剑指offer(专项突击版)
剑指 Offer II 001. 整数除法
给定两个整数 a 和 b ,求它们的除法的商 a/b ,要求不得使用乘号 '*'、除号 '/' 以及求余符号 '%' 。
注意:
整数除法的结果应当截去(truncate)其小数部分,例如:truncate(8.345) = 8 以及 truncate(-2.7335) = -2
假设我们的环境只能存储 32 位有符号整数,其数值范围是 [−231, 231−1]。本题中,如果除法结果溢出,则返回 231 − 1
-
不可以使用除法和乘法,则可以使用加法或位运算。
-
因为限制了只能使用23位有符号整数,所以不能使用long。数的范围为\(-2^{31} 到 2^{31}-1\)。
-
先考虑特殊情况:
- 当a为\(-2^{31}\),b为-1,则结果存在int32时的溢出情况,此时应返回\(2^{13}-1\)
- 当a为0或b为1,则直接返回a
- 剩余就是正常情况处理了;正常处理的时候,我们往往会先将符号位确定出来,然后全部当做正数去处理。这时候,存在一个陷阱:a为\(-2^{31}\)且b不为-1时,对a取绝对值,在java中存在溢出情况。那么,反之可以将其全部当做负数处理就不存在溢出情况了。
public int divide(int a, int b) { // 先考虑特殊情况 // 考虑溢出情况:-2^31 ~ 2^31 -1 // a=-2^31 b=-1 则出现上溢,返回2^31 -1 if (a == Integer.MIN_VALUE && b == -1) { return Integer.MAX_VALUE; } // 被除数为0或除数为1 if (a == 0 || b == 1) { return a; } // 考虑符号 int flag = (a > 0) ^ (b > 0) ? -1 : 1; // 正常处理,有一个陷阱,对-2^31取绝对值存在溢出 // 所以,反过来求值 if(a>0) {a=-a;} if(b>0) {b=-b;} int res = 0; while (a<=b){ a-=b; res++; } return flag*res; }显然,这样是最简单的方法,还有优化的空间。那就是采用位运算。如下所示可以加速上边代码的while过程:
a=14 b=-2
Step1:flag = -1
Step2:a=-14 b=-2
Step3:
res = 0
round1:
base=1;dividor=-2;dividor=dividor<<2=-8; base=base<<2=4; a=a-dividor=-6; res=res+4=4;
round2:
base=1;dividor=-2;dividor=dividor<<1=-4; base=base<<1=2; a=a-dividor=-2; res=res+2=6;
round3:
base=1;dividor=-2; (此时while内部循环不执行,base为1) a=a-dividor=0; res=res+base=7;
// 显然divide有更进一步的优化方法
public int divide1(int a, int b) {
// 先考虑特殊情况
// 考虑溢出情况:-2^31 ~ 2^31 -1
// a=-2^31 b=-1 则出现上溢,返回2^31 -1
if (a == Integer.MIN_VALUE && b == -1) {
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
// 被除数为0或除数为1
if (a == 0 || b == 1) {
return a;
}
// 考虑符号
int flag = (a > 0) ^ (b > 0) ? -1 : 1;
// 正常处理,有一个陷阱,对-2^31取绝对值存在溢出
// 所以,反过来求值
if(a>0) {a=-a;}
if(b>0) {b=-b;}
int res = 0;
// 这里可以使用位运算加速
while (a<=b){
int base = 1;
int dividor = b;
while (a-dividor<=dividor){
dividor<<=1;
base<<=1;
}
a-=dividor;
res+=base;
}
return flag*res;
}
剑指 Offer II 002. 二进制加法
给定两个 01 字符串
a和b,请计算它们的和,并以二进制字符串的形式输出。输入为 非空 字符串且只包含数字
1和0。输入: a = "1010", b = "1011"
输出: "10101”
- 每个字符串仅由字符
'0'或'1'组成。1 <= a.length, b.length <= 10^4- 字符串如果不是
"0",就都不含前导零。
因为字符串的长度足够大,所以必须采用字符串解决,而不能将其转为10进制数字后求和再转为2进制处理。
思路1:简单模拟。逆序同步扫描字符,进行累加,后分别对2求余数的商来更新结果。如下,时间复杂度\(O(n)\),空间复杂度\(O(1)\)。其中\(n=max(a.length(),b.length())\)。
public String addBinary(String a, String b) {
