实验2
四.实验结论
1.验证性实验部分
①函数声明只是表明有一个需要调用的函数:
返回类型 函数名(参数类型1 参数名1,·····,参数类型n 参数名n);
函数定义是将这个具体的函数体表现出来:
返回类型 函数名(参数类型1 参数名1,·····,参数类型n 参数名n)
{
函数体······
}
②行参是出现在函数定义中的参数,实参数是出现在函数调用中的函数。函数的参数的作用是作数据传送,调用函数时,把实参的值传给形参。函数返回值是指在函数在运算结束后向调用它的函数返回一个值。
③值传递只能由实参传给形参,当函数内部需要更改数据,并不希望影响调用者时使用值传递。引用传递的操作地址就是实参的内存地址,它的操作就是对实参的操作,修改后会改变内存地址对应储存的值。
2.编程实验部分
(1)2-28
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char n;
while (1) {
cout << "Menu: A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select one:" << endl;
cin >> n;
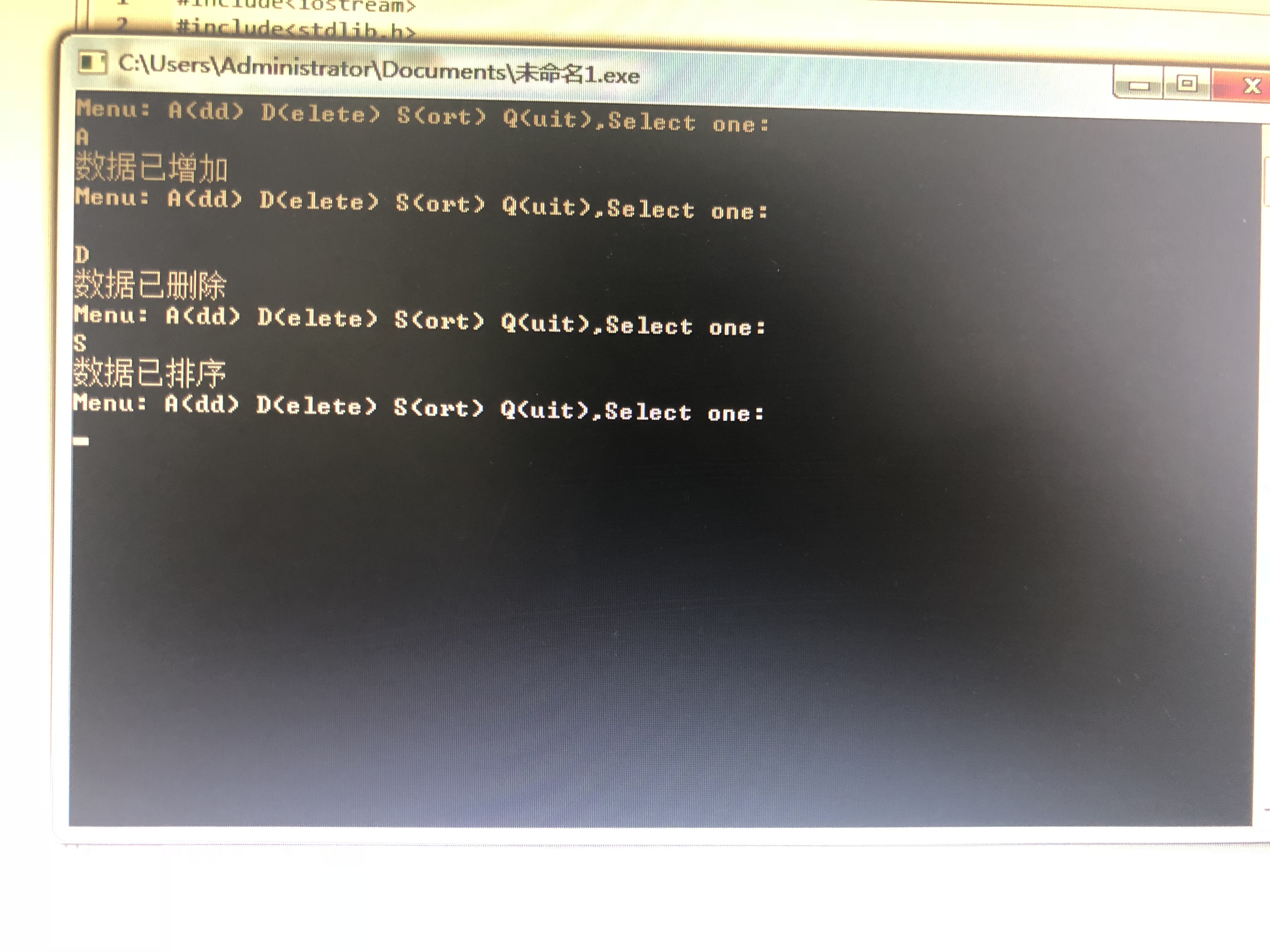
if (n == 'A')
{
cout << "数据已增加" << endl;
continue;
}
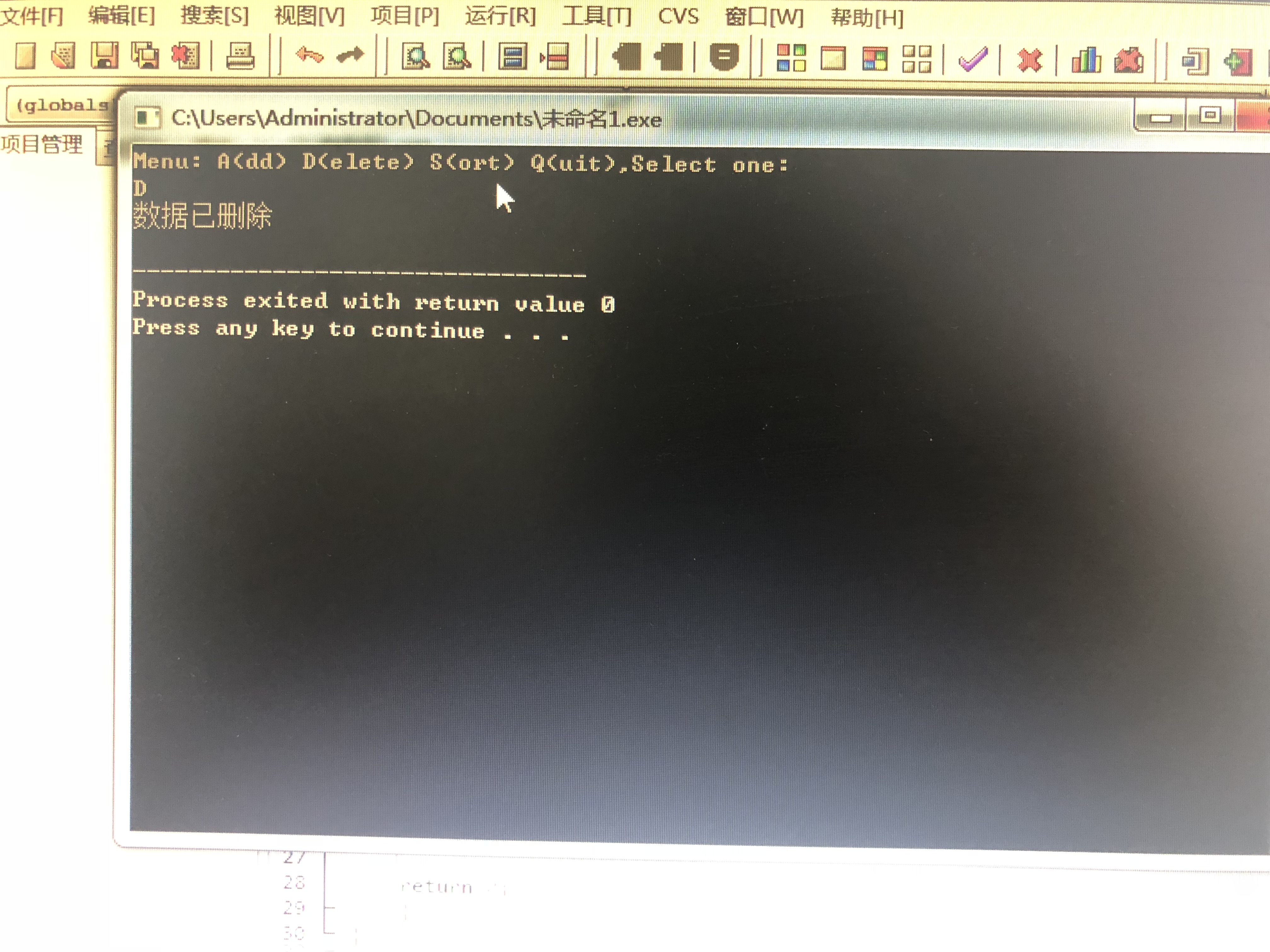
else if (n == 'D')
{
