题目集8-9总结性Blog
目录
正文
一、前言
这两次题目集总体而言考察的是类的设计的能力而并非复杂的算法,因此难度降低了许多。类的设计往往离不开类与类之间的关系,使用封装,继承与多态以及软件设计的七大原则可以大大提高我们类设计的质量。第八次题目集主要考查了前面点线面问题的重构,雨刷程序功能的扩展,这两道题目都考察了对前面已经写过的程序进行重构以使其满足新的需求,这就需要熟练的使用继承与多态,第一次航空货运管理系统的设计主要考察了单一职责原则、里氏代换原则、开闭原则、合成复用原则。第九次题目集主要考察的仍是继承与多态的使用,魔方问题便可以充分体现,除此之外还考察了容器类的使用也就是点线面问题再重构(容器类)还有软件设计的七大原则,这点在第二次航空货运管理系统上可以体现。在类的设计中运用软件设计七大原则虽然有些挑战但却大大提高程序的可读性,可维护性,可复用性,重构的时候可以为我们提供很多的便利。
二、第八次题目集
1.点线面问题(继承与多态)
在“点与线(类设计)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,以实现继承与多态的技术性需求。

2.雨刷程序功能设计
在给定的汽车手动风挡玻璃雨刷程序的基础上,对程序进行重构(Refactoring),使得程序可以对功能进行扩展。

3.第一次航空货运管理系统
1.题目介绍
https://images.ptausercontent.com/499d204b-fcef-4610-a9ca-c8fbf5e346d9.pdf
2.设计与分析
以下是第一次航空货运管理系统的类图设计:

以下是第一次航空货运管理系统的源代码:
点击查看代码
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Scanner;
class People{
private String name;
private String phone;
private String address;
public People() {
}
public People(String name, String phone, String address) {
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
this.address = address;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
class Customer extends People{
private People people;
private String customerNum;
public Customer() {
}
public Customer(People people, String customerNum) {
this.people = people;
this.customerNum = customerNum;
}
public String getCustomerNum() {
return customerNum;
}
public void setCustomerNum(String customerNum) {
this.customerNum = customerNum;
}
public People getPeople() {
return people;
}
public void setPeople(People people) {
this.people = people;
}
}
class Goods{
private String name;
private double length;
private double width;
private double height;
private int num;
private double weight;
public Goods() {
}
public Goods(String name, double length, double width, double height, int num, double weight) {
this.name = name;
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
this.num = num;
this.weight = weight;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
public double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(double weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public double calWeight(){
double cal = this.getLength() * this.getWidth() * this.getHeight() / 6000;
if(cal > this.getWeight()){
return cal;
}else{
return this.getWeight();
}
}
public double calRate(){
if(calWeight() < 20){
return 35.0;
}else if(calWeight() >= 20 && calWeight() < 50){
return 30.0;
}else if(calWeight() >= 50 && calWeight() < 100){
return 25.0;
}else if(calWeight() >= 100){
return 15.0;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
public double calMoney(){
return this.calWeight() * this.calRate();
}
public void show(){
System.out.println(this.name + "\t" + this.calWeight() + "\t" + this.calRate() + "\t" + this.calMoney());
}
}
class Flight{
private String num;
private String start;
private String end;
private String date;
private double maxWeight;
public Flight() {
}
