关于两次大作业和期中考试的总结
一.前言
(1).题量:毫无疑问,两次大作业以及期中考试的题量是不大的,作业四和作业五都是只有一题菜单题,期中考试的题相对简单,四题其实就是一题;
(2).知识点:作业四和作业五依旧是一如既往的菜单题,对于作业四,没有添加新的概念,要加的是对错误信息的处理,在考虑用户输入不同信息错误做出不同的处理,要做的事情还是挺多的,而作业五添加一个特色菜的概念,菜品被分为了不同菜系,不同菜系对应不同口味,且口味值有上限和下限,考察的还是对类的写法,怎么去设计类怎么去实现类,而期中考试题目来说的话,相比大作业是简单的,是抽象类和接口的内容,继承关系的运用,难一点的地方在实现接口,要明白内部类的大概怎么写的;
(3).难度:难度来说,作业四应该是他们中最难的,最麻烦的,也是我得分最低的,很遗憾,结束前没能尽量把能拿的分拿了。
二.设计与分析
(1).菜单计价-4:
1.整体分析:
本次大作业的错误信息判断我觉得是麻烦的一次,添加一个错误判断得考虑多方面的内容,还要思考用什么方式去实现错误判断,比如有些情况我用了boolean型的变量作为判断,也或者是类中的属性,不仅难想,而且实现起来也不轻松,最终截至得分也没有及格,后来才补起来某些测试点。
2.我的类图:
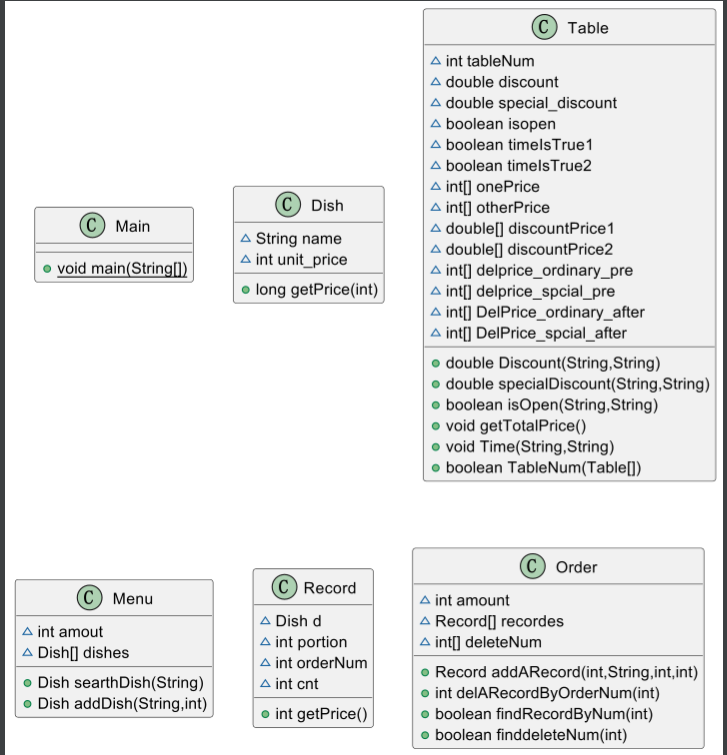
分析:总体类还是只有原来的几个类,并没有另外创建类,作为错误的判断,但是这样是不好的,对于错误的判断堆积在主程序里面,导致主程序是错综复杂的,而且让别人读代码也会感到迷茫,可能只有自己看得懂,这是失败的代码,从类图可以看出,Table太多内容了,分工太多,许多属性或许都谈不上属于桌子这一概念,对于实现当前问题来说或许可以,后续肯定会更加复杂的,代码就很难再添加完善下去,解决办法还是要重新构建类之间的结构,将大任务还要进行分工,不然Table类太乱了,Table承受了太多不属于它的东西了,太可怜了。
3.我的复杂度分析图:
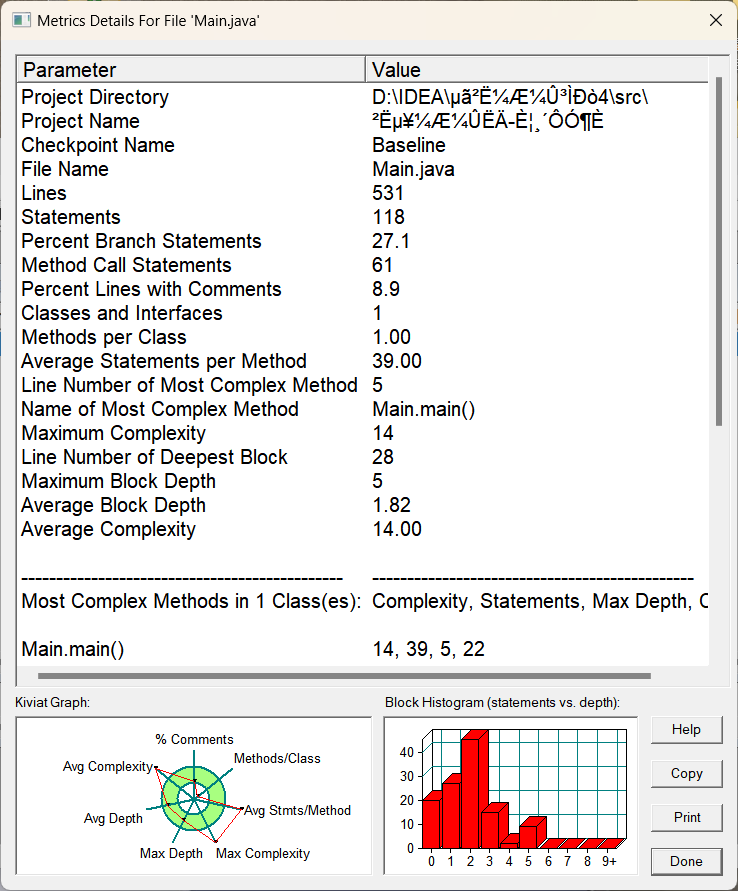
分析:从图中不难看出,Methonds per Class:平均每个类中就只有1个方法,但是Average Statements per Method : 平均每个方法中有39行语句,这说明代码复杂度是很高的,最复杂的方法也是main方法,如上面所说,错误判断语句都积累在了main方法中,是很导致复杂度高的,平均复杂度为14.00,也还是蛮高的,说明方法还是不简洁的,还要改进,特别是if-else语句,使用很多;再看左下角的雷达图(该图主要采用直观的方式表示该文件的代码的重构急迫性。当红色的圈在绿色圈以内时代码不需要重构,表示代码在安全范围内。但当红色圈在绿色圈意外时,代表代码急需重构):很大一部分超出绿色圆圈了,结构很差了,右下角的是三维柱状图:形描述语句长度与深度之间关系。
4.部分代码:
(1).两类折扣的计算方法:
