【SpringMVC】映射请求参数 & 请求头
映射请求参数 & 请求参数
请求处理方法签名
- Spring MVC 通过分析处理方法的签名,将 HTTP 请求信息绑定到处理方法的相应人参中。
- Spring MVC 对控制器处理方法签名的限制是很宽松的,几乎可以按喜欢的任何方式对方法进行签名。
- 必要时可以对方法及方法入参标注相应的注解( @PathVariable、@RequestParam、@RequestHeader 等)、Spring MVC 框架会将 HTTP 请求的信息绑定到相应的方法入参中,并根据方法的返回值类型做出相应的后续处理。
1. Optional包装参数
请求参数通过java.util.Optional包装
@GetMapping("/optional")
public Object optional(Optional<String> name) {
return String.format("请求参数: %s", name.orElse("")) ;
}
通过Optional接受参数,效果等同于
public Object optional(@RequestParam(required=false) String name){}
与将required设置为false效果一样(@RequestHeader同样)
使用 @RequestParam 绑定请求参数值
注意:这个注解即可以接收url中的
query string,又可以接收请求头为Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded请求体中的参数
在处理方法入参处使用 @RequestParam 可以把请求参数传递给请求方法
- value:参数名
- required:是否必须。默认为 true,表示请求参数中必须包含对应的参数,若不存在,将抛出异常
@RequestMapping("/hanlde5")
public String handle5(@RequestParam(value="userName",required=false) String userName,@RequestParam("age") int age) {
return "success";
}
这个可以看下源码中的注释说明,按照说明中的方式传参(queryParam, formData)都可以获取到In Spring MVC, "request parameters" map to query parameters, form data, and parts in multipart requests.
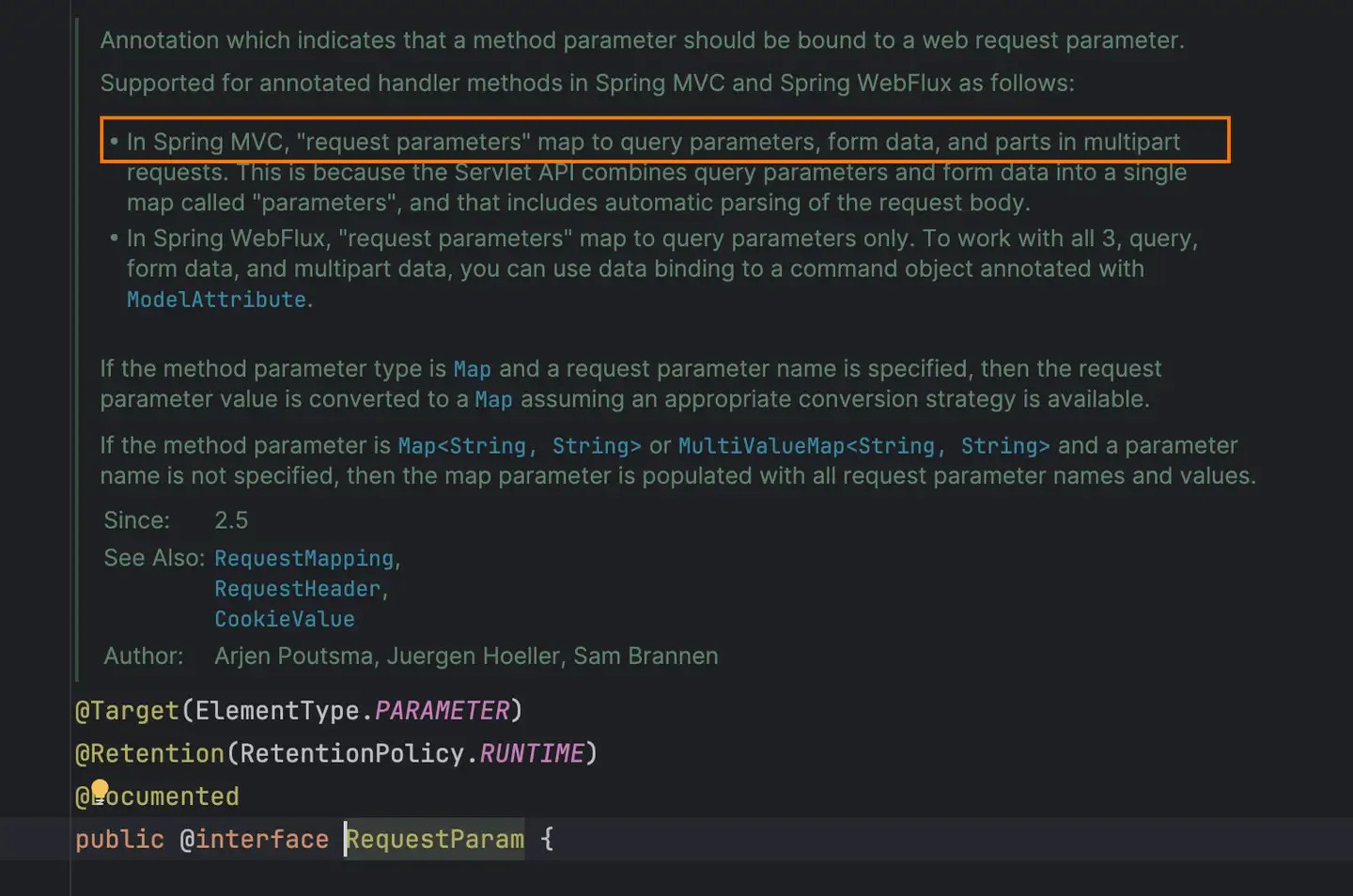
这说明在spring mvc中,请求参数queryParam和form-data中的数据都可以获取到,只要注意传参方式即可
请求参数queryParam在GET和POST方法中都可以使用,form-data需要在POST下使用
@RequestPart获取请求的部分
如果你的请求是multipart/form-data,那么你可以通过如下方式获取部分请求信息
@PostMapping("/requestpart")