cout << "数据已删除" << endl;
continue;
}
else if (n == 'S')
{
cout << "数据已增加" << endl;
continue;
}
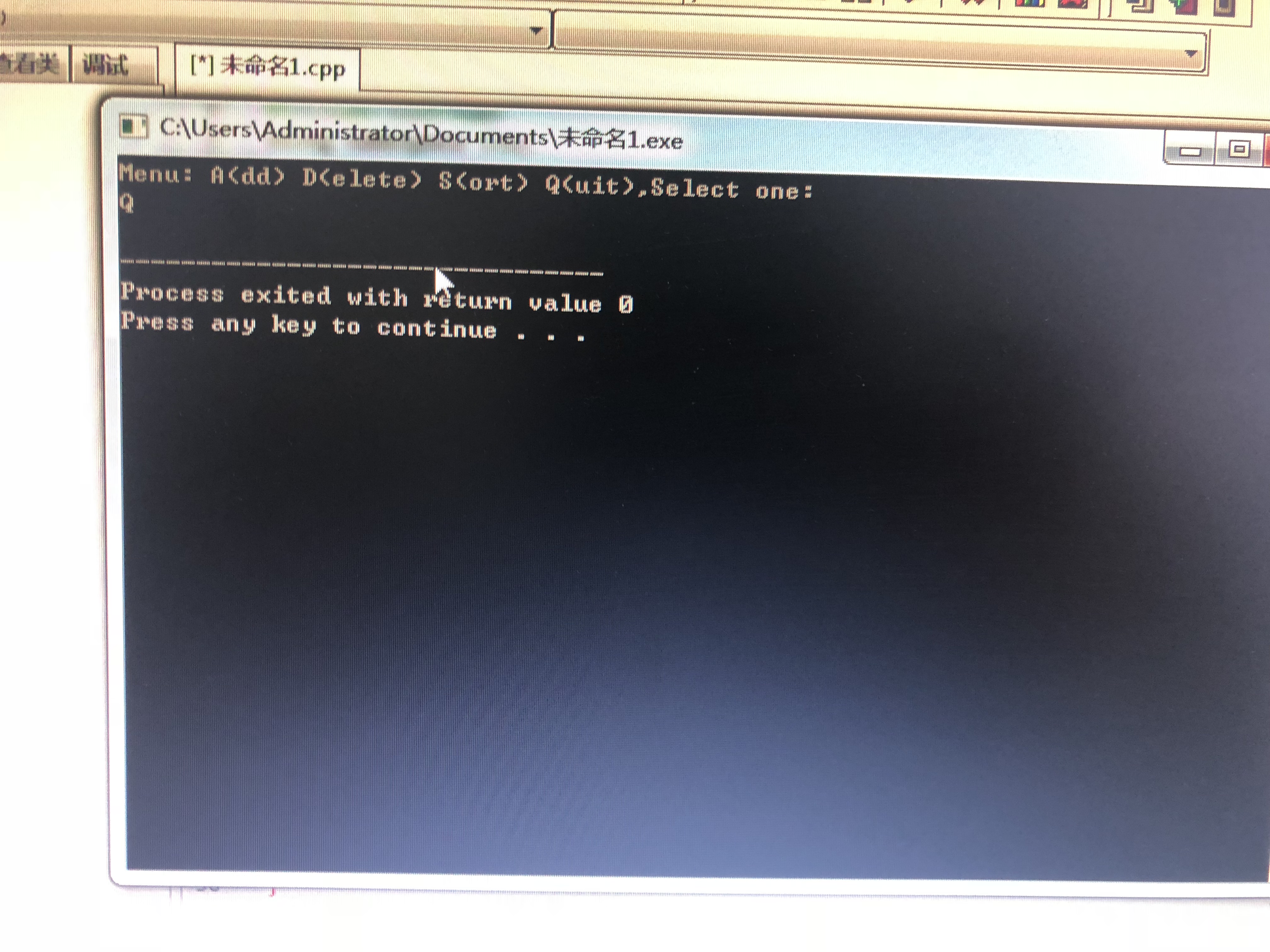
else if (n == 'Q')
{
exit(0);
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
#include< iostream >
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char n;
cout <<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select one:"<<endl;
do{
cin >>n;
switch(i)
{
case 'A':
cout <<"data has been added."<< endl;
break;
case'D':
cout <<"data has been deleted."<< endl;
break;
case'S':
cout <<"data has been sort"< <endl;
break;
}
}while(i!='Q');
return 0;
(2)2-29
①根据素数的定义,即只能被1或者自身整除的自然数(不包括1),称为质数。如果一个数是素数,那么它的最小质因数肯定<=它的开方。
②