public double Discount(String time1, String time2) { double discount = 0.0; String[] new_time1 = time1.split("/"); //年月日 String[] new_time2 = time2.split("/"); //时分秒 //处理年月日的时间 int year = Integer.parseInt(new_time1[0]); int month = Integer.parseInt(new_time1[1]); int day = Integer.parseInt(new_time1[2]); //处理时分秒的时间 int hh = Integer.parseInt(new_time2[0]); int ff = Integer.parseInt(new_time2[1]); int mm = Integer.parseInt(new_time2[2]); //转为LocalDate类型,获得星期几 LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); int zhouji = localDate.getDayOfWeek().getValue(); //秒数 int m = hh * 60 * 60 + ff * 60 + mm; //周一到周五 if (zhouji >= 1 && zhouji <= 5) { //17:00-20:30 if (m >= 17 * 3600 && m <= 20 * 3600 + 30 * 60) { discount = 0.8; } if (m >= 10 * 3600 + 30 * 60 && m <= 14 * 3600 + 30 * 60) { discount = 0.6; } } // //周六日 else discount = 1.0; return discount; } public double specialDiscount(String time1, String time2) { String[] new_time1 = time1.split("/"); //年月日 String[] new_time2 = time2.split("/"); //时分秒 //处理年月日的时间 int year = Integer.parseInt(new_time1[0]); int month = Integer.parseInt(new_time1[1]); int day = Integer.parseInt(new_time1[2]); //处理时分秒的时间 int hh = Integer.parseInt(new_time2[0]); int ff = Integer.parseInt(new_time2[1]); int mm = Integer.parseInt(new_time2[2]); //转为LocalDate类型,获得星期几 LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); int zhouji = localDate.getDayOfWeek().getValue(); //秒数 int m = hh * 60 * 60 + ff * 60 + mm; //周一到周五 if (zhouji >= 1 && zhouji <= 5) { //17:00-20:30 special_discount = 0.7; } //周六日 else special_discount = 1.0; return special_discount; }
(2).查序号是否重复删除:
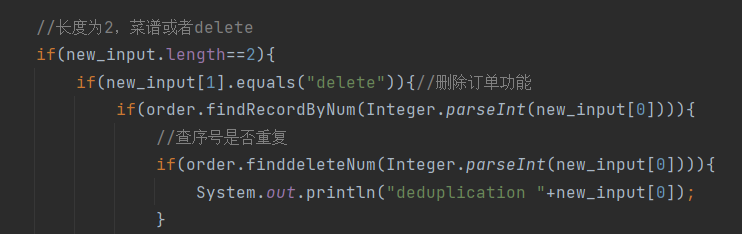
public boolean finddeleteNum(int deletenum){ for(int a=0;a<deleteNum.length;a++){ if(deleteNum[a]==deletenum) return true; } return false; }
(3).菜谱语句异常处理(正则表达式处理):
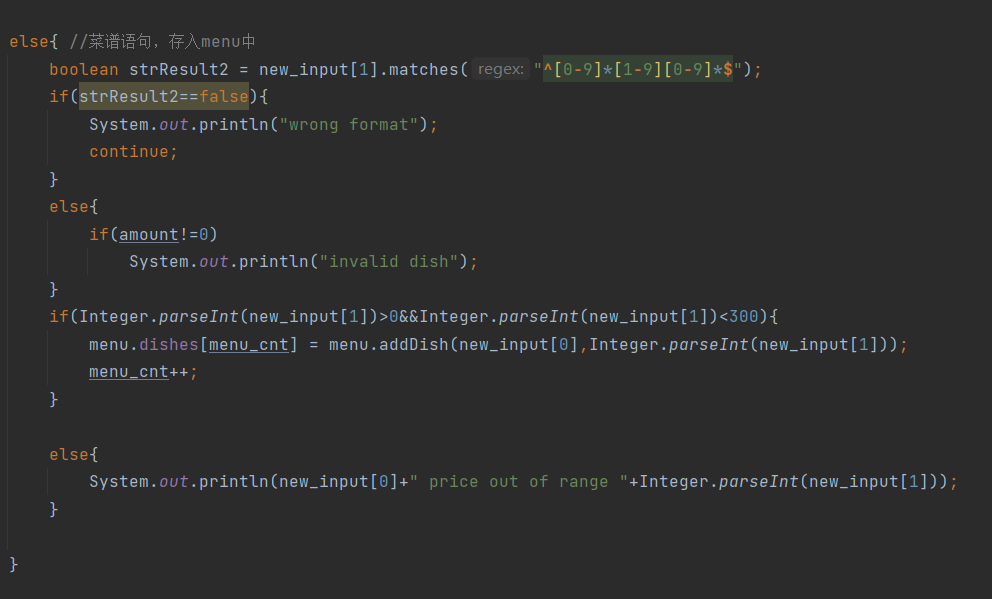
else{ //菜谱语句,存入menu中 boolean strResult2 = new_input[1].matches("^[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*$"); if(strResult2==false){ System.out.println("wrong format"); continue; } else{ if(amount!=0) System.out.println("invalid dish"); } if(Integer.parseInt(new_input[1])>0&&Integer.parseInt(new_input[1])<300){ menu.dishes[menu_cnt] = menu.addDish(new_input[0],Integer.parseInt(new_input[1])); menu_cnt++; } else{ System.out.println(new_input[0]+" price out of range "+Integer.parseInt(new_input[1])); } }
(4).同上当特色菜菜谱出错处理(判断当前的桌子是否为空,amonut代表桌子数量):
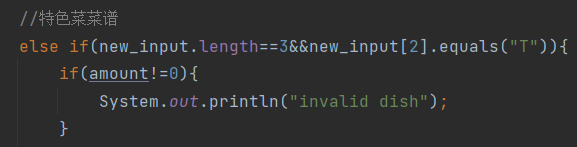
(5).table语句的判断(正则表达式不完善):
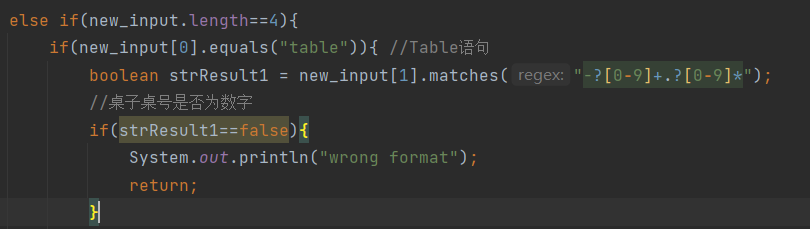
(2).菜单计价-5:
1.整体分析:
菜单5相对来说就简单许多了,实现特色菜方面还是可以做到的,难的是对类合理的设计,能想到更好的设计去实现,比如对特色菜新增的概念方面,甜辣度,一听都会觉得应该作为菜品的属性而存在,可是并没有考虑到除了特色菜之外,还是有普通的菜品的,这类菜没有甜辣度的概念,更没有菜系的说法,因此将新增的概念放在Dish类多少是有些不合理的,对于实际概念来说,在听了老师的分析之后,还是觉得采用继承关系来说比较合适,既然新增了概念,应该考虑概念作为类而实现的,做一个菜品的子类特色菜类继承菜品类,也就是Dish类,既有Dish类所有的基本属性,也有新增的菜系的属性等,特色菜类中再加上菜类型的属性,关联到“菜的类型”这个类,里面有类型名称和口味的属性概念,口味又是口味类型的属性,比如川菜,名称就是“川菜”,口味就是“辣”,然后再关联到“口味类型”这个类,包括名称,以及上限下限,如辣,等级0-5;按这样子来添加特色菜的概念,就比较合理了,从此看来,类的设计也是至关重要的一件事,而不是拿到题目就开始写代码,这样写出来的代码质量也不会高到哪里去,还得多分析多思考,这正是我欠缺的。
这边附上老师重构的类图:
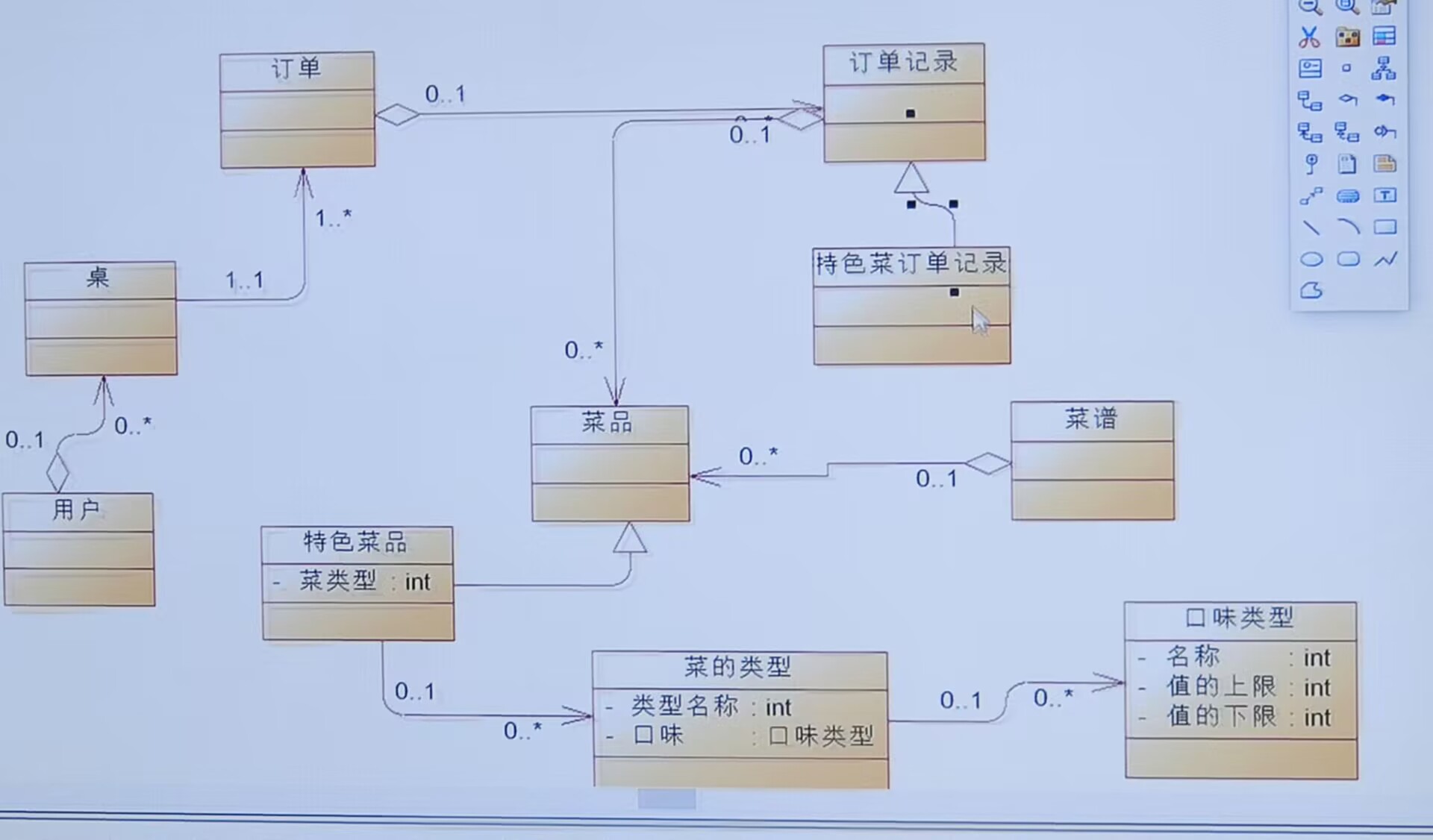
2.我的类图:
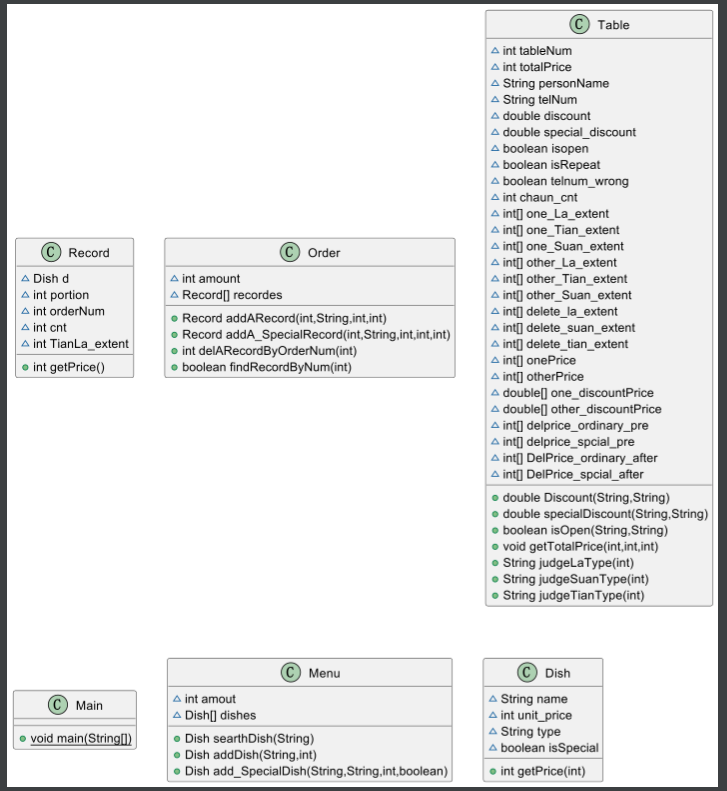
分析:想必第一眼看到的就是Table类了,太多了,相比上一次还要多,这就是不设计类图的弊端,emmmm从图中可以知道,类还是以往的类,并没有新添其他类,特色菜的添加我做为了属性去写,在Dish类加了一个菜的类型Type的属性,在记录类Record类中加了记录对应甜辣度的值的记录,这就是我的特色菜的概念的大概添加了,其他的都是具体的计算,以及输入输出语句了,倒也没什么都是简单的思路,就不一一分析了。
3.我的圈复杂度图:
(1).Dish类:
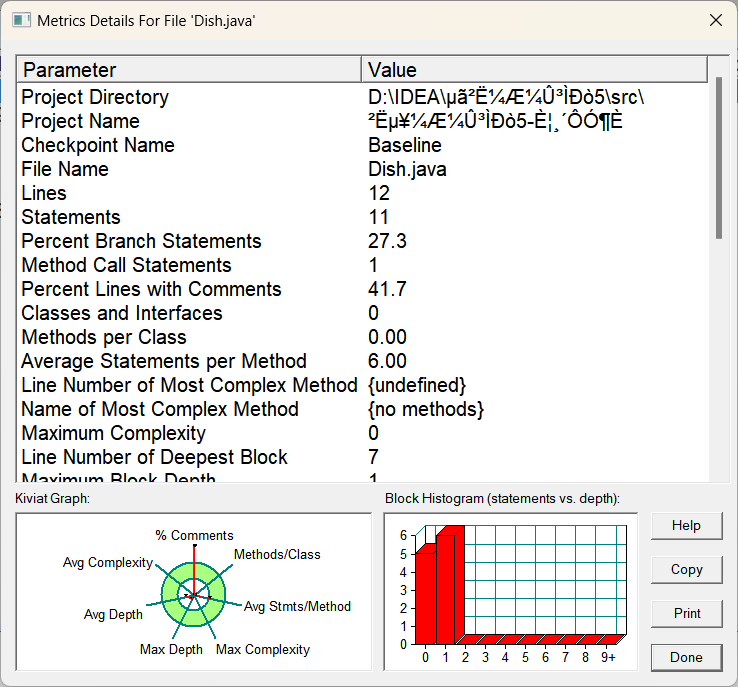
(2).Menu类:
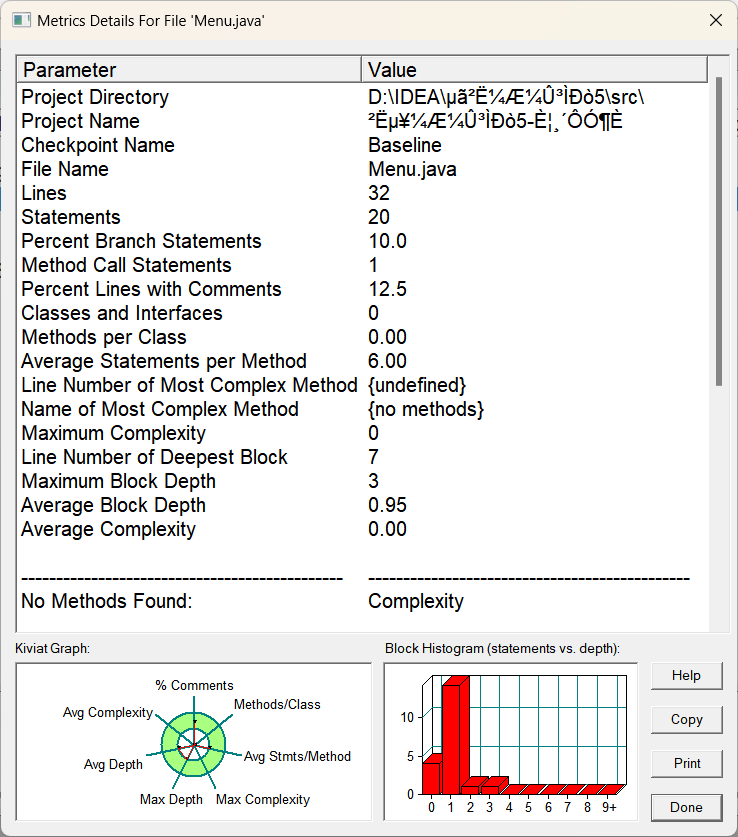
(3).Record类:
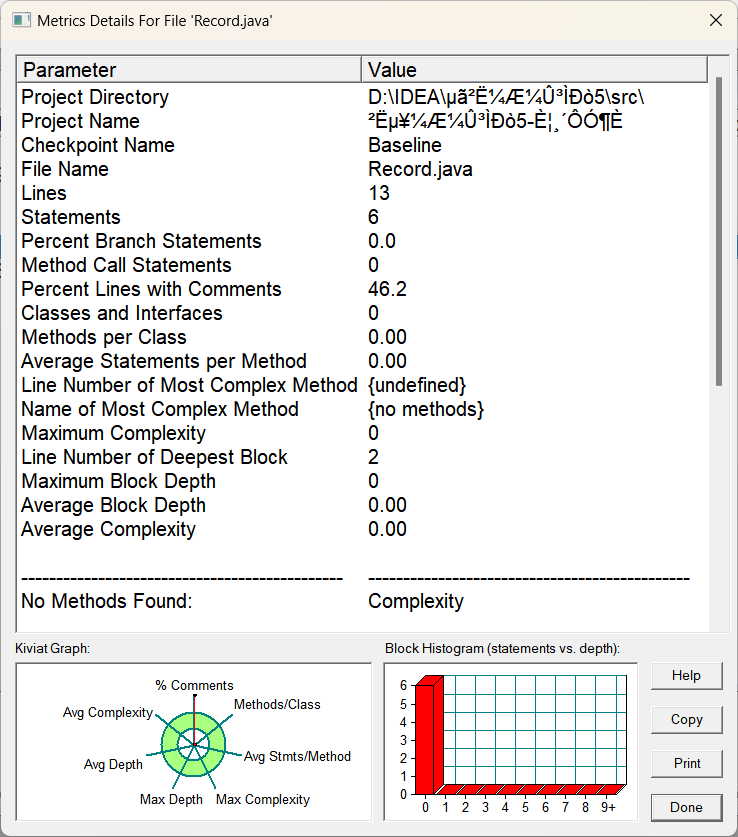
(4).Order类:
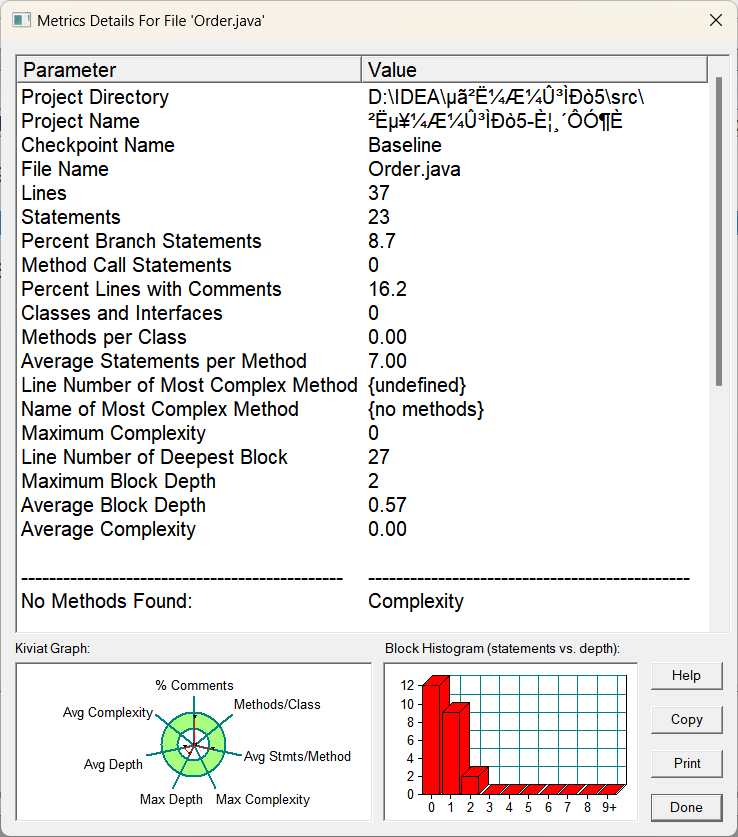
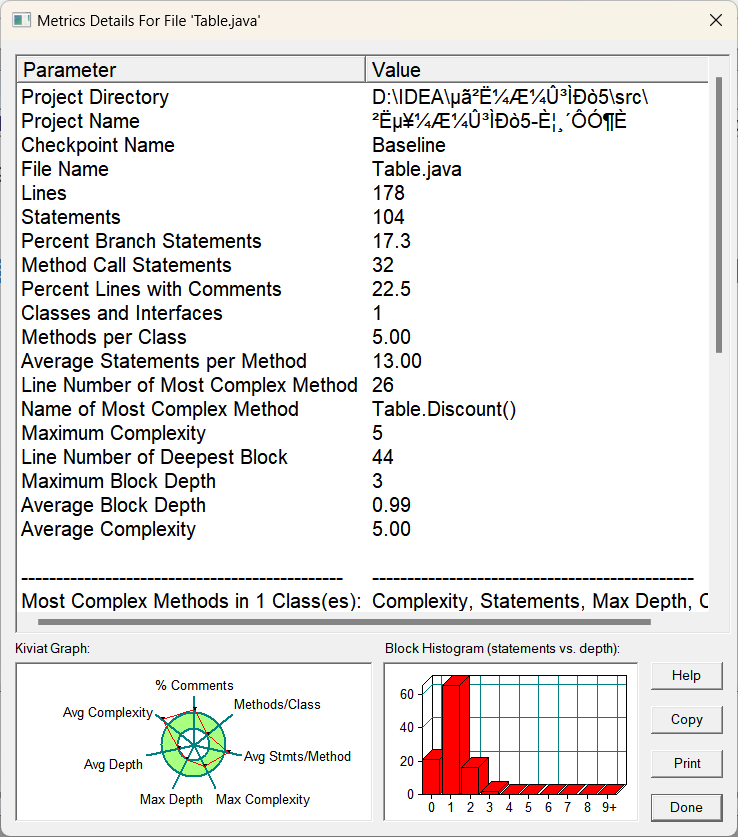
(5).Table类:
(6).main类:
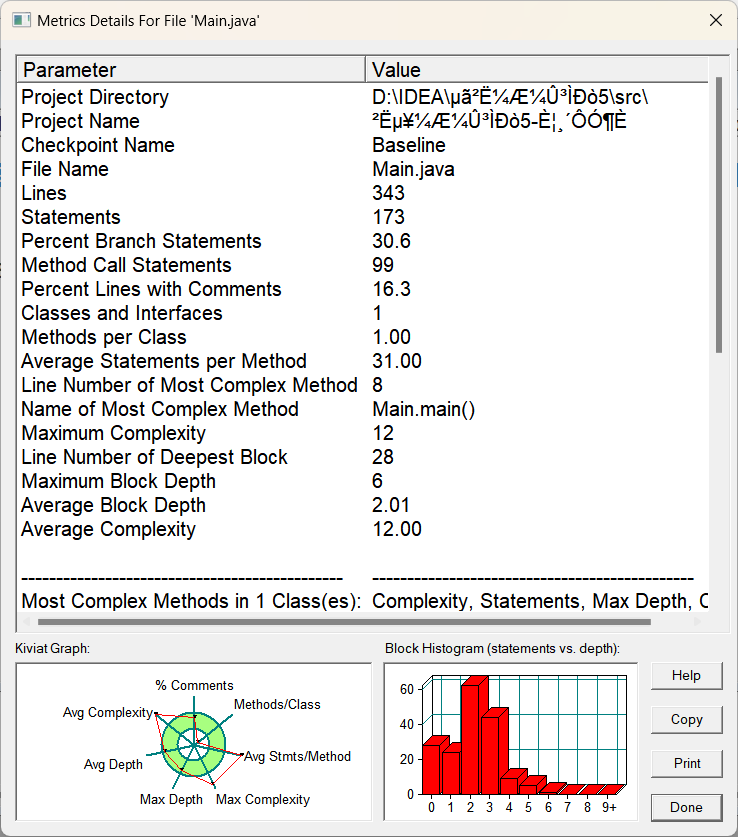
总体分析:像本身简单的类比如DIsh类,Menu类和Record类,基本是不会有什么大变化的,复杂度也不会高到哪里去,他们本身可能就一个方法,而且都是简单几句就实现的,不存在复杂的情况,但是Table类和main类还是一如既往的突出复杂,主打的就是复杂,我真的不故意的,在良好的设计面前,任何的其他的代码都显得很呆,只是往里面不断塞东西罢了,同理看他们的左下角的雷达图,都是多多少少超出了部分的绿色圆圈,类结构是比较糟糕的,常谈的问题了,还得看有没有良好的类设计和良好的方法实现,这样才不会导致复杂度的过于高了。
3.我的代码分析:
(1).准备工作
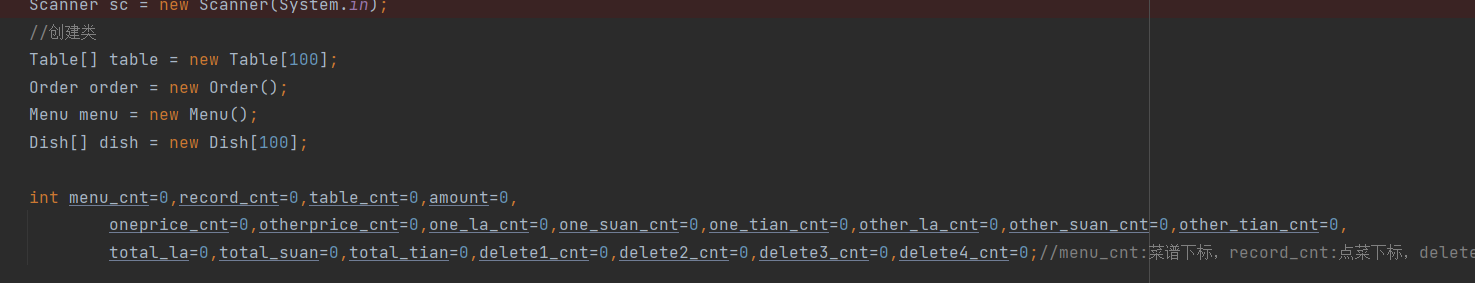
说明:上面就是在主方法里面所要用到的类的创建以及要用到的计数器的下标声明,因为我真的用了好多的数组,所以下标很多......