public Object requestpart(@RequestPart("user") String user) {
return user ;
}
请求结果
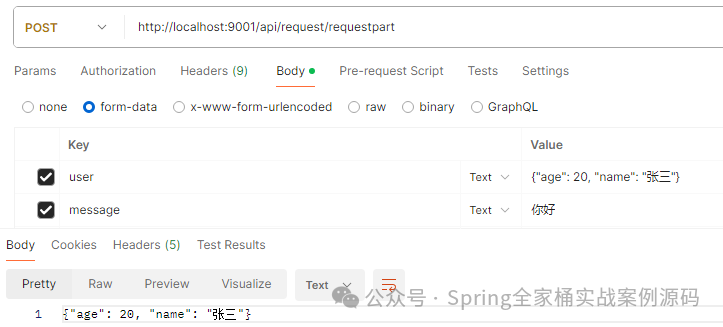
你还可以以JSON对象读取,如下:
public Object requestpart(@RequestPart("user") User user)
注意,对象接受时,你需要设置每part的Content-Type
Content-Type: multipart/mixed
--edt7Tfrdusa7r3lNQc79vXuhIIMlatb7PQg7Vp
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="user"
Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8
Content-Transfer-Encoding: 8bit
{
"age": 20,
"name": "张三"
}
没有设置Content-Type将会抛出415错误。
使用 @RequestHeader 绑定请求报头的属性值
请求头包含了若干个属性,服务器可据此获知客户端的信息,通过 @RequestHeader 即可将请求头中的属性值绑定到处理方法的入参中
@RequestMapping("/handle6")
public String handle6(@RequestHeader("Accept-Encoding") String encoding,@RequestHeader("Keep-Alive") long keepAlive) {
return "success";
}
使用 @CookieValue 绑定请求中的 Cookie 值
@CookieValue 可让处理方法入参绑定某个 Cookie 值
@RequestMapping("/handle7")
public String handle7(@CookieValue(value="sessionId") String sessionId,@RequestParam("age") long age) {
return "success";
}
使用 POJO 对象绑定请求参数值
Spring MVC 会按请求参数名和 POJO 属性名进行自动匹配,自动为该对象填充属性值。支持级联属性。
如:dept.deptId、dept.address.tel 等
@RequestMapping("/handle8")
public String handle8(User user) {
return "success";
}
//handle8.action?userName=nemo&dept.deptId=1&dept.address.tel=12345678
使用 Servlet API 作为入参
@RequestMapping("/handle9")
public String handle9(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
