实验七
实验1
实验源码

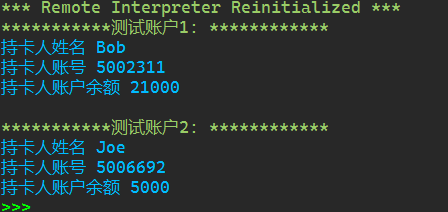
1 class Account: 2 def __init__(self,name,account_number,initial_amount = 10): 3 self._name = name 4 self._card_no = account_number 5 self._balance = initial_amount 6 7 def deposit(self,amount): 8 self._balance += amount 9 def withdraw(self,amount): 10 if self._balance < amount: 11 print('余额不足') 12 return 13 14 self._balance -= amount 15 def info(self): 16 print('持卡人姓名', self._name) 17 print('持卡人账号', self._card_no) 18 print('持卡人账户余额', self._balance) 19 def get_balance(self): 20 return self._balance 21 22 def main(): 23 print('测试账户1: '.center(30,'*')) 24 a1 = Account('Bob','5002311',20000) 25 a1.deposit(5000) 26 a1.withdraw(4000) 27 a1.info() 28 29 print() 30 31 print('测试账户2: '.center(30,'*')) 32 a2 = Account('Joe','5006692',20000) 33 a2.withdraw(10000) 34 a2.withdraw(5000) 35 a2.info() 36 37 if __name__ == '__main__': 38 main()
实验截图
实验2
shape.py
实验源码

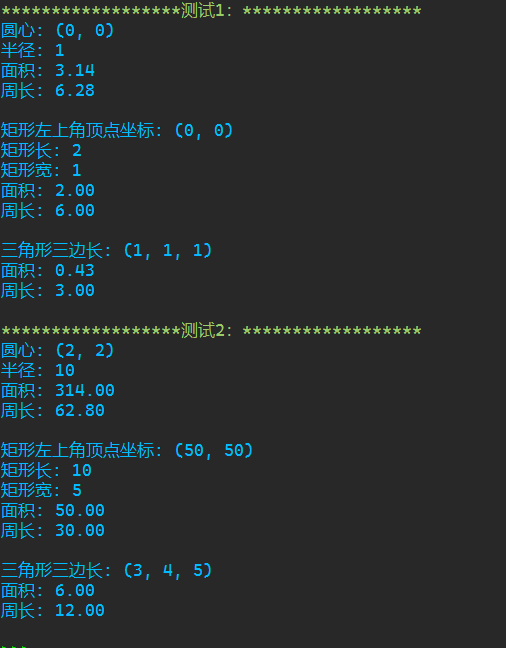
1 class Shape: 2 def info(self): 3 pass 4 def area(self): 5 pass 6 def preimeter(self): 7 pass 8 class Rect(Shape):#矩形类 9 def __init__(self, x = 0, y = 0, length = 2, width = 1): 10 self._x = x 11 self._y = y 12 self._width = width 13 self._length = length 14 def info(self):#打印图片信息 15 print(f'矩形左上角顶点坐标: ({self._x}, {self._y})') 16 print(f'矩形长: {self._length}') 17 print(f'矩形宽: {self._width}') 18 def area(self):#面积 19 return self._length * self._width 20 def perimeter(self):#周长 21 return (self._length + self._width) * 2 22 class Circle(Shape): 23 def __init__(self, x = 0, y = 0, radius = 1): 24 self._x = x 25 self._y = y 26 self._r = radius 27 def info(self): 28 print(f'圆心: ({self._x}, {self._y})') 29 print(f'半径: {self._r}') 30 def area(self): 31 return 3.14 * self._r * self._r 32 def perimeter(self): 33 return 2 * 3.14 * self._r 34 class Triangle(Shape): 35 def __init__(self, a = 1, b = 1, c = 1): 36 self._a, self._b, self._c = a, b, c 37 def info(self): 38 print(f'三角形三边长: ({self._a}, {self._b}, {self._c})') 39 def area(self): 40 s = (self._a + self._b + self._c) / 2 41 ans = (s*(s - self._a)*(s - self._b)*(s - self._c)) ** 0.5 42 return ans 43 def perimeter(self): 44 return (self._a + self._b + self._c) 45 def main(): 46 print('测试1:'.center(40, '*')) 47 shapes_lst1 = [Circle(), Rect(), Triangle()] 48 for t in shapes_lst1: 49 t.info() 50 print(f'面积: {t.area():.2f}') 51 print(f'周长: {t.perimeter():.2f}') 52 print() 53 print('测试2:'.center(40, '*')) 54 shapes_lst2 = [Circle(x = 2, y = 2, radius = 10), 55 Rect(x = 50, y = 50, length = 10, width = 5), 56 Triangle(a = 3, b = 4, c = 5)] 57 for t in shapes_lst2: 58 t.info() 59 print(f'面积: {t.area():.2f}') 60 print(f'周长: {t.perimeter():.2f}') 61 print() 62 if __name__ == '__main__': 63 main()
实验截图
task2.py
实验源码

