Django组件-ContentType
一 项目背景
路飞学成项目,有课程,学位课(不同的课程字段不一样),价格策略
问题,1 如何设计表结构,来表示这种规则
2 为专题课,添加三个价格策略
3 查询所有价格策略,并且显示对应的课程名称
4 通过课程id,获取课程信息和价格策略
二 版本一
一个课程表,包含学位课和专题课,一个价格策略表,一对多关联
三 版本二
学位课表,专题课表,装逼课表,价格策略表(在价格策略课表中加入多个FK跟课程表做关联):后期再加其它课程,可维护性差
四 最终版(使用ContentType)
通过Django提供的ContentType表,来构建

models层创建:
from django.db import models from django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentType from django.contrib.contenttypes.fields import GenericForeignKey, GenericRelation class Course(models.Model): title = models.CharField(max_length=32) # 不会在数据库中生成字段,只用于数据库操作 # policy = GenericRelation('PricePolicy',object_id_field='object_id',content_type_field='contentType') class DegreeCourse(models.Model): title = models.CharField(max_length=32) class PricePolicy(models.Model): # 跟ContentType表做外键关联 contentType = models.ForeignKey(to=ContentType) # 正数 object_id = models.PositiveIntegerField() # 引入一个字段,不会在数据库中创建,只用来做数据库操作 # content_obj = GenericForeignKey('contentType', 'object_id') period = models.CharField(max_length=32) price = models.FloatField()
views层:
from app01 import models def test(request): import json # 方式一插入价格规则 # ret=models.ContentType.objects.filter(model='course').first() # course=models.Course.objects.filter(pk=1).first() # print(ret.id) # models.PricePolicy.objects.create(period='30',price=100,object_id=course.id,contentType_id=ret.id) # 方式二插入价格规则 # course=models.Course.objects.filter(pk=1).first() # # content_obj=course 会自动的把课程id放到object_id上,并且去ContentType表中查询课程表的id,放到contentType上 # models.PricePolicy.objects.create(period='60',price=800,content_obj=course) # 增加学位课,价格规则 # degreecourse = models.DegreeCourse.objects.filter(pk=1).first() # models.PricePolicy.objects.create(period='60', price=800, content_obj=degreecourse) # 查询所有价格策略,并且显示对应的课程名称 # ret=models.PricePolicy.objects.all() # for i in ret: # print(i.price) # print(i.period) # # content_obj 就是代指关联的课程,或者学位课程的那个对象 # print(type(i.content_obj)) # print(i.content_obj.title) # 通过课程id,获取课程信息和价格策略 course=models.Course.objects.filter(pk=1).first() print(course.policy.all()) return render(request,'test.html')
