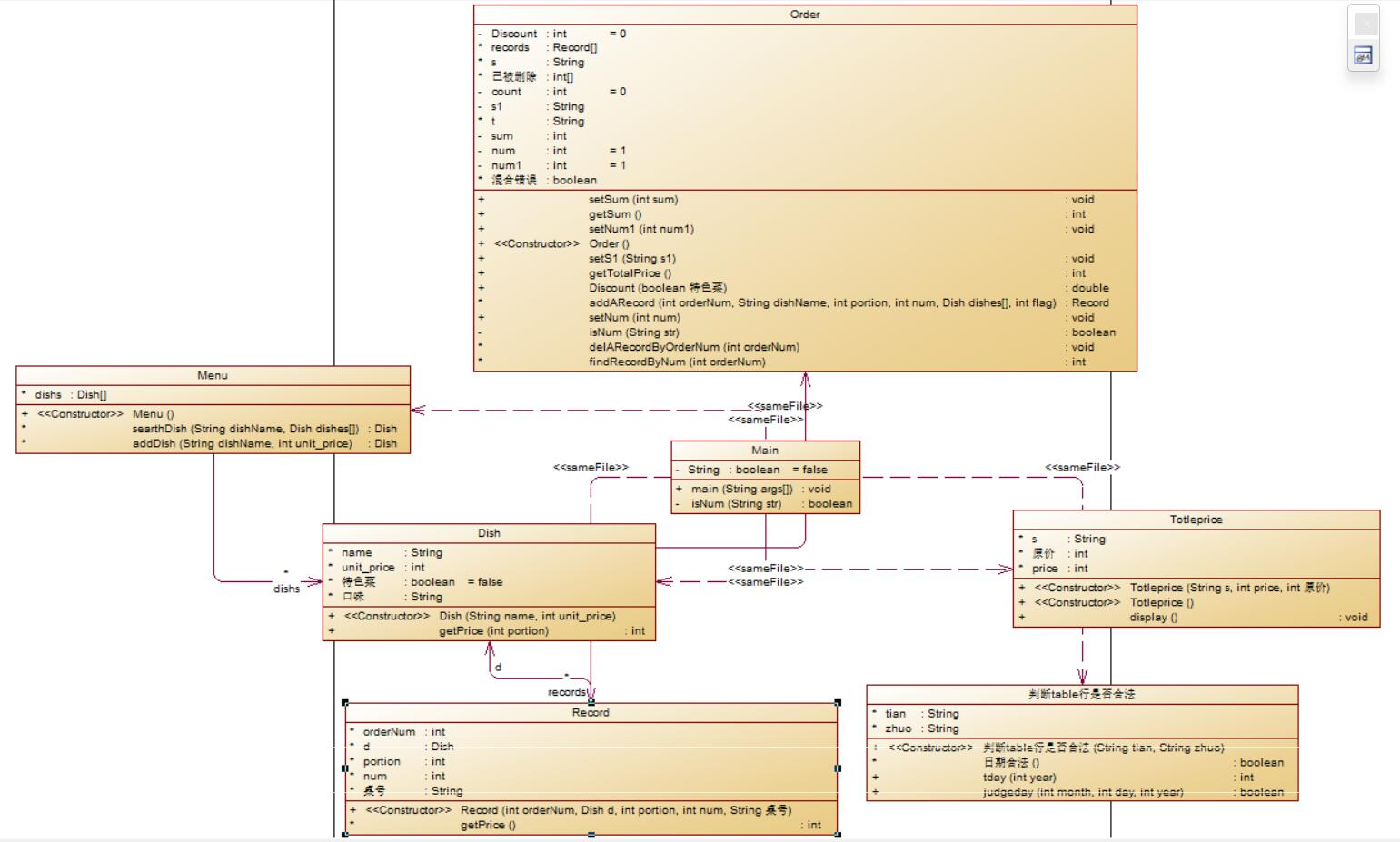
(2)类图
因为没有写出来,故只能附上类图。
(2)菜单计价程序-5

(1) 宏观分析
本题是一个比较复杂的餐厅点餐系统,需要考虑不同桌号、客户姓名、手机号码、点菜品种以及口味等因素。需要按照题目中的各种要求进行计算和输出,包括菜价的计算、折扣的计算、口味度的计算,还要考虑代点菜和多桌菜的情况,最后需 要按字母顺序输出每位客户需要支付的金额。这道题需要注意的地方较多,需要仔细阅读题目并理清题目中的逻辑。可以根据题目中已经提供的格式进行输出,但需要注意格式的准确性和排版的美观性。在处理数据时需要注意数据类型的转换和 取舍,并进行四舍五入等计算。还需要注意异常情况的处理,比如口味度的范围等。
(2)类图
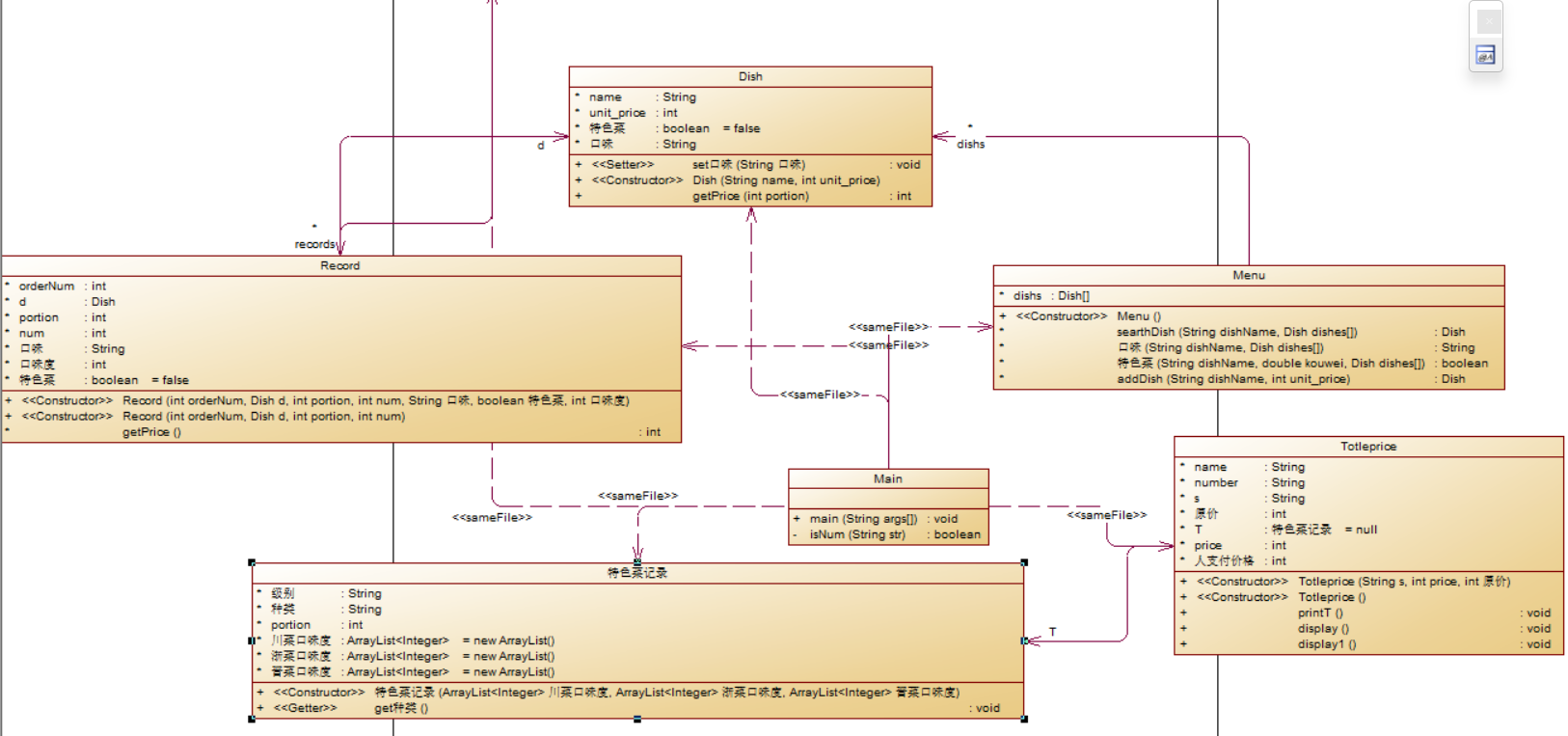
(3)源码
import java.util.*; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); Menu menu = new Menu(); Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance(); Map<Integer, Table> tables = new HashMap<>(); int tcd = 0; Table table = null; while (true) { try { String ipt = sc.nextLine(); if (ipt.equals("end")) break; String[] s = ipt.split(" "); if (s[0].equals("table") && s.length > 4) { if (s[3].length() > 10) { System.out.println("wrong format"); continue; } else if (11 != s[4].length()) { if (s[4].length() == 11) { } else { System.out.println("wrong format"); } } else { if (!s[4].matches("(^133|^135|^136|^180|^181|^189)\\d{8}$")) { System.out.println("wrong format"); continue; } } Table tb = new Table(s[5].split("/"), s[6].split("/")); if (checkTime(tb) == 1) { table = tb; table.name = s[3]; table.phone = s[4]; tcd = Integer.parseInt(s[1]); tables.put(tcd, table); System.out.println("table " + tcd + ": "); } else if (checkTime(tb) == 0) { tb.name = s[3]; tb.phone = s[4]; tcd = Integer.parseInt(s[1]); tables.put(tcd, tb); } else { System.out.println("wrong format"); } } else if (Pattern.matches("^\\d+\\s\\d+\\s\\S+\\s\\d+\\s\\d+\\s\\d+", ipt) && table != null) { // 1 1 醋浇羊肉 0 1 2 try { Dish dish = menu.find(s[2]); if (dish == null) { System.out.println(s[2] + " does not exist"); } else { if (dish.checkDegree(Integer.parseInt(s[3]))) { int tableNo = Integer.parseInt(s[0]); int ordern = Integer.parseInt(s[1]); int gg = Integer.parseInt(s[4]); int fs = Integer.parseInt(s[5]); Record rec = new Record(dish, fs, gg, Integer.parseInt(s[3])); table.otherMap.put(ordern, rec); tables.get(tableNo).DaiMap.put(ordern, rec); table.otherTableInfo.put(ordern, tableNo - 1); System.out.println(ordern + " table " + tcd + " pay for table " + tableNo + " " + rec.price); } } } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("wrong format"); } } else if (ipt.contains("T")) { Dish dish; if (ipt.contains("川")) { dish = new ChuanCai(s[0], Integer.parseInt(s[2])); dish.type = 3; } else if (ipt.contains("晋")) { dish = new JinCai(s[0], Integer.parseInt(s[2])); dish.type = 2; } else if (ipt.contains("浙")) { dish = new ZheCai(s[0], Integer.parseInt(s[2])); dish.type = 1; } else { System.out.println("wrong format"); continue; } menu.add(dish); } else