Linux逆向之ELF文件格式
1、ELF 文件格式
1.1 ELF 文件类型
ELF文件是一种用于二进制文件、可执行文件、目标代码、共享库和core转存格式文件。是UNIX系统实验室(USL)作为应用程序二进制接口(Application Binary Interface,ABI)而开发和发布的,也是Linux的主要可执行文件格式。ELF有四种类型:
- 可重定位文件:即.o文件。包含适合于其他目标文件链接起来创建可执行文件或者共享目标文件的代码和数据。
- 可执行文件:.out文件,包含社和与执行的一个程序,此文件规定了exec()如何创建一个程序的进程映像。
- 共享目标文件:.so文件,包含可在两种上下文中链接的代码和数据,链接编辑器可以将它和可重定位文件、目标共享文件一起处理生成另外一个目标文件;动态链接器可能将它和某个可执行文件以及共享目标一起组合,创建进程映像。
- 内核转储文件:存放当前进程执行的上下文,用于dump信号触发
1.2 ELF文件结构
ELF文件由4部分组成,分别是ELF头(ELF header)、程序头表(Program header table)、节(Section)和节头表(Section header table)。
注意:一个文件中不一定包含全部内容,而且他们的位置也是不固定的。只有ELF文件头是固定的。其余各部分的信息都由文件头来决定。
ELF文件头: 它的主要目的是定位文件的其他部分
linux中关于EF文件头格式的定义在:/usr/include/elf.h中。Elf32_Ehdr是32位ELF文件结构体, Elf64_Ehdr是64位ELF文件结构体。
typedef struct
{
unsigned char e_ident[EI_NIDENT]; /* Magic number and other info */
Elf32_Half e_type; /* Object file type */
Elf32_Half e_machine; /* Architecture */
Elf32_Word e_version; /* Object file version */
Elf32_Addr e_entry; /* Entry point virtual address */
Elf32_Off e_phoff; /* Program header table file offset */
Elf32_Off e_shoff; /* Section header table file offset */
Elf32_Word e_flags; /* Processor-specific flags */
Elf32_Half e_ehsize; /* ELF header size in bytes */
Elf32_Half e_phentsize; /* Program header table entry size */
Elf32_Half e_phnum; /* Program header table entry count */
Elf32_Half e_shentsize; /* Section header table entry size */
Elf32_Half e_shnum; /* Section header table entry count */
Elf32_Half e_shstrndx; /* Section header string table index */
} Elf32_Ehdr;
typedef struct
{
unsigned char e_ident[EI_NIDENT]; /* Magic number and other info */
Elf64_Half e_type; /* Object file type */
Elf64_Half e_machine; /* Architecture */
Elf64_Word e_version; /* Object file version */
Elf64_Addr e_entry; /* Entry point virtual address */
Elf64_Off e_phoff; /* Program header table file offset */
Elf64_Off e_shoff; /* Section header table file offset */
Elf64_Word e_flags; /* Processor-specific flags */
Elf64_Half e_ehsize; /* ELF header size in bytes */
Elf64_Half e_phentsize; /* Program header table entry size */
Elf64_Half e_phnum; /* Program header table entry count */
Elf64_Half e_shentsize; /* Section header table entry size */
Elf64_Half e_shnum; /* Section header table entry count */
Elf64_Half e_shstrndx; /* Section header string table index */
} Elf64_Ehdr;
程序头表: 列举了所有有效的段(segments)和他们的属性, 程序头是一个结构的数组,每一个结构都表示一个段(segments)。在可执行文件或者共享链接库中所有的节(sections)都被分为不同的几个段(segments)。
/* Program segment header. */
typedef struct
{
Elf32_Word p_type; /* Segment type */
Elf32_Off p_offset; /* Segment file offset */
Elf32_Addr p_vaddr; /* Segment virtual address */
Elf32_Addr p_paddr; /* Segment physical address */
Elf32_Word p_filesz; /* Segment size in file */
Elf32_Word p_memsz; /* Segment size in memory */
Elf32_Word p_flags; /* Segment flags */
Elf32_Word p_align; /* Segment alignment */
} Elf32_Phdr;
typedef struct
{
Elf64_Word p_type; /* Segment type */
Elf64_Word p_flags; /* Segment flags */
Elf64_Off p_offset; /* Segment file offset */
Elf64_Addr p_vaddr; /* Segment virtual address */
Elf64_Addr p_paddr; /* Segment physical address */