ContentType组件
ContentType是Django的内置的一个应用,可以追踪项目中所有的APP和model的对应关系,并记录在ContentType表中。
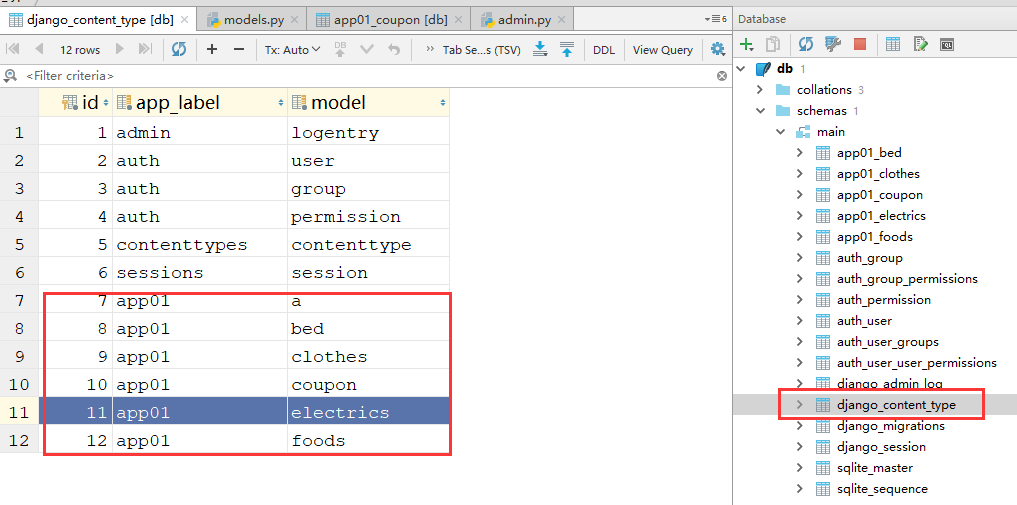
当项目做数据迁移后,会有很多django自带的表,其中就有django_content_type表
ContentType组件应用
- 在model中定义ForeignKey字段,并关联到ContentType表,通常这个字段命名为content-type
- 在model中定义PositiveIntergerField字段, 用来存储关联表中的主键,通常用object_id
- 在model中定义GenericForeignKey字段,传入上面两个字段的名字
- 方便反向查询可以定义GenericRelation字段
- postman

from django.db import models from django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentType from django.contrib.contenttypes.fields import GenericForeignKey, GenericRelation # Create your models here. class Food(models.Model): """ id title 1 面包 2 牛奶 """ title = models.CharField(max_length=32) # 不会生成字段 只用于反向查询 coupons = GenericRelation(to="Coupon") class Fruit(models.Model): """ id title 1 苹果 2 香蕉 """ title = models.CharField(max_length=32) # 如果有40张表 # class Coupon(models.Model): # """ # id title food_id fruit_id # 1 面包九五折 1 null # 2 香蕉满10元减5元 null 2 # """ # title = models.CharField(max_length=32) # food = models.ForeignKey(to="Food") # fruit = models.ForeignKey(to="Fruit") # class Coupon(models.Model): # """ # id title table_id object_id # 1 面包九五折 1 1 # 2 香蕉满10元减5元 2 2 # """ # title = models.CharField(max_length=32) # table = models.ForeignKey(to="Table") # object_id = models.IntegerField() # # # class Table(models.Model): # """ # id app_name table_name # 1 demo food # 2 demo fruit # """ # app_name = models.CharField(max_length=32) # table_name = models.CharField(max_length=32) class Coupon(models.Model): title = models.CharField(max_length=32) # 第一步:注意没有引号因为是导入的 content_type = models.ForeignKey(to=ContentType, on_delete=None) # 第二步 object_id = models.IntegerField() # 第三步 不会生成字段,用来操作增删改查 content_object = GenericForeignKey("content_type", "object_id")