if (Pattern.matches("^\\d+\\s\\S+\\s\\d+\\s\\d+\\s\\d+", ipt) && table != null) { //1 麻婆豆腐 4 1 9 try { Dish dish = menu.find(s[1]); if (dish == null) { System.out.println(s[1] + " does not exist"); } else { if (dish.checkDegree(Integer.parseInt(s[2]))) { int no = Integer.parseInt(s[0]); Record record = new Record(dish, Integer.parseInt(s[4]), Integer.parseInt(s[3]), Integer.parseInt(s[2])); table.records.put(no, record); table.ownFees += record.price; System.out.println(no + " " + dish.name + " " + record.price); } } } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("wrong format"); } } else if (s.length == 2) { if (s[1].equals("delete") && table != null) { //7 delete int i = Integer.parseInt(s[0]); if (!table.del(i)) { if (table.otherMap.remove(i) != null) { Integer t = table.otherTableInfo.get(i); tables.get(t).DaiMap.remove(i); } } // System.out.println("delete error;"); } else if (tcd == 0) { //麻婆豆腐 12 menu.add(s[0], Integer.parseInt(s[1])); } } else if (s.length == 4) if (s[0].equals("table")) { //table 1 : tom 13670008181 2023/5/1 21/30/00 } else { if (table != null) { try { //1 麻婆豆腐 2 2 Dish dish = menu.find(s[1]); if (dish == null) { System.out.println(s[1] + " does not exist"); } else if (dish.type != 0) { System.out.println("wrong format"); } else { int no = Integer.parseInt(s[0]); Record record = new Record(dish, Integer.parseInt(s[3]), Integer.parseInt(s[2])); table.records.put(no, record); table.ownFees += record.price; System.out.println(no + " " + dish.name + " " + record.price); } } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("wrong format"); } } } else if (s.length == 5 && table != null) { //1 4 麻婆豆腐 1 1 Dish dish = menu.find(s[2]); if (dish == null) { System.out.println(s[2] + " does not exist"); } else { try { int tableNo = Integer.parseInt(s[0]); int ordern = Integer.parseInt(s[1]); int heft = Integer.parseInt(s[3]); int fs = Integer.parseInt(s[4]); Record rec = new Record(dish, fs, heft); table.otherMap.put(ordern, rec); tables.get(tableNo).DaiMap.put(ordern, rec); table.otherTableInfo.put(ordern, tableNo - 1); System.out.println(ordern + " table " + tcd + " pay for table " + tableNo + " " + rec.price); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("wrong format"); } } } } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("wrong format"); } } Map<String, Integer> all = new TreeMap<>(); for (Map.Entry<Integer, Table> entryT : tables.entrySet()) { int ii = entryT.getKey(); Table t = entryT.getValue(); int year = Integer.parseInt(t.day[0]); int month = Integer.parseInt(t.day[1]) - 1; int day = Integer.parseInt(t.day[2]); int hour = Integer.parseInt(t.time[0]); cal.set(year, month, day); int week = cal.