Redis数据结构源码阅读学习
redis部分数据结构源码学习
如何查看redis源码
reids源码下载,通过该地址下载redis源码在使用编译器打开,本人使用的为VSCode
本文下载的版本为6.2.14,查看SRC目录
dict.h(key和value的映射关系)
redis是key-value的数据库,通过Dict来实现key和value的映射
typedef struct dictType {
uint64_t (*hashFunction)(const void *key);
void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key);
void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj);
int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2);
void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key);
void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);
int (*expandAllowed)(size_t moreMem, double usedRatio);
} dictType;
/* This is our hash table structure. Every dictionary has two of this as we
* implement incremental rehashing, for the old to the new table. */
/* 翻译:这是我们的哈希表结构。每个字典都有两个这样的哈希表,因为我们实现了增量重新散列,从旧表到新表。 */
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table; // 指向哈希表数组的指针,每个元素是一个 dictEntry 结构体指针
unsigned long size; // 大小
unsigned long sizemask;
unsigned long used;
} dictht;
// 字典
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type;
void *privdata;
dictht ht[2]; // 理解为哈希表头节点 ?
long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */
int16_t pauserehash; /* If >0 rehashing is paused (<0 indicates coding error) */
} dict;
// key-value
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key; // 键
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v; // 值
struct dictEntry *next; // 下一个Entry
} dictEntry;
可以理解为一个dict有两个Entry数组及其头节点
sds.h(动态字符串)
/* Note: sdshdr5 is never used, we just access the flags byte directly.
* However is here to document the layout of type 5 SDS strings. */
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr5 {
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, and 5 msb of string length */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 {
uint8_t len; /* used */ // 已经保存的字节数
uint8_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */ // 总字节数
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits 低3位表示类型,高5位未使用。 */ // SDS头类型
char buf[]; // 实际存储的字符串数据
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 {
uint16_t len; /* used */
uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr32 {
uint32_t len; /* used */
uint32_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr64 {
uint64_t len; /* used */
uint64_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
因为c语言的字符串本质是字符数组,并存在一些缺点;
- 获取字符串长度的需要通过运算O(你)
- 非二进制安全
- 缓冲区溢出
因此reids构造一种SDS(Simple Dynamic String),简单动态字符串,具有以下优点:
- 获取字符串长度为O(1)
- 支持动态扩容
- 减少内存分配次数
- 节省内存空间
- 二进制安全
二进制安全
定义: 二进制安全(Binary Safety)是指在计算机系统中处理、存储和传输二进制数据时,确保这些数据不会受到破坏、篡改或损坏的一系列措施和技术