from django.shortcuts import render from rest_framework.views import APIView from rest_framework.response import Response from .models import Food, Coupon from django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentType # Create your views here. class DemoView(APIView): def get(self, request): # 给面包创建一个优惠券 food_obj = Food.objects.filter(id=1).first() # Coupon.objects.create(title="面包九五折", content_type_id=8, object_id=1) # Coupon.objects.create(title="双十一面包九折促销", content_object=food_obj) #查询食物都有哪些优惠券 #定义了反向查询 coupons = food_obj.coupons.all() print(coupons) # 如果没定义反向查询 content = ContentType.objects.filter(app_label="app01", model="food").first() coupons = Coupon.objects.filter(content_type=content, object_id=1).all() print(coupons) # 优惠券查对象 # 查询优惠券id=1绑定了哪个商品 coupon_obj = Coupon.objects.filter(id=1).first() content_obj = coupon_obj.content_object print(coupon_obj.title,content_obj.title) # 通过ContentType表找表模型 content = ContentType.objects.filter(app_label="app01", model="food").first() # content=food 获取food表的表模型用model_class() model_class = content.model_class() ret = model_class.objects.all() print(ret) return Response("ContentType测试")

from django.db import models from django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentType from django.contrib.contenttypes.fields import GenericForeignKey, GenericRelation from django.contrib.auth.models import User class Post(models.Model): """帖子表""" author = models.ForeignKey(User) title = models.CharField(max_length=72) comments = GenericRelation('Comment') # 支持反向查找评论数据(不会在数据库中创建字段) class Picture(models.Model): """图片表""" author = models.ForeignKey(User) image = models.ImageField() comments = GenericRelation('Comment') # 支持反向查找评论数据(不会在数据库中创建字段) class Comment(models.Model): """评论表""" author = models.ForeignKey(User) content = models.TextField() content_type = models.ForeignKey(ContentType) # 外键关联django_content_type表 object_id = models.PositiveIntegerField() # 关联数据的主键 # 告诉Django,content_type和object_id是一组动态关联的数据,不会生成字段,用来操作增删改查 content_object = GenericForeignKey('content_type', 'object_id') ###################################################################################### class