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK); float discount; if (week == 1 || week == 7) { if ((hour >= 10 && hour <= 20) || (hour == 9 && Integer.parseInt(t.time[1]) >= 30) || (hour == 21 && Integer.parseInt(t.time[1]) == 30 && Integer.parseInt(t.time[2]) == 0)) { discount = 1.0F; } else { System.out.println("table " + (ii) + " out of opening hours"); continue; } } else { if ((hour >= 17 && hour <= 19) || (hour == 20 && Integer.parseInt(t.time[1]) <= 30 && Integer.parseInt(t.time[2]) == 0)) { discount = 0.8F; } else if ((hour >= 11 && hour <= 13) || (hour == 10 && Integer.parseInt(t.time[1]) >= 30) || (hour == 14 && Integer.parseInt(t.time[1]) <= 30 && Integer.parseInt(t.time[2]) == 0) ) { discount = 0.6F; } else { System.out.println("table " + (ii) + " out of opening hours"); continue; } } if (all.get(t.name + " " + t.phone) == null) { all.put(t.name + " " + t.phone, t.allhou(discount)); } else { Integer r = all.get(t.name + " " + t.phone); r += t.allhou(discount); all.put(t.name + " " + t.phone, r); } System.out.println("table " + (ii) + ": " + t.allqian() + " " + t.allhou(discount) + t.getT()); } for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : all.entrySet()) { System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " " + entry.getValue()); } } public static int checkTime(Table t) { try { Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance(); int year = Integer.parseInt(t.day[0]); int month = Integer.parseInt(t.day[1]) - 1; int day = Integer.parseInt(t.day[2]); int hour = Integer.parseInt(t.time[0]); cal.set(year, month, day); int week = cal.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK); if (week == 1 || week == 7) { if ((hour >= 10 && hour <= 20) || (hour == 9 && Integer.parseInt(t.time[1]) >= 30) || (hour == 21 && Integer.parseInt(t.time[1]) == 30 && Integer.parseInt(t.time[2]) == 0)) { return 1; } else { return 0; } } else { if ((hour >= 17 && hour <= 19) || (hour == 20 && Integer.parseInt(t.time[1]) <= 30 && Integer.parseInt(t.time[2]) == 0)) { return 1; } else if ((hour >= 11 && hour <= 13) || (hour == 10 && Integer.parseInt(t.time[1]) >= 30) || (hour == 14 && Integer.parseInt(t.time[1]) <= 30 && Integer.parseInt(t.time[2]) == 0) ) { return 1; } else { return 0; } } }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println("wrong format"); return -1; } } } class Dish { String name; int price; int type; public Dish(String name, int price) { this.name = name; this.price = price; } boolean checkDegree(int degree) { return true; } } class ChuanCai extends Dish { public ChuanCai(String name, int