PTA前三次作业总结
一、前言
第一次作业题量较大,难度适中,涉及到了Scanner类和String类的使用,主要是为了让我门熟系java的编译环境。
第二次题目集的题量较少,难度也第一次更低。主要是为了让我们熟悉java中数组的定义和使用。
第三次题目集,只有四题,但是难度较前两次有所上升了,涉及到上一次作业代码的迭代,主要是让我们熟悉类的设计的以及属性的getter和setter方法。
二、设计分析,踩坑心得与改进建议
题目集二 从一个字符串中移除包含在另一个字符串中的字符
从一个字符串中移除包含在另一个字符串中的字符。输入两行字符串,将第一行字符串中包括第二行字符串中的所有字母去除。输出去除后保留的字符串。
输入格式:
第一行输入一个字符串
第二行输入一个字符串
输出格式:
输出移除后的字符串
要求是从一个字符串中移除包含在另一个字符串中的字符,这题我定义了两个String类的字符串和一个StringBuffer类的字符串(用来存放新生成的字串), 设置两个 for循环,在遍历第一行的字符串的for循环里面套上遍历第二行的字符串的for循环,在字符串2中对字符串1的每一个字符进行遍历比较,如果找到了字符串2中没有的字符,则将该字符存入之前定义的StringBuffer类字符串中,相关代码如下所示
for(int i=0;i<a.length();i++) { flag=1; ch1=a.charAt(i); for(int j=0;j<b.length();j++) { ch2=b.charAt(j); if(ch1==ch2) flag=0; } if (flag==1) str.append(ch1); }
踩坑心得:一开始将flag标志定义在for循环里面,导致每一次循环时,flag的值都不能改变。
题目集一:7-1长度质量计量单位换算
长度、质量的计量有多重不同的计算体系,有标准的国际单位制:千克与米,也有各个国家自己的计量方法如:磅、英寸;1磅等于0.45359237千克, 1英寸等于 0.0254米,请编写程序实现国际单位制与英制之间的换算。
输入格式:
两个浮点数,以空格分隔,第一个是质量(以千克为单位)、第二个是长度(以米为单位)。例如:0.45359237 0.0254。
输出格式:
两个浮点数,以空格分隔,第一个是质量(以磅为单位)、第二个是长度(以英寸为单位)。例如:1.0 1.0。
踩坑心得: 这道题目虽然很简单,但是测试点有个坑,需要将double类型强制转化为float类型进行输出。
System.out.print((float)(kg/0.45359237)+" "+(float)(meter/0.0254));
题目集2 7-6 巴比伦法求平方根近似值
巴比伦法求n的近似值可以用以下公式:
nextGuess = (lastGuess+n/lastGuess)/2
程序初始运行时lastGuess可赋予一个最初的猜测值。当由公式求得的nextGuess和lastGuess相差较大时,把nextGuess的值赋给lastGuess,继续以上过程,直至 nextGuess和lastGuess几乎相同,此时lastGuess或者nextGuess就是平方根的近似值。
本题要求:nextGuess和lastGuess的差值小于0.00001时认为两者几乎相同
输入格式:
两个浮点数,以空格分隔,第一个是n,第二个是lastGuess最初的猜测值。例如:2 1。
若输入的两个数中包含负数或者lastGuess初始输入为0,认定为非法输入。
输出格式:
输出n的平方根近似值:lastGuess。例如:1.4142157
非法输入时输出:"Wrong Format"
踩坑心得:这题只能用float类型数做计算,后面我没有考虑到nextGuess小于lastGuess的情况,导致测试点不过,后来运用了Math.abs解决。
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main { 3 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 6 float next; 7 float last; 8 float n; 9 Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); 10 n=in.nextFloat(); 11 last=in.nextFloat(); 12 next=(last+n/last)/2; 13 if(n<0||last<=0) { 14 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 15 return; 16 } 17 while(Math.abs(next-last)>=0.00001) { 18 last=next; 19 next=(last+n/last)/2; 20 } 21 System.out.println((float)last); 22 23 } 24 25 }
题目集2 7-8 判断三角形类型
输入三角形三条边,判断该三角形为什么类型的三角形。
输入格式:
在一行中输入三角形的三条边的值(实型数),可以用一个或多个空格或回车分隔,其中三条边的取值范围均为[1,200]。
输出格式:
(1)如果输入数据非法,则输出“Wrong Format”;
(2)如果输入数据合法,但三条边不能构成三角形,则输出“Not a triangle”;
(3)如果输入数据合法且能够成等边三角形,则输出“Equilateral triangle”;
(4)如果输入数据合法且能够成等腰直角三角形,则输出“Isosceles right-angled triangle”;
(5)如果输入数据合法且能够成等腰三角形,则输出“Isosceles triangle”;