Post(models.Model): """帖子表""" author = models.ForeignKey(User) title = models.CharField(max_length=72) comments = GenericRelation('Comment',object_id_field='obj_id',content_type_field='table_name') # 支持反向查找评论数据(不会在数据库中创建字段) class Picture(models.Model): """图片表""" author = models.ForeignKey(User) image = models.ImageField() comments = GenericRelation('Comment',object_id_field='obj_id',content_type_field='table_name') # 支持反向查找评论数据(不会在数据库中创建字段) class Comment(models.Model): """评论表""" author = models.ForeignKey(User) content = models.TextField() table_name = models.ForeignKey(ContentType) # 外键关联django_content_type表 obj_id = models.PositiveIntegerField() # 关联数据的主键 content_object = GenericForeignKey('table_name', 'obj_id') #不会生成字段,用来操作增删改查 ###################################################################################### import os if __name__ == "__main__": os.environ.setdefault("DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE", "about_contenttype.settings") import django django.setup() from app01.models import Post, Picture, Comment from django.contrib.auth.models import User # 准备测试数据 user_1 = User.objects.create_user(username='aaa', password='123') user_2 = User.objects.create_user(username='bbb', password='123') user_3 = User.objects.create_user(username='ccc', password='123') post_1 = Post.objects.create(author=user_1, title='Python入门教程') post_2 = Post.objects.create(author=user_2, title='Python进阶教程') post_3 = Post.objects.create(author=user_1, title='Python入土教程') picture_1 = Picture.objects.create(author=user_1, image='小姐姐01.jpg') picture_2 = Picture.objects.create(author=user_1, image='小姐姐02.jpg') picture_3 = Picture.objects.create(author=user_3, image='小哥哥01.jpg') # 给帖子创建评论数据 comment_1 = Comment.objects.create(author=user_1, content='好文!', content_object=post_1) # 给图片创建评论数据 comment_2 = Comment.objects.create(author=user_2, content='好美!', content_object=picture_1) #查询示例: #定义了反向查询 post_1 = Post.objects.filter(id=1).first() comment_list = post_1.comments.all()
