《超越单链表的局限:双链表“哨兵位”设计模式,如何让边界处理代码既优雅又健壮?》 - 教程


@晨非辰Tong:个人主页
专栏:《C语言》、《数据结构与算法》、《数据结构与算法刷题集》
学习阶段:C语言、数据结构与算法初学者
⏳“人理解迭代,神理解递归。”
引言:从基础实现到完美收官,如何让双链表的代码既优雅又可靠?答案便是 “哨兵位” 设计。本篇作为终章,将彻底解决边界与销毁问题,助你写出工业级强度的数据结构。
目录
三、双链表其他功能实现
3.1 双链表查找节点
--先将查找函数实现,为后续的插入做准备。
//定义_查找
DLTNode* DLTFind(DLTNode* phead, DLTDataType* x)
{
//判空
assert(!DLTEmpty(phead));
DLTNode* pcur = phead->next;//临时指针接收
//循环遍历
while (pcur != phead)
{
if (pcur->data == x)
{
return pcur;//找到了,返回指针
}
pcur = pcur->next;//后移
}
//没找到,返回空
return NULL;
}查找算法很简单,首先是要进行循环遍历,条件语句找到相应的data指针,就返回节点的指针,反之返回空(未找到)。
void test01()
{
DLTNode* plist = NULL;//不是双向链表,初始化
//初始化
DLTInit(&plist);//传址
//尾插
DLTPushBack(plist, 1);
DLTPushBack(plist, 2);
DLTPushBack(plist, 3);
DLTPushBack(plist, 4);
DLTPrint(plist);
//查找
DLTNode* pos = DLTFind(plist, 4);
if (DLTFind)
{
printf("找到了!\n");
}
else
{
printf("没找到!\n");
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
3.2 在指定位置之后插入
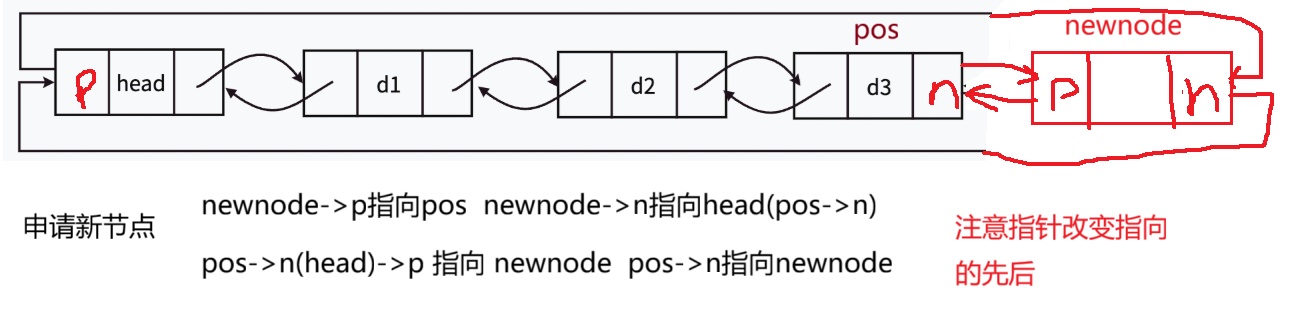
--注意,指定节点不能是头节点(“哨兵位”)。
DList.c文件
#include "DList.h"
//定义_在指定位置之后插入
void DLTInset(DLTNode* pos, DLTDataType* x)
{
assert(pos);
//申请新节点
DLTNode* newnode = DLTBuyNode(x);
newnode->prev = pos;
newnode->next = pos->next;
pos->next->prev = newnode;
pos->next = newnode;
}这个算法也是,先申请新节点空间,根据前面定义好的查找函数,找到指定节点,将节点指针用新指针pos接收后,根据图示,改变相应指针。
(注意:为实现普遍情况,其他节点的改变用pos的相关指针表示)
test.c文件