Elf64_Xword p_filesz; /* Segment size in file */
Elf64_Xword p_memsz; /* Segment size in memory */
Elf64_Xword p_align; /* Segment alignment */
} Elf64_Phdr;
节头表: 包含对节(sections)的描述。每个section描述了这个段的信息,比如每个段的段名、段的长度、在文件中的偏移、读写权限及段的其它属性。
节区名存储在.shstrtab字符串表中,sh_name是表中偏移。
/* Section header. */
typedef struct
{
Elf32_Word sh_name; /* Section name (string tbl index) */
Elf32_Word sh_type; /* Section type */
Elf32_Word sh_flags; /* Section flags */
Elf32_Addr sh_addr; /* Section virtual addr at execution */
Elf32_Off sh_offset; /* Section file offset */
Elf32_Word sh_size; /* Section size in bytes */
Elf32_Word sh_link; /* Link to another section */
Elf32_Word sh_info; /* Additional section information */
Elf32_Word sh_addralign; /* Section alignment */
Elf32_Word sh_entsize; /* Entry size if section holds table */
} Elf32_Shdr;
typedef struct
{
Elf64_Word sh_name; /* Section name (string tbl index) */
Elf64_Word sh_type; /* Section type */
Elf64_Xword sh_flags; /* Section flags */
Elf64_Addr sh_addr; /* Section virtual addr at execution */
Elf64_Off sh_offset; /* Section file offset */
Elf64_Xword sh_size; /* Section size in bytes */
Elf64_Word sh_link; /* Link to another section */
Elf64_Word sh_info; /* Additional section information */
Elf64_Xword sh_addralign; /* Section alignment */
Elf64_Xword sh_entsize; /* Entry size if section holds table */
} Elf64_Shdr;
查看各个节表信息
| sh_name | sh_type | description | 查看方式 |
|---|---|---|---|
| .text | SHT_PROGBITS | 代码段,包含程序的可执行指令 | objdump -s -d initenv |
| .data | SHT_PROGBITS | 包含初始化了的数据,将出现在程序的内存映像中 | objdump -x -s -d initenv |
| .bss | SHT_NOBITS | 未初始化数据,因为只有符号所以 | |
| .rodata | SHT_PROGBITS | 包含只读数据 | |
| .comment | SHT_PROGBITS | 包含版本控制信息 | |
| .eh_frame | SHT_PROGBITS | 它生成描述如何unwind 堆栈的表 | |
| .debug | SHT_PROGBITS | 此节区包含用于符号调试的信息 | |
| .dynsym | SHT_DYNSYM | 此节区包含了动态链接符号表 | |
| .shstrtab | SHT_STRTAB | 存放section名,字符串表。Section Header String Table | |
| .strtab | SHT_STRTAB | 字符串表 | readelf -S initenv |
| .symtab | SHT_SYMTAB | 符号表 | readelf -s initenv |
| .got | SHT_PROGBITS | 全局偏移表 | |
| .plt | SHT_PROGBITS | 过程链接表 | |
| .relname | SHT_REL | 包含了重定位信息,例如 .text 节区的重定位节区名字将是:.rel.text | readelf -r initenv |
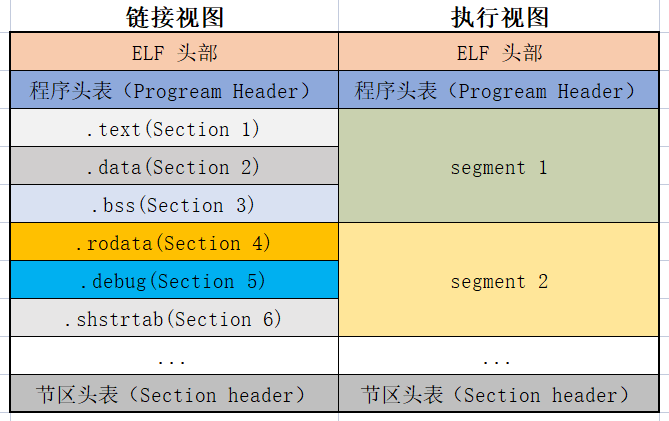
1.3 ELF文件视图
在解释elf文件试图之前先明确两个概念:Segment和Section。
Segment: 从运行额角度描述EFL文件,对应ELF文件的执行视图。
- 用于告诉内核,在在执行ELF文件时应该如何映射内存
- 每个Segmnet主要包含加载地址、文件中的范围、内存权限、对齐方式等
- 是运行时必须提供的信息
Section: 从链接角度来描述ELF文件,对应ELF文件的链接视图。
- 用于告诉链接器。ELF文件中每个部分是什么,哪里是代码、那里是制度数据、哪里是重定位数据
- 每个Section主要包含Section类型、文件中的位置、大小等
- 链接器依赖Section信息将不同的对象文件中的代码、数据信息合并,并修复互相引用
Segment和Section的关系:
- 相同权限的Section会放到同一个Segment中
- 一个Segment包含许多个Section
2、ELF文件格式解析
2.1 文件格式解析工具
用于查看elf文件的工具很多,如010Editor、readelf、objdump等。 这里以readelf为例进行演示说明(测试程序: initenv)。
readelf具体用法可以通过:readefl --help查看。
查看ELF文件头: readelf -h initenv
ELF Header:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Class: ELF64
Data: 2's complement, little endian
Version: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
ABI Version: 0
Type: EXEC (Executable file) //elf文件类型
Machine: Advanced Micro Devices X86-64
Version: 0x1
Entry point address: 0x45e4c0 //程序入口点