说明
通过django的contentType表来搞定一个表里面有多个外键的简单处理: 摘自:https://blog.csdn.net/aaronthon/article/details/81714496
contenttypes 是Django内置的一个应用,可以追踪项目中所有app和model的对应关系,并记录在ContentType表中。
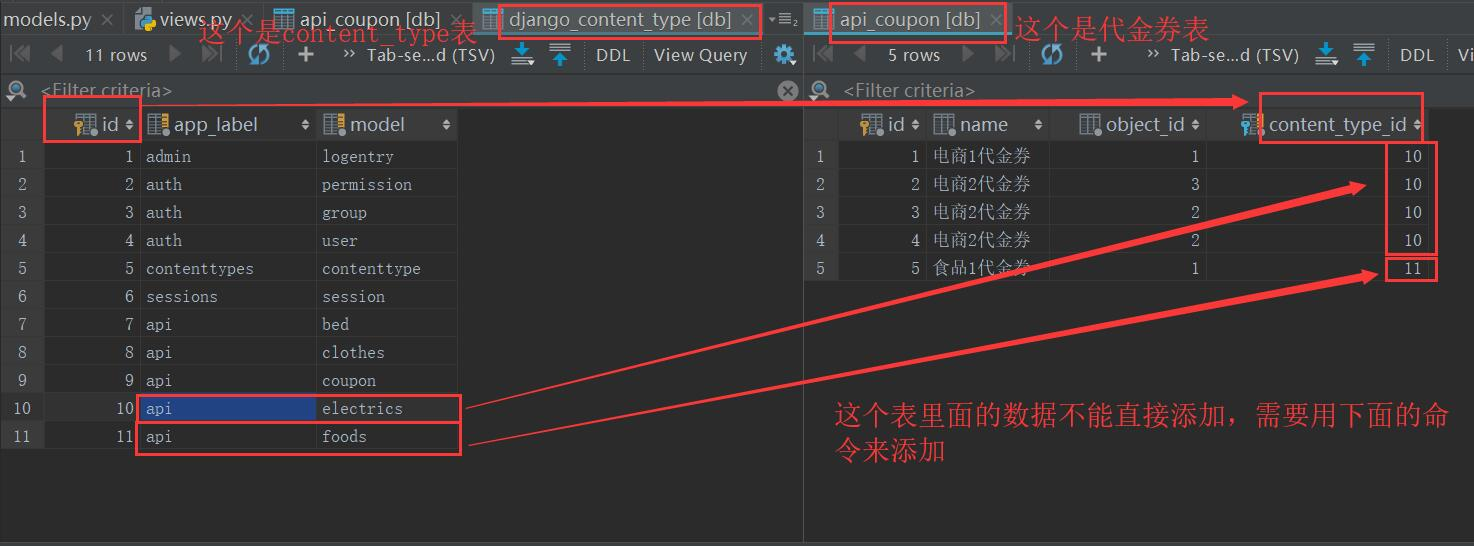
models.py文件的表结构写好后,通过makemigrations和migrate两条命令迁移数据后,在数据库中会自动生成一个django_content_type表,比如我们有在models.py中写了这么几张表:
from django.db import models class Electrics(models.Model): """ id name 1 日立冰箱 2 三星电视 3 小天鹅洗衣机 """ name = models.CharField(max_length=32) class Foods(models.Model): """ id name 1 面包 2 烤鸭 """ name = models.CharField(max_length=32) class Clothes(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=32) class Coupon(models.Model): # 特殊关系表 """ id name electric_id food_id cloth_id more... # 每增加一张表,关系表的结构就要多加一个字段。 1 通用优惠券 null null null 2 冰箱满减券 2 null null 3 面包狂欢节 null 1 null """ name = models.CharField(max_length=32) electric = models.ForeignKey(to='Electrics', null=True) food = models.ForeignKey(to='Foods', null=True) cloth = models.ForeignKey(to='Clothes', null=True)
如果是通用优惠券,那么所有的ForeignKey为null,如果仅限某些商品,那么对应商品ForeignKey记录该商品的id,不相关的记录为null。但是这样做是有问题的:实际中商品品类繁多,而且很可能还会持续增加,那么优惠券表中的外键将越来越多,但是每条记录仅使用其中的一个或某几个外键字段。
contenttypes 应用
通过使用contenttypes 应用中提供的特殊字段GenericForeignKey,我们可以很好的解决这个问题。只需要以下三步:
在model中定义ForeignKey字段,并关联到ContentType表。通常这个字段命名为“content_type”
在model中定义PositiveIntegerField字段,用来存储关联表中的主键。通常这个字段命名为“object_id”
在model中定义GenericForeignKey字段,传入上述两个字段的名字。
为了更方便查询商品的优惠券,我们还可以在商品类中通过GenericRelation字段定义反向关系。
示例代码:models.py文件:
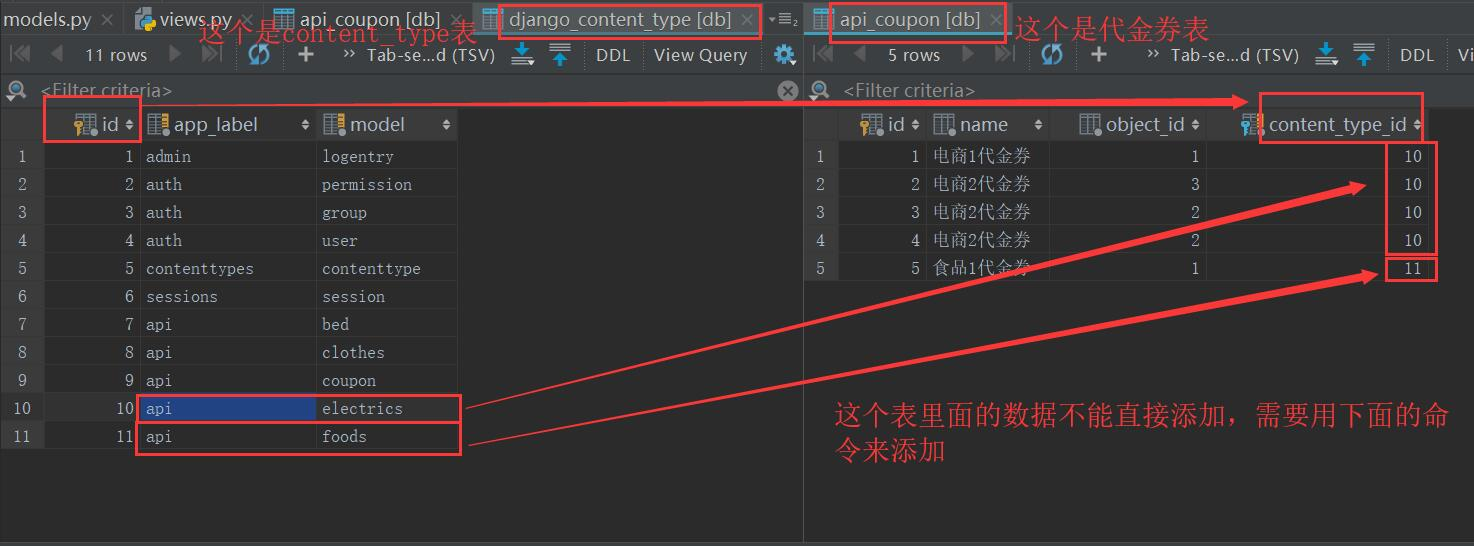
from django.db import models from django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentType from django.contrib.contenttypes.fields import GenericForeignKey, GenericRelation class Electrics(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=32) price = models.IntegerField(default=100) coupons = GenericRelation(to='Coupon') # 用于反向查询,不会生成表字段 def __str__(self): return self.name class Foods(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=32) price=models.IntegerField(default=100) coupons = GenericRelation(to='Coupon') def __str__(self): return self.name class Clothes(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=32) price = models.IntegerField(default=100) coupons = GenericRelation(to='Coupon') def __str__(self): return self.name class bed(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=32) price = models.IntegerField(default=100) coupons = GenericRelation(to='Coupon') class Coupon(models.Model): """ Coupon id name content_type_id object_id_id 美的满减优惠券 9(电器表electrics) 3 猪蹄买一送一优惠券 10 2 南极被子买200减50优惠券 11 1 """ name = models.CharField(max_length=32) content_type = models.ForeignKey(to=ContentType,on_delete=models.CASCADE) # step 1 既然没有直接和关联表进行外键关系,我们通过这一步先找到关联表 object_id = models.PositiveIntegerField() # step 2 #存的是关联的那个表的对应的那条记录的id content_object = GenericForeignKey('content_type', 'object_id') # step 3 对象.content_object直接就拿到了这个优惠券对象关联的那个商品记录对象。 def __str__(self): return self.name
注意:ContentType只运用于1对多的关系!!!并且多的那张表中有多个ForeignKey字段。
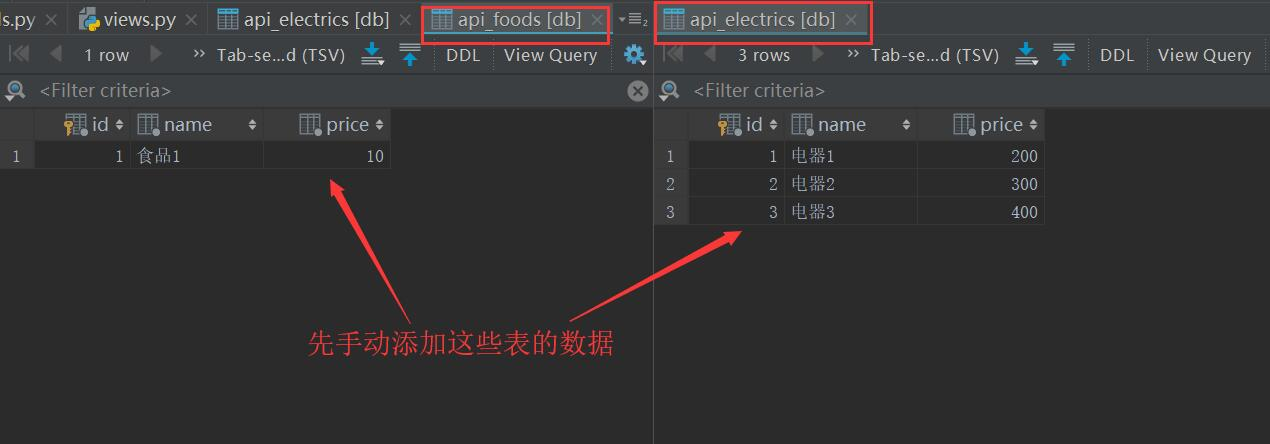
数据化迁移,再给每张表添加数据
衣服表,电器表,床上用品表,美食表
添加完之后,数据迁移,python manage.py makemigrations 和 python manage.py migrate
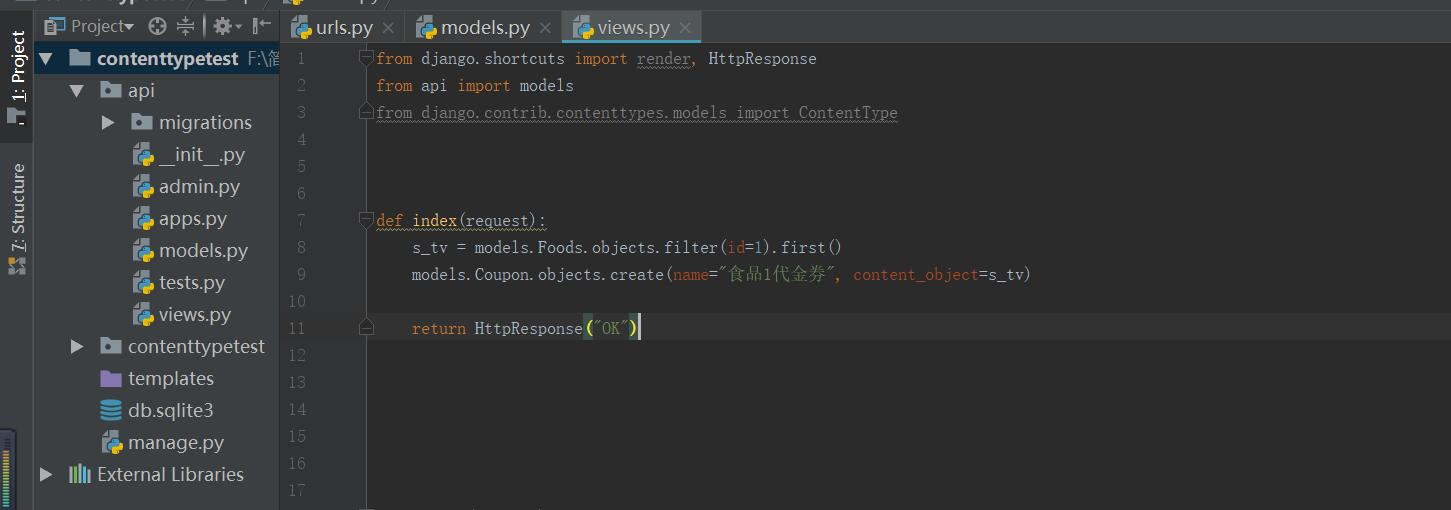
创建记录和查询 from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse from api import models from django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentType def test(request): if request.method == 'GET': # ContentType表对象有model_class() 方法,取到对应model content = ContentType.objects.filter(app_label='api', model='electrics').first() # 表名小写 cloth_class = content.model_class() # cloth_class 就相当于models.Electrics res = cloth_class.objects.all() print(res) # 为三星电视(id=2)创建一条优惠记录 s_tv = models.Electrics.objects.filter(id=2).first() models.Coupon.objects.create(name='电视优惠券', content_object=s_tv) # 查询优惠券(id=1)绑定了哪个商品 coupon_obj = models.Coupon.objects.filter(id=1).first() prod = coupon_obj.content_object print(prod) # 查询三星电视(id=2)的所有优惠券 res = s_tv.coupons.all() print(res)
总结: 当一张表和多个表FK关联,并且多个FK中只能选择其中一个或其中n个时,可以利用contenttypes app,只需定义三个字段就搞定!
