Day02_运算符
运算符
Java语言支持如下运算符
- 算数预算福+ - * / % ++ --
- 赋值运算符 =
- 关系运算符> < >= <= == != instanceof
- 逻辑运算符&& || !
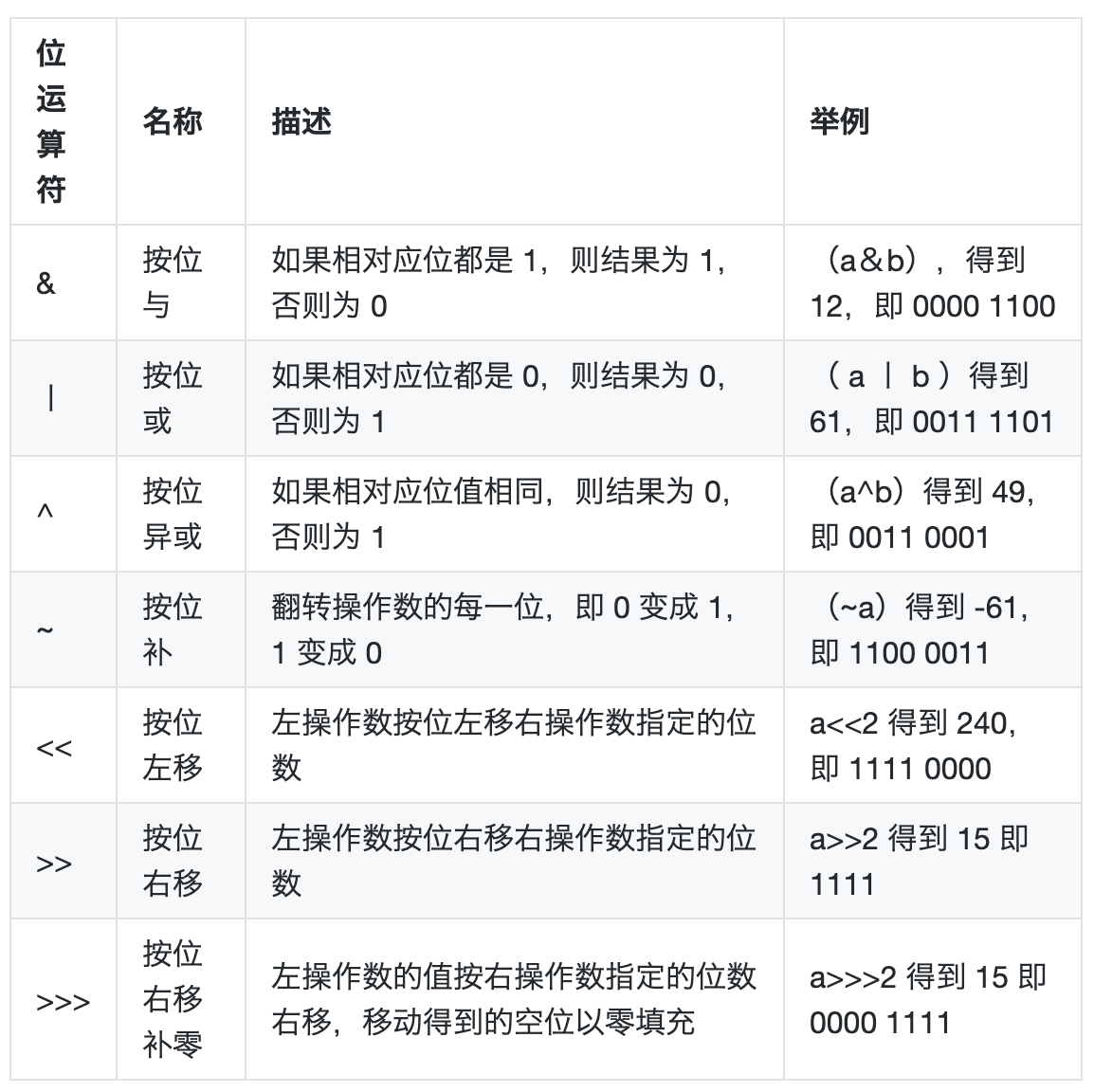
- 位运算符& | ^ ~ >> << >>>(<<是对二进制的操作)
- 条件运算符 (三元运算符)? :(必须掌握)
- 扩展赋值运算符 += -= *= /=
前四个重点掌握
算数计算时如果没哟Long类型的数据,计算之后会自动升为Int类型
自增自减
int a = 3;
int b = a++;
int c = ++a;
总结:离等号近的先赋值,在运算。反之亦然
幂运算
我们使用一些工具类来操作
double pow = Math.pow(2, 3);
System.out.println(pow);
逻辑运算符短路计算
int c = 4;
boolean d = (--c < 4)&(c++ < 4);
System.out.println(d);
System.out.println(c);
false
5
int c = 4;
boolean d = (c < 4)&&(c++ < 4);
System.out.println(d);
System.out.println(c);
false
4
短路与会从真执行到假,遇到假之后就不进行后面的运算
位运算
/*
A,B为二进制数
A = 0011 1100
B = 0000 1101
---------------
A&B = 0000 1100
A|B = 0011 1101
A^B = 0011 0001(相同为0,不相同为1)
2*8的最快计算方法是位运算
2*8==2*2^3==0010<<3==0010000==2^4==16
*/
System.out.println(3<<3);
/*
0000 0000 0
0000 0001 1
0000 0010 2
0000 0100 4
3对应的二进制是
0000 0011
左移三位就是
0001 1000 24
*/
表格中的例子中,变量 a 的值为 60(二进制:00111100),变量 b 的值为 13(二进制:00001101):
字符串连接(+)
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
System.out.println(""+a+b);
System.out.println(a+b+"");
1020
30
条件运算符
double score = 61;
String result = score > 60 ? "及格" : "不及格";
System.out.println(result);
x ? y : z
x为真返回y,x为假返回z
优先级
建议使用()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号