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int judge(int);
int main()
{
int i=2,j;
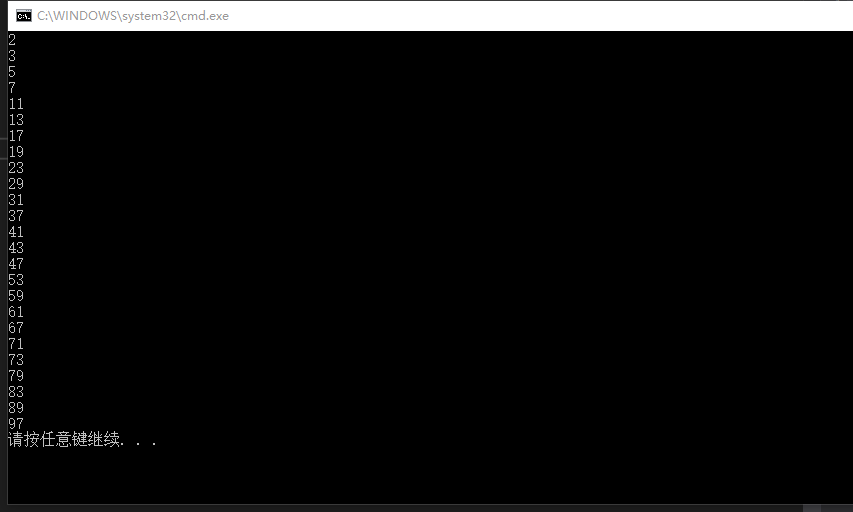
for(i=2;i<=100;i++)
{
if(judge(i))
cout<<i<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
int judge(int j)
{
int i,flag=1;
for(i=2;i<=sqrt(j);i++)
{
if(j%i==0)
{
flag=0;
break;
}
}
return flag;
}
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int judge(int j)
{
int a = 2,flag = 1;
do {
if (j%a == 0)
{
flag = 0;
++j;
}
} while (a > j);
return flag;
}
int main()
{
int i = 2;
cout << 2 << " ";
do{
if (judge(i))
cout << i << " ";
++i;
} while (i < 100);
return 0;
}
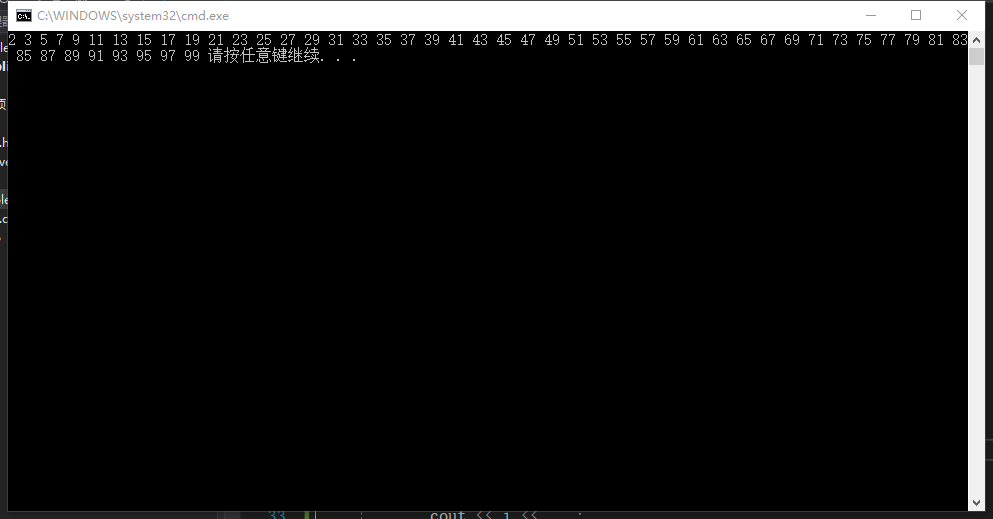
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int judge(int j)
