10.29算法训练——poj1475双重BFS
题目描述就不多说了,网址在这里——>> http://poj.org/problem?id=1475
看到这题没有一点头绪,于是百度找代码观摩,可是就算这样也是对别人的解法半知半解,不能说找到了完全正确的答案,但对结题过程有了大致了解。
总体思路就是在队箱子bfs的同时,也对人进行bfs. 每移动箱子一个,就对人进行bfs. 对人bfs的目的是判断人能不能走到箱子移动前的后一个位置。
灵魂画师上线: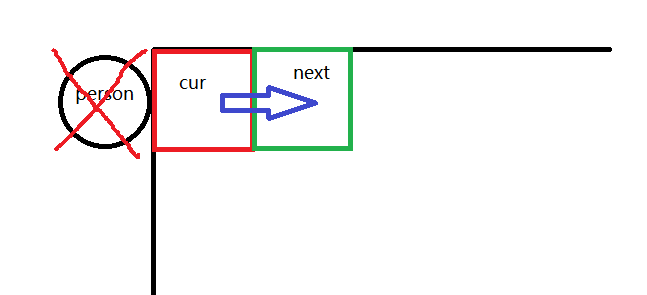
图中的例子就是人无法推导箱子的位置,也就是说这次bfs无效,开始返回上一步的bfs
网上找的AC代码,看懂它在看什么倒是很容易,去深究每个语句的话就不一定了,哎,就这样吧。
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <string> using namespace std; #define MAXN 22 char P[4]={'N','S','W','E'}; char M[4]={'n','s','w','e'}; int R,C; int dir[4][2]={-1,0,1,0,0,-1,0,1}; char map[MAXN][MAXN]; struct point { int x,y; int p_x,p_y;//当前状态person所在的地方 string ans; }; bool isok(int x,int y) { if(x>=0 && x<R && y>=0 && y<C && map[x][y] != '#') return true; return false; } string tmp; bool bfs_person(point en,point cu) { tmp=""; point st; st.x=en.p_x; st.y=en.p_y; st.ans=""; queue<point>q; bool vis[MAXN][MAXN]; memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); while(!q.empty()) q.pop(); q.push(st); while(!q.empty()) { point cur,next; cur=q.front(); q.pop(); if(cur.x==en.x && cur.y==en.y) { tmp=cur.ans; return true; } for(int i=0;i<4;i++) { next=cur; next.x=cur.x+dir[i][0]; next.y=cur.y+dir[i][1]; if(!isok(next.x,next.y)) continue; if(next.x==cu.x && next.y==cu.y) continue; if(vis[next.x][next.y]) continue; vis[next.x][next.y]=1; next.ans=cur.ans+M[i]; q.push(next); } } return false; } string bfs_box() { bool vis[MAXN][MAXN][4];//某点四个方向是否访问!!0==N,1==S,2==W,3==E point st; st.x=st.y=-1; st.p_x=st.p_y=-1; st.ans=""; for(int i=0;i<R && (st.x==-1 || st.p_x==-1);i++) for(int j=0;j<C && (st.x==-1 || st.p_x==-1);j++) if(map[i][j]=='B') { st.x=i; st.y=j; map[i][j]='.'; } else if(map[i][j]=='S') { st.p_x=i; st.p_y=j; map[i][j]='.'; } queue<point> q; while(!q.empty()) q.pop(); q.push(st); memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); while(!q.empty()) { point cur=q.front();q.pop(); point next,pre; if(map[cur.x][cur.y]=='T') return cur.ans; for(int i=0;i<4;i++) { next=cur; next.x=cur.x+dir[i][0]; next.y=cur.y+dir[i][1]; if(!isok(next.x,next.y)) continue; if(vis[next.x][next.y][i]) continue; pre=cur; switch(i) { case 0: pre.x=cur.x+1;break; case 1: pre.x=cur.x-1;break; case 2: pre.y=cur.y+1;break; case 3: pre.y=cur.y-1;break; } if(!bfs_person(pre,cur))//搜寻人是否能走到特定的位置 continue; vis[next.x][next.y][i]=1; next.ans=cur.ans+tmp; next.ans=next.ans+P[i]; next.p_x=cur.x;next.p_y=cur.y; q.push(next); } } return "Impossible."; } int main() { int cas=1; while(scanf("%d%d",&R,&C) && (R+C)) { getchar(); for(int i=0;i<R;i++) gets(map[i]); printf("Maze #%d\n",cas++); cout<<bfs_box()<<endl<<endl; } return 0; }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号