(2).长度为2,则为 ”普通菜菜谱“ 或者 ”删除语句“
String old_input = sc.nextLine(); String[] new_input = old_input.split(" "); //分割 if(new_input.length==1) break; //为end,跳出循环 //长度为2,则为 ”普通菜菜谱“ 或者 ”删除语句“ else if(new_input.length==2){ if(new_input[1].equals("delete")){ //查找序号是否存在 if(order.findRecordByNum(Integer.parseInt(new_input[0]))){ int record_flag=0; for(int b=0;b<record_cnt;b++){ if(order.recordes[b].orderNum==Integer.parseInt(new_input[0])){ //查找记录序号并记录下标 record_flag = b; } } //System.out.println(record_flag); //特色菜删除 if(order.recordes[record_flag].d.isSpecial){ //利用序号找到的下标判断是否为特色菜 table[table_cnt-1].delprice_spcial_pre[delete2_cnt] = order.recordes[record_flag].getPrice(); //特色菜打折前的 table[table_cnt-1].DelPrice_spcial_after[delete4_cnt] = Math.toIntExact(Math.round(table[table_cnt - 1].special_discount * table[table_cnt-1].delprice_spcial_pre[delete2_cnt])); //删除特色菜点菜的价格(打折后) //删除口味值 if(order.recordes[record_flag].d.type.equals("川菜")){ table[table_cnt-1].chaun_cnt-=order.recordes[record_flag].cnt; }if(order.recordes[record_flag].d.type.equals("晋菜")){ table[table_cnt-1].jin_cnt-=order.recordes[record_flag].cnt; }if(order.recordes[record_flag].d.type.equals("浙菜")){ table[table_cnt-1].zhe_cnt-=order.recordes[record_flag].cnt; } delete2_cnt++; delete4_cnt++; } else{ //普通菜删除 table[table_cnt-1].delprice_ordinary_pre[delete1_cnt] = order.recordes[record_flag].getPrice(); //普通菜打折前的 table[table_cnt-1].DelPrice_ordinary_after[delete3_cnt] = Math.toIntExact(Math.round(table[table_cnt - 1].discount * table[table_cnt-1].delprice_ordinary_pre[delete1_cnt])); //删除普通菜的价格(打折后) delete1_cnt++; delete3_cnt++; } } else{ //没找到该序号 System.out.println("delete error;"); } }
说明:当识别到分割后字符串的长度为2,再看第一个是不是"delete",是则说明是删除语句,要将对应桌子的点菜记录删除,当然首先要做的是看这个序号是否存在,不存在就输出不存在了,然后序号存在的话我做的处理是:先根据这个序号去查找哪个桌子所点的,因为我碰到过两桌序号相同的情况,则根据序号删除会将第一桌的菜给删除导致错误删除,所以要先进行一下查找,当然疑问来了,查找不是也会查到上一桌的序号嘛,对的,但是如果我查找到我并没有结束查找呢,而是记下下标,继续查找,直到查完序号,最后一个找到的不就是我此桌所对应的序号嘛,查找的目的主要是得到下标,那么就有了当前桌的所有信息了。查找完后,就要正式删除了,分两种情况,一种是特色菜的删除,因为是有口味值的概念在里面的,和普通菜的删除是不一样的,具体删除如上代码。如果第一个字符串不是"delete",就说明是正常情况下的普通菜语句,添加到菜谱中即可。
(3).长度为4,则为 ”特色菜菜谱语句“ 或者 ”普通菜点菜语句“
//长度为4,则为 ”特色菜菜谱语句“ 或者 ”普通菜点菜语句“ else if(new_input.length==4){ if(new_input[3].equals("T")){ for(int i=0;i<menu_cnt;i++){ if(new_input[0].equals(menu.dishes[i].name)){ menu.dishes[i] = menu.add_SpecialDish(new_input[0],new_input[1],Integer.parseInt(new_input[2]),true); } } //特色菜的菜谱 存入菜谱中 menu.dishes[menu_cnt] = menu.add_SpecialDish(new_input[0],new_input[1],Integer.parseInt(new_input[2]),true); menu_cnt++; } else{ //普通菜点菜 先看菜谱中查找有没有 dish[record_cnt] = menu.searthDish(new_input[1]); if(table[table_cnt - 1].isopen &&table[table_cnt-1].telnum_wrong==false){ if(dish[record_cnt]!=null){ //存在该菜 //添加到记录中 order.recordes[record_cnt] = order.addARecord(Integer.parseInt(new_input[0]),new_input[1],Integer.parseInt(new_input[2]),Integer.parseInt(new_input[3])); order.recordes[record_cnt].d = dish[record_cnt]; //计算本次点菜的价格 table[table_cnt-1].onePrice[oneprice_cnt] = order.recordes[record_cnt].getPrice(); //根据时间进行打折 table[table_cnt-1].one_discountPrice[oneprice_cnt] = Math.round(table[table_cnt-1].onePrice[oneprice_cnt] * table[table_cnt-1].discount); //输出价格(未打折) System.out.println(order.recordes[record_cnt].orderNum+" "+order.recordes[record_cnt].d.name+" "+(int) table[table_cnt-1].onePrice[oneprice_cnt]); record_cnt++; oneprice_cnt++; } else{ System.out.println(new_input[1]+" does not exist"); } } } }
说明:当识别到字符串长度为4时,证明可能是特色菜菜谱或者普通菜的点菜语句,这时候就需要判断是否为特色菜了,特色菜菜谱的标志就是看最后字符是否为T,如果是的话,那就明显是特色菜菜谱,将本句的菜加入到菜谱中即可,反之,另外一种情况,是普通菜的点菜语句,那么首先就要在菜谱中查找是否存在该菜,如果菜谱中并没有这个菜,那肯定就点不了了,输出某某菜不存在即可,如果存在该菜, 继续就添加到记录,并开始计算价格,以及打折后的价格,折扣是由本桌的语句得到的,但是注意下标,由于在table语句最后会将下标加1,所以本桌的折扣实际上是下标减去1的桌子的折扣。
(4).长度为5,则为 ”特色菜点菜语句“ 或者 ”普通菜代点菜语句“
//长度为5,则为 ”特色菜点菜语句“ 或者 ”普通菜代点菜语句“ else if(new_input.length==5){ dish[record_cnt] = menu.searthDish(new_input[1]); if(table[table_cnt-1].isopen==true&&table[table_cnt-1].telnum_wrong==false){ if(dish[record_cnt]!=null&&dish[record_cnt].isSpecial==true){ //是特色菜则是点菜 不是代点普通菜 //添加到记录中 order.recordes[record_cnt] = order.addA_SpecialRecord(Integer.parseInt(new_input[0]),new_input[1],Integer.parseInt(new_input[2]),Integer.parseInt(new_input[3]),Integer.parseInt(new_input[4])); order.recordes[record_cnt].d = dish[record_cnt]; if(dish[record_cnt].type.equals("川菜")&&(Integer.parseInt(new_input[2])>5||Integer.parseInt(new_input[2])<0)){ System.out.println("spicy num out of range :"+Integer.parseInt(new_input[2])); continue; } if(dish[record_cnt].type.equals("晋菜")&&(Integer.parseInt(new_input[2])>4||Integer.parseInt(new_input[2])<0)){ System.out.println("acidity num out of range :"+Integer.parseInt(new_input[2])); continue; } if(dish[record_cnt].type.equals("浙菜")&&(Integer.parseInt(new_input[2])>3||Integer.parseInt(new_input[2])<0)){ System.out.println("sweetness num out of range :"+Integer.parseInt(new_input[2])); continue; } if(dish[record_cnt].type.equals("川菜")){ //菜系的订单数 table[table_cnt-1].chaun_cnt+=order.recordes[record_cnt].cnt; table[table_cnt-1].one_La_extent[one_la_cnt]+=order.recordes[record_cnt].TianLa_extent*order.recordes[record_cnt].cnt; one_la_cnt++; } if(dish[record_cnt].type.equals("晋菜")){ table[table_cnt-1].jin_cnt+=order.recordes[record_cnt].cnt; table[table_cnt-1].one_Suan_extent[one_suan_cnt]+=order.recordes[record_cnt].TianLa_extent*order.recordes[record_cnt].cnt; one_suan_cnt++; } if(dish[record_cnt].type.equals("浙菜")){ table[table_cnt-1].zhe_cnt+=order.recordes[record_cnt].cnt; table[table_cnt-1].one_Tian_extent[one_tian_cnt]+=order.recordes[record_cnt].TianLa_extent*order.recordes[record_cnt].cnt; one_tian_cnt++; } //计算本次点菜的价格 table[table_cnt-1].onePrice[oneprice_cnt] = order.recordes[record_cnt].getPrice(); //根据时间进行打折 table[table_cnt-1].one_discountPrice[oneprice_cnt] = Math.round(table[table_cnt-1].onePrice[oneprice_cnt] * table[table_cnt-1].special_discount); //输出价格(未打折) System.out.println(order.recordes[record_cnt].orderNum+" "+order.recordes[record_cnt].d.name+" "+(int) table[table_cnt-1].onePrice[oneprice_cnt]); record_cnt++; oneprice_cnt++; } else if(dish[record_cnt]==null){ System.out.println(new_input[1]+" does not exist"); } else{ //普通菜代点菜 order.recordes[record_cnt] = order.addARecord(Integer.parseInt(new_input[1]),new_input[2],Integer.parseInt(new_input[3]),Integer.parseInt(new_input[4])); order.recordes[record_cnt].d = dish[record_cnt]; table[table_cnt-1].otherPrice[otherprice_cnt] = order.recordes[record_cnt].getPrice(); table[table_cnt-1].other_discountPrice[otherprice_cnt] = Math.round(table[table_cnt-1].otherPrice[otherprice_cnt] * table[table_cnt-1].discount); System.out.println(order.recordes[record_cnt].orderNum+" table "+table[table_cnt-1].tableNum+" pay for table "+ Integer.parseInt(new_input[0]) +" "+(int)table[table_cnt-1].otherPrice[otherprice_cnt]); record_cnt++; otherprice_cnt++; } } }