(6)如果输入数据合法且能够成直角三角形,则输出“Right-angled triangle”;
(7)如果输入数据合法且能够成一般三角形,则输出“General triangle”。
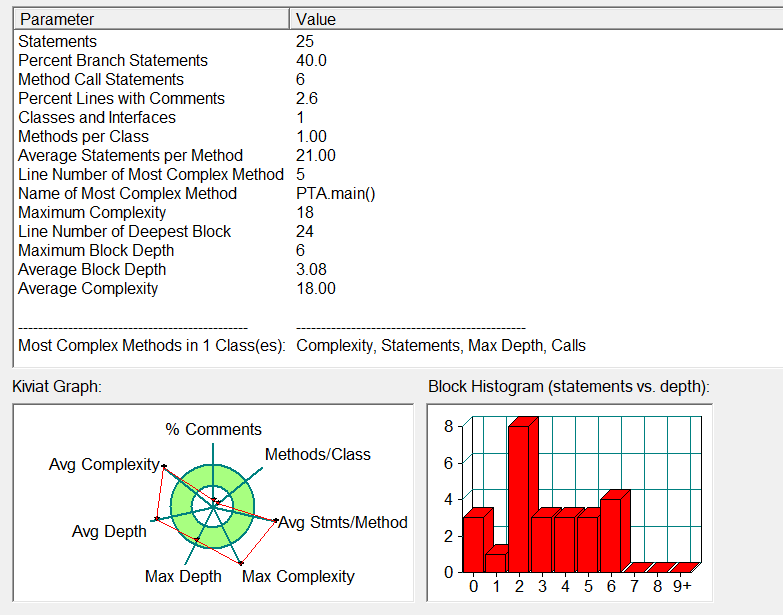
踩坑心得:在代码中涉及到了直角三角形的判断,一开始我是直接运用勾股定理a*a+b*b=c*c来判断,感觉没有逻辑错误,但就是一直过不了相关的测试点,后来老师上课讲到精度的问题,doble类型的值不能做精确的计算,于是我对我的代码进行改进,改成Math.abs(a*a+b*b-c*c)<0.00001,这样就提高了 double类型精确丢失的容错率。
if(a*a+b*b-c*c<0.000001||a*a+c*c==b*b||c*c+b*b==a*a)
改进建议:根据SourceMonitor的软件分析,这道题的代码的圈复杂度为18,说明代码还存在一定缺陷,其本质上就是用多了for循环,对代码进行分析后发现,“判断输入的三个值是否能构成三角形”这一环节可以不用for循环,这样就降低了代码的圈复杂度。以后还是要多学习通过构造方法来解决判断问题,这样 就有助于代码圈复杂度的降低。
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main { 3 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 6 double a,b,c; 7 Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); 8 a=in.nextDouble(); 9 b=in.nextDouble(); 10 c=in.nextDouble(); 11 if(a<1||a>200||b<1||b>200) 12 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 13 else { 14 if(a+b<=c||a+c<=b||b+c<=a) 15 System.out.println("Not a triangle"); 16 else { 17 if(a==b&&b==c) 18 System.out.println("Equilateral triangle"); 19 else { 20 if(a==b||b==c||a==c) 21 System.out.println("Isosceles triangle"); 22 else { 23 if(a*a+b*b-c*c<0.000001||a*a+c*c==b*b||c*c+b*b==a*a) 24 System.out.println("Right-angled triangle"); 25 else 26 System.out.println("General triangle"); 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 }
题目集3 7-3 定义日期类
定义一个类Date,包含三个私有属性年(year)、月(month)、日(day),均为整型数,其中:年份的合法取值范围为[1900,2000] ,月份合法取值范围为[1,12] ,日期合法取值范围为[1,31] 。
输入格式:
在一行内输入年月日的值,均为整型数,可以用一到多个空格或回车分隔。
输出格式:
当输入数据非法及输入日期不存在时,输出“Date Format is Wrong”;
当输入日期合法,输出下一天,格式如下:Next day is:年-月-日
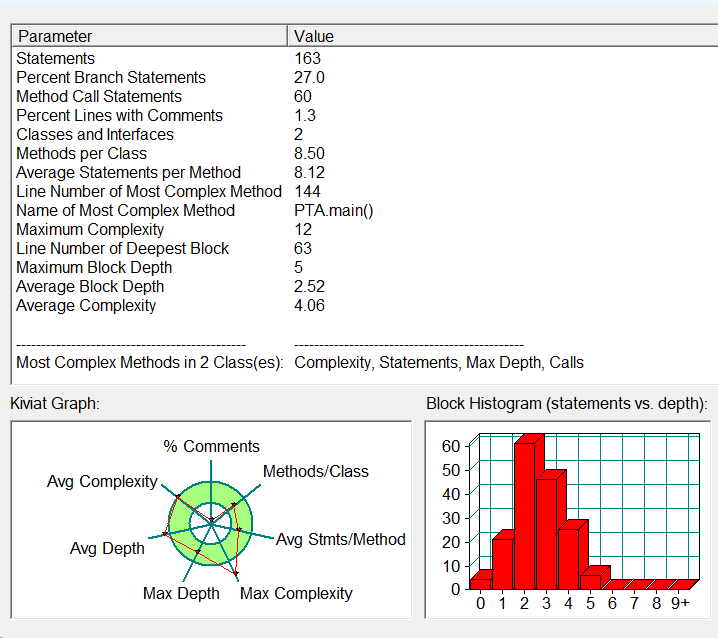
踩坑心得:首先是写代码时没有仔细确定年的正常范围,导致判断年正常值的测试点不过;其次是对平闰年的判断不清晰导致出错;还有就是判断下一天时,首先要判断日期是否为该月的最后一天,一开始我是把大月小月都列出来了,设计一个判断语句来判断是大月,小月,闰年二月还是平年二月,大月大于31天则月份加一,小月大于30天则月份加一,闰年二月大于29则月份加一,平年二月大于28则月份加一,但是这样显然增加了代码的复杂度,不利于代码后期的维护,于是后来我定义了一个数组,用来存放对应月份的天数,这样就使代码变得更简洁清晰了。
改进意见:根据sourcemonitor的分析结果来看,我们定义了多个类来进行封装各部分功能,降低了代码的圈复杂度,但是代码的最大复杂度还是超出正常值 水平,其本质上还是过多使用了if else语句,这样降低了代码的可读性和维护性,例如对于是否跨月和是否跨年的操作,可以给他们分别定义一个类,这样就 不仅使得代码更加简洁美观,还是得代码的效率大大提高,增加了后期代码的维护性。
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 class Date{ 3 private int year; 4 private int month; 5 private int day; 6 public int[]mon_maxnum=new int[] {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 7 public Date() { 8 this.year=year; 9 this.month=month; 10 this.day=day; 11 } 12 public Date(int year,int month,int day) { 13 this.year=year; 14 this.month=month; 15 this.day=day; 16 } 17 public int getYear() { 18 return this.year; 19 } 20 public int getMonth() { 21 return this.month; 22 } 23 public int getDay() { 24 return this.day; 25 } 26 public void setYear(int year) { 27 this.year=year; 28 } 29 public void setMonth(int month) { 30 this.month=month; 31 } 32 public void setDay(int day) { 33 this.day=day; 34 } 35 public boolean isLeapYear(int year) { 36 if(this.year%100!