{
int a = 2,flag = 1;
while (a <= j)
{
if (j%a == 0)
{
flag = 0;
++j;
}
}
return flag;
}
int main()
{
int i = 2;
while (i < 100)
{
if (judge(i))
cout << i << " ";
++i;
}
return 0;
}
(3)2-32
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i, n = 0;
cin >> i;
while (i != n)
{
cout << "Enter the number you guess:" << "\n";
cin >> n;
if (n>i)
cout << "The number is larger than the right one.Try again" << "\n";
if (n<i)
cout << "The number is smaller than the right one.Try again" << "\n";
}
cout << "Congratulations!" << endl;
return 0;
}
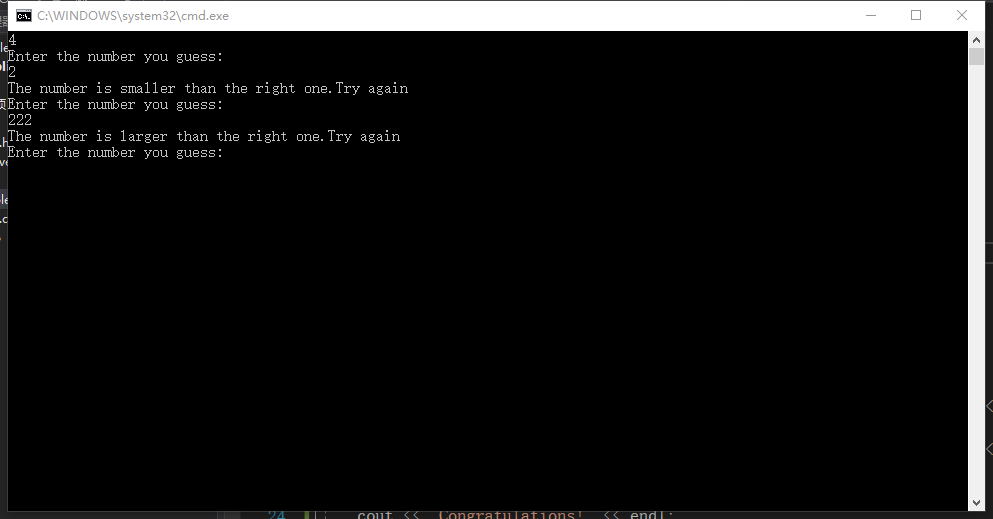
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i, n = 0;
cin >> i;
do
{