public Flight(String num,String start, String end, String date, double maxWeight) {
this.num = num;
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
this.date = date;
this.maxWeight = maxWeight;
}
public String getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(String num) {
this.num = num;
}
public String getStart() {
return start;
}
public void setStart(String start) {
this.start = start;
}
public String getEnd() {
return end;
}
public void setEnd(String end) {
this.end = end;
}
public String getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(String date) {
this.date = date;
}
public double getMaxWeight() {
return maxWeight;
}
public void setMaxWeight(double maxWeight) {
this.maxWeight = maxWeight;
}
}
class Order{
private String orderNum;
private String orderDate;
public Order() {
}
public Order(String orderNum, String orderDate) {
this.orderNum = orderNum;
this.orderDate = orderDate;
}
public String getOrderNum() {
return orderNum;
}
public void setOrderNum(String orderNum) {
this.orderNum = orderNum;
}
public String getOrderDate() {
return orderDate;
}
public void setOrderDate(String orderDate) {
this.orderDate = orderDate;
}
}
abstract class Payment{
public abstract String pay();
}
class Control{
private Customer customer;
private Goods goods;
private Flight flight;
private Payment payment;
private LinkedList<Goods> list = new LinkedList<>();
private Order order;
private People ship;
private People receive;
public Control() {
}
public Control(Customer customer, Flight flight, Payment payment, LinkedList<Goods> list, Order order,People ship,People receive) {
this.customer = customer;
this.flight = flight;
this.payment = payment;
this.list = list;
this.order = order;
this.receive = receive;
this.ship = ship;
}
public Customer getCustomer() {
return customer;
}
public void setCustomer(Customer customer) {
this.customer = customer;
}
public Goods getGoods() {
return goods;
}
public void setGoods(Goods goods) {
this.goods = goods;
}
public Flight getFlight() {
return flight;
}
public void setFlight(Flight flight) {
this.flight = flight;
}
public Payment getPayment() {
return payment;
}
public void setPayment(Payment payment) {
this.payment = payment;
}
public LinkedList<Goods> getList() {
return list;
}
public void setList(LinkedList<Goods> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public Order getOrder() {
return order;
}
public void setOrder(Order order) {
this.order = order;
}
public People getShip() {
return ship;
}
public void setShip(People ship) {
this.ship = ship;
}
public People getReceive() {
return receive;
}
public void setReceive(People receive) {
this.receive = receive;
}
public double getSumWeight() {
double sum = 0;
for (Goods goods : list) {
sum += goods.calWeight();
}
return sum;
}
public double getSumMoney() {
double sum = 0;
for (Goods goods : list) {
sum += goods.calMoney();
}
return sum;
}
public void show(){