#include "DList.h"
void test01()
{
DLTNode* plist = NULL;//不是双向链表,初始化
//初始化
DLTInit(&plist);//传址
//尾插
DLTPushBack(plist, 1);
DLTPushBack(plist, 2);
DLTPushBack(plist, 3);
DLTPushBack(plist, 4);
DLTPrint(plist);
//插入
DLTNode* pos = DLTFind(plist, 4);
DLTInset(pos, 5);
DLTPrint(plist);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
3.3 删除指定位置的节点
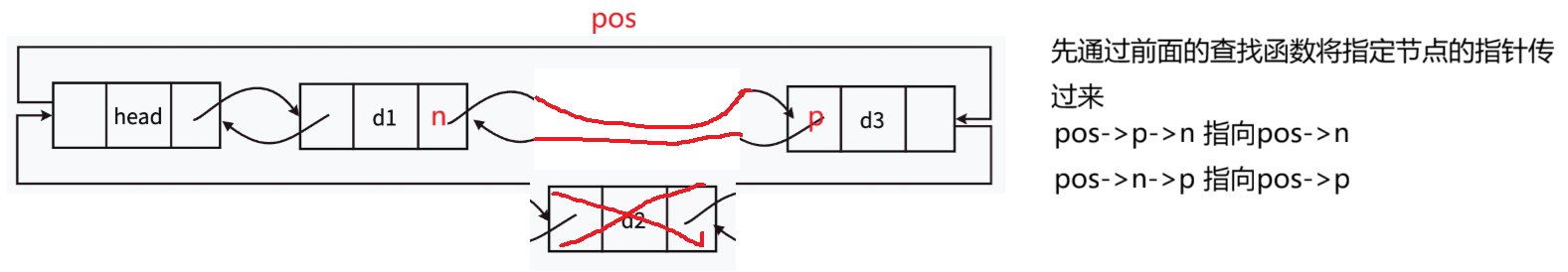
DList.c文件
#include "DList.h"
//定义_删除指定位置的节点
void DLTErase(DLTNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
pos->prev->next = pos->next;
pos->next->prev = pos->prev;
//释放被删除的节点空间
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
}删除指定算法更加简单,只需要将pos传给函数,在按照图示改变pos前后节点相关指针的指向即可。
(注意:还是,为实现普遍情况,pos前后的节点,用pos相关指针表示)
test.c文件
#include "DList.h"
void test01()
{
DLTNode* plist = NULL;//不是双向链表,初始化
//初始化
DLTInit(&plist);//传址
//尾插
DLTPushBack(plist, 1);
DLTPushBack(plist, 2);
DLTPushBack(plist, 3);
DLTPushBack(plist, 4);
DLTPrint(plist);
//删除指定位置的节点
DLTNode* pos = DLTFind(plist, 3);
DLTErase(pos);
DLTPrint(plist);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
3.4 销毁链表
//定义_销毁
void LTDestory(DLTNode* phead)
{
DLTNode* pcur = phead->next;
while (pcur != phead)
{
DLTNode* next = pcur->next;
free(pcur);
pcur = next;
}
free(phead);
phead = NULL;
}--实现销毁算法,也是寻要进行遍历,在遍历过程中每次销毁一个节点之前就要先把它的下一个节点( ->next)用临时指针存下来,最后销毁完后通过临时指针的来到下一个位置.