cout << "Enter the number you guess:" << endl;
cin >> n;
if (n > i)
{
cout << "The number is larger than the right one.Try again" << endl;
}
else if (n < i) {
cout << "The number is smaller than the right one.Try again" << endl;
}
else cout << "The number is the right one." << endl;
} while (i != n);
return 0;
}
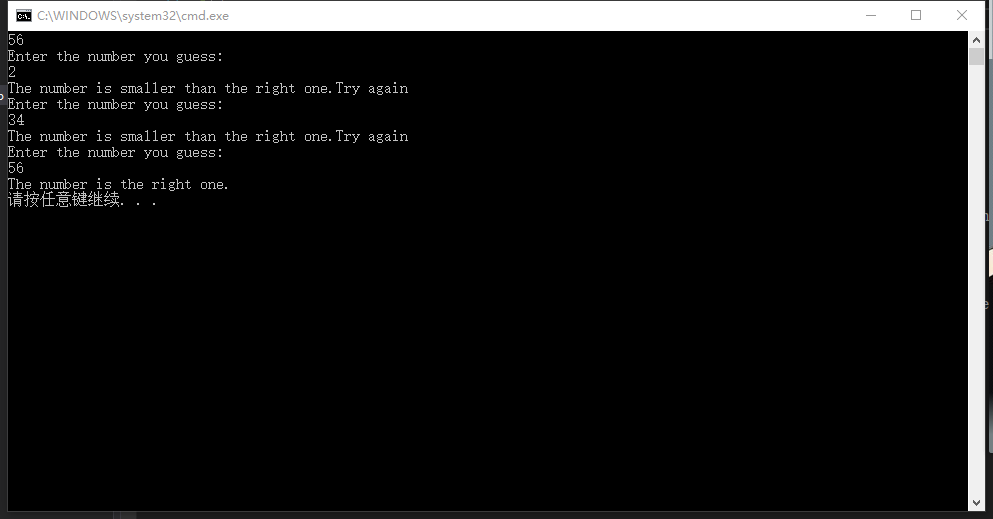
(4)2-34
①用递归的方法实现不同组合。
②
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
enum color { red, yellow, blue, white, black };
color pri;
int i, j, k, n = 0, loop;
for (i = red; i <= black; i++)
{
for (j = red; j <= black; j++)
{
if (i != j)
{
for (k = red; k <= black; k++)
{
if (k != i && k != j)
{
n = n + 1;
cout << setw(3) << n;
