论文学习7——TinyFusion: Diffusion Transformers Learned Shallow
Abstract
Diffusion Transformers have remarkable performance in image generation but considerable inference. The authors designed a pruned model called TinyFusion which was designed to move redundant layers from diffusion transformers.
Introduction
The authors’ work follows one perspective that pruned model is then fine-tuned for performance recovery. They proposed a learnable depth pruning method that effectively integrates pruning and fine-tuning of a diffusion transformer, enabling superior post-fine-tuning performance.
This way craft shallows diffusion transformers from pre-trained ones.
Related Works
The depth reduction has gained significant attention in the past few years, which can get better speedup proportional to the pruning ratio.
There are many efforts to develop efficient diffusion transformers, and the authors focus on compressing the depth of pre-trained diffusion model and optimizing recoverability.
Method
Shallow Generative Transformers by Pruning
The author wants to get a shallow diffusion transformer by pruning a pre-trained model. But they encountered two challenges:1)The non-differentiable nature of layer selection. 2) The computationally intractable problem to explore the entire search spaces.
TinyFusion: Learnable Depth Pruning
Probabilistic Perspective
To model the Eq2, the authors hypothesis the mask m should follow a certain distribution. However, this paradigm could cause a massive waste of search space. To overcome this challenge, the author introduce an advanced algorithm capable of using evaluation results as feedback to iteratively refine the mask distribution.
Sampling Local Structures
The authors proposed an N:M scheme for local pruning instead of global layer pruning. Through this way, the system will tend to sample those positive frequently and keep activate explorations in other local blocks.
Differentiable Sampling
To apply the N:M scheme and sample the masks, the authors proposed a \(\hat{m}^{N:M}\) matrix and use Gumbel-Softmax.
Joint Optimization with Recoverability
The authors key idea is to update the co-optimized \(\Delta \Phi\) to maximize the recoverability of sampled masks. To avoid the large processing cost and inefficiency, they used LoRA to reduce the number of parameters and facilitate efficient exploration of different pruning decisions.
Experiments
Results on Diffusion Transformers
The authors extend their models to DiTs, MARs and SiTs. The result show that the compressed Tiny-plused model reach higher performance.
Analytical Experiments
Calibration Loss
The author verify that the calibration loss doesn’t influence the model performance directly. It is worthy noting that the “recoverability“ appears to be more critical.
Learnable Modeling of Recoverability
The authors use different layer pruning rate and find that smaller blocks significantly reduce optimization and offer greater flexibility.
Visualization of Learnable Decisions
The authors visualize the learning process in different layers of the pruned-model and the transparency of each data point indicates the probability of being sampled. Finally, they select the layers with the highest probabilities for subsequent fine-tuning.
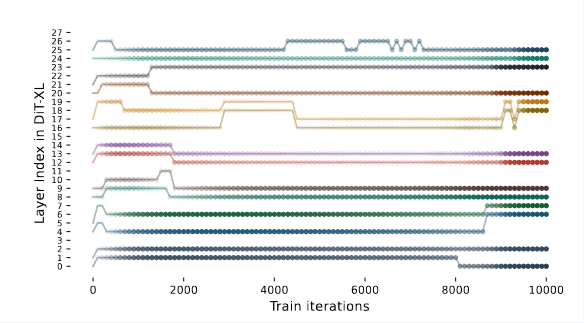
Knowledge Distillation for Recovery
The authors apply the vanilla knowledge distillation approach to fine-tune a TinyDiT-D14, using a bigger pre-trained DiT-XL/2 as a teacher model, which results in better performance.
Masked Knowledge Distillation
When the authors transfer hidden states from the teacher to the student, they encounter the difficulty that massive activations, existing in the hidden states, directly been distilled can cause high loss value. So they employ a simple thresholding method \(|x-\mu_{x}|<k\sigma_{x}\), which ignores the loss associated with these extreme activations.
Conclusion
TinyFusion is a learnable method to accelerating diffusion transformers by redundant layers.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号