四、部分代码改良(保证接口一致性)
对实现的所有接口进行观察:大部分传一级指针本身,少部分二级指针。为了使用体验和一致性,全部改成传指针本身。
4.1 初始化接口
//头节点初始化的优化
DLTNode* DLTInit()
{
DLTNode* phead = LTBuyNode(-1);
return phead;
}--这串代码的简化了在使用时要传二级指针,实现了接口的一致性-->传指针本身,不会再混淆什么时候一级,什么时候二级。
4.2 销毁接口
//销毁
void DLTDestory(DLTNode* phead)//形参
{
DLTNode* pcur = phead->next;
while (pcur != phead)
{
DLTNode* next = pcur->next;
free(pcur);
pcur = next;
}
free(phead);
phead = NULL;
}--进行传值调用,在函数中,由于除头节点外,其他节点通过地址访问-->代表可以真正的改变节点。而头节点(实参)要额外在调用结束后手动将节点释放。
五、全部代码展示
5.1 .h文件
--下面会呈现双链表从无到实现各种功能的完整代码。
DList.h
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
//定义双链表基本结构
typedef int DLTDataType;
typedef struct DListNode
{
DLTDataType data;
struct DListNode* next;//指向下一个节点
struct DListNode* prev;//指向前一个节点
}DLTNode;
//声明_创建新节点
DLTNode* DLTBuyNode(DLTDataType x);
//声明_初始化
void DLTInit(DLTNode** pphead);//二级指针接收“哨兵位”地址-->改变结构(test.c传的头节点)
//声明_打印
void DLTPrint(DLTNode* phead);
//声明_尾插
void DLTPushBack(DLTNode* phead, DLTDataType x);
//声明_头插
void DLTPushFront(DLTNode* phead, DLTDataType x);
//声明_判空
bool DLTEmpty(DLTNode* phead);
//声明_尾删
void DLTPopBack(DLTNode* phead);
//声明_头删
void DLTPopFront(DLTNode* phead);
//声明_查找
DLTNode* DLTFind(DLTNode* phead, DLTDataType* x);
//声明_在指定位置之后插入
void DLTInset(DLTNode* pos, DLTDataType* x);
//声明_删除指定位置的节点
void DLTErase(DLTNode* pos);
//声明_销毁
//void LTDestory(DLTNode* phead);
void DLTDestory(DLTNode* phead);//形参 5.2 .c文件
DList.c
#include "DList.h"
//定义_由数值创建新节点
DLTNode* DLTBuyNode(DLTDataType x)
{
//申请空间
DLTNode* newnode = (DLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(DLTNode));
//判断非空
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
return 1;//申请失败
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = newnode->prev = newnode;//新节点先指向自己
return newnode;
}
//定义_初始化
//void DLTInit(DLTNode** pphead)//二级指针接收“哨兵位”地址-->改变结构(test.c传的头节点)
//{
// ////申请空间
// //*pphead = (DLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(DLTNode));//*pphead 是 phead
// ////判断非空
// //if (*pphead == NULL)
// //{
// // perror("malloc");
// // return 1;//申请失败
// //}
//
// //(*pphead)->data = -1;//随便一个值,后续不用
// //(*pphead)->next = (*pphead)->prev = *pphead;//指向自己
// *pphead = DLTBuyNode(-1);
//}
//头节点初始化的优化
DLTNode* DLTInit()
{
DLTNode* phead = LTBuyNode(-1);
return phead;
}
//定义_打印
void DLTPrint(DLTNode* phead)
{
DLTNode* pcur = phead->next;//指向第一个节点
//循环遍历
while (pcur != phead)
{
printf("%d->", pcur->data);
pcur = pcur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
//定义_尾插
void DLTPushBack(DLTNode* phead, DLTDataType x)//一级指针,只需要知道是哪个链表
{
//断言
assert(phead);
//创建新节点
DLTNode* newnode = DLTBuyNode(x);
//先对newnode进行改变,防止phead、尾节点指向改变
newnode->prev = phead->prev;
newnode->next = phead;
phead->prev->next = newnode;//->prev->next代表尾节点next
phead->prev = newnode;
}
//定义_头插
void DLTPushFront(DLTNode* phead, DLTDataType x)
{
//断言
assert(phead);
//申请新节点
DLTNode* newnode = DLTBuyNode(x);
newnode->next = phead->next;