说明:当长度为时,此时又是两种情况,为 ”特色菜点菜语句“ 或者 ”普通菜代点菜语句“,既然都是点菜语句,那么都是要在菜谱中查找是否存在这个菜的,如果不存在这个菜,就没有后文了,直接输出该菜不存在即可,当然存在的话,怎么分辨这两种情况呢,那么就要用到菜品的属性之一,菜品是否为特色菜的boolean标志了,查找到的结果就有用了,因为查找的方法返回值是Dish类型的,根据这个就可以判断是否为特色菜点菜了。
查找方法代码如图:
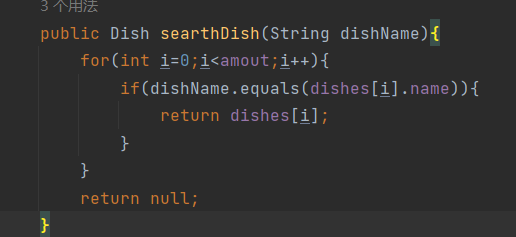
两种情况分开以后各自进行操作就好了,是特色菜点菜就将记录添加,然后判断甜辣度值是否超出范围,给出输出,然后接着将口味值记录,计算价格以及打折价格,最后下标加一,普通菜代点菜同理。
(5).长度为6,则为特色菜代点菜语句
//长度为6,则为特色菜代点菜语句 else if(new_input.length==6){ // if(new_input[0].equals("table")){ // System.out.println("wrong format"); // return; // } dish[record_cnt] = menu.searthDish(new_input[2]); if(table[table_cnt-1].isopen==true&&table[table_cnt-1].telnum_wrong==false){ if(dish[record_cnt]!=null){ int table_flag = 0; //记录被代点菜桌的桌子数组下标 order.recordes[record_cnt] = order.addA_SpecialRecord(Integer.parseInt(new_input[1]),new_input[2],Integer.parseInt(new_input[3]),Integer.parseInt(new_input[4]),Integer.parseInt(new_input[5])); order.recordes[record_cnt].d = dish[record_cnt]; for(int a=0;a<amount;a++){ if(table[a].tableNum==Integer.parseInt(new_input[0])){ table_flag = a; break; } } if(dish[record_cnt].type.equals("川菜")&&(Integer.parseInt(new_input[3])>5||Integer.parseInt(new_input[3])<0)){ System.out.println("spicy num out of range :"+Integer.parseInt(new_input[3])); continue; } if(dish[record_cnt].type.equals("晋菜")&&(Integer.parseInt(new_input[3])>4||Integer.parseInt(new_input[3])<0)){ System.out.println("acidity num out of range :"+Integer.parseInt(new_input[3])); continue; } if(dish[record_cnt].type.equals("浙菜")&&(Integer.parseInt(new_input[3])>3||Integer.parseInt(new_input[3])<0)){ System.out.println("sweetness num out of range :"+Integer.parseInt(new_input[3])); continue; } //注意:代点的口味值加到对方的桌上 if(dish[record_cnt].type.equals("川菜")){ //菜系的订单数 table[table_flag].chaun_cnt+=order.recordes[record_cnt].cnt; table[table_flag].other_La_extent[other_la_cnt]+=order.recordes[record_cnt].TianLa_extent*order.recordes[record_cnt].cnt; other_la_cnt++; } if(dish[record_cnt].type.equals("晋菜")){ table[table_flag].jin_cnt+=order.recordes[record_cnt].cnt; table[table_flag].other_Suan_extent[other_suan_cnt]+=order.recordes[record_cnt].TianLa_extent*order.recordes[record_cnt].cnt; other_suan_cnt++; } if(dish[record_cnt].type.equals("浙菜")){ table[table_flag].zhe_cnt+=order.recordes[record_cnt].cnt; table[table_flag].other_Tian_extent[other_tian_cnt]+=order.recordes[record_cnt].TianLa_extent*order.recordes[record_cnt].cnt; other_tian_cnt++; } table[table_cnt-1].otherPrice[otherprice_cnt] = order.recordes[record_cnt].getPrice(); table[table_cnt-1].other_discountPrice[otherprice_cnt] = Math.round(table[table_cnt-1].otherPrice[otherprice_cnt] * table[table_cnt-1].special_discount); System.out.println(order.recordes[record_cnt].orderNum+" table "+table[table_cnt-1].tableNum+" pay for table "+ Integer.parseInt(new_input[0]) +" "+(int)table[table_cnt-1].otherPrice[otherprice_cnt]); record_cnt++; otherprice_cnt++; } else{ System.out.println(new_input[2]+" does not exist"); } } }
说明:长度为6,为特色菜的代点菜语句,操作和正常点菜差不多,只是口味值的记录要记录到被代点的桌子上,对此,我也进行了一次桌号的查找,知道找到被代点的桌子后,记录下那个桌子的下标,然后与正常点菜同理,记录下来点菜语句,只是不同的是口味值的添加是加到被点菜的桌子上,查找到的下标就派上用场了,利用下标就好。其他不再加以说明,同理。
(6).其他长度则为table语句
//其他长度则为table语句 else if(new_input.length==7){ if(new_input[0].equals("table")){ amount++; Table table1 = new Table(); //桌号,姓名,电话号码记录 table1.tableNum = Integer.parseInt(new_input[1]); table1.personName = new_input[3]; table1.telNum = new_input[4]; //得到折扣 table1.discount = table1.Discount(new_input[5],new_input[6]); table1.special_discount = table1.specialDiscount(new_input[5],new_input[6]); table[table_cnt] = table1; String regex = "^table\\s\\d{1,2}\\s:\\s[a-zA-Z]{1,10}\\s(180|181|189|133|135|136)\\d{8}\\s\\d{4}/(0?[1-9]|1[0-2])/(0?[1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01])\\s([01]?[0-9]|2[0-3])/[0-5][0-9]/[0-5][0-9]$"; // 创建Pattern对象 Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex); // 创建Matcher对象 Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(old_input); if (!matcher.matches()){ System.out.println("wrong format"); table[table_cnt].telnum_wrong = true; table_cnt++; continue; } // //对电话号码判断 // String s = new_input[4].substring(0,3); // if((!(s!="180"&&s!="181"&&s!="189"&&s!="133"&&s!="136"&&s!="135"))||(new_input[4].length()!=11)||(new_input[3].length()>10)){ // System.out.println("wrong format"); // table[table_cnt].telnum_wrong = true; // table_cnt++; // continue; // } //判断该桌时间是否营业 table[table_cnt].isopen = table[table_cnt].isOpen(new_input[5],new_input[6]); if(table[table_cnt].isopen==false){ System.out.println("table "+table[table_cnt].tableNum+" out of opening hours"); } if(table[table_cnt].isopen&&table[table_cnt].telnum_wrong==false){ System.out.println("table "+table[table_cnt].tableNum+": "); } table_cnt++; } } else{ System.out.println("wrong format"); }
说明:其实说其他长度的语句就是table语句是不合理的,而且很多不合理,这只针对于正确的输入,其他长度的语句也有可能是table语句的,因为有可能是格式错误,但是还是table开头的,因此差的最后一个测试点就是在这了,我当识别到第一个字符串为“table”时,我不能保证这个语句是正确的,因此这里需要一个正则表达式的帮助,规范正确的table语句是这样的,那么就可以判断,理论上来说这样是没错了,但是还有bug,如果长度为4或5或者是上述情况的长度时,又怎么办?每种长度语句的开头都做判断嘛,虽然麻烦,但是能行的麻烦也还好,但是真的行吗,如果没理解错的话,当table语句错误的时候,这个桌子后面所有的操作都是不做处理的,又该怎么写,我...卡住了,添加boolean标志也试过了,又会引发空指针问题........