price) { super(name, price); } @Override boolean checkDegree(int degree) { if (degree < 0 || degree > 5) { System.out.println("spicy num out of range :" + degree); return false; } return true; } } class JinCai extends Dish { public JinCai(String name, int price) { super(name, price); } @Override boolean checkDegree(int degree) { if (degree < 0 || degree > 4) { System.out.println("acidity num out of range :" + degree); return false; } return true; } } class ZheCai extends Dish { public ZheCai(String name, int price) { super(name, price); } @Override boolean checkDegree(int degree) { if (degree < 0 || degree > 3) { System.out.println("sweetness num out of range :" + degree); return false; } return true; } } class Menu { int count = 0; Map<String, Dish> dishes = new HashMap(); public void add(String name, int price) { dishes.put(name, new Dish(name, price)); // dishes[count] = new Dish(name, price); count++; } public void add(Dish dish) { dishes.put(dish.name, dish); count++; } public Dish find(String name) { return dishes.get(name); } } class Record { Dish dish; int unit_price; int heft; int price; int degree; public Record(Dish dish, int fs, int heft) { this.degree = -1; this.dish = dish; this.heft = heft; this.unit_price = fs; if (heft == 1) { price = dish.price * fs; } else if (heft == 2) { price = Math.round((float) dish.price * 1.5f) * fs; } else if (heft == 3) { price = dish.price * 2 * fs; } } public Record(Dish dish, int fs, int heft, int degree) { this.dish = dish; this.degree = degree; this.heft = heft; this.unit_price = fs; if (heft == 1) { price = dish.price * fs; } else if (heft == 2) { price = Math.round((float) dish.price * 1.5f) * fs; } else if (heft == 3) { price = dish.price * 2 * fs; } } } class Table { Map<Integer, Record> records = new HashMap<>(); String[] day; String[] time; String name; String phone; int ownFees = 0; Map<Integer, Record> otherMap = new HashMap<>(); Map<Integer, Integer> otherTableInfo = new HashMap<>(); Map<Integer, Record> DaiMap = new HashMap<>(); public Table(String[] day, String[] time) { this.day = day; this.time = time; } public boolean del(int no) { if (records.get(no) == null) { return false; } else { ownFees -= records.get(no).price; records.remove(no); return true; } } public int allqian() { int sum = 0; for (Record record : records.values()) { if (record == null) continue; sum += record.price; } for (Record value : otherMap.values()) { sum += value.price; } return sum; } public int allhou(float discount) { if (discount == 0.6F) { int sum = 0; for (Record record : records.values()) { if (record == null) continue; if (record.dish.type == 0) { sum += Math.round((float) record.price * discount); } else { sum += Math.round((float) record.price * 0.7); } } for (Record value : otherMap.values()) { if (value.dish.type == 0) { sum += Math.round((float) value.price * discount); } else { sum += Math.round((float) value.price * 0.7); } } return sum; } else if (discount == 0.8F) { int sum = 0; for (Record record : records.values()) { if (record == null) continue; if (record.dish.type == 0) { sum += Math.round((float) record.price * discount); } else { sum += Math.round((float) record.price * 0.7); } } for (Record value : otherMap.values()) { if (value.dish.type == 0) { sum += Math.round((float) value.price * discount); } else { sum += Math.round((float) value.price * 0.7); } } return sum; } else { return allqian(); } } public String getT() { List<Record> chuanCai = new ArrayList<>(); List<Record> jinCai = new ArrayList<>(); List<Record> zheCai = new ArrayList<>(); String r = " "; for (Record record : records.values()) { if (record == null) { continue; } switch (record.dish.type) { case 1 : zheCai.add(record); case 2 : jinCai.add(record); case 3 : chuanCai.add(record); } } for (Map.Entry<Integer, Record> entry : DaiMap.entrySet()) { switch (entry.getValue().dish.type) { case 1 : zheCai.add(entry.getValue()); case 2 : jinCai.add(entry.getValue()); case 3 : chuanCai.add(entry.getValue()); } } if (chuanCai.size() != 0) { int degree = 0; int unit_price = 0; for (Record record : chuanCai) { degree += record.degree * record.unit_price; unit_price += record.unit_price; } int pingjun = Math.round((float) degree / (float) unit_price); String[] ll = {"不辣", "微辣", "稍辣", "辣", "很辣", "爆辣"}; r = r + " 川菜 " + unit_price + " " + ll[pingjun]; } if (jinCai.size() != 0) { int degree = 0; int unit_price = 0; for (Record record : jinCai) { degree += record.degree * record.unit_price; unit_price += record.unit_price; } int pingjun = Math.round((float) degree / (float) unit_price); String[] ll = {"不酸", "微酸", "稍酸", "酸", "很酸"}; r = r + " 晋菜 " + unit_price + " " + ll[pingjun]; } if (zheCai.size() != 0) { int degree = 0; int unit_price = 0; for (Record record : zheCai) { degree += record.degree * record.unit_price; unit_price += record.unit_price; } int pingjun = Math.round((float) degree / (float) unit_price); String[] ll = {"不甜", "微甜", "稍甜", "甜"}; r = r + " 浙菜 " + unit_price + " " + ll[pingjun]; } return r.replaceAll(" {2}", " "); } }
这次努力尝试了一次,有所成绩但并不能让我满意,只有38分,还是在输出部分有较大问题,有将近一半的测试点没法通过,分析如下
1. 数据的输入和存储:对于每个桌号,需要建立一个存储其订单信息的数据结构,比如一个字典,将订单信息存储在其中,方便后续对数据的处理和计算。需要注意,不同桌号的订单信息需要分别存储,避免混淆。
2.数据的计算:包括菜品单价的计算、折扣的计算、口味度的计算等。计算时需要注意数据类型的转换和取舍,并进行四舍五入等计算。另外,需要注意口味度的范围限制,对于超出范围的情况,需要进行相应的异常处理。