//.....
}
@RequestMapping("/handle10")
public String handle10(HttpServletRequest request) {
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView("success");
//.....
}
@RequestMapping("/handle11")
public String handle11(HttpSession session) {
//.....
return "success";
}
@RequestMapping("/handle12")
public String handle12(HttpServletRequest request,@RequestParam("userName") String userName) {
//.....
return "success";
}
MVC 的 Handler 方法可以接受哪些 ServletAPI 类型的参数
- HttpServletRequest
- HttpServletResponse
- HttpSession
- java.security.Principal
- Locale
- InputStream
- OutputStream
- Reader
- Writer
get和post传参实例
(1)@GetMapping只能通过url传参数。所对应的接口参数只能是用@RequestParam注解或者不注解
(2)@PostMapping既可以通过url传参数,也可以通过body传json参数。所对应的接口参数可以有@RequestParam注解,也可以有@RequestBody注解,也可以没有注解。
(3)不管是@GetMapping还是@PostMapping,除了@RequestBody注解对应的参数是通过json在body里面传参数外,@RequestParam注解和没有注解都是在url中传参数.
(4)用@RequestParam注解修饰的字段前端必须有对应的参数传过来,用@RequestBody修饰的类,前端至少要传一个空的json串,json串内容不一定需要和类对应,json串中只要有类的字段,后端的类就会从中取出对应的字段并赋值。
(5)对于类对象的参数,不管对于@RequestBody还是@RequestParam还是没有注解,前端不管传来多少个字段,后端的类对象只取类中包含的对象。
举个例子,比如后端有一个类User的对象:
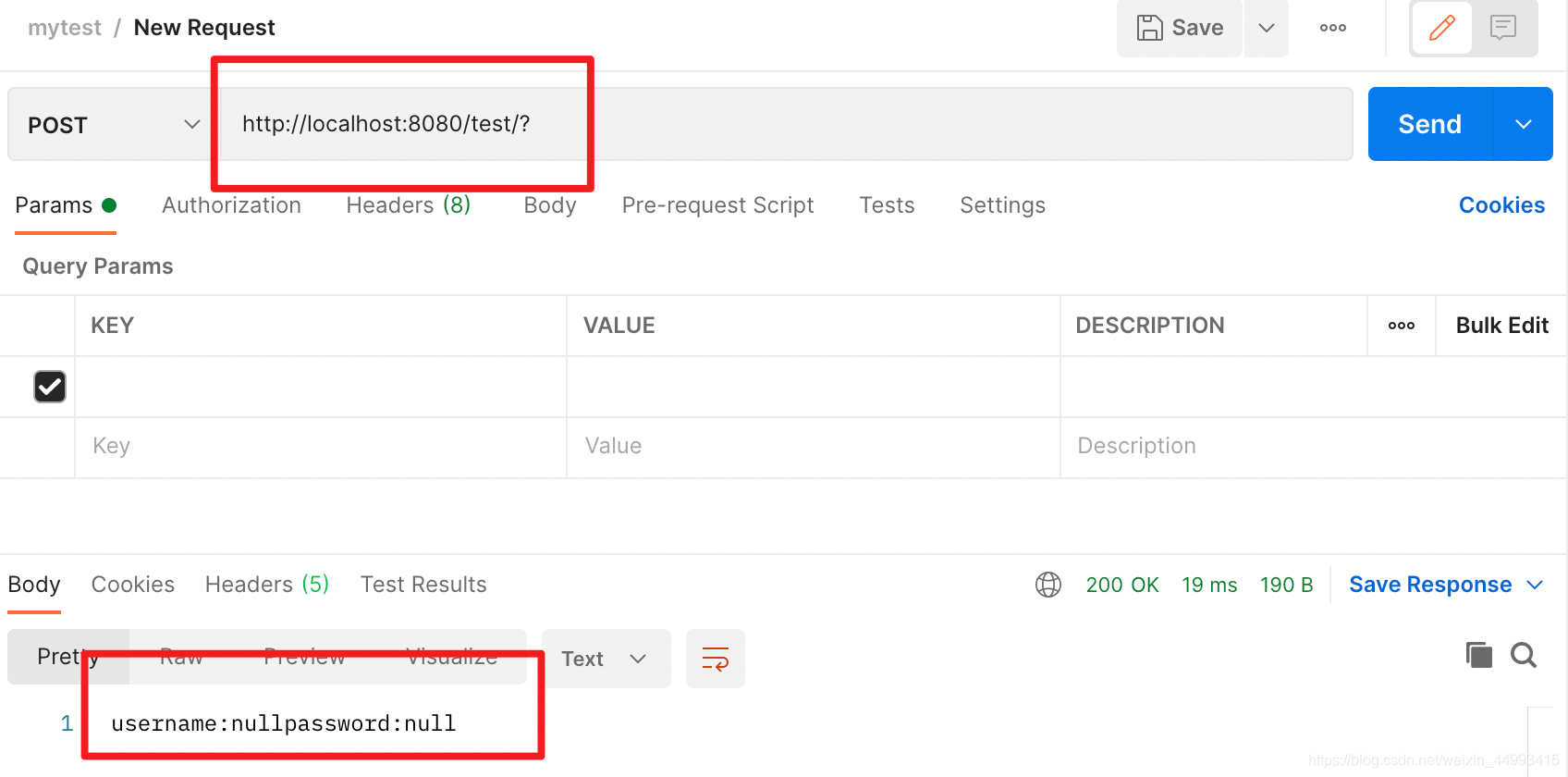
假设未用@RequestBody修饰,只能通过url传参:

@PostMapping("/test")
public String test(User user) {
StringBuilder t = new StringBuilder();
t.append("username:" + user.getUsername());
t.append("password:" + user.getPassword());
return String.valueOf(t);
}