System.out.println("客户:"+ customer.getPeople().getName() + "(" + customer.getPeople().getPhone() + ")订单信息如下:");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.println("航班号:" + flight.getNum());
System.out.println("订单号:" + order.getOrderNum());
System.out.println("订单日期:" + order.getOrderDate());
System.out.println("发件人姓名:" + ship.getName());
System.out.println("发件人电话:" + ship.getPhone());
System.out.println("发件人地址:" + ship.getAddress());
System.out.println("收件人姓名:" + receive.getName());
System.out.println("收件人电话:" + receive.getPhone());
System.out.println("收件人地址:" + receive.getAddress());
System.out.println("订单总重量(kg):" + getSumWeight());
System.out.print(paying(payment));
System.out.println(getSumMoney());
System.out.println();
System.out.println("货物明细如下:");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.println("明细编号\t货物名称\t计费重量\t计费费率\t应交运费");
int i = 1;
for (Goods goods : list) {
System.out.print(i + "\t");
goods.show();
i++;
}
}
//使用里氏代换原则,将一个基类对象替换成它的子类对象
public String paying(Payment payment) {
return payment.pay();
}
}
//使用里氏代换原则,子类继承父类,可以使用父类引用调用子类方法
class Wechat extends Payment{
@Override
public String pay() {
return "微信支付金额:";
}
}
class Alipay extends Payment{
@Override
public String pay() {
return "支付宝支付金额:";
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
LinkedList<Goods> list = new LinkedList<>();
String customerNum = s.next();
String customerName = s.next();
String customerPhone = s.next();
String address = s.next();
int goodsNum = s.nextInt();
int n = goodsNum;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
int num = s.nextInt();
String name = s.next();
double width = s.nextDouble();
double length = s.nextDouble();
double height = s.nextDouble();
double weight = s.nextDouble();
Goods goods = new Goods(name,length,width,height,num,weight);
list.add(goods);
}
String flightNum = s.next();
String start = s.next();
String end = s.next();
String date = s.next();
double max = s.nextDouble();
String orderNum = s.next();
String orderDate = s.next();
String address1 = s.next();
String name1 = s.next();
String phone1 = s.next();
String address2 = s.next();
String name2 = s.next();
String phone2 = s.next();
People people = new People(customerName,customerPhone,address);
Customer customer = new Customer(people,customerNum);
People people1 = new People(name1,phone1,address1);
People people2 = new People(name2,phone2,address2);
Flight flight = new Flight(flightNum,start,end,date,max);
Order order = new Order(orderNum,orderDate);
Wechat wechat = new Wechat();
Payment payment = wechat;
Control control = new Control(customer,flight,payment,list,order,people1,people2);
if(control.getSumWeight() > max){
System.out.println("The flight with flight number:" + flightNum + " has exceeded its load capacity and cannot carry the order.");
return;
}
control.show();
}
}
以下是第一次航空货运管理系统代码的分析


| 名称 | 数量 |
|---|---|
| 语句数 | 270 |
| 方法调用语句数 | 60 |
| 每个类方法数 | 8.11 |
