C# 数据结构 总结
int[] numbers = new int[5]; // 创建一个包含 5 个整数的整数数组
string[] names = new string[3]; // 创建一个包含 3 个字符串的字符串数组ArrayList list = new ArrayList(); // 创建一个空的 ArrayList
list.Add(10); // 向 ArrayList 中添加整数
list.Add("Hello"); // 向 ArrayList 中添加字符串
list.Add(true); // 向 ArrayList 中添加布尔值二、集合接口
1、 IEnumerable
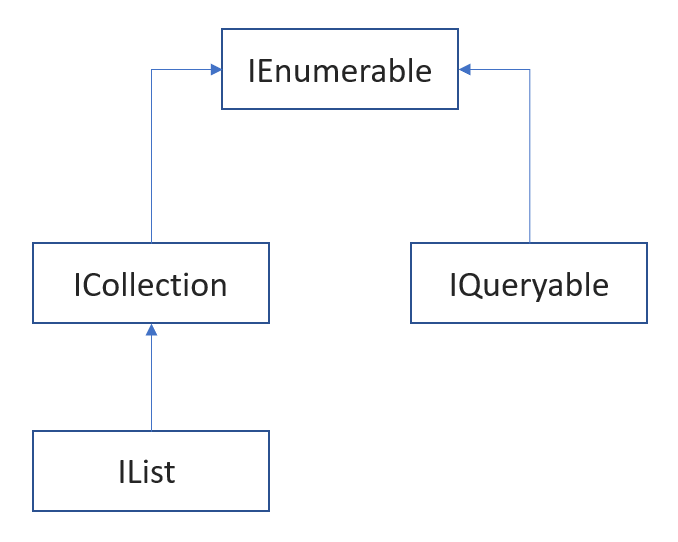
是所有非泛型集合的基本接口
namespace System.Collections
{
public interface IEnumerable
{
IEnumerator GetEnumerator();
}
}能力:
(1)用于迭代使用,里面有GetEnumerator()方法(即用foreach遍历)。
(2)支持使用where linq查询
2、IEnumerable<out T>
namespace System.Collections.Generic
{
public interface IEnumerable<out T> : IEnumerable
{
new IEnumerator<T> GetEnumerator();
}
}3、ICollection
继承了IEnumerable接口,主要用于集合,像ArrayList、List、LinkedList均实现了该接口。
namespace System.Collections
{
public interface ICollection : IEnumerable
{
int Count { get; } // 获取集合中的元素数量。
bool IsSynchronized { get; } // 返回访问是否同步,即是否线程安全。
object SyncRoot { get; } // 获取一个对象,用于在多线程环境中同步对集合的访问。
void CopyTo(Array array, int index); // 将集合的元素复制到一个数组中,从指定的索引位置开始。
}
}能力:
(1)该接口可以确定集合的大小(Count),
(2)集合是否包含某个元素(Contains),
(3)复制集合到另外一个数组(ToArray),
(4)集合是否是只读的(IsReadOnly)。
(5)如果一个集合是可编辑的,那么可以调用Add,Remove和Clear方法操作集合中的元素。
(6)因为该接口继承IEnumerable<T>,所以可以使用foreach语句遍历集合,支持使用where linq查询
4、ICollection<T>
namespace System.Collections.Generic
{
public interface ICollection<T> : IEnumerable<T>, IEnumerable
{
int Count { get; } // 获取集合中元素的数量。
bool IsReadOnly { get; } // 获取一个布尔值,指示集合是否为只读。
void Add(T item); // 向集合中添加一个元素。
bool Contains(T item); // 判断集合是否包含指定元素。
void CopyTo(T[] array, int arrayIndex); // 将集合的元素复制到指定数组中,从指定索引开始。
bool Remove(T item); // 从集合中移除指定元素。
}
}当我们出现以下情况时,可以考虑使用 ICollection<T> :
- 统计集合元素数量
- 需要编辑集合元素
- 搜索集合
- 使用
IEnumerable<T>接口中Where扩展方法进行过滤操作
5、IList
继承了IEnumerable 和 ICollection,实现IList接口的数据接口可以使用索引访问,表示在内存上是连续分配的,比如Array、List。
namespace System.Collections
{
public interface IList : ICollection, IEnumerable
{
bool IsFixedSize { get; } // 获取一个布尔值,指示列表是否具有固定大小。
bool IsReadOnly { get; } // 获取一个布尔值,指示列表是否为只读。
object? this[int index] { get; set; } // 获取或设置指定索引处的元素。
int Add(object? value); // 向列表中添加一个元素,并返回新元素的索引。
void Clear(); // 从列表中移除所有元素。
bool Contains(object? value); // 判断列表是否包含指定的元素。