=0&&this.year%4==0||this.year%400==0) 37 return true; 38 else 39 return false; 40 } 41 public boolean checkInputValidity() { 42 if(this.year<1900||this.year>2000) 43 return false; 44 if(this.month<1||this.month>12) 45 return fals46 if(this.day<1||this.day>31) 47 return false; 48 if(isLeapYear(this.year)&&this.month==2) { 49 if(this.day>29) 50 return false; 51 else 52 return true; 53 } 54 else if(this.day>mon_maxnum[this.month-1]) 55 return false; 56 else 57 return true; 58 } 59 public void getNextDate() { 60 this.day=this.day+1; 61 if(isLeapYear(this.year)&&this.month==2) { 62 if(this.day>29) { 63 this.month=3; 64 this.day=1; 65 } 66 } 67 else { 68 if(this.day>mon_maxnum[this.month-1]) { 69 this.month=this.month+1; 70 this.day=1; 71 } 72 } 73 if(this.month>12) { 74 this.year+=1; 75 this.month=1; 76 } 77 System.out.println("Next day is:"+this.year+"-"+this.month+"-"+this.day); 78 } 79 } 80 public class Main { 81 82 public static void main(String[] args) { 83 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 84 Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); 85 int year=in.nextInt(); 86 int month=in.nextInt(); 87 int day=in.nextInt(); 88 Date date1=new Date(year,month,day); 89 if(date1.checkInputValidity()) 90 date1.getNextDate(); 91 else 92 System.out.println("Date Format is Wrong"); 93 } 94 95 }
PTA题目集三 7-4 日期类设计
设计一个类DateUtil,该类有三个私有属性year、month、day(均为整型数),其中,year∈[1820,2020] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 除了创建该类的构造方法、属性的getter及setter方法外,需要编写如下方法:
public boolean checkInputValidity(); //检测输入的年、月、日是否合法 public boolean isLeapYear(int year);//判断year是否为闰年 public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n); //取得year-month-day的下n天日期 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n);//取得year-month-day的前n天日期 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date); //比较当前日期与date的大小(先后) public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date);//判断两个日期是否相等 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date); //求当前日期与date之间相差的天数 public String showDate();//以“year-month-day”格式返回日期值
应用程序共测试三个功能:
- 求下n天
- 求前n天
- 求两个日期相差的天数
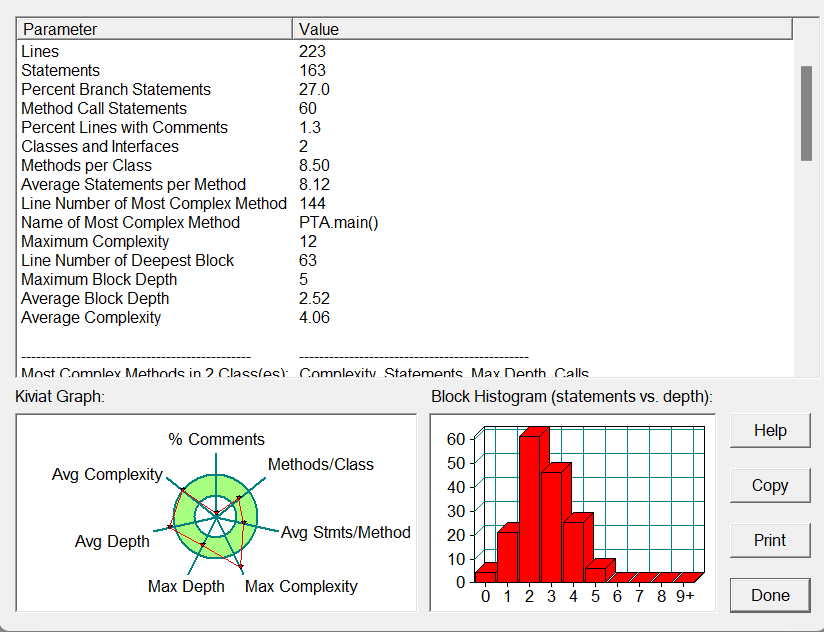