| 最大嵌套深度 | 8 |
| 平均嵌套深度 | 1.61 |
| 平均复杂度 | 1.18 |
- 设计模式与原则:
- 里氏替换原则(LSP):在Control.paying()中,父类引用(Payment)可替换为子类对象(Wechat/Alipay)。
- 单一职责原则(SRP):Goods 类负责计算货物重量、费率和费用,符合 SRP。
- 开闭原则(OCP):添加新的支付方式时,只需新增子类,无需修改现有代码,符合 OCP。
- 代码复杂度分析:
- 类的职责较多,整体而言还需优化。
三、 第九次题目集
1.魔方问题
魔方问题主要考查了多态的使用,难度比较简单。
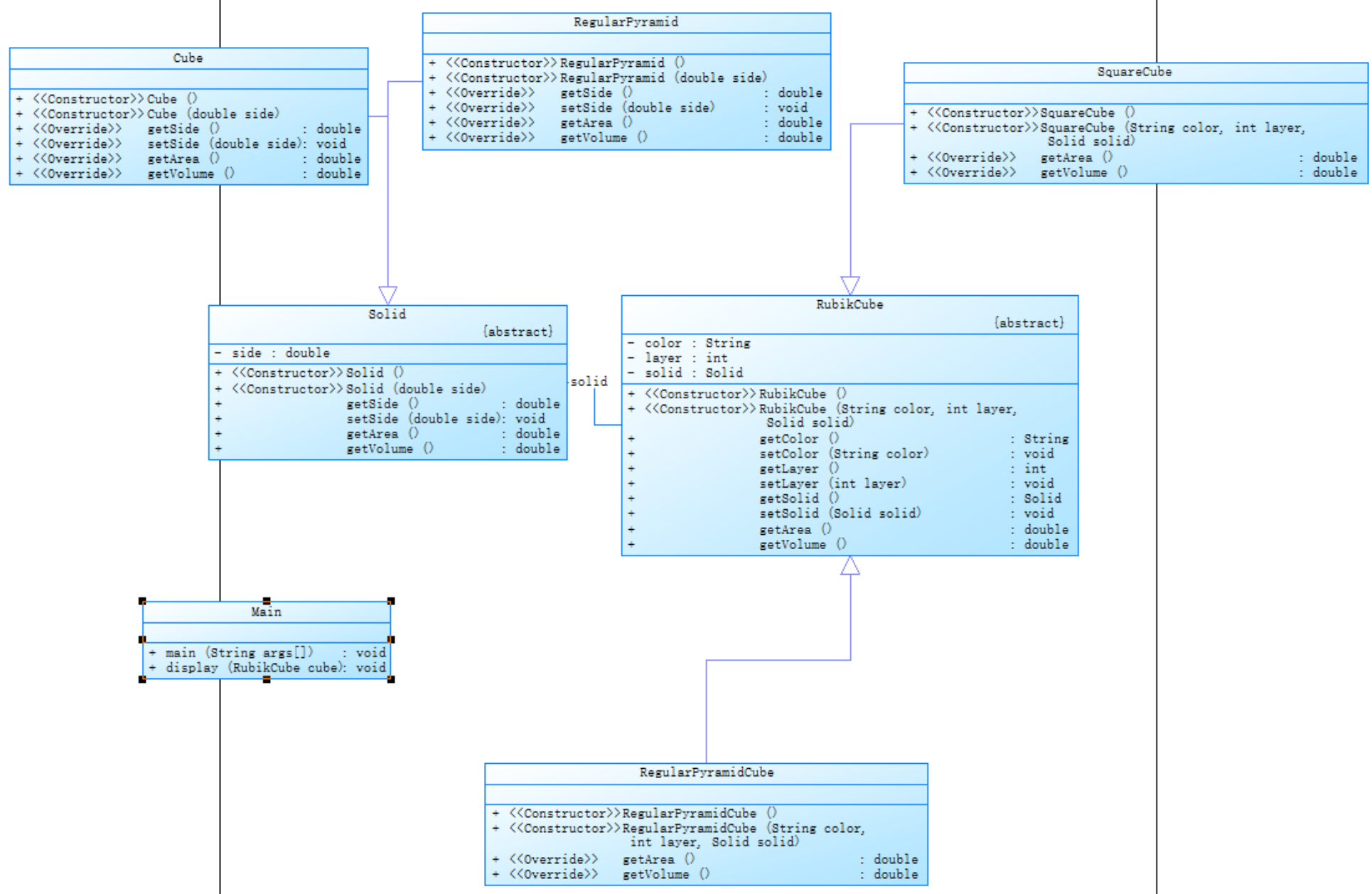
2.点线面问题(容器类)
在“点与线(继承与多态)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,增加容器类保存点、线、面对象,并对该容器进行相应增、删、遍历操作。

3.第二次航空货运管理系统
1.题目介绍
https://images.ptausercontent.com/b9cec79b-8012-4901-843e-3d48f27d28a6.pdf
2.设计与分析
以下是第二次航空货运管理系统的类图设计:

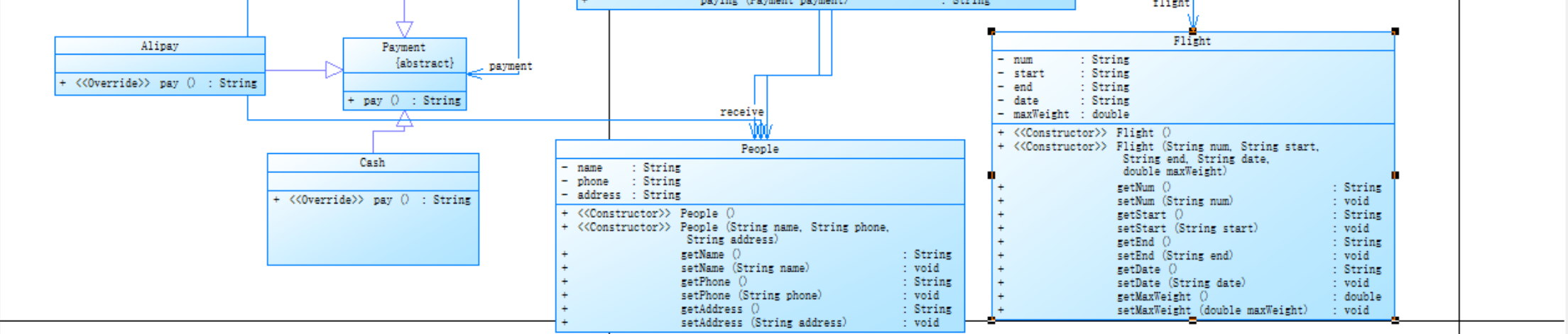
以下是第二次航空货运管理系统的源代码:
点击查看代码
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Scanner;
class People{
private String name;
private String phone;
private String address;
public People() {
}
public People(String name, String phone, String address) {
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
this.address = address;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
class Customer{
private String type;
private People people;
private String customerNum;
public Customer() {
}
public Customer(People people, String customerNum,String type) {
this.people = people;
this.customerNum = customerNum;
this.type = type;
}
public String getCustomerNum() {
return customerNum;
}
public void setCustomerNum(String customerNum) {
this.customerNum = customerNum;
}
public People getPeople() {
return people;
}
public void setPeople(People people) {
this.people = people;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
}
abstract class Goods{
private String name;
private double length;
private double width;
private double height;
private int num;
private String type;
private double weight;
public Goods() {
}
public Goods(String name, double length, double width, double height, int num, double weight,String type) {
this.name = name;
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
this.num = num;
this.weight = weight;
this.type = type;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
public double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(double weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public double calWeight(){
double cal = this.getLength() * this.getWidth() * this.getHeight() / 6000;
if(cal > this.getWeight()){
return cal;
}else{
return this.getWeight();
}
}
public abstract double calRate();
public double calMoney(){
return this.calWeight() * this.calRate();
}
public void show(){
System.out.println(this.name + "\t" + this.calWeight() + "\t" + this.calRate() + "\t" + this.calMoney());
}
}
class NormalRate extends Goods {
public NormalRate(String name, double length, double width, double height, int num, double weight, String type) {
super(name, length, width, height, num, weight, type);
}
@Override
public double calRate() {
if (calWeight() < 20) {
return 35.0;
} else if (calWeight() >= 20 && calWeight() < 50) {
return 30.0;
