touch事件的分发和消费机制
Android 中与 Touch 事件相关的方法包括:dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)、onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)、onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev);能够响应这些方法的控件包括:ViewGroup、View、Activity。继承ViewGroup的大多是容器控件,如LinearLayout等,而继承View的大部分是显示控件比如TextView,ImageView等(当然,ViewGroup本身是继承View的),显示控件没有onInterceptTouchEvent。
来看一些例子。
情形1
package com.example.toucheventdemo; import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import android.view.MotionEvent; public class MainActivity extends Activity { private static final String TAG = "MainActivity"; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } @Override public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { switch (ev.getAction()) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_UP"); break; } return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev); } @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { switch (event.getAction()) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_UP"); break; } return super.onTouchEvent(event); } }
日志信息:

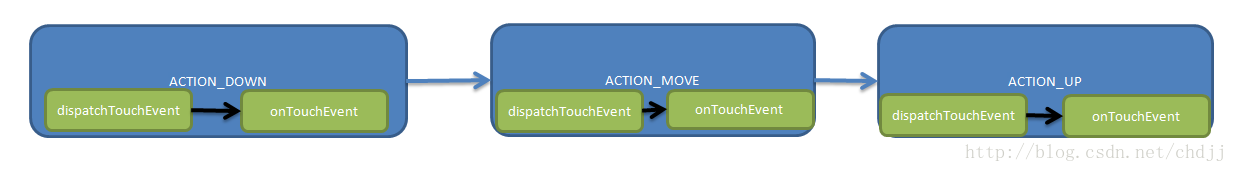
可以看到:总是先执行dispatchTouchEvent,再执行onTouchEvent.。
情形2:

package com.example.toucheventdemo; import android.content.Context; import android.util.AttributeSet; import android.util.Log; import android.view.MotionEvent; import android.widget.Button; public class MyButton extends Button { private static final String TAG = "MyButton"; public MyButton(Context context) { super(context); } public MyButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); } @Override public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { switch (ev.getAction()) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_UP"); break; } return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev); } @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { switch (event.getAction()) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_UP"); break; } return super.onTouchEvent(event); } }
mainActivity代码如下:
package com.example.toucheventdemo; import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import android.view.MotionEvent; import android.view.View; import android.view.View.OnClickListener; public class MainActivity extends Activity { private static final String TAG = "MainActivity"; private MyButton but = null; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); but = (MyButton) findViewById(R.id.but); } @Override public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { switch (ev.getAction()) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_UP"); break; } return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev); } @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { switch (event.getAction()) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_UP"); break; } return super.onTouchEvent(event); } }
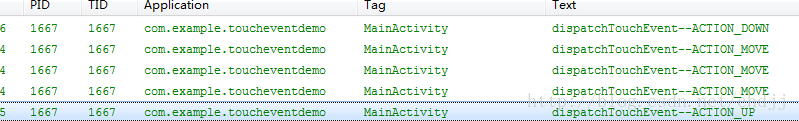
此时点击Button按钮,查看日志:

执行流程是首先由activity捕获到ACTION_DWON事件,然后调用activity的dispatchTouchEvent,接着绕开activity的onTouchEvent直接将事件传递给子控件,调用MyButton的dispatchTouchEvent,在之后调用该控件的onTouchEvent,ACTION_UP事件也是一样的流程。

情形4:
跟情形2类似,将情形3的activity的DispatchTouchEvent的返回值改为true,点击按钮,很显然,touch事件将不会被分发给Button,所以点击按钮日志是这样的:
日志信息:

情形5:
将情形3的myButton的DispatchTouchEvent的返回值改为true,点击按钮,很显然,当touch事件传递到button时,先被dispatchTouchEvent捕获,由于返回true,所以事件被消费,便不往下面传递,所以Button的onTouchEvent方法不被调用。
日志信息:


package com.example.toucheventdemo; import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import android.view.MotionEvent; import android.view.View; import android.view.View.OnClickListener; import android.view.View.OnTouchListener; public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener,OnTouchListener { private static final String TAG = "MainActivity"; private MyButton but = null; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); but = (MyButton) findViewById(R.id.but); but.setOnClickListener(this); but.setOnTouchListener(this); } @Override public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { switch (ev.getAction()) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_UP"); break; } return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev); } @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { switch (event.getAction()) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_UP"); } return super.onTouchEvent(event); } @Override public void onClick(View v) { Log.i("MyButton","ONCLICK"); } @Override public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) { switch (event.getAction()) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: Log.i("MyButton","onTouch--ACTION_DOWN"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: Log.i("MyButton","onTouch--ACTION_MOVE"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: Log.i("MyButton","onTouch--ACTION_UP"); break; } return false; } }
现在点击按钮日志打印如下信息:
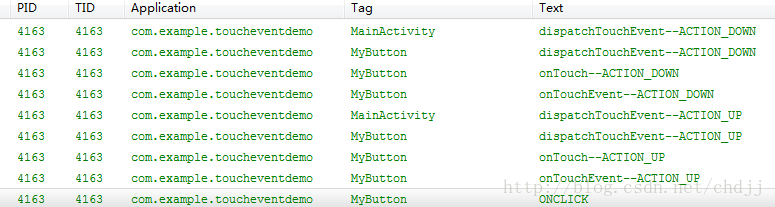
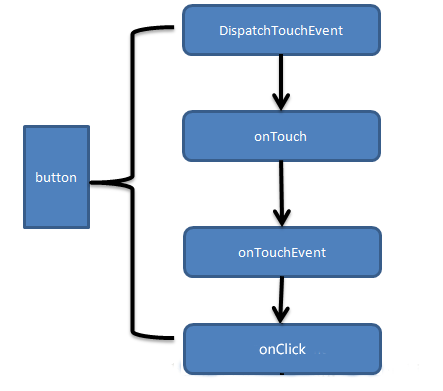
首先touch事件由activity捕获,调用activity的dispatchTouchEvent,紧接着调用Button的dispatchTouchEvent继续分发touch事件,接着并没有调用button的onTouchEvent,而是先调用了onTouch方法,这是因为button按钮注册了onTouchListener的缘故,待onTouch事件处理完之后,由于返回值为false,所以touch事件传递给了button的onTouchEvent。接着ACTION_UP事件也是类似的过程,但当Button的onTouchEvent结束后,还调用了Onclick方法。
情形8:

case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: boolean prepressed = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PREPRESSED) != 0; if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) != 0 || prepressed) { // take focus if we don't have it already and we should in // touch mode. boolean focusTaken = false; if (isFocusable() && isFocusableInTouchMode() && !isFocused()) { focusTaken = requestFocus(); } if (prepressed) { // The button is being released before we actually // showed it as pressed. Make it show the pressed // state now (before scheduling the click) to ensure // the user sees it. setPressed(true); } if (!mHasPerformedLongPress) { // This is a tap, so remove the longpress check removeLongPressCallback(); // Only perform take click actions if we were in the pressed state if (!focusTaken) { // Use a Runnable and post this rather than calling // performClick directly. This lets other visual state // of the view update before click actions start. if (mPerformClick == null) { mPerformClick = new PerformClick(); } if (!post(mPerformClick)) { performClick(); } } } if (mUnsetPressedState == null) { mUnsetPressedState = new UnsetPressedState(); } if (prepressed) { postDelayed(mUnsetPressedState, ViewConfiguration.getPressedStateDuration()); } else if (!post(mUnsetPressedState)) { // If the post failed, unpress right now mUnsetPressedState.run(); } removeTapCallback(); } break;
在ACTION_UP分支上执行了click操作,具体由performClick方法执行:
public boolean performClick() { sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_CLICKED); ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo; if (li != null && li.mOnClickListener != null) { playSoundEffect(SoundEffectConstants.CLICK); li.mOnClickListener.onClick(this); return true; } return false; }
情形9:
package com.example.toucheventdemo; import android.content.Context; import android.util.AttributeSet; import android.util.Log; import android.view.MotionEvent; import android.widget.LinearLayout; public class MyLinearLayout extends LinearLayout { private static final String TAG = "MyLinearLayout"; public MyLinearLayout(Context context) { super(context); } public MyLinearLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); } @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { switch (event.getAction()) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_UP"); } return super.onTouchEvent(event); } @Override public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { switch (ev.getAction()) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_UP"); } return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev); } @Override public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { switch (ev.getAction()) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: Log.i(TAG,"onInterceptTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: Log.i(TAG,"onInterceptTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: Log.i(TAG,"onInterceptTouchEvent--ACTION_UP"); } return super.onInterceptTouchEvent(ev); } }
此时再点击按钮,查看日志:

可以看到,由于加了一层容器控件,所以activity执行完dispatchTouchEvent之后将touch事件分发给容器控件MyLinearLayout,紧接着并不是直接将touch事件传递给button,而是先执行了onInterceptTouchEvent,这个方法返回false,并没有拦截touch事件,所以接下来会将touch事件传递给button。


- 隧道方式:从根元素依次往下传递直到最内层子元素或在中间某一元素中由于某一条件停止传递。
- 冒泡方式:从最内层子元素依次往外传递直到根元素或在中间某一元素中由于某一条件停止传递。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号