这一题的代码涉及到上一天的迭代,有上一题的求一下一天扩展到求下N天,然后逐步深入,要求我们实现求前N天的功能,我的思路是给求下一天的相关代码套上一个for循环,这样就实现了求下N天,然后在此基础之上,运用逆向思维,求前N天。
踩坑心得:首先还是在判断日期是否合法这里掉了坑,因为这一题的checkInputValidity()方法我是直接拷贝7-3的相关代码,但是后来发现7-3和7-4的年的合法范围是不一样的,所以以后还是要仔细阅读题目要求。还有就是求下n天和前n天的时候,忽略了跨年的情况。还有就是在设计"计算两个日期相差的天数"这一个类时,我在while循环里定义了一个count来记录他们相差的天数,在其中调用了求下n天的方法,但是我是以count作为他的参数,造成死循环,应该是以1为参数,相关代码如下
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) { int count=0; if(compareDates(date)) { while(!this.equalTwoDates(date) ) { this.equals(this.getPreviousNDays(1)); count++; } return count; } else { while(!this.equalTwoDates(date) ) { getNextNDays(1); count++; } return count; } }
改进意见:有了上一题的基础,这一题的代码质量相对来说稍微高一些,但是还存在不完善的地方,例如再求下n天和前n天的时候,可以分别给他们设计一个判断是否跨月和跨年的类,来增减代码的可读性,另外,在Date类里面虽然定义了setter方法,但是似乎并没有用到,说明我对属性的setter方法的认识还不太够,并且这样显然不利于后期代码的修改与维护,在后续学习中还是要试着去使用它。
附本题代码:
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 class DateUtil{ 3 private int year; 4 private int month; 5 private int day; 6 public int[]mon_maxnum=new int[] {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 7 public DateUtil() { 8 9 } 10 public DateUtil(int year,int month,int day) { 11 this.year=year; 12 this.month=month; 13 this.day=day; 14 } 15 public int getYear() { 16 return this.year; 17 } 18 public int getMonth() { 19 return this.month; 20 } 21 public int getDay() { 22 return this.day; 23 } 24 public void setYear(int year) { 25 this.year=year; 26 } 27 public void setMonth(int month) { 28 this.month=month; 29 } 30 public void setDay(int day) { 31 this.day=day; 32 } 33 public boolean isLeapYear(int year) { 34 if(this.year%100!=0&&this.year%4==0||this.year%400==0) 35 return true; 36 else 37 return false; 38 } 39 public boolean checkInputValidity() { 40 if(this.year<1820||this.year>2020) 41 return false; 42 if(this.month<1||this.month>12) 43 return false; 44 if(this.day<1||this.day>31) 45 return false; 46 if(isLeapYear(this.year)&&this.month==2) { 47 if(this.day>29) 48 return false; 49 else 50 return true; 51 } 52 else if(this.day>mon_maxnum[this.month-1]) 53 return false; 54 else 55 return true; 56 } 57 public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) { 58 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { 59 this.day=this.day+1; 60 if(isLeapYear(this.year)&&this.month==2) { 61 if(this.day>29) { 62 this.month=3; 63 this.day=1; 64 } 65 } 66 else { 67 if(this.day>mon_maxnum[this.month-1]) { 68 this.month=this.month+1; 69 this.day=1; 70 } 71 } 72 if(this.month>12) { 73 this.year+=1; 74 this.month=1; 75 } 76 } 77 return this; 78 } 79 