3.数据的输出:需要按照题目中要求的格式进行输出,包括输入顺序输出每一桌的订单记录处理信息、输出每一桌所有菜品的价格、按字母顺序输出每位客户需要支付的金额等。在输出时,需要注意格式的准确性和排版的美观性,注意将数据进行四舍五入等处理,以及对异常情况进行适当的处理,保证程序的稳定性和可靠性。
4.异常的处理:需要考虑到各种异常的情况,在程序中进行相应的处理。比如,存在不能识别的菜名时,需要输出“** does not exist”;删除记录的序号不存在时,需要输出“delete error”等。还需要注意口味度的范围限制等异常情况的处理,使程序具有较好的健壮性。
(3)期中考试测验1-圆类设计

分析如下:
这道题是一道基础的面向对象的编程题,需要掌握基本的类的定义和成员变量的声明、构造函数的使用等基础知识。题目要求实现一个圆形类,包含一个私有半径属性和一个计算圆面积的方法。在实现类的时候,需要注意以下几点:
1.类名为 Circle,包含一个私有的半径属性 radius。、
2.实现一个构造方法 Circle(double radius),用于初始化半径属性。
3.实现一个公有方法 getArea(),用于计算圆的面积。计算方法为 π* radius^2,其中 π 取3.1415926。
4.在输入圆的半径后,首先需要对输入的数据进行判断,判断输入数据是否非法。比如输入的非数值数据(比如字母)等,也需要判断半径是否为 0 或者负数。
当判断输入数据合法后,就可以创建 Circle 对象,调用 getArea() 方法,并使用 String.format("%.2f", area) 对面积值进行格式化输出。
最后需要注意一点,由于涉及到圆面积的计算,精度问题需要考虑,建议使用 double 类型。
类图:

源码:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); if (scanner.hasNextDouble()) { double radius = scanner.nextDouble(); if (radius > 0) { Circle circle = new Circle(); circle.setRadius(radius); double area = circle.getArea(); System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", area)); } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } scanner.close(); } } class Circle { private double radius; public Circle() { } public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } public double getRadius() { return radius; } public double getArea() { return Math.PI * radius * radius; } }
(4)期中考试测验2-类结构设计

分析如下:
这道题涉及到面向对象的编程设计,需要实现一个矩形类,其中需要包含左上角和右下角两个点的坐标。在构造方法中,需要根据左上角和右下角两个点的坐标计算出矩形的长和宽,进而计算出矩形面积。
在具体实现类的时候,需要注意以下几点:
1. 类名为Rectangle,包含一个私有的左上角点和右下角点属性。
2.在实现构造方法时,需要处理两个点的坐标输入,可以使用另外一个构造方法或者使用具有默认参数的构造方法。
3.可以提供对左上角点和右下角点属性的获取和修改的方法。通过这些方法可以计算出矩形的长和宽。
4.可以提供一个公有的方法 getArea(),用于计算矩形的面积。计算方法为长乘以宽。
在输入坐标值后,首先需要对输入的数据进行判断,判断输入数据是否越界或输入数据格式是否正确。接着,就可以创建 Rectangle 对象,调用 getArea() 方法,并使用 String.format("%.2f", area) 对面积值进行格式化输出。
最后需要注意一点,由于涉及到矩形面积的计算,精度问题需要考虑,建议使用 double 类型。
源码:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); if (scanner.hasNextDouble()) { double x1 = scanner.nextDouble(); double y1 = scanner.nextDouble(); double x2 = scanner.nextDouble(); double y2 = scanner.nextDouble(); Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(); rectangle.setX1(x1); rectangle.setY1(y1); rectangle.setX2(x2); rectangle.setY2(y2); double area = rectangle.getArea(); System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", area)); } scanner.close(); } } class Rectangle { private double x1, y1, x2, y2; public Rectangle() {} public void setX1(double x1) { this.x1 = x1; } public double getX1() { return x1; } public void setY1(double y1) { this.y1 = y1; } public double getY1() { return y1; } public void setX2(double x2) { this.x2 = x2; } public double getX2() { return x2; } public void setY2(double y2) { this.y2 = y2; } public double getY2() { return y2; } public double getArea() { return Math.abs((x2 - x1) * (y2 - y1)); } }