创建记录
关系表的结构
用语法给关系表加记录。
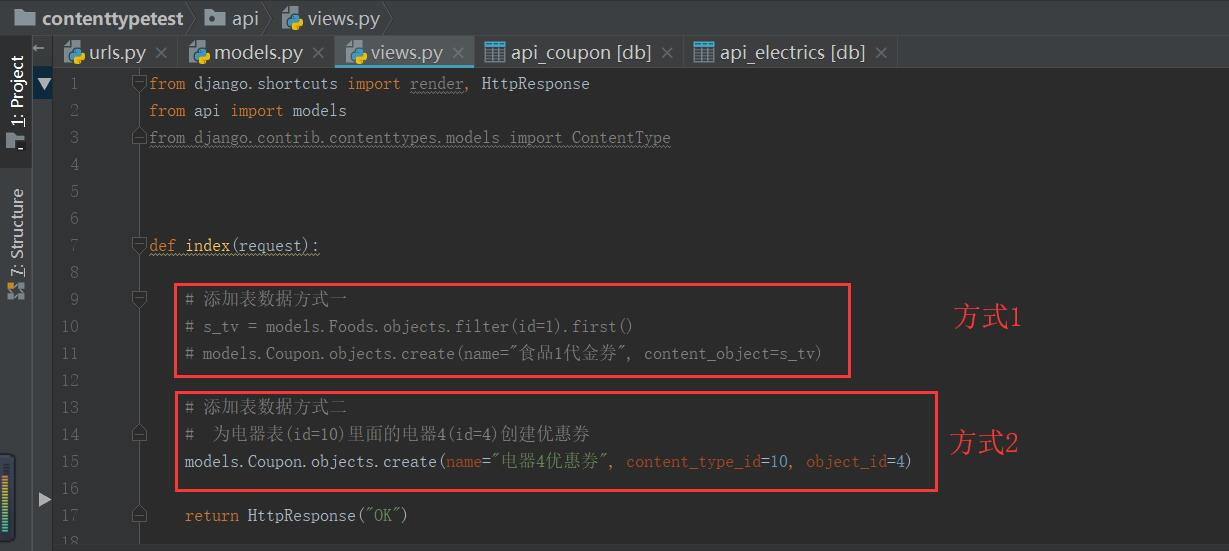
添加方式1:
接下来用postmen来发送请求
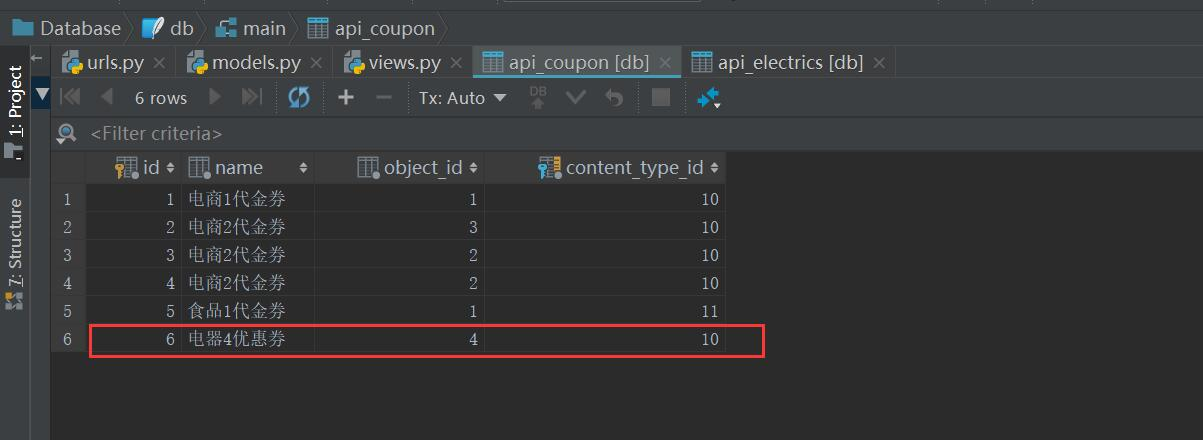
然后代金券表数据就添加完成了
添加方式2:
通过postmen发送请求结果