(7).其他:
整体table行的输出:
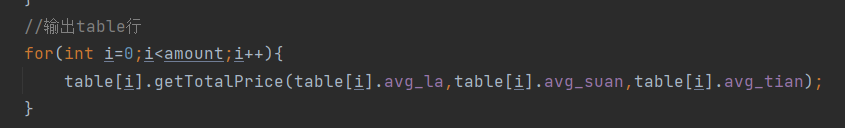
public void getTotalPrice(int la,int suan,int tian){ int tatalPrice_final=0,tatalPrice_pre=0; for(int q=0;q<one_discountPrice.length;q++){ tatalPrice_pre += onePrice[q] + otherPrice[q] - delprice_ordinary_pre[q] - delprice_spcial_pre[q]; //一张桌子的总价格等于点菜的价格加上代点菜的价格减去删除的价格 tatalPrice_final += (one_discountPrice[q] + other_discountPrice[q] - DelPrice_ordinary_after[q]) - DelPrice_spcial_after[q]; } totalPrice = tatalPrice_final; if(isopen&&telnum_wrong==false&&(chaun_cnt!=0||jin_cnt!=0||zhe_cnt!=0)){ System.out.println("table "+tableNum+": "+tatalPrice_pre+" "+tatalPrice_final +judgeLaType(la)+judgeSuanType(suan)+judgeTianType(tian)); } if(isopen&&telnum_wrong==false&&chaun_cnt==0&&jin_cnt==0&&zhe_cnt==0) System.out.println("table "+tableNum+": "+tatalPrice_pre+" "+tatalPrice_final +" "); }
名字行的输出:
//输出名字行 for(int m=0;m<amount;m++){ for(int n=m+1;n<amount;n++){ //如果名字一样,价格加到一起 if(table[n].personName.equals(table[m].personName)){ table[m].totalPrice+=table[n].totalPrice; table[n].totalPrice=0; table[n].isRepeat=true; } if(table[n].personName.compareToIgnoreCase(table[m].personName)<0){ Table table0 = new Table(); table0 = table[n]; table[n] = table[m]; table[m] = table0; } } }
for(int i=0;i<amount;i++){
if(table[i].isopen&&table[i].isRepeat==false&&table[i].telnum_wrong==false){
System.out.println(table[i].personName+" "+table[i].telNum+" "+table[i].totalPrice);
}
}
以上就是个人部分代码的分析,写的不好,看看就好。
(3).期中考试:
1.总体分析:
整体来说,这次考试更多的是类的设计,并且题目还给出的主要的设计,比如第三题连类图都给了,只要照着类图写代码,而且每个方法里面基本都是一两句就可以写完,直接返回的更是一大片,更考验的还是临场的经验,保持心态,不管写的来还是写不来,要说难一点的就是最后的Comparable接口了,刚开始看到没反应过来,确实是看不懂要写的是什么,接口本身是没几句可以写好的,主方法也给好了,复制过来用就好。
2.题目详细分析:
(1).7-1

分析:对于7-1其他的都没什么,这个错误判断,是我后面补的,开始的时候确实没发现什么问题,因为我是照着题目翻译的,半径取大于0的,所以我的写法是如果输入的是小于0的,则输出"wrong format",这样子提交是过不了全部的测试点的,后面好好想想,原因可能是输入的半径可不一定是个数,也可以是字母也可能,但ASCII码是double,所以后面改变了判断,结果正确。
代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); Circle circle = new Circle(); double area,banjin; banjin = sc.nextDouble(); if(!(banjin>0)){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else{ circle.setBanjin(banjin); area = circle.getarea(); System.out.printf("%.2f",area); } } } class Circle{ private double banjin; public double getBanjin() { return banjin; } public void setBanjin(double banjin) { this.banjin = banjin; } public double getarea(){ return banjin*banjin*Math.PI; } }
(2).7-2

分析:正常写法,不做分析了
代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); double x1,x2,y1,y2; x1 = sc.nextDouble(); y1 = sc.nextDouble(); x2 = sc.nextDouble(); y2 = sc.nextDouble(); Point point1 = new Point(x1,y1); Point point2 = new Point(x2,y2); Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(point1,point2); double length,height; length = rectangle.getLength(); height = rectangle.getHeight(); System.out.printf("%.2f",length*height); } } class Rectangle{ Point point1; Point point2; public Rectangle(Point point1, Point point2) { this.point1 = point1; this.point2 = point2; } public double getLength(){ return Math.abs(point1.x-point2.x); } public double getHeight(){ return Math.abs(point1.y - point2.y); } public double getArea(){ return getHeight()*getLength(); } public Point getPoint1() { return point1; } public Point getPoint2() { return point2; } public void setPoint1(Point point1) { this.point1 = point1; } public void setPoint2(Point point2) { this.point2 = point2; } } class Point{ double x; double y; public Point(){ } public Point(double x, double y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } public double getX() { return x; } public double getY() { return y; } public void setX(double x) { this.x = x; } public void setY(double y) { this.y = y; } }
(3).7-3
分析:主方法已给出,并且还有类图,照着写就好了不做分析。
代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int choice = input.nextInt(); switch(choice) { case 1://Circle double banjin = input.nextDouble(); if(!(banjin>0)){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); break; }else{ shape circle = new Circle(banjin); printArea(circle); break; } case 2://Rectangle double x1 = input.nextDouble(); double y1 = input.nextDouble(); double x2 = input.nextDouble(); double y2 = input.nextDouble(); Point leftTopPoint = new Point(x1,y1); Point lowerRightPoint = new Point(x2,y2); Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(leftTopPoint,lowerRightPoint); printArea(rectangle); break; } } private static void printArea(shape circle) { System.out.printf("%.2f",circle.getArea()); } } abstract class shape{ public shape() { } abstract double getArea(); } class Rectangle extends shape{ Point point1; Point point2; public Rectangle(Point point1, Point point2) { this.point1 = point1; this.point2 = point2; } public double getLength(){ return Math.abs(point1.x-point2.x); } public double getHeight(){ return Math.abs(point1.y - point2.y); } public double getArea(){ return getHeight()*getLength(); } public Point getPoint1() { return point1; } public Point getPoint2() { return point2; } public void setPoint1(Point point1) { this.point1 = point1; } public void setPoint2(Point point2) { this.point2 = point2; } } class Point { double x; double y; public Point(){ } public Point(double x, double y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } public double getX() { return x; } public double getY() { return y; } public void setX(double x) { this.x = x; } public void setY(double y) { this.y = y; } } class Circle extends shape{ private double banjin; public Circle(double banjin) { this.banjin = banjin; } public double getBanjin() { return banjin; } public void setBanjin(double banjin) { this.banjin = banjin; } public double getArea(){ return banjin*banjin*Math.PI; } }
(4).7-4
在测验3的题目基础上,重构类设计,实现列表内图形的排序功能(按照图形的面积进行排序)。
提示:题目中Shape类要实现Comparable接口。
其中,Main类源码如下(可直接拷贝使用):
public class Main {
public static void main(String\[\] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
ArrayList<Shape> list = new ArrayList<>();
int choice = input.nextInt();
while(choice != 0) {
switch(choice) {
case 1://Circle
double radiums = input.nextDouble();
Shape circle = new Circle(radiums);
list.add(circle);
break;
case 2://Rectangle
double x1 = input.nextDouble();
double y1 = input.nextDouble();
double x2 = input.nextDouble();
double y2 = input.nextDouble();
Point leftTopPoint = new Point(x1,y1);
Point lowerRightPoint = new Point(x2,y2);
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(leftTopPoint,lowerRightPoint);
list.add(rectangle);
break;
}
choice = input.nextInt();
}
list.sort(Comparator.naturalOrder());//正向排序
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(String.format("%.2f", list.get(i).getArea()) + " ");
}
}
}输入格式:
输入图形类型(1:圆形;2:矩形;0:结束输入)
输入图形所需参数
输出格式:
按升序排序输出列表中各图形的面积(保留两位小数),各图形面积之间用空格分隔。
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1
2.3
2
3.2
3
6
5
1
2.3
0输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
5.60 16.62 16.62 接口分析:

实际上是两个面积的比较,但是传入参数得是Object类型,所以做了判断,如果是instanceof某个类,就强制转换为某个类型的类型,再和本身类的面积进行比较,小于则返回-1,大于则返回1,否则返回0。
这一题的主要也就是这个接口的代码,其他的都是前面写好的,复制过来即可。
代码如下:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); ArrayList<shape> list = new ArrayList<>(); int choice = input.nextInt(); while(choice != 0) { switch(choice) { case 1://Circle double radiums = input.nextDouble(); shape circle = new Circle(radiums); list.add(circle); break; case 2://Rectangle double x1 = input.nextDouble(); double y1 = input.nextDouble(); double x2 = input.nextDouble(); double y2 = input.nextDouble(); Point leftTopPoint = new Point(x1,y1); Point lowerRightPoint = new Point(x2,y2); Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(leftTopPoint,lowerRightPoint); list.add(rectangle); break; } choice = input.nextInt(); } list.sort(Comparator.naturalOrder());//正向排序 for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { System.out.print(String.format("%.2f", list.get(i).getArea()) + " "); } } } abstract class shape implements Comparable { public shape() { } abstract double getArea(); } class Rectangle extends shape{ Point point1; Point point2; public Rectangle(Point point1, Point point2) { this.point1 = point1; this.point2 = point2; } public double getLength(){ return Math.abs(point1.x-point2.x); } public double getHeight(){ return Math.abs(point1.y - point2.y); } public double getArea(){ return getHeight()*getLength(); } public Point getPoint1() { return point1; } public Point getPoint2() { return point2; } public void setPoint1(Point point1) { this.point1 = point1; } public void setPoint2(Point point2) { this.point2 = point2; } public int compareTo(Object o) { if(o instanceof shape){ shape shape = (shape) o; if(this.getArea()<shape.getArea()){ return -1; } else return 1; } return 0; } } class Circle extends shape{ private double banjin; public Circle(double banjin) { this.banjin = banjin; } public double getBanjin() { return banjin; } public void setBanjin(double banjin) { this.banjin = banjin; } public double getArea(){ return banjin*banjin*Math.PI; } public int compareTo(Object o) { if(o instanceof shape){ shape shape = (shape) o; if(this.getArea()<shape.getArea()){ return -1; } else return 1; } return 0; } } class Point { double x; double y; public Point(){ } public Point(double x, double y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } public double getX() { return x; } public double getY() { return y; } public void setX(double x) { this.x = x; } public void setY(double y) { this.y = y; } }
三.踩坑心得
(1)踩坑一:
印象最深刻的一个坑,或许算不上坑,但是你一定遇到过,不是代码问题,而是使用平台要注意的,那就是编译环境!!!