(5) 期中考试测验3-继承与多态

分析如下:
这道题是一道较为复杂的面向对象的编程题,需要掌握继承、抽象类、多态等知识点。首先需要设计出一个 Shape 的抽象类,它包含一个抽象方法 getArea(),代表图形面积的计算。Circle 和 Rectangle 类继承自 Shape,并实现 getArea() 方 法。在实现类的时候,需要注意以下几点:
1.类图中的 Circle 和 Rectangle 类需要实现 Shape 类。
2.Circle 类包含私有的半径属性,重载了 getArea() 方法。
3.Rectangle 类包含私有的左上角点和右下角点属性,重载了 getArea() 方法。
4.可以提供对 Circle 和 Rectangle 类的特定属性的获取和修改的方法。
在主方法中,根据输入的 type 值判断用户想要创建哪一种类型的图形,然后通过输入的数据创建对象,并使用 printArea() 函数输出面积值。使用抽象类 Shape 将各种形状进行统一,对于 printArea() 方法,参数为一个 Shape 对象,这个方法 既适用于 Circle 对象,也适用于 Rectangle 对象。也就是说,这个方法的参数形式虽然统一,但是可以接收不同的实际参数,调用不同的方法,从而实现多态。最后需要注意一点,由于涉及到图形面积的计算,精度问题需要考虑,建议使用 double 类型。
源码:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int choice = input.nextInt(); switch (choice) { case 1: // Circle double radiums = input.nextDouble(); if (radiums <= 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } Shape circle = new Circle(radiums); printArea(circle); break; case 2: // Rectangle double x1 = input.nextDouble(); double y1 = input.nextDouble(); double x2 = input.nextDouble(); double y2 = input.nextDouble(); Point leftTopPoint = new Point(x1, y1); Point lowerRightPoint = new Point(x2, y2); Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(leftTopPoint, lowerRightPoint); printArea(rectangle); break; } } public static void printArea(Shape shape) { System.out.printf("%.2f", shape.getArea()); } } abstract class Shape { public abstract double getArea(); } class Circle extends Shape { private double radiums; public Circle(double radiums) { this.radiums = radiums; } @Override public double getArea() { return Math.PI * radiums * radiums; } } class Rectangle extends Shape { private Point leftTopPoint; private Point lowerRightPoint; public Rectangle(Point leftTopPoint, Point lowerRightPoint) { this.leftTopPoint = leftTopPoint; this.lowerRightPoint = lowerRightPoint; } @Override public double getArea() { double width = Math.abs(lowerRightPoint.getX() - leftTopPoint.getX()); double height = Math.abs(lowerRightPoint.getY() - leftTopPoint.getY()); return width * height; } } class Point { private double x; private double y; public Point(double x, double y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } public double getX() { return x; } public double getY() { return y; } }
(6)期中考试测验4-抽象类与接口

分析如下:
这道题要求输入多个图形的信息,并计算、排序,输出排序后的各个图形的面积。在类设计上,要符合题目的要求,并实现 Comparable 接口,方便后面进行排序。在具体实现类的时候,需要注意以下几点:
1.在类图中,Circle 和 Rectangle 继承自抽象类 Shape,并实现 Shape 类中的 getArea() 和 Comparable 中的 compareTo() 方法。其中 getArea() 计算图形面积,compareTo() 比较图形面积大小,以面积从小到大排序。