} else if (calWeight() >= 50 && calWeight() < 100) {
return 25.0;
} else if (calWeight() >= 100) {
return 15.0;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}
class ExpediteRate extends Goods{
public ExpediteRate(String name, double length, double width, double height, int num, double weight, String type) {
super(name, length, width, height, num, weight, type);
}
@Override
public double calRate() {
if(calWeight() < 20){
return 60.0;
}else if(calWeight() >= 20 && calWeight() < 50){
return 50.0;
}else if(calWeight() >= 50 && calWeight() < 100){
return 40.0;
}else if(calWeight() >= 100){
return 30.0;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
}
class DangerousRate extends Goods{
public DangerousRate(String name, double length, double width, double height, int num, double weight, String type) {
super(name, length, width, height, num, weight, type);
}
@Override
public double calRate() {
if(calWeight() < 20){
return 80.0;
}else if(calWeight() >= 20 && calWeight() < 50){
return 50.0;
}else if(calWeight() >= 50 && calWeight() < 100){
return 30.0;
}else if(calWeight() >= 100){
return 20.0;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
}
class Flight{
private String num;
private String start;
private String end;
private String date;
private double maxWeight;
public Flight() {
}
public Flight(String num,String start, String end, String date, double maxWeight) {
this.num = num;
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
this.date = date;
this.maxWeight = maxWeight;
}
public String getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(String num) {
this.num = num;
}
public String getStart() {
return start;
}
public void setStart(String start) {
this.start = start;
}
public String getEnd() {
return end;
}
public void setEnd(String end) {
this.end = end;
}
public String getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(String date) {
this.date = date;
}
public double getMaxWeight() {
return maxWeight;
}
public void setMaxWeight(double maxWeight) {
this.maxWeight = maxWeight;
}
}
class Order{
private String orderNum;
private String orderDate;
public Order() {
}
public Order(String orderNum, String orderDate) {
this.orderNum = orderNum;
this.orderDate = orderDate;
}
public String getOrderNum() {
return orderNum;
}
public void setOrderNum(String orderNum) {
this.orderNum = orderNum;
}
public String getOrderDate() {
return orderDate;
}
public void setOrderDate(String orderDate) {
this.orderDate = orderDate;
}
}
abstract class Payment{
public abstract String pay();
}
class Control{
private Customer customer;
private Goods goods;
private Flight flight;
private Payment payment;
private LinkedList<Goods> list = new LinkedList<>();
private Order order;
private People ship;
private People receive;
public Control() {
}
public Control(Customer customer, Flight flight, Payment payment, LinkedList<Goods> list, Order order,People ship,People receive) {