int carry = 0;
int n = Math.max(a.length(), b.length());
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 定位导数第i个元素,并累加
carry += i < a.length() ? (a.charAt(a.length() - i - 1) - '0') : 0;
carry += i < b.length() ? (b.charAt(b.length() - i - 1) - '0') : 0;
stringBuffer.append((char) (carry % 2 + '0'));
carry /= 2;
}
if(carry>0){
stringBuffer.append('1');
}
stringBuffer.reverse();
return stringBuffer.toString();
}
剑指 Offer II 003. 前 n 个数字二进制中 1 的个数
给定一个非负整数
n,请计算0到n之间的每个数字的二进制表示中 1 的个数,并输出一个数组。输入: n = 2
输出: [0,1,1]
解释:
0 --> 0
1 --> 1
2 --> 10
思路1:分别对每一个数字进行位统计。2进制位1的个数,可以采用Brian Kernighan算法,其统计的时间复杂度为\(O(logn)\). 该算法是这样的:
令: \(x=x\&(x-1)\) ,该操作可以将x的二进制位的最后一个1置为0,当x为0的时候,x的二进制位中就没有1了。
该思路整体的时间复杂度为\(O(nlogn)\)。
public int[] countBits(int n) {
int[] res = new int[n+1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
res[i] = getBits1(i);
}
return res;
}
private int getBits1(int i) {
int count = 0;
while (i>0){
i = i&(i-1);
count++;
}
return count;
}
思路2:动态规划;dp[i]表示i的二进制中1的个数,则有\(dp[i]=dp[i\&(i-1)]+1\)。该方法时间复杂度为\(O(n)\)。初识dp[0]=0;
public int[] countBits(int n) {
int[] res = new int[n+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
res[i] = res[i&(i-1)]+1;
}
return res;
}
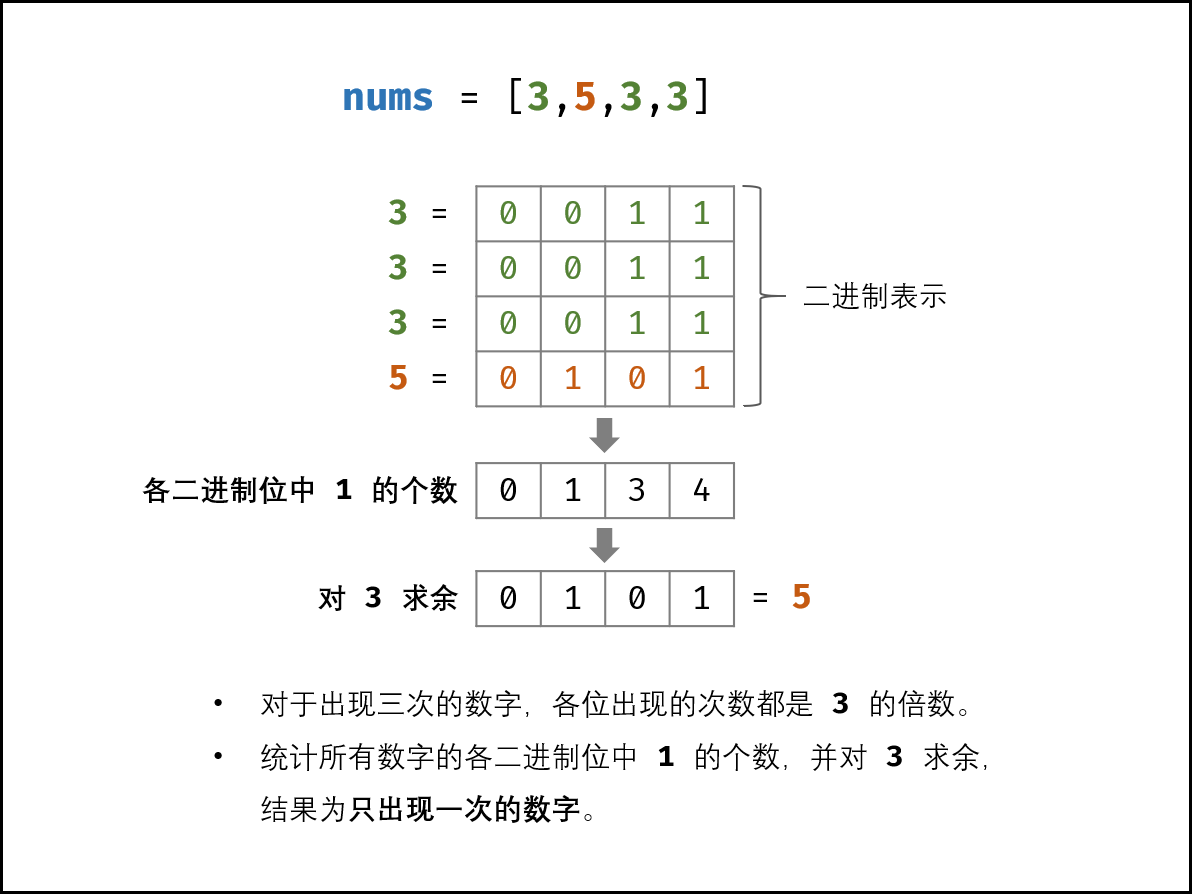
剑指 Offer II 004. 只出现一次的数字
给你一个整数数组
nums,除某个元素仅出现 一次 外,其余每个元素都恰出现 三次 。请你找出并返回那个只出现了一次的元素。输入:nums = [2,2,3,2]
输出:3
方法1:显然这是使用位运算。我们可以统计每个数的每个位的情况。若每个数的第i位求和后,对3求余数为0,则目标数的第i位也为0,否则为1。那么这样目标数的二进制位情况便可以统计出来。
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
// int的32位,对应位累加求和对3求余数,余数不为0,则当前位是那个只出现一次的数的对应位
int res = 0;
for(int i=0;i<32;i++){
int total = 0;
for(int num:nums){
total+=(num>>i)&1;
}
if(total%3!=0){
res |= (1<<i);
}
}
return res;
}
剑指 Offer II 005. 单词长度的最大乘积
给定一个字符串数组 words,请计算当两个字符串 words[i] 和 words[j] 不包含相同字符时,它们长度的乘积的最大值。假设字符串中只包含英语的小写字母。如果没有不包含相同字符的一对字符串,返回 0。
示例1:
输入: words = ["abcw","baz","foo","bar","fxyz","abcdef"]
输出: 16
解释: 这两个单词为 "abcw", "fxyz"。它们不包含相同字符,且长度的乘积最大。示例2:
输入: words = ["a","aa","aaa","aaaa"]
输出: 0
解释: 不存在这样的两个单词
思路:将判断两个字符串是否含有相同字符的判断的时间复杂度降为\(O(1)\),是关键。可以采用位运算。时间复杂度:\(O(L+n^2)\),L指全部单词的长度之和,n指单词数组的长度。
public int maxProduct(String[] words) {
// 关键是将判断两个字符串是否含有相同的字符的时间复杂度降到O(1)
// 可以使用位操作,将一个字符串的字母映射到26个位上,则该二进制所对应的数字可以代表该字符串
// 采用&操作,可以判断两个字符串是否含有相同的字符