情况一:传的参数与类对应:

情况二:传的参数与类不对应:


假设使用@RequestBody修饰,只能通过body的json字符串传参(当然url里面也可以传值,只是不会被@RequestBody接收,只能被@RequestParam和无注解的接收):

@PostMapping("/test")
public String test(@RequestBody User user) {
StringBuilder t = new StringBuilder();
t.append("username:" + user.getUsername());
t.append("password:" + user.getPassword());
return String.valueOf(t);
}
情况一:传的参数与类对应:
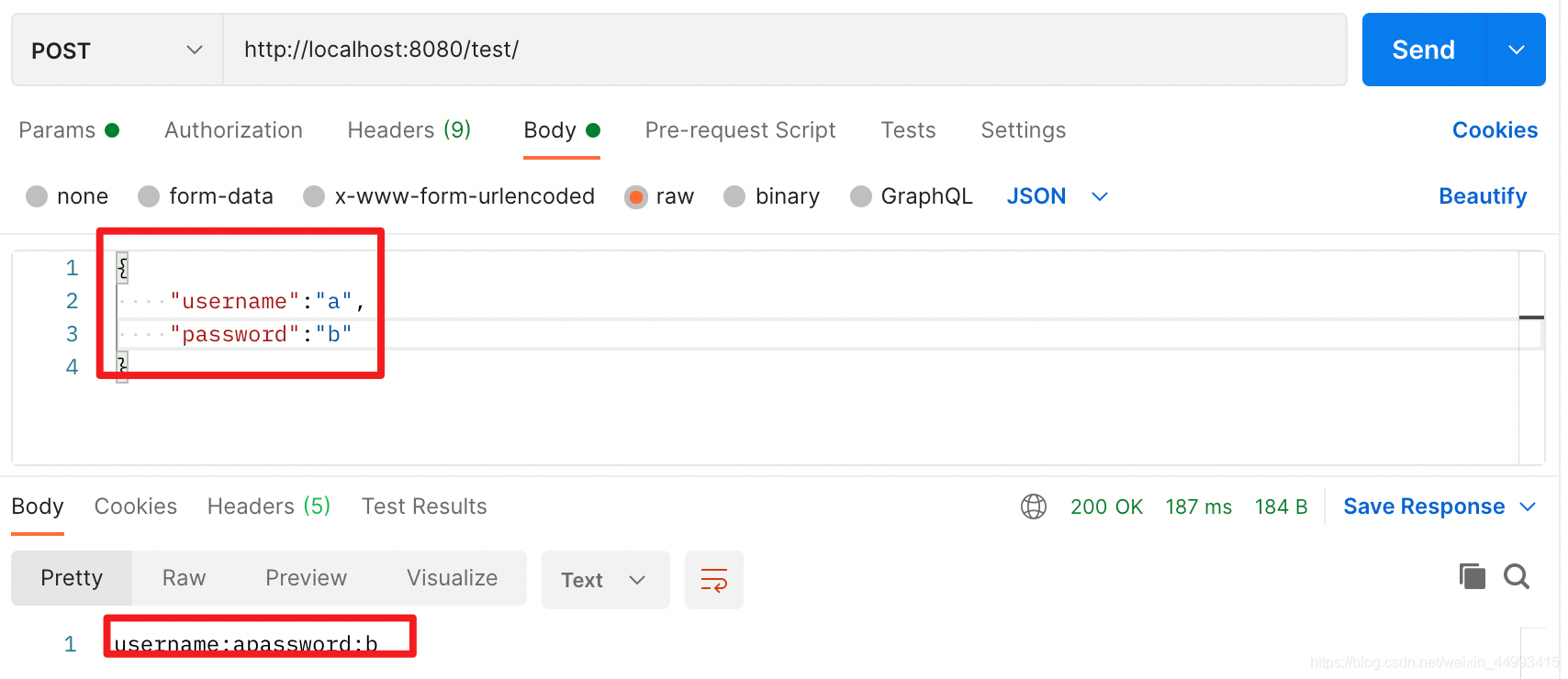
情况二:传的参数与类不对应:
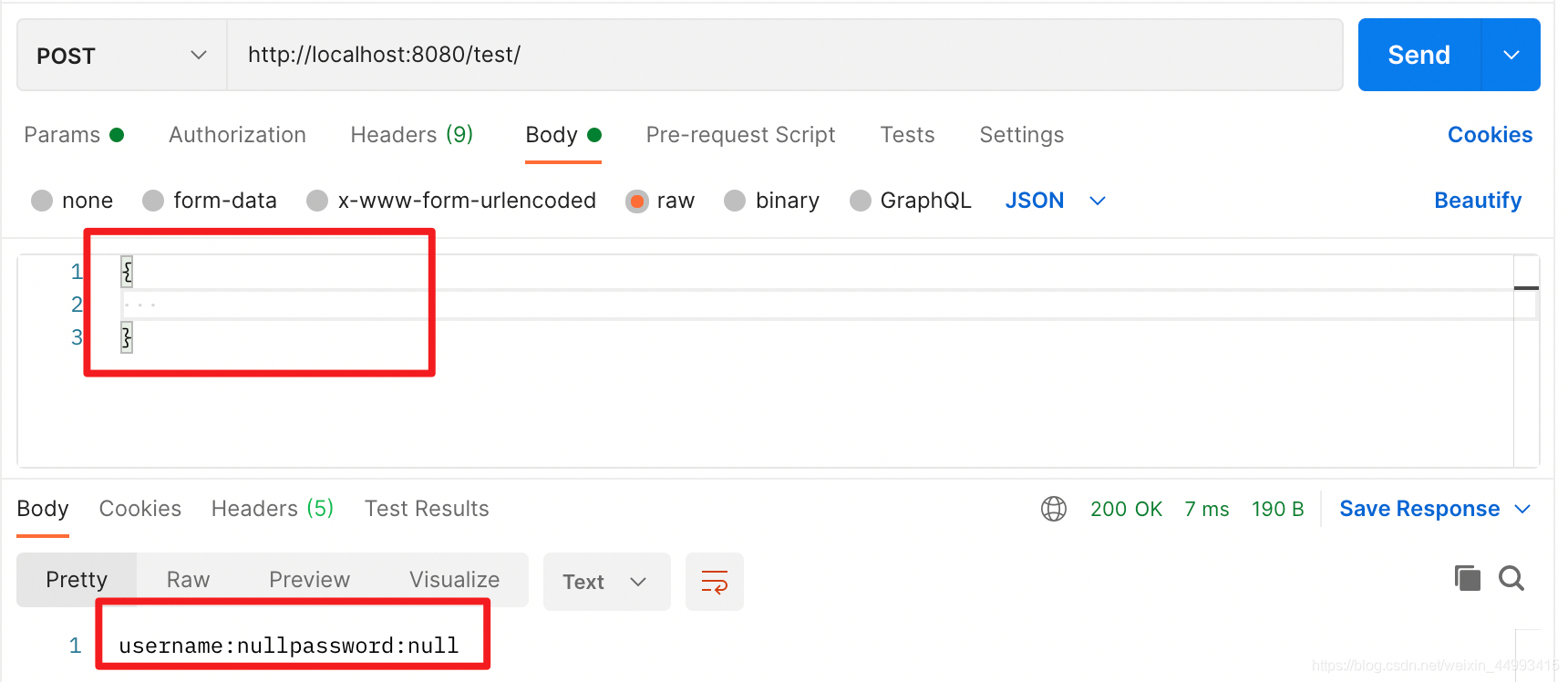
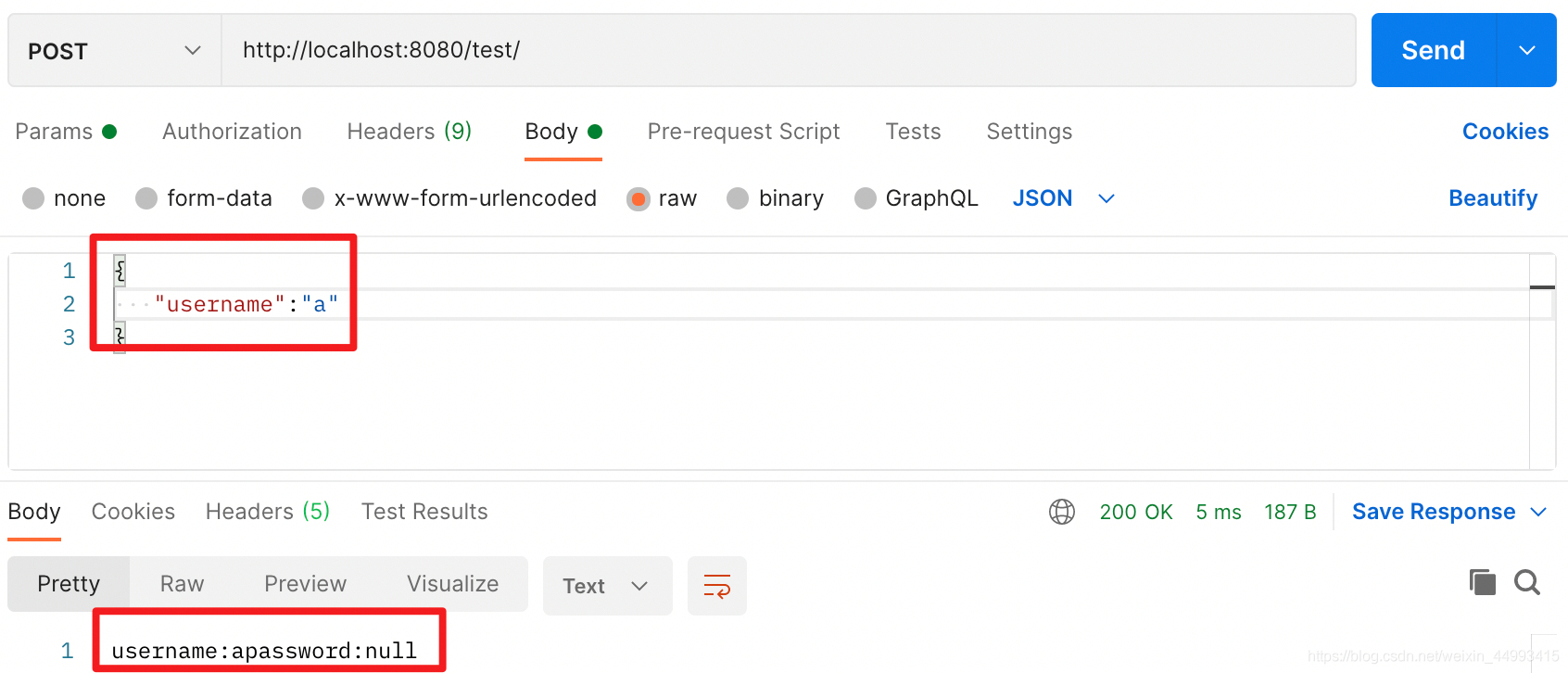
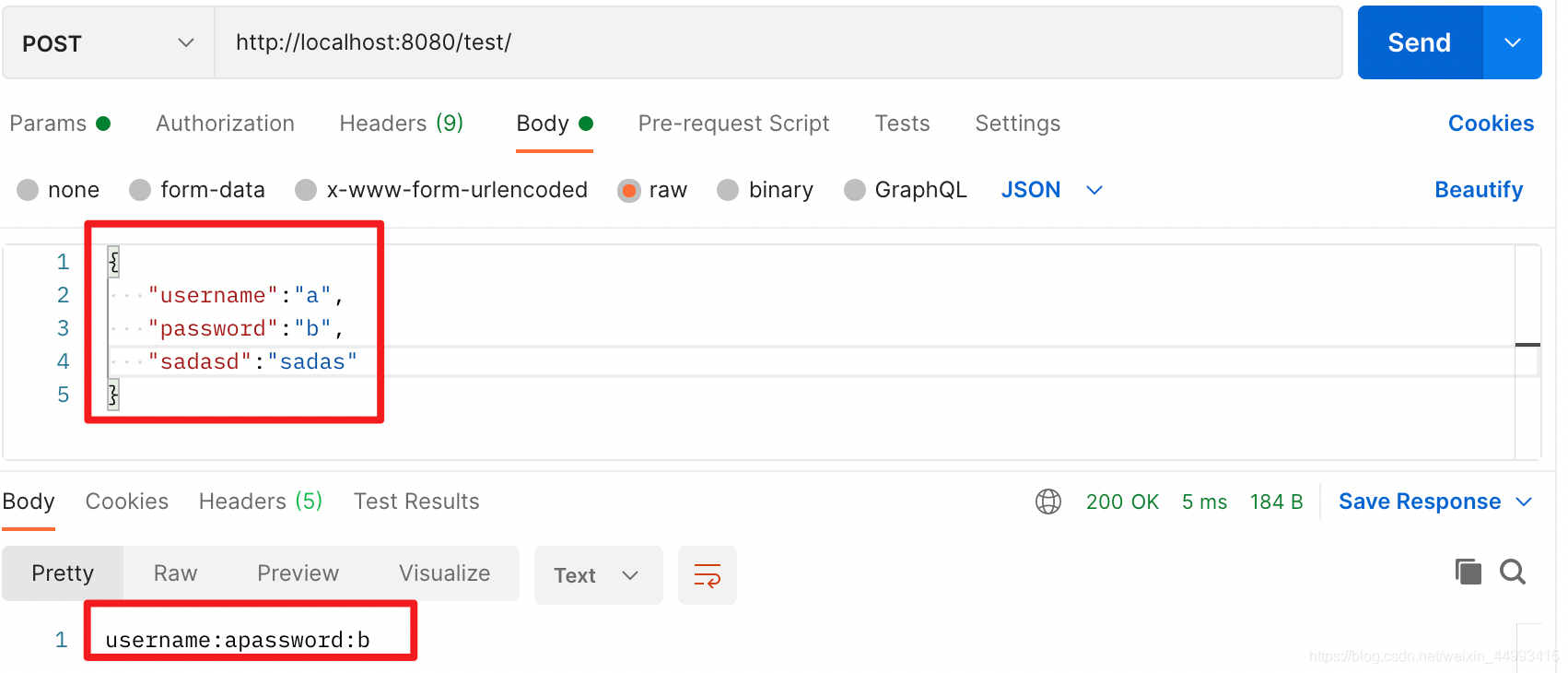
总结:不管是url传参,还是body传参,对于后端的参数来说(包括普通变量和类变量),我们可以把类变量看成是很多普通变量的集合,后端只要求前端必须传被注解的变量,未被注解的变量前端可传可不传,前端传了后端就会取,不传后端默认该变量为null。也就是说,前端传的参数不一定与类变量一一对应也是不会报错的,但最好还是一一对应。@RequestParam("easd")指定了前端必须传的参数名,而@RequestBody只指定前端必须传一个json在body里面,至于json字符串的内容,不一定与类变量一一对应,这点与get命令是相似的。
参数无注解实例
注意:无注解时,如果我们的参数类型为引用类型,那即使为空,也只是置为null,不是必须的;如果是基本数据类型,则必须包含。
当参数为基本类型时
@GetMapping("/example1")
public void example1(Float money, String product){
System.out.println("product:"+ product);//product:洗洁精
System.out.println("money:"+ money);//money:123.0
}
//请求url:http://localhost:8888/example1?money=123&product=洗洁精
当参数为数组时
@GetMapping("/example2")
public void example2(String[] keywords){
if (keywords != null){
for (int i=0; i<keywords.length; i++){
System.out.println(keywords[i]);//123 456
}
}
}
//请求url:http://localhost:8888/example2?keywords=123,456
123456789