this.customer = customer;
this.flight = flight;
this.payment = payment;
this.list = list;
this.order = order;
this.receive = receive;
this.ship = ship;
}
public Customer getCustomer() {
return customer;
}
public void setCustomer(Customer customer) {
this.customer = customer;
}
public Goods getGoods() {
return goods;
}
public void setGoods(Goods goods) {
this.goods = goods;
}
public Flight getFlight() {
return flight;
}
public void setFlight(Flight flight) {
this.flight = flight;
}
public Payment getPayment() {
return payment;
}
public void setPayment(Payment payment) {
this.payment = payment;
}
public LinkedList<Goods> getList() {
return list;
}
public void setList(LinkedList<Goods> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public Order getOrder() {
return order;
}
public void setOrder(Order order) {
this.order = order;
}
public People getShip() {
return ship;
}
public void setShip(People ship) {
this.ship = ship;
}
public People getReceive() {
return receive;
}
public void setReceive(People receive) {
this.receive = receive;
}
public double getSumWeight() {
double sum = 0;
for (Goods goods : list) {
sum += goods.calWeight();
}
return sum;
}
public double getSumMoney() {
double sum = 0;
for (Goods goods : list) {
sum += goods.calMoney();
}
if(customer.getType().equals("Individual")){
return sum * 0.9;
}else{
return sum * 0.8;
}
}
public void show(){
System.out.println("客户:"+ customer.getPeople().getName() + "(" + customer.getPeople().getPhone() + ")订单信息如下:");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.println("航班号:" + flight.getNum());
System.out.println("订单号:" + order.getOrderNum());
System.out.println("订单日期:" + order.getOrderDate());
System.out.println("发件人姓名:" + ship.getName());
System.out.println("发件人电话:" + ship.getPhone());
System.out.println("发件人地址:" + ship.getAddress());
System.out.println("收件人姓名:" + receive.getName());
System.out.println("收件人电话:" + receive.getPhone());
System.out.println("收件人地址:" + receive.getAddress());
System.out.println("订单总重量(kg):" + getSumWeight());
System.out.print(paying(payment));
System.out.println(getSumMoney());
System.out.println();
System.out.println("货物明细如下:");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.println("明细编号\t货物名称\t计费重量\t计费费率\t应交运费");
int i = 1;
for (Goods goods : list) {
System.out.print(i + "\t");
goods.show();
i++;
}
}
//使用里氏代换原则,将一个基类对象替换成它的子类对象
public String paying(Payment payment) {
return payment.pay();
}
}
//使用里氏代换原则,子类继承父类,可以使用父类引用调用子类方法
class Wechat extends Payment{
@Override
public String pay() {
return "微信支付金额:";
}
}
class Alipay extends Payment{
@Override
public String pay() {
return "支付宝支付金额:";
}
}
class Cash extends Payment{
@Override
public String pay() {
return "现金支付金额:";
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
LinkedList<Goods> list = new LinkedList<>();
String customerType = s.next();
String customerNum = s.next();
String customerName = s.next();