2.在主方法中,根据输入的 type 值判断用户想要创建哪一种类型的图形,然后将对象添加到列表中,最后对列表进行排序。
3.对于列表的排序,可以使用 sort() 和 reverse() 函数。sort() 函数会正向排序,而 reverse() 函数会反向排序。
最后需要注意一点,由于涉及到图形面积的计算,精度问题需要考虑,建议使用 double 类型。
类图:
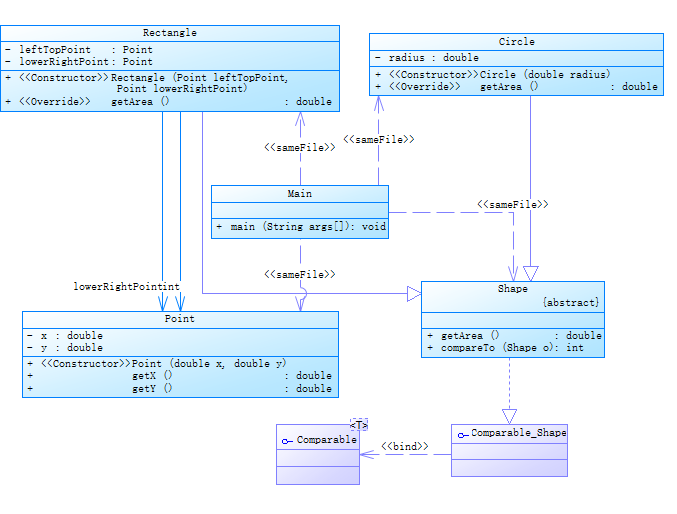
源码:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Collections; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); ArrayList<Shape> list = new ArrayList<>(); int choice = input.nextInt(); while (choice != 0) { switch (choice) { case 1: // Circle double radiums = input.nextDouble(); Shape circle = new Circle(radiums); list.add(circle); break; case 2: // Rectangle double x1 = input.nextDouble(); double y1 = input.nextDouble(); double x2 = input.nextDouble(); double y2 = input.nextDouble(); Point leftTopPoint = new Point(x1, y1); Point lowerRightPoint = new Point(x2, y2); Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(leftTopPoint, lowerRightPoint); list.add(rectangle); break; } choice = input.nextInt(); } Collections.sort(list); for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { System.out.print(String.format("%.2f", list.get(i).getArea()) + " "); } } } abstract class Shape implements Comparable<Shape> { public abstract double getArea(); @Override public int compareTo(Shape o) { return Double.compare(this.getArea(), o.getArea()); } } class Circle extends Shape { private double radiums; public Circle(double radiums) { this.radiums = radiums; } @Override public double getArea() { return Math.PI * radiums * radiums; } } class Rectangle extends Shape { private Point leftTopPoint; private Point lowerRightPoint; public Rectangle(Point leftTopPoint, Point lowerRightPoint) { this.leftTopPoint = leftTopPoint; this.lowerRightPoint = lowerRightPoint; } @Override public double getArea() { double width = Math.abs(lowerRightPoint.getX() - leftTopPoint.getX()); double height = Math.abs(lowerRightPoint.getY() - leftTopPoint.getY()); return width * height; } } class Point { private double x; private double y; public Point(double x, double y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } public double getX() { return x; } public double getY() { return y; } }
三、踩坑心得:
1.学会利器——正则表达式,对于字符串的识别有奇效
2.谨慎注意输入输出格式的正确
3.切记在做题之前做好类的设计,否则会十分被动无从下手
四、改进建议:
1.主要困难:主要还是自己太菜,在面对大题目的时候茫然,不知所措,基础不扎实,需要掌握的基础知识不到位
2.建议:来点简单的题啊求求了
五、总结:
- 在学习Java的初期,需要掌握基本语法、数据类型、运算符等基本知识,同时需要学习面向对象编程的概念和相关知识。
- 学习Java需要编写程序,并通过编写程序来巩固所学知识。需要经常花时间思考和练习。
- Java语言具有严格的语法和规范,需要注意命名规范、代码风格等细节问题。
- 在学习Java的过程中,可以掌握Java SE中的常用类和API,例如集合类、IO流、多线程等。
- 在学习过程中,可以使用一些编程工具,如Eclipse或IntelliJ IDEA,以提高效率和编码质量。
- 最后,学习Java是一个持续性的过程,需要不断学习和实践,多看书、多写代码、多请教他人都是不错的学习方法。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号