当参数为简单对象时
@GetMapping("/example3")
public void example3(SubTest1 subTest1){
System.out.println(subTest1);//SubTest1{content='测试内容'}
}
//请求url:http://localhost:8888/example3?content=测试内容
public class SubTest1 {
private String content;
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SubTest1{" +
"content='" + content + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
当参数的对象中嵌套着对象,对象中的属性为list和map时
@GetMapping("/example4")
public void example4(TestDto testDto){
System.out.println(testDto);//TestDto{title='测试标题', subTest=SubTest{ids=[123, 456], map={k=value}}, subTest1=SubTest1{content='测试内容'}}
}
//请求url:http://localhost:8888/example4?title=测试标题&subTest.ids[0]=123&subTest.ids[1]=456&subTest.map[k]=value&SubTest1.content=测试内容
public class TestDto {
private String title;
private SubTest subTest;
private SubTest1 subTest1;
public SubTest1 getSubTest1() {
return subTest1;
}
public void setSubTest1(SubTest1 subTest1) {
this.subTest1 = subTest1;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "TestDto{" +
"title='" + title + '\'' +
", subTest=" + subTest +
", subTest1=" + subTest1 +
'}';
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public SubTest getSubTest() {
return subTest;
}
public void setSubTest(SubTest subTest) {
this.subTest = subTest;
}
}
public class SubTest {
private List<Long> ids;
private Map map;
public Map getMap() {
return map;
}