newnode->prev = phead;
phead->next->prev = newnode;
phead->next = newnode;
}
//定义-判空
bool DLTEmpty(DLTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
return phead->next == phead;
}
//定义_尾删
void DLTPopBack(DLTNode* phead)
{
assert(!DLTEmpty(phead));
//首先定义指针指向尾节点
DLTNode* del = phead->prev;
del->prev->next = phead;
phead->prev = del->prev;
//对del节点空间进行释放
free(del);
del = NULL;
}
//定义_头删
void DLTPopFront(DLTNode* phead)
{
assert(!DLTEmpty(phead));
//定义指针指向第1个节点
DLTNode* del = phead->next;
phead->next = del->next;
del->next->prev = phead;
//释放del
free(del);
del = NULL;
}
//定义_查找
DLTNode* DLTFind(DLTNode* phead, DLTDataType* x)
{
//判空
assert(!DLTEmpty(phead));
DLTNode* pcur = phead->next;//临时指针接收
//循环遍历
while (pcur != phead)
{
if (pcur->data == x)
{
return pcur;//找到了,返回指针
}
pcur = pcur->next;//后移
}
//没找到,返回空
return NULL;
}
//定义_在指定位置之后插入
void DLTInset(DLTNode* pos, DLTDataType* x)
{
assert(pos);
//申请新节点
DLTNode* newnode = DLTBuyNode(x);
newnode->prev = pos;
newnode->next = pos->next;
pos->next->prev = newnode;
pos->next = newnode;
}
//定义_删除指定位置的节点
void DLTErase(DLTNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
pos->prev->next = pos->next;
pos->next->prev = pos->prev;
//释放被删除的节点空间
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
}
//定义_销毁
//void DLTDestory(DLTNode** pphead)
//{
// DLTNode* pcur = phead->next;
// while (pcur != *pphead)
// {
// DLTNode* next = pcur->next;
// free(pcur);
// pcur = next;
// }
// free(*pphead);
// *pphead = NULL;
//}
//销毁
void DLTDestory(DLTNode* phead)//形参
{
DLTNode* pcur = phead->next;
while (pcur != phead)
{
DLTNode* next = pcur->next;
free(pcur);
pcur = next;
}
free(phead);
phead = NULL;
}5.3 测试文件
#include "DList.h"
//测试
void test01()
{
DLTNode* plist = NULL;//不是双向链表,初始化
//初始化
DLTInit(&plist);//传址
//尾插
DLTPushBack(plist, 1);
DLTPushBack(plist, 2);
DLTPushBack(plist, 3);
DLTPushBack(plist, 4);
DLTPrint(plist);
////头插
//DLTPushFront(plist, 1);
//DLTPushFront(plist, 2);
//DLTPushFront(plist, 3);
//DLTPushFront(plist, 4);
////尾删
//DLTPopBack(plist);
//DLTPrint(plist);
//DLTPopBack(plist);
//DLTPrint(plist);
//DLTPopBack(plist);
//DLTPrint(plist);
//DLTPopBack(plist);
//DLTPrint(plist);
////头删
//DLTPopFront(plist);
//DLTPrint(plist);
//DLTPopFront(plist);
//DLTPrint(plist);
//DLTPopFront(plist);
//DLTPrint(plist);
//DLTPopFront(plist);
//DLTPrint(plist);
//查找
/*DLTNode* pos = DLTFind(plist, 4);
if (DLTFind)
{
printf("找到了!\n");
}
else
{
printf("没找到!\n");
}*/
////插入
//DLTNode* pos = DLTFind(plist, 4);
//DLTInset(pos, 5);
//DLTPrint(plist);
//删除指定位置的节点
DLTNode* pos = DLTFind(plist, 3);
DLTErase(pos);
DLTPrint(plist);
//销毁
DLTDestory(plist);//形参
plist == NULL;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}回顾:
结语:掌握了双链表的灵活与自由,我们已然能够在数据的海洋中随意徜徉。然而,在特定的战场上,“限制”往往能催生出更极致的效率。接下来,我们将进入一个纪律严明的世界:栈与队列——看它们如何用“先进后出”和“先进先出”的简单规则,解决复杂的现实问题。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号