int[] mask = new int[words.length];
// 初始化mask数组
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < words[i].length(); j++) {
mask[i] |= 1<<(words[i].charAt(j)-'a');
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < words.length-1; i++) {
for (int j = i+1; j < words.length; j++) {
// 若没有相同的字母,则更新max
if((mask[i]&mask[j])==0){
res = Math.max(res,words[i].length()* words[j].length());
}
}
}
return res;
}
当然该方法还可以进一步优化,存在两个串其未表示相同,eg:‘a’,’aaaa’,则可以使用一个hashMap来记录,对应mask值得最大字符串长度,然后,更新两串长度乘积最大值得时候,只需变量hashMap的key即可。
public int maxProduct(String[] words) {
// 关键是将判断两个字符串是否含有相同的字符的时间复杂度降到O(1)
// 可以使用位操作,将一个字符串的字母映射到26个位上,则该二进制所对应的数字可以代表该字符串
// 采用&操作,可以判断两个字符串是否含有相同的字符
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// 初始化mask数组
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
int mask = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < words[i].length(); j++) {
mask |= 1<<(words[i].charAt(j)-'a');
}
if(words[i].length()>map.getOrDefault(mask,0)){
map.put(mask,words[i].length());
}
}
int res = 0;
Set<Integer> keySet = map.keySet();
for(Integer mask1:keySet){
for(Integer mask2:keySet){
if((mask1&mask2)==0){
res = Math.max(res,map.get(mask1)*map.get(mask2));
}
}
}
return res;
}
剑指 Offer II 007. 数组中和为 0 的三个数
给定一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a ,b ,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?请找出所有和为 0 且 不重复 的三元组。
输入:nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4]
输出:[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
该题目的关键是降低时间复杂度,可以先枚举一个数,寻找另外两个数的和为第一个数的相反数。外层循环枚举第一个数,内层循环采用双指针将问题转换为两数之和的问题。题目要求不重复。则需要先排序,排序的时间复杂度为\(O(logn)\) 。之后可以利用排序后的特点,进行重复情况的排除。
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 结果需要不重复,所以此处需要排除重复
if(i>0 && nums[i]==nums[i-1]){
continue;
}
int target = -nums[i];
int third = nums.length-1;
for (int second = i+1; second < nums.length; second++) {
// 此处排序第二个数的重复情况
if(second>i+1 && nums[second]==nums[second-1]){
continue;
}
// 寻找第三个数
while (second<third && nums[second]+nums[third]>target){
third--;
}
if (third==second){
break;
}
// 更新res
if((nums[second]+nums[third])==target){
List<Integer> cur = new ArrayList<>();
cur.add(nums[i]);
cur.add(nums[second]);
cur.add(nums[third]);
res.add(cur);
}
}
}
return res;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号