public void setMap(Map map) {
this.map = map;
}
public List<Long> getIds() {
return ids;
}
public void setIds(List<Long> ids) {
this.ids = ids;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SubTest{" +
"ids=" + ids +
", map=" + map +
'}';
}
}
//TODO:在直接用list作为参数的时候,程序会报错的;直接用map作为参数的时候,没办法获取到值,都是null,但是不会报错;不知道是姿势错误,还是本身不支持;
实例
在API开发中,请求参数的读取和处理是核心内容之一。SpringBoot通过注解提供了多种灵活的方式来读取这些参数。这些方式包括路径参数、查询参数、表单参数和请求体参数,每一种都有其特定的使用场景和优点。
路径参数
技巧:这个参数可以将多个接口混合为一个接口来使用,也可以将一个接口拆分为多个接口来使用。
如果预计这个接口将来有可能会被拆分的话,可以采用这个注解来增加扩展性
路径参数是URL路径中的一部分,可以使用@PathVariable注解来获取。例如:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class ProductController {
@GetMapping("/products/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Product> getProductById(@PathVariable Long id) {
// 业务逻辑
Product product = productService.findById(id);
return ResponseEntity.ok(product);
}
}
在上述代码中,{id}就是路径参数,通过@PathVariable注解将其绑定到方法参数id上。
查询参数
查询参数是URL中?后面的参数,可以使用@RequestParam注解来获取。例如:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class ProductController {
@GetMapping("/products")
public ResponseEntity<List<Product>> getProductsByCategory(@RequestParam String category) {
// 业务逻辑
List<Product> products = productService.findByCategory(category);
return ResponseEntity.ok(products);
}
}
在上述代码中,URL可能是/api/products?category=electronics,通过@RequestParam注解将查询参数category绑定到方法参数category上。
定义如下Controller