在c语言中,字符数组以“\0” 字符作为结尾标记,会以“\0”符号作为字符串结尾,最先被程序读入的 “\0” 字符将被误认为是字符串结尾,因此,无法存储一些如图像的二进制数据,而SDS使用len变量来纪录长度
缓冲区溢出
它发生在程序试图向一个固定大小的内存区域(即缓冲区)写入超过其容量的数据时,导致额外的数据溢出到相邻的内存空间,从而覆盖了其他重要的数据或控制信息。
在C语言中使用如strcpy()、strcat()、sprintf()等函数处理字符串可能会发生缓冲区溢出
在SDS中通添加alloc可以记录分配的总字节数(不包括头部和终止符),在通过与len进行运算即可获取剩余的可用空间,判断是否需要扩容
节省内存空间
flags成员变量表示 SDS 类型,一共有5中,分别是 sdshdr5、sdshdr8、sdshdr16、sdshdr32 和 sdshdr64
其区别在于不同的数据类型uint8_t 、uint16_t······
uint8_t表示无符号8位整数类型,其他数据类型也是如此,通过设计不同类型的结构体,可以灵活保存不同大小的字符串,从而节省内存空间
同时__attribute__ ((packed))也起到节省内存空间的作用,__attribute__ ((packed))告诉编译器取消结构体在编译过程中的优化对齐,按照实际占用字节数进行对齐
字节对齐
字节对齐(Byte Alignment)是计算机系统中为了提高数据访问效率而采用的一种内存布局策略。它指的是在将数据存储到内存时,按照一定的规则调整数据起始地址,使得数据的起始地址能够被某个特定数值整除
举例
int a;
char c;
在字节对齐方式下会占用a(4字节) + c(4字节) = 8字节,即char为了和int对齐会占用4字节
取消后则占用5字节(4+1)
zskiplist (跳表)
基本结构 : server.h的1008行 - 1027
以命令 zadd name 10 tom为例
/* ZSETs use a specialized version of Skiplists */
typedef struct zskiplistNode {
sds ele; // name + tom
double score; // 分数
struct zskiplistNode *backward; // 后向指针,使得跳表第一层组织为双向链表
struct zskiplistLevel { // 结点的层级
struct zskiplistNode *forward; // 前向结点
unsigned long span; // 跨度 某一层距离下一个结点的跨度
} level[]; // level本身是一个柔性数组,最大值为32,由 ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL 定义
} zskiplistNode;
typedef struct zskiplist {
struct zskiplistNode *header, *tail; // 跳跃表的表头节点和表尾节点
unsigned long length; //长度,即一共有多少个元素
int level; //最大层级,即跳表目前的最大层级
} zskiplist;
typedef struct zset {
dict *dict;
zskiplist *zsl;
} zset;
通过level数组和span变量实现了跳表的层级关系
span记录当前节点和下一个节点的距离 , 如对节点3 来说:
level[0]: 1level[1]:2level[2]:null
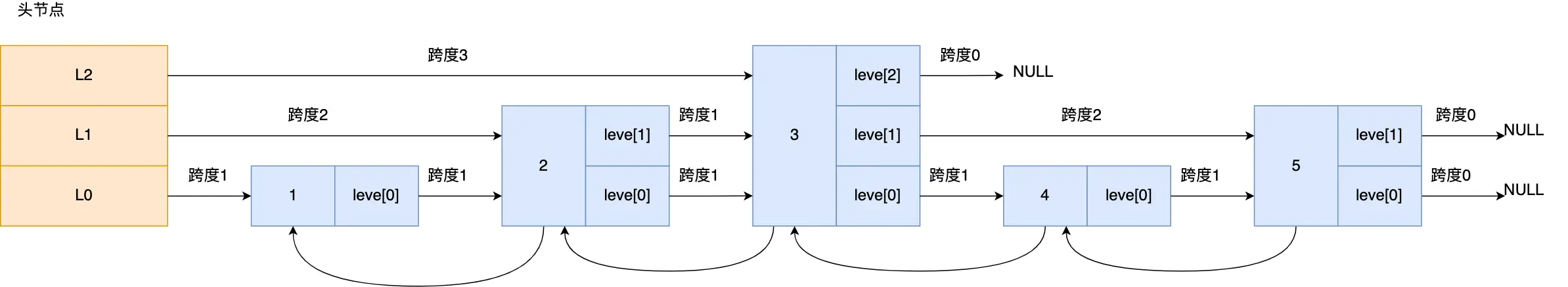
图片来自 小林coding
zset创建和dict
// object.c
robj *createZsetObject(void) {
zset *zs = zmalloc(sizeof(*zs));
robj *o;
zs->dict = dictCreate(&zsetDictType,NULL);
zs->zsl = zslCreate();
o = createObject(OBJ_ZSET,zs);
o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST;
return o;
}
// dict.c
/* Create a new hash table */
dict *dictCreate(dictType *type,
void *privDataPtr)
{
dict *d = zmalloc(sizeof(*d));
_dictInit(d,type,privDataPtr);
return d;
}
/* Initialize the hash table */
int _dictInit(dict *d, dictType *type,
void *privDataPtr)
{
_dictReset(&d->ht[0]);
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
d->type = type;
d->privdata = privDataPtr;
d->rehashidx = -1;
d->pauserehash = 0;
return DICT_OK;
}
为什么还要加dict?
zskiplist跳表的初始化
// server.h
#define ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL 32 /* Should be enough for 2^64 elements (应该足以支持 2 的 64 次方个元素) */
/* Create a skiplist node with the specified number of levels.