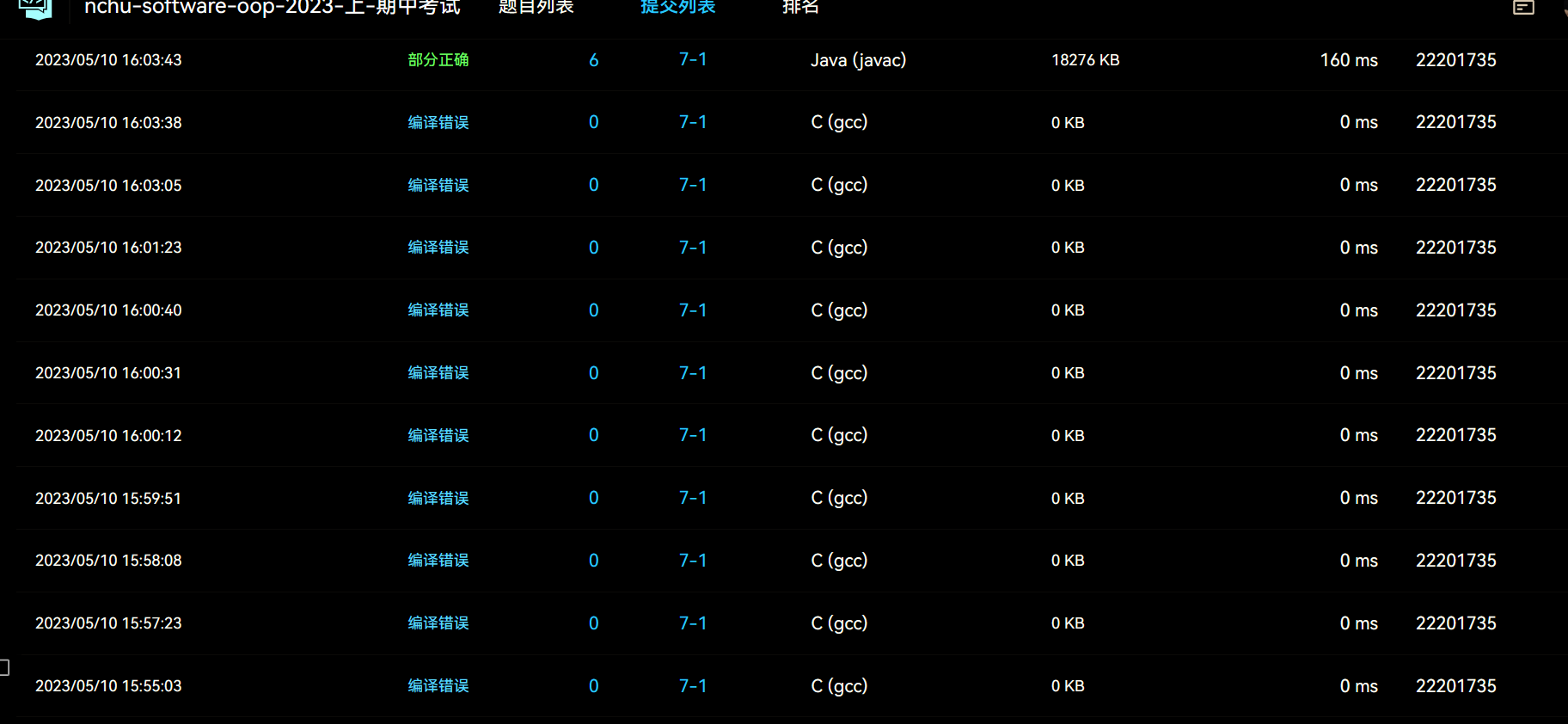
这一串的编译错误都是心酸啊,一看编译环境是C语言.....很小的错误,但是很容易发生,当反应过来的时候已经过了将近10分钟了,这不纯纯浪费时间嘛,属于是没必要的错误,在以后比赛环境中,一定要先看自己的环境是否配置正确,不然耽误的时间,怎么也补不回来的!!!
(2)踩坑二:
在菜单5中有一个测试点如下

我的报错是格式错误,当时怎么想都想不明白,后面问了同学才知道,就是当没有任何一个特色菜时,最后的table行输出是又一个空格的,我的运行是没有的
于是,
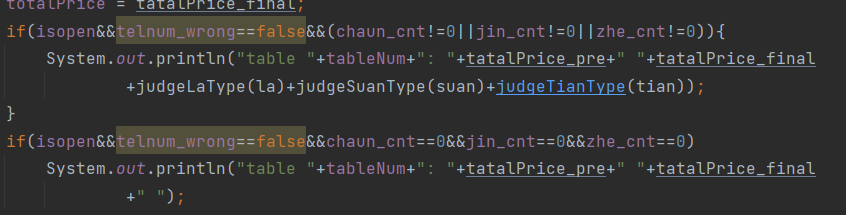
我加了一个判断,当每个菜系的数量都是0的时候,最后输出加了一个空格,测试点就通过了。
(3)踩坑三:
菜单5中的名字行输出,测试点如下:
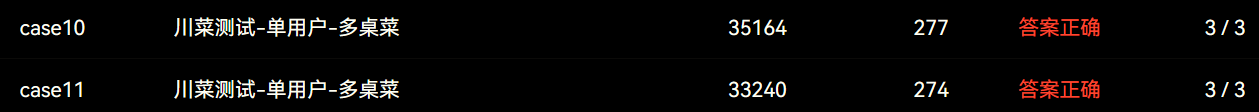
当一个人点了两个桌的菜时,碰到的最后的价格怎么去处理的问题,每桌的价钱是记在每桌里面,两个桌之间怎么去价钱的合并是个问题,后来我的解决方法是,通过查找名字,找到相同名字的桌的话,将后面桌的价格加到前面桌上,然后本桌的价格变成0,这样就解决了价格计算的问题,代码如图:
(4)踩坑四:
菜单5中,当删除点菜信息时,由于两桌点了相同序号的菜,删除信息时会导致删除了上一桌的点菜信息,导致最终价格的计算出现问题
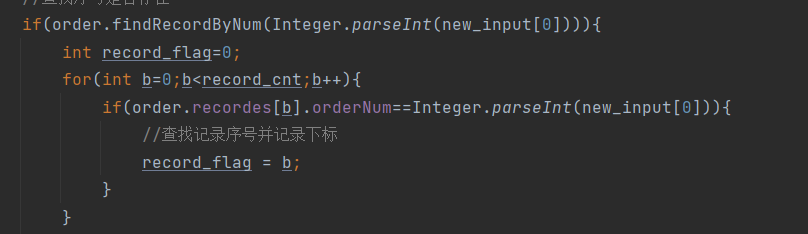
我是这样解决的:增加了一个序号的查询,因为点菜的序号是存储在了order类的记录里面的,每一次点菜的点菜序号都是记录其中,所以是可以查找到的,查到后,继续查找,当查到最后一个序号等于要删除的序号时,跳出循环,记录下标,就可以根据这个下标去删除本桌想要删除的菜的信息了,最终的计价也就不会出现问题。
四.主要困难以及改进意见
主要困难:
1.最最大的困难我觉得应该还是类的设计了,一个类的设计的好坏直接关系到整体的代码质量,并且如果要改进代码,有好的类也会更加轻松,可以做到可持续改进,拿我自己的菜单4 5来说的话,想添加某一个点会非常麻烦,而且分工不明确,Table类做了太多不是很相关的工作,是不太合理的,所在在我调试代码时候,会非常麻烦,我感觉这也是我菜单5知道最后一个测试点却无能为力的原因了,虽然能实现正常的点菜以及其他功能,但是一遇到错误判断,会很麻烦。
2.代码重复量太多,在我的代码里很明显里感觉到代码的重复很多,在多个if-else语句里,总会有重复的代码语句,比如同样是菜谱语句,但是分为特色菜菜谱和普通菜菜谱,我得分别写在两个地方,但是他们的代码几乎是一模一样的,只是属于不同的情况,似乎也不知道如何改进,如果归在某个方法里,那这个方法又该放在哪个地方,分工给谁比较合适都是个问题。
3.正则表达式和集合相关知识的不熟悉,在每次碰到写正则表达式的地方,都得去查资料学习怎么写,细节到底是怎样的,这方面知识还需要继续加强。
改进意见:
1.在碰到实际问题的时候,多思考,先画类图然后设计类的结构,多想是否有更加优化的类设计方案;
2.巩固语法的基本知识,多补充自己的知识库;
五.总结
这次做的两次大作业和一次期中考试,应该最卡的难受的就是作业四了,不得不说,我感觉是比那些添加概念的题目难写的,增加错误判断会有大量的代码要添加,而且还不好想,各种问题会涌出来,不过相比较与作业四,作业五我觉得最大的问题就是没有多想想类的设计和结构,只顾着将题目都需求实现出来,虽然实现了,但是我觉得确实同时是比较失败的,还得重构结构,期中考试就没什么好说的了,得到了小小锻炼就好,三次pta下来,还是会有很大的收获的,代码调试能力上去了,我慢慢悟得从哪里去调,又该怎么调,找出代码漏洞所在,还有不得不一提的就是,找测试点,这件事真不是一个好差事,需要很丰富的经验,不然真的不知道测试点到底是什么,想破脑袋都没用的那种,真的有时候会挺无奈的,死活找不出测试点的时候,无奈感涌上心头,感觉并不是我写不来,只是我不知道要解决的问题在哪,不过归根结底还是实力不够,“革命尚未成功,同志还需努力“。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号