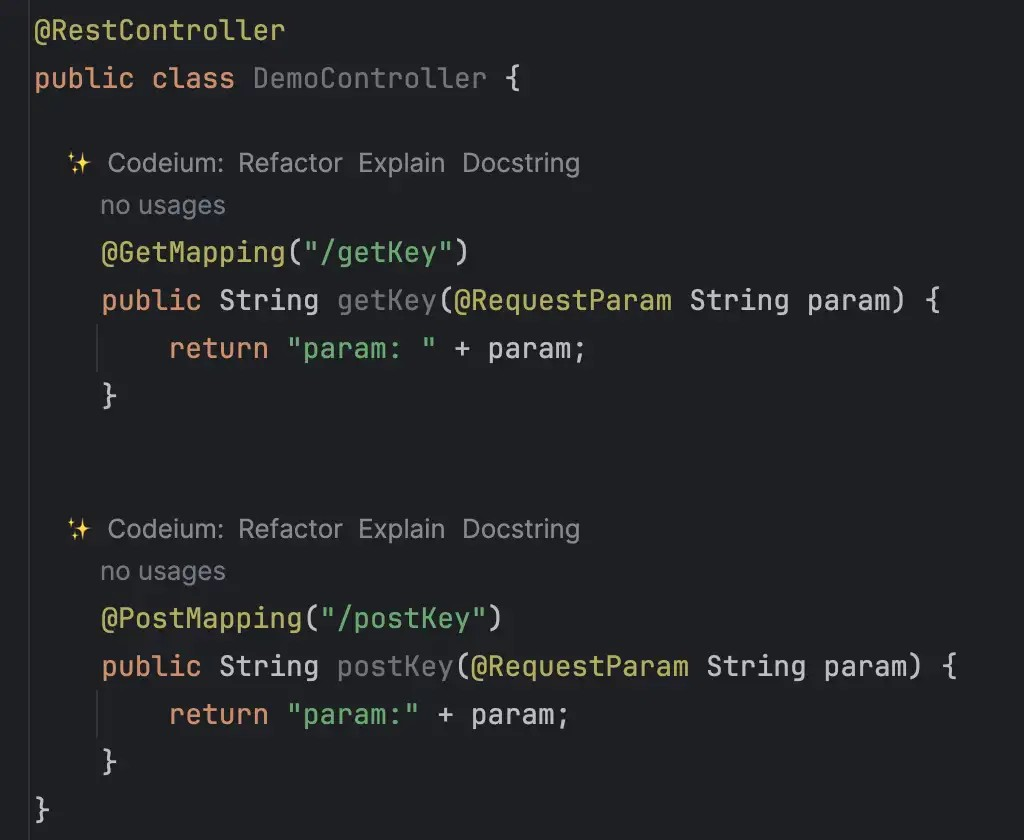
首先GET方法是没有问题的
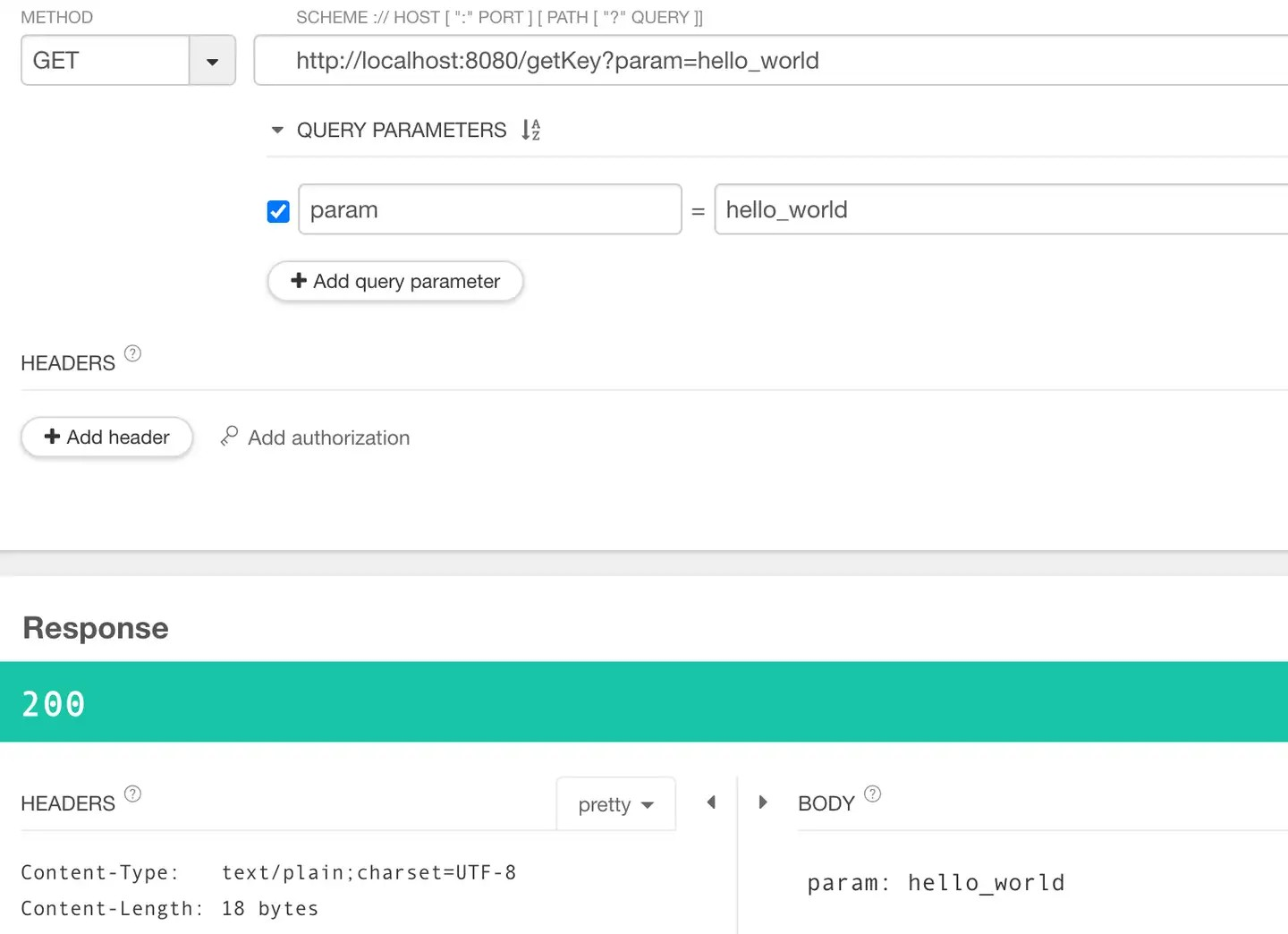
curl -X GET 'http://localhost:8080/getKey?param=hello_world'
接着再来试一下 POST 方法(queryParam)
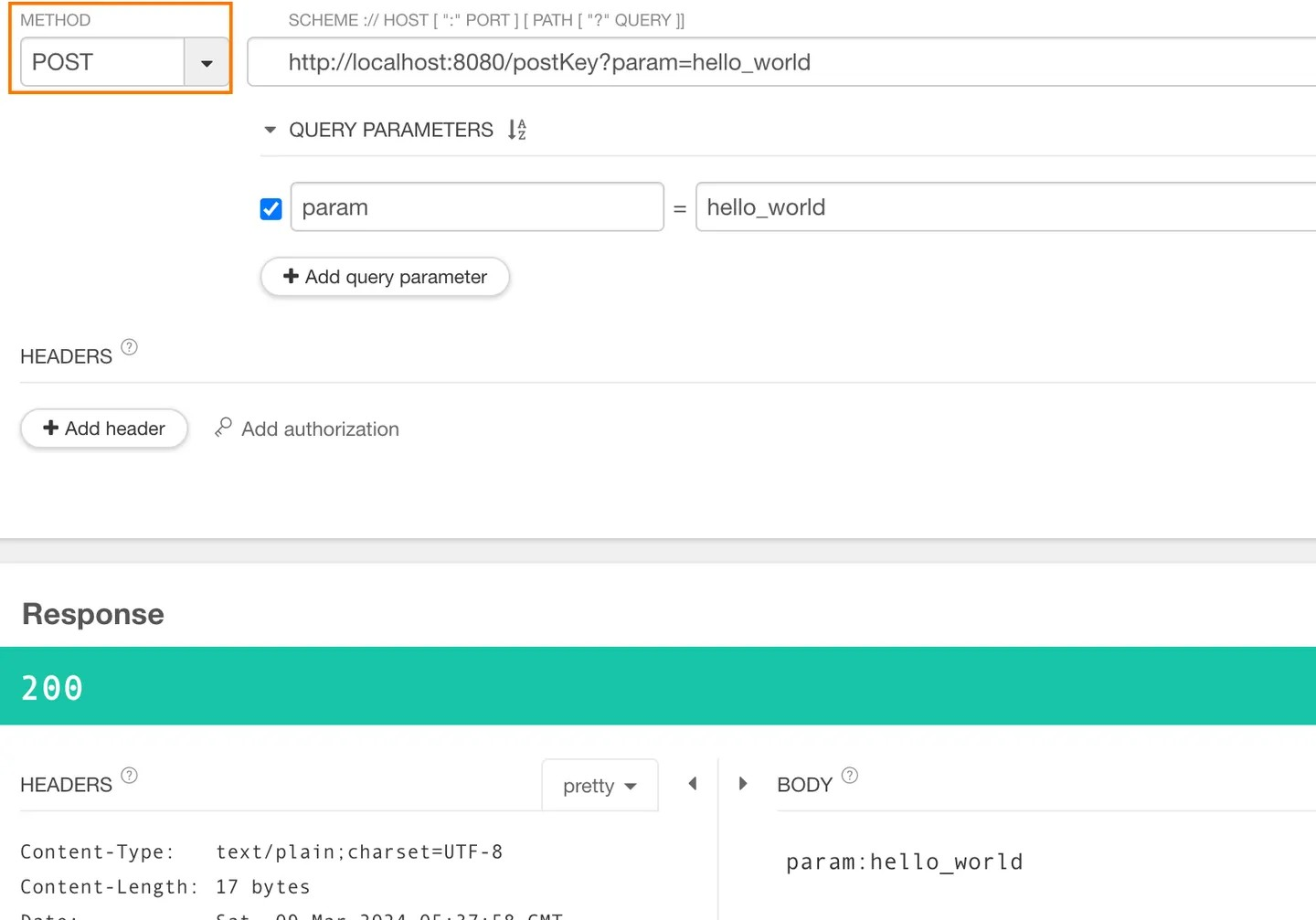
curl -X POST 'http://localhost:8080/postKey?param=hello_world'
表单参数
表单参数通常用于POST请求,可以使用@RequestParam注解获取。
请求头设置,内容类型为x-www-form-urlencoded格式,请求体为url编码的数据,如name=Nemo&price=666
例如:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class ProductController {
@PostMapping("/products")
public ResponseEntity<Product> createProduct(@RequestParam String name, @RequestParam double price) {
// 业务逻辑
Product product = new Product(name, price);
productService.save(product);
return ResponseEntity.ok(product);
}
}
在上述代码中,通过@RequestParam注解获取表单参数name和price。
下面再来试试POST的 form-data方式传参
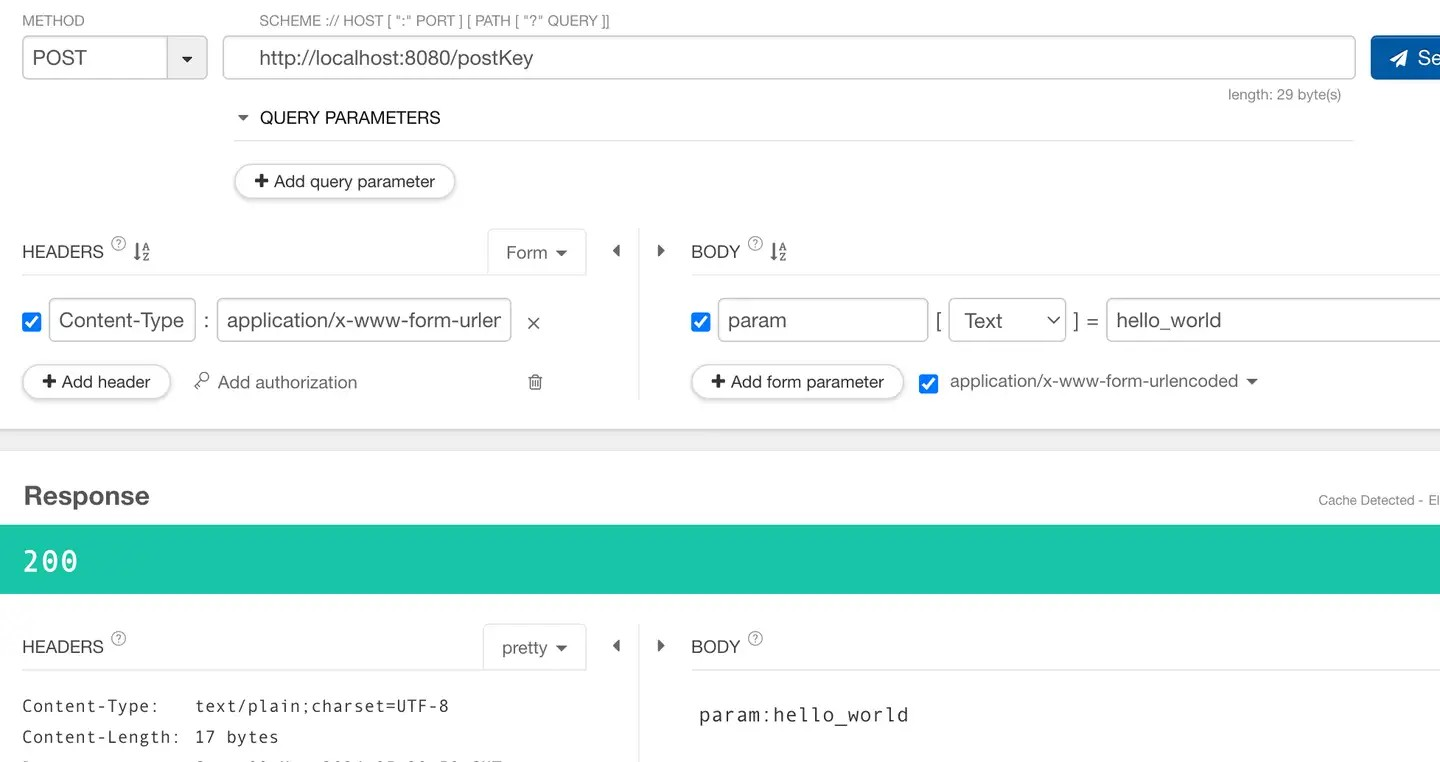
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
-d "param=hello_world" \
'http://localhost:8080/postKey'
请求体参数
请求体参数用于传递复杂的对象,可以使用@RequestBody注解来获取。
请求头中的发送内容为application/json,请求体为JSON格式的数据。
例如:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class ProductController {
@PostMapping("/products/details")
public ResponseEntity<Product> createProductDetails(@RequestBody Product product) {
// 业务逻辑
productService.save(product);
return ResponseEntity.ok(product);
}
}
在上述代码中,通过@RequestBody注解将请求体中的JSON对象绑定到方法参数product上。
综合示例
