numpy中array 和mat 以及 list的使用
1 import matplotlib 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 import numpy as np 4 from numpy import *;#导入numpy的库函数 5 import sys 6 # Numpy matrices必须是2维的,但是 numpy arrays (ndarrays) 可以是多维的(1D,2D,3D····ND). 7 # Matrix是Array的一个小的分支,包含于Array。所以matrix 拥有array的所有特性。 8 9 # 一维 array 10 tem1 = [1, 2, 3] 11 atem1 = np.array(tem1) 12 13 # 添加元素 14 tem1.insert(0, 4) 15 atem1_i = np.insert(atem1, 0, values=4, axis=0) 16 #atem1_i = np.insert(atem1, 0, values=4) # 省略最后一个 参数也可以,是默认的 17 18 #删除元素 19 tem1.pop(0) 20 21 #切片提取 22 atem1_i = atem1[1:] 23 atem1_i = atem1[0: atem1.size - 1] 24 25 # list 对应 也是一维 的 26 tolist1 = atem1_i.tolist() 27 28 # 二维 array 29 a = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]) 30 b = np.array([[0,0,0]]) 31 c = np.insert(a, 0, values=b, axis=0) 32 d = np.insert(a, 0, values=b, axis=1) 33 34 # 切片提取 35 tem = d[0][1:] 36 37 # list 对应 也是二维 的 38 tolist1 = d.tolist() 39 40 # 三维 41 a = np.array([[[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]]) 42 43 # list 对应 也是二维 的 44 tolist1 = a.tolist()
array 的结构,每个子模块都是一个array
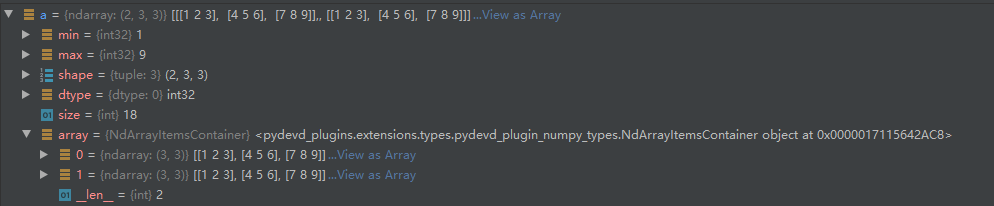
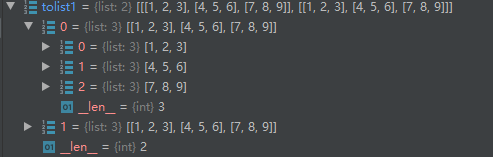
转化成对应维数的list:
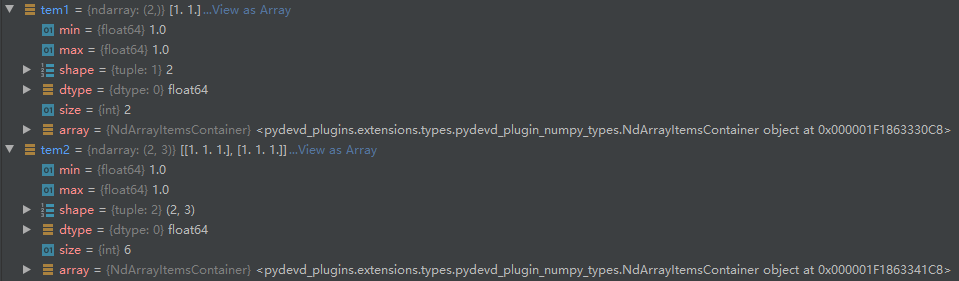
1 # 固定维数数据生成 2 def ones(shape, dtype=None, order='C'): 3 """ 4 Return a new array of given shape and type, filled with ones. 5 6 Parameters 7 ---------- 8 shape : int or sequence of ints 9 Shape of the new array, e.g., ``(2, 3)`` or ``2``. 10 dtype : data-type, optional 11 The desired data-type for the array, e.g., `numpy.int8`. Default is 12 `numpy.float64`. 13 order : {'C', 'F'}, optional, default: C 14 Whether to store multi-dimensional data in row-major 15 (C-style) or column-major (Fortran-style) order in 16 memory. 17 18 Returns 19 ------- 20 out : ndarray 21 Array of ones with the given shape, dtype, and order. 22 23 See Also 24 -------- 25 ones_like : Return an array of ones with shape and type of input. 26 empty : Return a new uninitialized array. 27 zeros : Return a new array setting values to zero. 28 full : Return a new array of given shape filled with value. 29 30 # 对应的得到的就是array 类型 31 # 通过参数shape(tuple类型) 设置得到的维数,一维设置需要特别注意 32 tem1 = np.ones((2,)) 33 tem2 = np.ones((2, 3)) 34 #tem2 = np.array(np.ones((2,))) 本身就是array ,所以这个转化是多余的
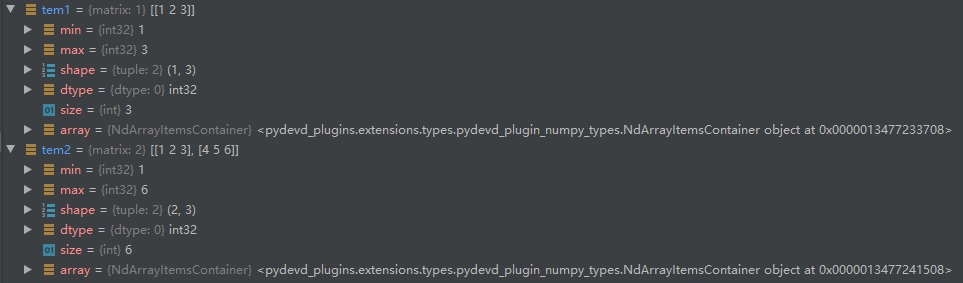
1 # Numpy matrices必须是2维的,但是 numpy arrays (ndarrays) 可以是多维的(1D,2D,3D····ND). 2 # Matrix是Array的一个小的分支,包含于Array。所以matrix 拥有array的所有特性。 3 4 # 一维的list会默认转成 1*n 5 tem1 = np.mat([1, 2, 3]) 6 # 二维的list 对应 m*n 7 tem2 = np.mat([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]) 8 # 三维的list ,此时执行会报错,不允许 9 #tem2 = np.mat([[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]])
互相转化:
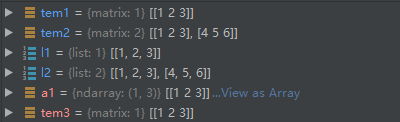
l1 = tem1.tolist() l2 = tem2.tolist() a1 = np.asarray(tem1) tem3 = np.asmatrix(a1)
array 可迭代特性检查及使用:
1 from collections.abc import Iterable 2 3 # 一维 array 4 tem1 = [1, 2, 3] 5 atem1 = np.array(tem1) 6 print(isinstance(atem1, Iterable)) # true 7 for x in atem1: 8 print(x) 9 #1 10 #2 11 #3 12 13 # 二维 array 14 a = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]) 15 print(isinstance(a, Iterable)) # true 16 17 for x in a: 18 print(x) 19 #[1 2 3] 20 #[4 5 6] 21 #[7 8 9] 22 for x, y, z in a[0], a[1], a[2]: 23 print(x, y, z) 24 #1 2 3 25 #4 5 6 26 #7 8 9
记录每天生活的点点滴滴,呵呵呵呵呵呵




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号