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) { 80 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { 81 this.day=this.day-1; 82 if(this.day==0) { 83 this.month=this.month-1; 84 if(this.month==0) { 85 this.month=12; 86 this.year-=1; 87 } 88 if(isLeapYear(this.year)&&this.month==2) 89 this.day=29; 90 else 91 this.day=mon_maxnum[this.month-1]; 92 } 93 } 94 return this; 95 } 96 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) { 97 if(this.year>date.getYear()) 98 return true; 99 else if(this.year<date.getYear()) 100 return false; 101 else if(this.month>date.getMonth()) 102 return true; 103 else if(this.month<date.getMonth()) 104 return false; 105 else if(this.day>date.getDay()) 106 return true; 107 else if(this.day<date.getDay()) 108 return false; 109 return false; 110 } 111 public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) { 112 int flag=1; 113 if(this.year!=date.getYear()||this.month!=date.getMonth()||this.day!=date.getDay()) 114 flag=0; 115 if (flag==1) 116 return true; 117 else 118 return false; 119 } 120 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) { 121 int count=0; 122 if(compareDates(date)) { 123 while(!this.equalTwoDates(date) ) { 124 this.equals(this.getPreviousNDays(1)); 125 count++; 126 } 127 return count; 128 } 129 else { 130 while(!this.equalTwoDates(date) ) { 131 getNextNDays(1); 132 count++; 133 } 134 return count; 135 } 136 137 } 138 public String showDate() { 139 return this.year+"-"+this.month+"-"+this.day; 140 } 141 } 142 public class Main { 143 public static void main(String[] args) { 144 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 145 int year = 0; 146 int month = 0; 147 int day = 0; 148 149 int choice = input.nextInt(); 150 151 if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method 152 int m = 0; 153 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 154 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 155 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 156 157 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 158 159 if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { 160 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 161 System.exit(0); 162 } 163 164 m = input.nextInt(); 165 166 if (m < 0) { 167 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 168 System.exit(0); 169 } 170 171 System.out.print(date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " next " + m + " days is:"); 172 System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate()); 173 } else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method 174 int n = 0; 175 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 176 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 177 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 178 179 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 180 181 if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { 182 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 183 System.exit(0); 184 } 185 186 n = input.nextInt(); 187 188 if (n < 0) { 189 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 190 System.exit(0); 191 } 192 193 System.out.print( 194 date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " previous " + n + " days is:"); 195 System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); 196 } else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method 197 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 198 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 199 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 200 201 int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 202 int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 203 int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 204 205 DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 206 DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay); 207 208 if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) { 209 System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() + 210 " and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:" 211 + fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); 212 } else { 213 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 214 System.exit(0); 215 } 216 } 217 else{ 218 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 219 System.exit(0); 220 } 221 } 222 }
三、总结
通过这三次的PTA学习,让我对循环结构、分支结构,以及flag标志的使用更加熟练,题目集一让我对String和StringBuffer的使用有了更深一步的认识,例如在“去掉重复的字符串”这一题目中,让我学习到了String类的contains方法可以判断字符串中是否包含指定内容,substring方法可以用来切割字符串,“从一个字符串中移除包含在另一个字符串中的字符”这一题目中,我学到了可以通过append方法来对StringBuffer类的字符串进行添加功能。题目集二的“判断三角形类型”题目让我认识到,计算机不能对浮点数进行精确的计算,因此判断两个浮点数是否相等时,可以让他们两个相减,差小于一个很小的数则认为他们相等。题目集三涉及到类的设计,这让我对面向对象的特点有了进一步的认识,认识到属性的public和private修饰符,外部如果要访问或者修改类的private特征属性需要调用getter、setter方法。此外,这四道题目还让我认识到我们可以们定义多个类来进行封装各部分功能,降低代码的圈复杂度,这体现了类的单一职责原则。
这三次题目的代码都还不够完善,类的设计使用太少,做很多题目时都是“为了编程而编程”,想着只要通过测试点就行了,没有考虑到类的设计原则,使得代码的耦合度太高,复杂度太高。要去多学学解构去修改代码,让它的可读性争强,可修改性更好。
这三次题目的学习还让我认识到了debug调试的重要性,很多逻辑错误光看是很难看出来的,运用debug调试,可以高效地找出代码哪里出了问题。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号