论文学习2——Attention Is All You Need
Abstract
The authors propose a new simple network which is based solely on attention mechanisms, dispensing with recurrence and convolutions entirely.
Introduction
For recurrent models, although some work has achieved significant improvements in computational efficiency and conditional computation, the fundamental constraint of sequential computation precludes the training examples.
Attention mechanisms have become an integral part of compelling sequence modeling. The authors propose the Transformer, a model entirely rely on an attention mechanism to model global dependencies between input and output.
Background
The typical models which use convolutional neural networks as basic building block difficultly learn dependencies between distant positions, because the number of operations will grow according to the model like ConvS2S and ByteNet. (Maybe this paradigm about operations limits the calculating ability of model.)
Self-attention as the specialty of Transformer relates all different positions of a single sequence differing from the typical ways which use End-to-end instead of RNNs or convolution.
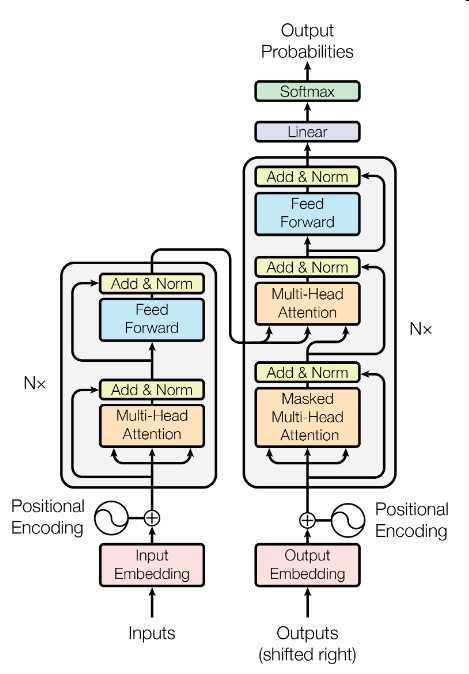
Model Architecture
Encoder and Decoder Stacks
The encoder is composed of a stack of N=6 identical layers. Each layers have two sub-layers. The first is Multi-Head Attention mechanism, the second is a simple feed-forward layer. What’s more, the authors employ a residual connection around each of the two sub-layers.
The decoder is also composed of a stack of N=6 identical layers. But in addition to the sub-layers, the authors add Masked Multi-Head Attention in order to prevent positions from attending to subsequent positions(it perplexes me).
Attention
First, we should know that an attention function is likely a mapping function which maps the query and a set of key-value pairs to an output.
Scales Dot-Product Attention
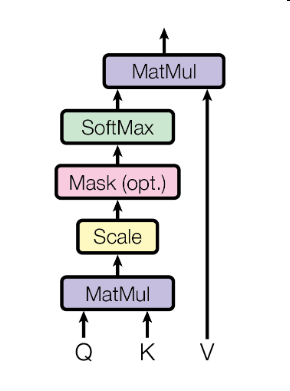
The input consists of queries and keys of dimension \(d_k\), and values of dimension \(d_v\)
There are two most commonly used attention functions. The first is additive attention, the second is dot-product attention. The two are similar in theoretical complexity. So why choose the dot-product attention? . The reasons are:
1. Dot-product attention is identical to the authors' algorithm.
2. Dot-product attention is much faster and more-efficient in practice.
But after choosing dot-product attention, the authors divide the values by \(\sqrt{d_k}\) since additive attention outperforms dot product attention without scaling for larger values of \(d_k\).
Multi-Head Attention
The authors find that it is beneficial to linearly project the queries, keys and values h times with different. They employ \(h=8\) parallel attention layers and use \(d_k = d_v = d_{model/h}=64\)
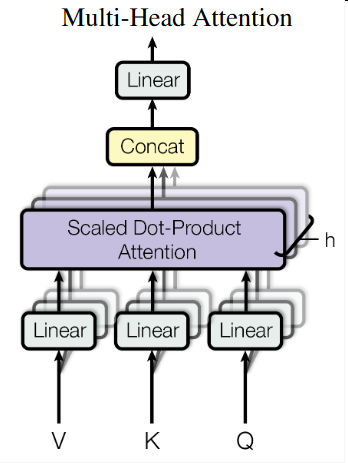
Applications of Attention in our Model
First, we should know that the queries come from the previous decoder layer and the memory keys and values come from the output of the encoder.
Self-attention. In a self-attention layer all of the keys, values and queries come from the same place.(Maybe it is like a recurrent)
The position. Each position in encoder can attend to all positions in the previous layer of the encoder. In addition to this, each position in the decoder can also attend to all positions in the decoder because of the self-attention. However, the authors say it is bad that the leftward information flow in the decoder converge on the encoder. It may cause the auto-regressive property.
Embedding and Softmax
In Transformer, the authors also use learned embedding to convert input tokens and output tokens to vectors of dimension \(d_{model}\) like other sequence transduction model. They also use the linear transformation and softmax function to convert the decoder output to predicted next-token probabilities.
Positional Encoding
In order to inject some information about the relative or absolute position of the tokens in the sequence, the authors add “positional embedding“ to the input embedding at the bottom of the encoder and decoder stacks.
The authors use sine and cosine functions to make positional encoding and they choose the sinusoidal version.
Why self-Attention
One key factor affecting the ability to learn long-range dependencies is the length of the paths forward and backward signals have to traverse in the network. The shorter paths will easily learn long-range dependencies.
Self-attention has advantages in the case of the sequence length n is smaller than the representation dimensionality d. In order to improve the computation performance for tasks involving long sequence, self-attention should calculate a neighborhood of size r in the input sequence.
The stack of separable convolutions layers has low computation complexity than the common convolutions layer. However, the complexity of separable convolutions is equal to the self-attention layer and a point-wise feed-forward layer designed by the authors.
Self-attention model can learn to perform different models and exhibit its powerful comprehension of the syntactic and semantic tasks.
Results
Machine Translation
The Transformer(big model) outperforms previous model and establishes a new state-of-the-art BLEU score.
Model Variations
The authors evaluate the importance of different components of the Transformer. They investigate how elements such as model size, dropout, key size, and so on affect the performance.
Conclusion
Transformer is the first model based entirely on attention, replacing the recurrent and convolution layers. What’s more, the Transformer achieve a new state-of-the-art in English-to-German and English-to-French tasks. Next step, the authors plan to dilate the application scopes of Transformer such as image, audio and video.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号