for (loop = 1; loop <= 3; loop++)
{
switch (loop)
{
case 1:pri = color(i); break;
case 2:pri = color(j); break;
case 3:pri = color(k); break;
default:break;
}
switch (pri)
{
case red:cout << setw(8) << "red"; break;
case yellow:cout << setw(8) << "yellow"; break;
case blue:cout << setw(8) << "blue"; break;
case white:cout << setw(8) << "white"; break;
case black:cout << setw(8) << "black"; break;
default:break;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
}
}
}
}
cout << "total:" << n << endl;
return 0;
}
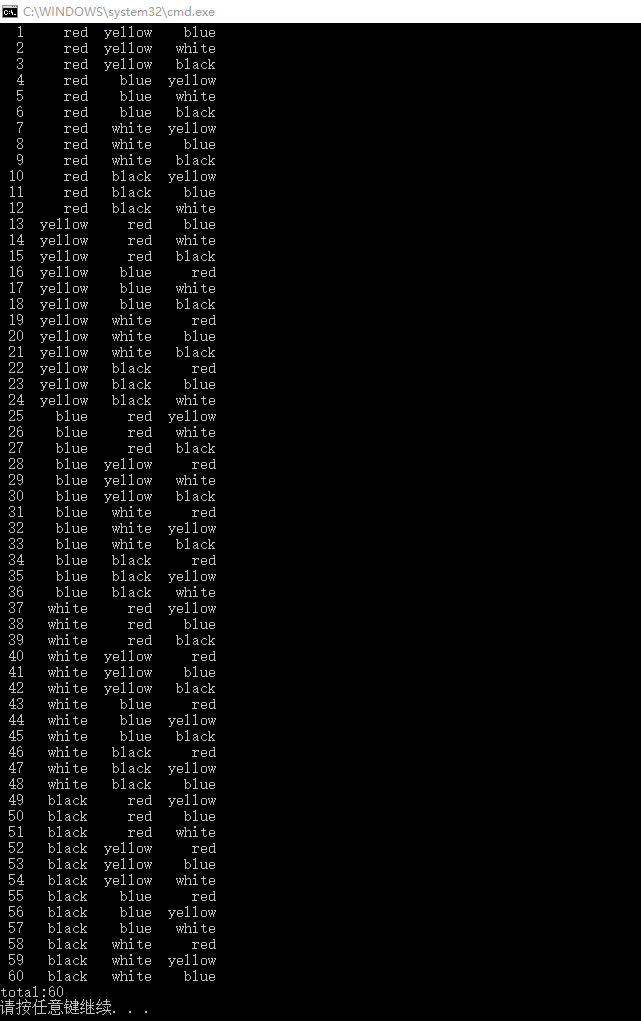
五.实验总结和体会
很多题目都可以有两种以上的解法,可以使用循环也可以不使用循环,各种语句都各有优势,重要的是要注意各个循环语句所需要的条件以及语法特点。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号