int IndexOf(object? value); // 获取指定元素的第一个匹配项的索引。
void Insert(int index, object? value); // 在指定索引处插入一个元素。
void Remove(object? value); // 从列表中移除指定的元素。
void RemoveAt(int index); // 移除指定索引处的元素。
}
}能力:
(1) Add():该方法用于在集合中添加元素。对于数组,该方法会抛出NotSupportedException异常。
(2) Clear():该方法可以清除数组中的所有元素。值类型设置为0,引用类型设置为NULL
(3) Contains():该方法可以确定某个元素是否在数组中。其返回值是true或false.这个方法会对数组中的所有元素进行线性搜索,直到找到所需元素为止。
(4) IndexOf():该方法与Contains()方法类似,也是对数组中的所有元素进行线性搜索。不同的是IndexOf()方法会返回所找到的第一个元素的索引。
(5) Insert()、Remove()、RemoveAt():对于集合,Insert()方法用于插入元素,Remove()和RemoveAt()可删除元素。对于数组,这些方法都抛出NotSupportedException异常
(6) IsFixedSize:数组的大小总是固定的,所以这个属性问题返回true
(7) IsReadOnly:数组总是可读/写的,所以这个属性返回false.
(8) Item:该属性可以用整形索引访问数组。
6、IList<T>
namespace System.Collections.Generic
{
public interface IList<T> : ICollection<T>, IEnumerable<T>, IEnumerable
{
T this[int index] { get; set; }
int IndexOf(T item);
void Insert(int index, T item);
void RemoveAt(int index);
}
}如果超出 ICollection<T> 接口中提供的功能,且有以下两点中的情形,那么就可以考虑使用 IList 或 IList<T> 接口。
- 需要修改集合中的元素
- 需要快速定位集合中的元素或排序
7、IQueryable
这里主要和IEnumerable接口进行对比。
namespace System.Linq
{
public interface IQueryable : IEnumerable
{
Type ElementType { get; }
Expression Expression { get; }
IQueryProvider Provider { get; }
}
}它存在于 System.Linq 命名空间中
8、IQueryable<T>
namespace System.Linq
{
public interface IQueryable<out T> : IEnumerable<T>, IEnumerable, IQueryable
{
}
}9、IQueryable<T>与IEnumerable<T> 在LINQ查询中的性能对比
- IEnumerable<T>:
- 这是一个在内存中进行操作的接口。它适用于对本地集合或内存中的数据执行操作。
- 执行查询操作时,所有数据都被加载到内存中,然后根据查询进行过滤、排序、分组等操作。这会占用较多内存,但在小数据集上性能较好。
- IQueryable<T>:
- 这是一个能够构建查询并在数据库中执行的接口。它适用于对数据库或其他远程数据源执行操作。
- 执行查询操作时,构建的查询表达式会被翻译成数据库查询语言(如 SQL)并在数据库中执行。只有在需要结果时才会从数据库中获取数据,因此它适用于大数据集,避免了一次性加载全部数据到内存中。
总结:
- 如果你正在操作内存中的数据,比如一个 List<T>,IEnumerable<T> 可能更合适,因为它简单且性能较好。
三、IEnumerable Range
namespace System.Linq
{
public static class Enumerable
{
public static IEnumerable<int> Range(int start, int count);
}
} //生成指定范围内的整数的序列。
var enu = Enumerable.Range(1, 5)
.Select(a => a)
.ToArray();//转数组
Console.Write(enu.GetType());
foreach (var item in enu)
{
Console.Write(item);//12345
} 四、yield、迭代器
yield
1. yield必须出现在IEunmerable中
2. yield是迭代器的状态机,能做到延迟查询,使用的时候才查询,可以实现按序加载



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号