* The SDS string 'ele' is referenced by the node after the call. */
zskiplistNode *zslCreateNode(int level, double score, sds ele) {
zskiplistNode *zn =
zmalloc(sizeof(*zn)+level*sizeof(struct zskiplistLevel));
zn->score = score;
zn->ele = ele;
return zn;
}
/* Create a new skiplist. */
zskiplist *zslCreate(void) {
int j;
zskiplist *zsl;
zsl = zmalloc(sizeof(*zsl));
zsl->level = 1;
zsl->length = 0;
zsl->header = zslCreateNode(ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL,0,NULL); // 头节点
for (j = 0; j < ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL; j++) {
zsl->header->level[j].forward = NULL;
zsl->header->level[j].span = 0;
}
zsl->header->backward = NULL;
zsl->tail = NULL;
return zsl;
}
插入
/* Insert a new node in the skiplist. Assumes the element does not already
* exist (up to the caller to enforce that). The skiplist takes ownership
* of the passed SDS string 'ele'. */
/* 翻译: 在跳跃表中插入一个新节点。假设该元素尚不存在(调用者需要确保这一点)。
* 跳跃表将获取传递的 SDS 字符串 'ele' 的所有权。 */
zskiplistNode *zslInsert(zskiplist *zsl, double score, sds ele) {
zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL], *x;
unsigned int rank[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL]; //
int i, level;
// 第一步: 根据目前传入的score找到插入位置x,并且将各层的前置节点保存至update[]中
serverAssert(!isnan(score));
x = zsl->header; //跳表头结点
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {// 从最上层开始遍历每一层 ,i 表示层数
/* store rank that is crossed to reach the insert position */
/* “存储到达插入位置时经过的排名”
* 这句话的意思是在插入新节点时,记录下在跳跃表中到达插入位置时经过的所有节点的排名。
*/
rank[i] = i == (zsl->level-1) ? 0 : rank[i+1];
// 前置节点存在 且 前置节点的score<当前的score 或 前置节点的score==当前的score 且 前置节点的ele<当前的ele
while (x->level[i].forward &&
(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||
(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&
sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) < 0))) //sdscmp()方法注释: Compare two sds strings s1 and s2 with memcmp(). positive if s1 > s2.
{
rank[i] += x->level[i].span;
x = x->level[i].forward; // 跳到下一个节点
}
// 当前层插入节点的节点, 插入在 x 和 x->level[i].forward 之间
update[i] = x;
}
/* we assume the element is not already inside, since we allow duplicated
* scores, reinserting the same element should never happen since the
* caller of zslInsert() should test in the hash table if the element is
* already inside or not. */
/* 我们假设该元素不在跳跃表中,因为我们允许重复的分数。
* 重新插入相同的元素不应该发生,因为 zslInsert() 的调用者应该在哈希表中测试该元素是否已经存在。 */
level = zslRandomLevel(); // 获取一个level, 为什么随机获取/返回值可能大于最大level
/*zslRandomLevel()方法: Returns a random level for the new skiplist node we are going to create.
* The return value of this function is between 1 and ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL
* (both inclusive), with a powerlaw-alike distribution where higher
* levels are less likely to be returned. */
// 大于最大level就更新最大leve值
if (level > zsl->level) {
for (i = zsl->level; i < level; i++) {
rank[i] = 0;
update[i] = zsl->header;
update[i]->level[i].span = zsl->length;
}
zsl->level = level;
}
x = zslCreateNode(level,score,ele); // 插入的节点
// 遍历每一层, 配置x, 给x的每一层赋值
for (i = 0; i < level; i++) {
// x 的level数组forward节点
x->level[i].forward = update[i]->level[i].forward;
update[i]->level[i].forward = x;
/* update span covered by update[i] as x is inserted here */
/* 更新 update[i] 所覆盖的节点的soan值,因为 x 在这里插入 */
// 更新span
x->level[i].span = update[i]->level[i].span - (rank[0] - rank[i]);
update[i]->level[i].span = (rank[0] - rank[i]) + 1;
}
/* increment span for untouched levels */
/* 为未受影响的层增加跨度 */
for (i = level; i < zsl->level; i++) {
update[i]->level[i].span++;
}
// x 的后向指针
x->backward = (update[0] == zsl->header) ? NULL : update[0];
// 最底层x的后向指针
if (x->level[0].forward)
x->level[0].forward->backward = x;
else
zsl->tail = x;
// 长度+1
zsl->length++;
return x;
}
查询
/* Find the rank for an element by both score and key.
* Returns 0 when the element cannot be found, rank otherwise.
* Note that the rank is 1-based due to the span of zsl->header to the
* first element. */
/* 通过分数和键查找元素的排名。
* 如果找不到该元素,返回 0;否则返回排名。
* 注意,排名是从 1 开始的,因为 zsl->header 到第一个元素之间有一个span。 */
unsigned long zslGetRank(zskiplist *zsl, double score, sds ele) {
zskiplistNode *x;
unsigned long rank = 0;
int i;
// 头节点
x = zsl->header;
// 从最高层往下遍历 从小到大
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->level[i].forward &&
(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||
(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&
sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) <= 0))) {
rank += x->level[i].span;
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
/* x might be equal to zsl->header, so test if obj is non-NULL */
/* x 可能等于 zsl->header,因此需要检查 obj 是否非空 */
if (x->ele && sdscmp(x->ele,ele) == 0) {
return rank;
}
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号