String customerPhone = s.next();
String address = s.next();
String goodsType = s.next();
int goodsNum = s.nextInt();
int n = goodsNum;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
int num = s.nextInt();
String name = s.next();
double width = s.nextDouble();
double length = s.nextDouble();
double height = s.nextDouble();
double weight = s.nextDouble();
Goods goods;
if(goodsType.equals("Normal")){
goods = new NormalRate(name,length,width,height,num,weight,goodsType);
}else if(goodsType.equals("Expedite")){
goods = new ExpediteRate(name,length,width,height,num,weight,goodsType);
}else{
goods = new DangerousRate(name,length,width,height,num,weight,goodsType);
}
list.add(goods);
}
String flightNum = s.next();
String start = s.next();
String end = s.next();
String date = s.next();
double max = s.nextDouble();
String orderNum = s.next();
String orderDate = s.next();
String address1 = s.next();
String name1 = s.next();
String phone1 = s.next();
String address2 = s.next();
String name2 = s.next();
String phone2 = s.next();
String payType = s.next();
People people = new People(customerName,customerPhone,address);
Customer customer = new Customer(people,customerNum,customerType);
People people1 = new People(name1,phone1,address1);
People people2 = new People(name2,phone2,address2);
Flight flight = new Flight(flightNum,start,end,date,max);
Order order = new Order(orderNum,orderDate);
Payment payment;
if(payType.equals("Wechat")){
payment = new Wechat();
}else if(payType.equals("ALiPay")){
payment = new Alipay();
}else{
payment = new Cash();
}
Control control = new Control(customer,flight,payment,list,order,people1,people2);
if(control.getSumWeight() > max){
System.out.println("The flight with flight number:" + flightNum + " has exceeded its load capacity and cannot carry the order.");
return;
}
control.show();
}
}
以下是第二次航空货运管理系统代码的分析

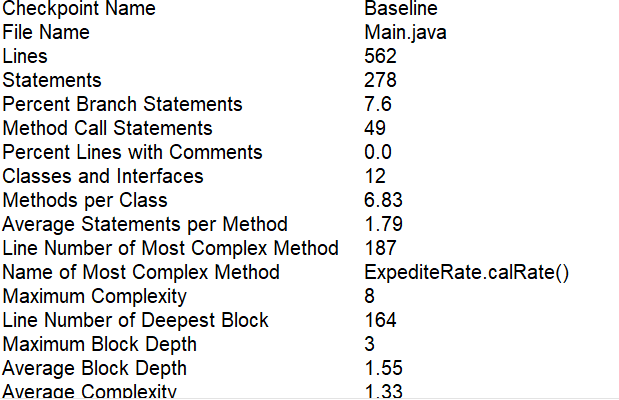
| 名称 | 数量 |
|---|---|
| 语句数 | 278 |
| 方法调用语句数 | 49 |
| 每个类方法数 | 6.83 |
| 最大嵌套深度 | 8 |
| 平均嵌套深度 | 1.55 |
| 平均复杂度 | 1.33 |
- 设计模式与原则:
- 单一职责原则(SRP):Goods抽象类仅负责货物基础属性,子类专注于不同计费逻辑。
- 开闭原则(OCP):新增货物类型时,只需创建新子类实现calRate(),无需修改现有代码,符合 OCP。
- 依赖倒置原则(DIP):Control依赖抽象类Goods和Payment,而非具体实现类。
- 代码复杂度分析:代码整体复杂度中等,但存在嵌套层数较深的问题。
四、 踩坑心得
- 第一次航空货运管理系统类设计的时候还是比较顺畅的,因此也没有遇到太多的问题。只是犯了一点小的错误,以后应该注意。
![]()
- 第二次航空货运管理系统是在第一次类的设计上进行重构,逻辑上没有太大问题,但是因为设计类的时候要考虑单一职责原则、里氏代换原则、开闭原则、合成复用原则、依赖倒转原则,我原本的类设计计算不同类型的货物的费率时都放在一个类中然后通过if-else语句来区分不同的类型,但这样违背了开闭原则,因此我将这三种类型的货物设计成了三个类,这样在进行添加新的货物类型也不会改变原来的代码,真正意义上满足了开闭原则。
- 第二次航空货运管理系统我还遇见了不知该如何运用依赖倒转原则的问题,后来在对类图的分析中确定了Control 类依赖于抽象的 Payment 类,而不是具体的支付方式类(Wechat、Alipay、Cash)。在 Control 类中,使用 Payment 类型的引用作为成员变量可以根据需要传入不同的支付方式对象,符合依赖倒转原则。
五、 改进建议
- Control类其复杂度较高还需优化,将其拆分为更多独立的方法。
- 类的设计还要优化使其更加符合软件设计七大原则。
六、 总结
- 这两次题目集当中我深刻体会到了类设计的重要性,如果类设计的合理那么在后续的重构中可以省下很大的功夫。
- 软件设计七大原则的运用还是不够熟练,不能够在类设计的时候将其融会贯通,这在后续的学习中应该加强训练。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号