Start of program headers: 64 (bytes into file) //程序头的起始位置
Start of section headers: 456 (bytes into file) //段表开始位置
Flags: 0x0
Size of this header: 64 (bytes) //文件头的大小
Size of program headers: 56 (bytes) //程序头的大小
Number of program headers: 7 //程序头中的项数
Size of section headers: 64 (bytes) //段表长度
Number of section headers: 23 //段表中的项数
Section header string table index: 3
查看程序头表: readelf -l initenv
Elf file type is EXEC (Executable file)
Entry point 0x45e4c0
There are 7 program headers, starting at offset 64
Program Headers:
Type Offset VirtAddr PhysAddr
FileSiz MemSiz Flags Align
PHDR 0x0000000000000040 0x0000000000400040 0x0000000000400040
0x0000000000000188 0x0000000000000188 R 0x1000
NOTE 0x0000000000000f9c 0x0000000000400f9c 0x0000000000400f9c
0x0000000000000064 0x0000000000000064 R 0x4
LOAD 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000400000 0x0000000000400000
0x00000000000812dd 0x00000000000812dd R E 0x1000
LOAD 0x0000000000082000 0x0000000000482000 0x0000000000482000
0x000000000008e988 0x000000000008e988 R 0x1000
LOAD 0x0000000000111000 0x0000000000511000 0x0000000000511000
0x0000000000017f40 0x000000000004bae8 RW 0x1000
GNU_STACK 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 RW 0x8
LOOS+0x5041580 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 0x8
Section to Segment mapping:
Segment Sections...
00
01 .note.go.buildid
02 .text .note.go.buildid
03 .rodata .typelink .itablink .gosymtab .gopclntab
04 .go.buildinfo .noptrdata .data .bss .noptrbss
05
06
这里可以看到:该程序共有7个Segmnet,将23个Section分别映射到了01、02、03、04四个segment中。映射到同一Segmnet中的Section有着相同的属性。需要注意的是Section .note.go.buildid映射到了两个Segment中。
查看节头表:readelf -S initenv ,信息与Elf32_Shdr定义对应。
There are 23 section headers, starting at offset 0x1c8:
Section Headers:
[Nr] Name Type Address Offset
Size EntSize Flags Link Info Align
[ 0] NULL 0000000000000000 00000000
0000000000000000 0000000000000000 0 0 0
[ 1] .text PROGBITS 0000000000401000 00001000
00000000000802dd 0000000000000000 AX 0 0 32
[ 2] .rodata PROGBITS 0000000000482000 00082000
0000000000037667 0000000000000000 A 0 0 32
[ 3] .shstrtab STRTAB 0000000000000000 000b9680
000000000000016e 0000000000000000 0 0 1
[ 4] .typelink PROGBITS 00000000004b9800 000b9800
00000000000004dc 0000000000000000 A 0 0 32
[ 5] .itablink PROGBITS 00000000004b9ce0 000b9ce0
0000000000000058 0000000000000000 A 0 0 32
[ 6] .gosymtab PROGBITS 00000000004b9d38 000b9d38
0000000000000000 0000000000000000 A 0 0 1
[ 7] .gopclntab PROGBITS 00000000004b9d40 000b9d40
0000000000056c48 0000000000000000 A 0 0 32
[ 8] .go.buildinfo PROGBITS 0000000000511000 00111000
0000000000000110 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 16
[ 9] .noptrdata PROGBITS 0000000000511120 00111120
00000000000105e0 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 32
[10] .data PROGBITS 0000000000521700 00121700
0000000000007830 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 32
[11] .bss NOBITS 0000000000528f40 00128f40
000000000002f020 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 32
[12] .noptrbss NOBITS 0000000000557f60 00157f60
0000000000004b88 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 32
