Java并发编程线程任务返回值及顺序问题解决方案
目录
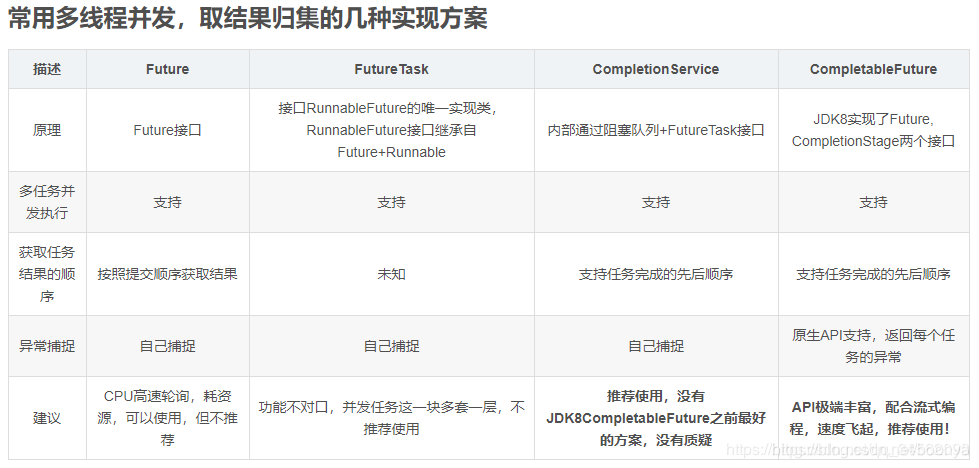
Future FutureTask CompletionService CompletableFutrue比较
核心知识点
无返回值并发执行顺序控制
- CountDownLatch
- CyclicBarrier
有返回值或先后顺序控制
- FutureTask
- CompletionService
- CompletableFuture
Future FutureTask CompletionService CompletableFutrue比较
下图参考自:https://blog.csdn.net/u011726984/article/details/79320004
可回调实现方式
Callable
接口定义:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Callable<V> {
/**
* Computes a result, or throws an exception if unable to do so.
*
* @return computed result
* @throws Exception if unable to compute a result
*/
V call() throws Exception;
}接口实现:
package thread;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
/**
*
* @function 功能:线程可回调任务
* @author PJL
* @package thread
* @filename CountTask.java
* @time 2020年4月1日 下午12:50:16
*/
public class CallableTask implements Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
int count=new Random().nextInt(10000);
Thread.sleep(count);
System.out.println("---"+count);
return count;
}
}
Supplier
接口定义:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Supplier<T> {
/**
* Gets a result.
*
* @return a result
*/
T get();
}接口实现:
package thread;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
/**
*
* @function 功能:可回调的Supplier顺序处理线程任务
* @author PJL
* @package thread
* @filename SupplierTask.java
* @time 2020年4月1日 下午1:06:27
*/
public class SupplierTask implements Supplier<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer get() {
int count=new Random().nextInt(10000);
try {
Thread.sleep(count);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("---"+count);
return count;
}
}
并发工具类
CountDownLatch
CountDownLatch 中文名叫闭锁,通俗的叫法叫栅栏发令枪。它可以模拟用户同时到达开始并发执行业务的场景,比如秒杀。
package thread;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
/**
* 同步辅助类CountDownLatch等待组线程执行完毕
* @author admin
* @link {@link https://www.cnblogs.com/liun1994/p/7396026.html}
* @screen 场景:
* <li>分布式计算进行汇总最终结果</li>
* <li>主线程等待子线程执行完的操作</li>
* <li>等待最终执行如初始化资源完成操作</li>
* <li>等待最终执行如系统资源汇总计算</li>
*/
public class WorkerCountDownLatch {
final static SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(2);// 两个工人的协作
Worker worker1 = new Worker("zhang san", 5000, latch);
Worker worker2 = new Worker("li si", 8000, latch);
worker1.start();//线程就绪
worker2.start();//线程就绪
latch.await();// 等待所有工人完成工作
System.out.println("all work done at " + sdf.format(new Date()));
}
static class Worker extends Thread {
String workerName;
int workTime;
CountDownLatch latch;
public Worker(String workerName, int workTime, CountDownLatch latch) {
this.workerName = workerName;
this.workTime = workTime;
this.latch = latch;
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("Worker " + workerName + " do work begin at " + sdf.format(new Date()));
doWork();// 工作了
System.out.println("Worker " + workerName + " do work complete at " + sdf.format(new Date()));
latch.countDown();// 工人完成工作,计数器减一
}
private void doWork() {
try {
Thread.sleep(workTime);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
测试结果:
Worker zhang san do work begin at 2020-04-01 13:47:45
Worker li si do work begin at 2020-04-01 13:47:45
Worker zhang san do work complete at 2020-04-01 13:47:50
Worker li si do work complete at 2020-04-01 13:47:53
all work done at 2020-04-01 13:47:53
CyclicBarrier
CyclicBarrier内部采用了可重入锁ReentrantLock和Runnable接口,可以控制多任务循环串行。
package thread;
import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;
/**
*
* @function 功能:CyclicBarrier允许线程之间互相等待
* @author PJL
* @package thread
* @filename WorkerCyclicBarrier.java
* @time 2020年4月1日 下午1:27:51
*/
public class WorkerCyclicBarrier {
static class TaskThread extends Thread {
CyclicBarrier barrier;
public TaskThread(CyclicBarrier barrier) {
this.barrier = barrier;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 循环执行A直到完成
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(getName() + " 执行任务A");
barrier.await();
System.out.println(getName() + " 执行任务 A完成");
// 循环执行B直到完成
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(getName() + " 执行任务B");
barrier.await();
System.out.println(getName() + " 执行任务 B完成");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int threadNum = 5;
CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(threadNum, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 回调处理
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 完成最后任务");
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < threadNum; i++) {
new TaskThread(barrier).start();
}
}
}
运行打印结果:
Thread-0 执行任务A
Thread-1 执行任务A
Thread-2 执行任务A
Thread-4 执行任务A
Thread-3 执行任务A
Thread-3 完成最后任务
Thread-3 执行任务 A完成
Thread-2 执行任务 A完成
Thread-0 执行任务 A完成
Thread-4 执行任务 A完成
Thread-1 执行任务 A完成
Thread-0 执行任务B
Thread-4 执行任务B
Thread-3 执行任务B
Thread-2 执行任务B
Thread-1 执行任务B
Thread-1 完成最后任务
Thread-1 执行任务 B完成
Thread-2 执行任务 B完成
Thread-3 执行任务 B完成
Thread-4 执行任务 B完成
Thread-0 执行任务 B完成
FutureTask
FutureTask 实现了RunnableFuture接口
/**
* A cancellable asynchronous computation. This class provides a base
* implementation of {@link Future}, with methods to start and cancel
* a computation, query to see if the computation is complete, and
* retrieve the result of the computation. The result can only be
* retrieved when the computation has completed; the {@code get}
* methods will block if the computation has not yet completed. Once
* the computation has completed, the computation cannot be restarted
* or cancelled (unless the computation is invoked using
* {@link #runAndReset}).