下面是一个综合示例,展示了如何在一个控制器中同时使用多种请求参数读取方式:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class ProductController {
@GetMapping("/products/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Product> getProductById(@PathVariable Long id) {
Product product = productService.findById(id);
return ResponseEntity.ok(product);
}
@GetMapping("/products")
public ResponseEntity<List<Product>> getProductsByCategory(@RequestParam String category) {
List<Product> products = productService.findByCategory(category);
return ResponseEntity.ok(products);
}
@PostMapping("/products")
public ResponseEntity<Product> createProduct(@RequestParam String name, @RequestParam double price) {
Product product = new Product(name, price);
productService.save(product);
return ResponseEntity.ok(product);
}
@PostMapping("/products/details")
public ResponseEntity<Product> createProductDetails(@RequestBody Product product) {
productService.save(product);
return ResponseEntity.ok(product);
}
}
上述示例展示了如何在一个控制器中处理路径参数、查询参数、表单参数和请求体参数。
结论
SpringBoot提供了灵活且强大的请求参数读取机制,能够满足不同的API设计需求。通过熟练掌握这些技术,开发者可以更高效地开发和维护API,提升代码的可读性和可维护性。在实际项目中,根据具体需求选择合适的参数读取方式,是提升API性能和用户体验的关键。
笔者将不定期更新【考研或就业】的专业相关知识以及自身理解,希望大家能【关注】我。
如果觉得对您有用,请点击左下角的【点赞】按钮,给我一些鼓励,谢谢!
如果有更好的理解或建议,请在【评论】中写出,我会及时修改,谢谢啦!
本文来自博客园,作者:Nemo&
转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/blknemo/p/13496820.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号