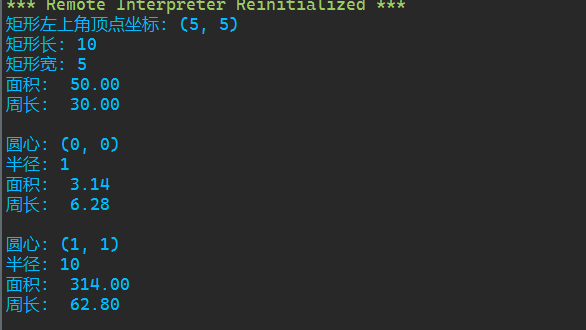
1 from shape import Rect, Circle 2 3 shape_lst = [Rect(5,5,10,5),Circle(),Circle(1,1,10)] 4 5 for i in shape_lst: 6 i.info() 7 print(f'面积: {i.area(): .2f}') 8 print(f'周长: {i.perimeter(): .2f}') 9 print()
实验截图
实验3
实验源码

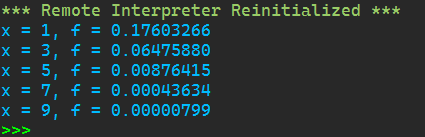
1 from math import* 2 3 def func(x): 4 m = 0 5 s = 2 6 a = 1/(s* (2*pi)**0.5) 7 b = exp(-0.5* (x/s)**2) 8 return a*b 9 10 for i in [1,3,5,7,9]: 11 print(f'x = {i}, f = {func(i):.8f}')
实验截图
实验4
random_walk.py
实验源码

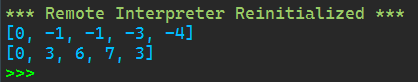
1 from random import choice 2 3 class RandomWalk(): 4 def __init__(self,num_points = 5000): 5 self.num_points = num_points 6 7 self.x_values = [0] 8 self.y_values = [0] 9 def fill_walk(self): 10 while len(self.x_values) < self.num_points: 11 x_direction = choice([1,-1]) 12 x_distanse = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) 13 x_step = x_direction * x_distanse 14 15 y_direction = choice([1,-1]) 16 y_distanse = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) 17 y_step = y_direction * y_distanse 18 19 20 if x_step == 0 and y_step == 0: 21 continue 22 23 next_x = self.x_values[-1] + x_step 24 next_y = self.y_values[-1] + y_step 25 26 self.x_values.append(next_x) 27 self.y_values.append(next_y) 28 29 def main(): 30 rw = RandomWalk(5) 31 rw.fill_walk() 32 print(rw.x_values) 33 print(rw.y_values) 34 35 if __name__ == '__main__': 36 main()
实验截图
task4
实验源码