查询记录
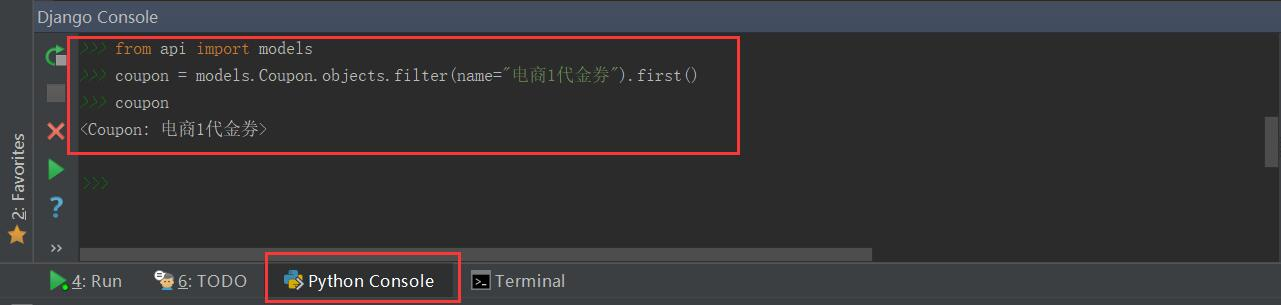
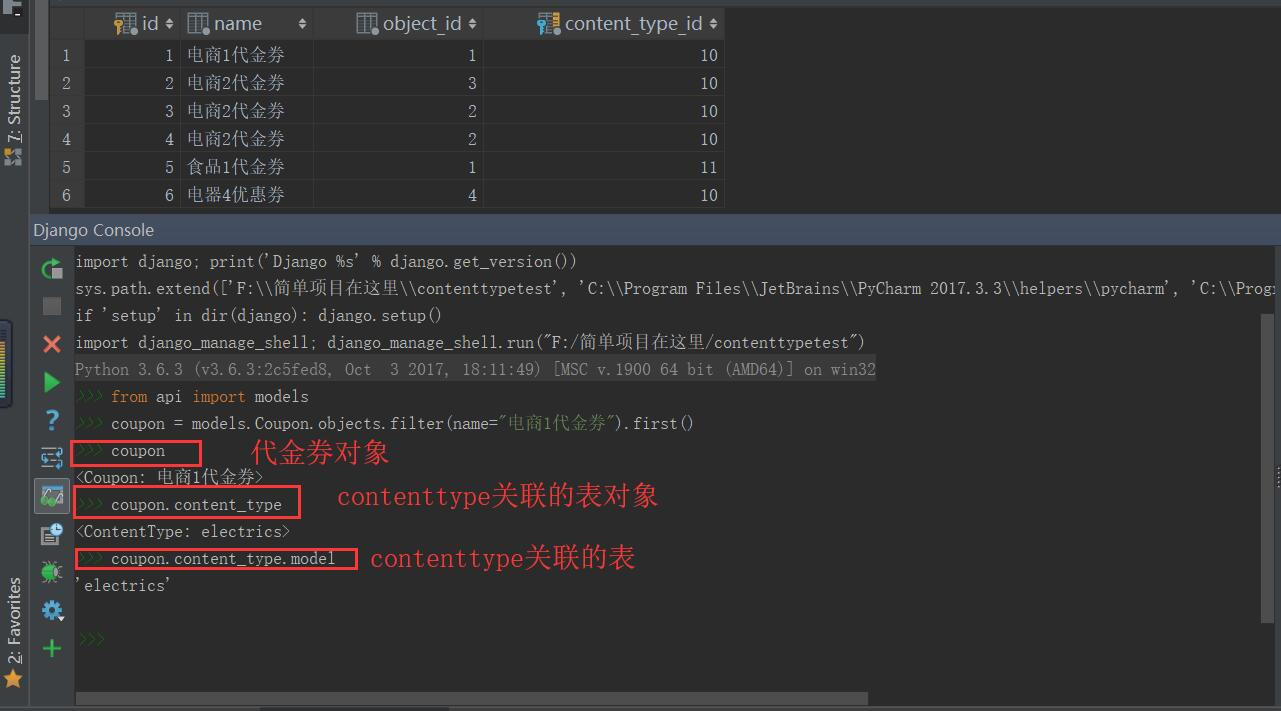
查询name="电商1代金券"的代金券信息







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号