*
* <p>A {@code FutureTask} can be used to wrap a {@link Callable} or
* {@link Runnable} object. Because {@code FutureTask} implements
* {@code Runnable}, a {@code FutureTask} can be submitted to an
* {@link Executor} for execution.
*
* <p>In addition to serving as a standalone class, this class provides
* {@code protected} functionality that may be useful when creating
* customized task classes.
*
* @since 1.5
* @author Doug Lea
* @param <V> The result type returned by this FutureTask's {@code get} methods
*/
public class FutureTask<V> implements RunnableFuture<V> {而RunnableFutrue接口继承自Runnable和Future接口
/**
* A {@link Future} that is {@link Runnable}. Successful execution of
* the {@code run} method causes completion of the {@code Future}
* and allows access to its results.
* @see FutureTask
* @see Executor
* @since 1.6
* @author Doug Lea
* @param <V> The result type returned by this Future's {@code get} method
*/
public interface RunnableFuture<V> extends Runnable, Future<V> {
/**
* Sets this Future to the result of its computation
* unless it has been cancelled.
*/
void run();
}
FutureTask测试:
package thread;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
/**
*
* @function 功能:FutureTask线程返回值获取方式
* @author PJL
* @package thread
* @filename WorkerFutureTask.java
* @time 2020年4月1日 下午1:11:41
*/
public class WorkerFutureTask {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
FutureTask<Integer> task1 = new FutureTask<Integer>(new CallableTask());
FutureTask<Integer> task2 = new FutureTask<Integer>(new CallableTask());
FutureTask<Integer> task3 = new FutureTask<Integer>(new CallableTask());
executor.execute(task1);
executor.execute(task2);
executor.execute(task3);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("task1结果=" + task1.get());
System.out.println("task2结果=" + task2.get());
System.out.println("task3结果=" + task3.get());
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("总共耗时=" + (end - start) + "ms");
}
}
测试结果:
---181
---2594
task1结果=2594
task2结果=181
---2816
task3结果=2816
总共耗时=2817ms
注意:FutureTask的get()方法是阻塞的,不区分完成先后顺序,所以最长的时间可能是加起来所有任务耗时的总和。
CompletionService
CompletionService 是通过线程干预的模式对线程完成状态进行监控,它是JDK并发包的接口,其实现是java.util.concurrent.ExecutorCompletionService,需要结合线程池来使用。
测试示例:
package thread;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletionService;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorCompletionService;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
/**
*
* @function 功能:线程完成顺序干预先后排序
* @author PJL
* @package thread
* @filename WorkerCompletionService.java
* @time 2020年4月1日 下午1:20:14
*/
public class WorkerCompletionService {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
CompletionService<Integer> completionService=new ExecutorCompletionService<Integer>(executor);
Future<Integer> task1=completionService.submit(new CallableTask());
Future<Integer> task2=completionService.submit(new CallableTask());
Future<Integer> task3=completionService.submit(new CallableTask());
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("task1结果=" + task1.get());
System.out.println("task2结果=" + task2.get());
System.out.println("task3结果=" + task3.get());
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("总共耗时=" + (end - start) + "ms");
}
}
测试结果:
---1539
task1结果=1539
---5169
task2结果=5169
---9412
task3结果=9412
总共耗时=9414ms
CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture 实现了Future和CompletionState接口,可实现线程先后完成排序。
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T> {测试示例:
package thread;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
*
* @function 功能:多线程任务按照完成先后顺序返回
* @author PJL
* @package thread
* @filename WorkerCompletableFuture.java
* @time 2020年4月1日 下午1:04:00
*/
public class WorkerCompletableFuture {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
CompletableFuture<Integer> task1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new SupplierTask(), executor);
CompletableFuture<Integer> task2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new SupplierTask(), executor);
CompletableFuture<Integer> task3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new SupplierTask(), executor);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("task1结果=" + task1.get());
System.out.println("task2结果=" + task2.get());
System.out.println("task3结果=" + task3.get());
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("总共耗时=" + (end - start) + "ms");
}
}
测试结果:
---609
---782
task1结果=782
task2结果=609
---5614
task3结果=5614
总共耗时=5615ms
纸上得来终觉浅,绝知此事要躬行。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号