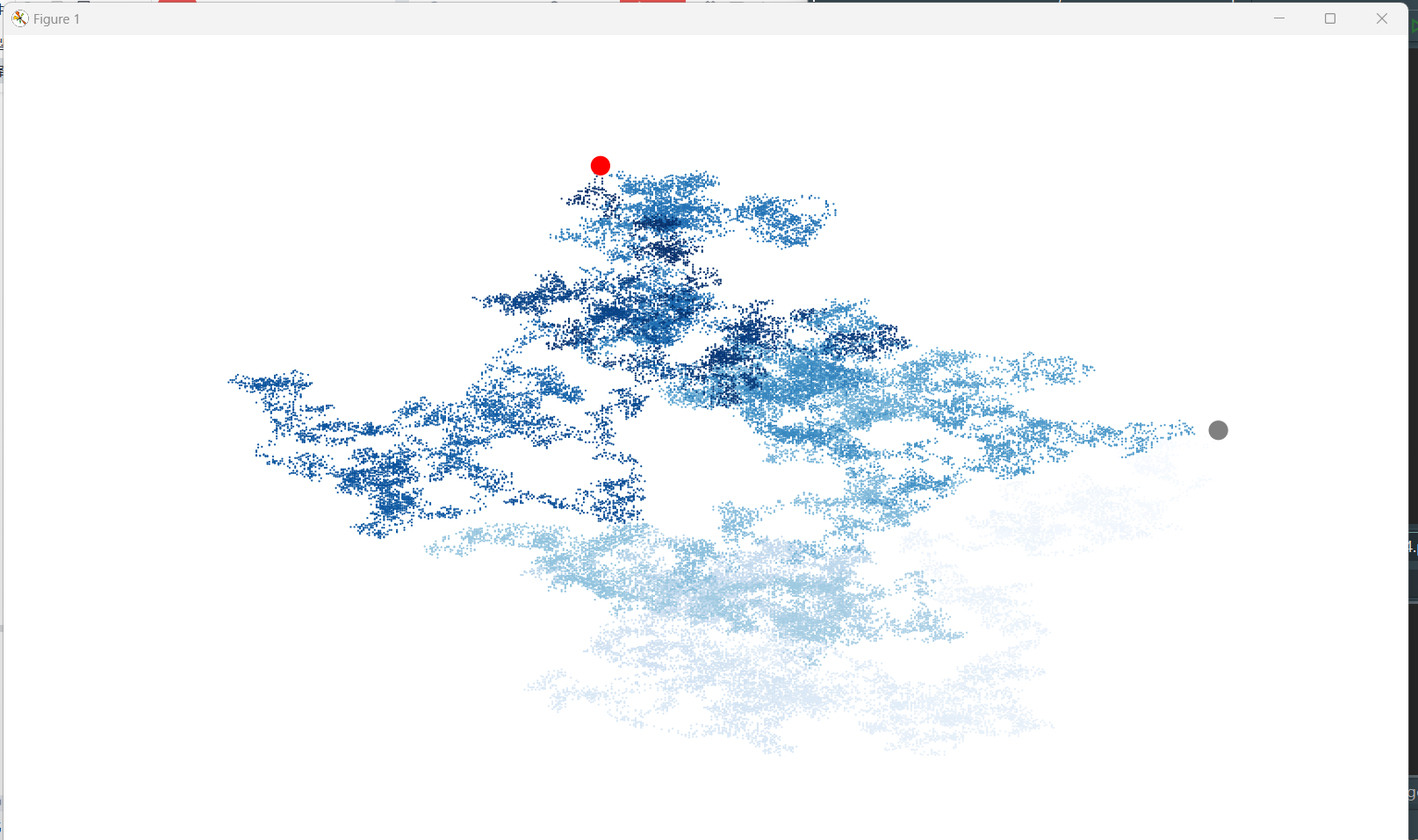
1 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 2 from random_walk import RandomWalk 3 from time import sleep 4 5 # 代码范例中,模拟两次随机漫步过程 6 n = 0 7 while n < 2: 8 n += 1 9 # 创建一个RandomWalk对象,调用其方法生成随机游走坐标 10 rw = RandomWalk(50000) 11 rw.fill_walk() 12 # 用散点图进行可视化绘制 13 plt.figure(figsize=(10,6), dpi= 128) 14 point_numbers = list(range(rw.num_points)) 15 plt.scatter(rw.x_values,rw.y_values,c = point_numbers, 16 cmap = plt.cm.Blues,edgecolor='none',s = 1) 17 # 终点和起点 18 plt.scatter(0,0,c = 'grey', edgecolors='none', s=100) 19 plt.scatter(rw.x_values[-1],rw.y_values[-1],c = 'red', 20 edgecolors='none',s=100) 21 # 隐藏坐标轴 22 plt.axis('off') 23 plt.show()
实验截图




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号