[13] .debug_abbrev PROGBITS 0000000000000000 00129000
0000000000000133 0000000000000000 C 0 0 1
[14] .debug_line PROGBITS 0000000000000000 00129133
000000000001c216 0000000000000000 C 0 0 1
[15] .debug_frame PROGBITS 0000000000000000 00145349
0000000000005724 0000000000000000 C 0 0 1
[16] .debug_gdb_s[...] PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0014aa6d
000000000000002e 0000000000000000 0 0 1
[17] .debug_info PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0014aa9b
0000000000034e48 0000000000000000 C 0 0 1
[18] .debug_loc PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0017f8e3
000000000001bdf1 0000000000000000 C 0 0 1
[19] .debug_ranges PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0019b6d4
0000000000009187 0000000000000000 C 0 0 1
[20] .note.go.buildid NOTE 0000000000400f9c 00000f9c
0000000000000064 0000000000000000 A 0 0 4
[21] .symtab SYMTAB 0000000000000000 001a4860
000000000000c5e8 0000000000000018 22 98 8
[22] .strtab STRTAB 0000000000000000 001b0e48
000000000000b2f3 0000000000000000 0 0 1
Key to Flags:
W (write), A (alloc), X (execute), M (merge), S (strings), I (info),
L (link order), O (extra OS processing required), G (group), T (TLS),
C (compressed), x (unknown), o (OS specific), E (exclude),
D (mbind), l (large), p (processor specific)
2.2 实现文件解析器
Golang标准库debug/elf包实现了对ELF文件的访问。可以用来实现解析ELF文件。
....
// Indexes into the Header.Ident array.
const (
EI_CLASS = 4 /* Class of machine. */
EI_DATA = 5 /* Data format. */
EI_VERSION = 6 /* ELF format version. */
EI_OSABI = 7 /* Operating system / ABI identification */
EI_ABIVERSION = 8 /* ABI version */
EI_PAD = 9 /* Start of padding (per SVR4 ABI). */
EI_NIDENT = 16 /* Size of e_ident array. */
)
const (
ET_NONE Type = 0 /* Unknown type. */
ET_REL Type = 1 /* Relocatable. */
ET_EXEC Type = 2 /* Executable. */
ET_DYN Type = 3 /* Shared object. */
ET_CORE Type = 4 /* Core file. */
ET_LOOS Type = 0xfe00 /* First operating system specific. */
ET_HIOS Type = 0xfeff /* Last operating system-specific. */
ET_LOPROC Type = 0xff00 /* First processor-specific. */
ET_HIPROC Type = 0xffff /* Last processor-specific. */
)
...
具体实现逻辑:读取ELF文件到内存,按照ELF文件格式去解析数据即可,没有什么难度。以下是读取ELF文件头的部分代码:
func readHeader(filedata []byte) {
// analysis elf file
fmt.Println("ELF Header:")
fmt.Print(" Magic: ")
for i := 0; i < int(elf.DT_INIT); i++ {
fmt.Printf("%02x ", filedata[i])
}
//1、get magic
var elfHeader elf.FileHeader
elfHeader.Class = elf.Class(filedata[4])
fmt.Print("\n Class: ")
switch filedata[4] {
case 0:
fmt.Println("Invailed Class")
case 1:
fmt.Println("ELF32")
case 2:
fmt.Println("ELF64")
case 3:
fmt.Println("Error")
}
//2. get data
fmt.Print(" Data: ")
switch filedata[5] {
case 0:
fmt.Println("Invalid encoding data")
case 1:
fmt.Println("2's complement, little endian")
case 2:
fmt.Println("2's complement, little endian")
default:
fmt.Println("Error")
}
//3. get Version OS/ABI API Version
fmt.Print(" Version: 1(current)\n")
fmt.Print(" OS/ABI: UNIX - Sytem V\n")
fmt.Print(" API Version: 0\n")
//4.get type
fmt.Print(" Type: ")
switch filedata[elf.EI_NIDENT] {
case 0:
fmt.Println("no file type")
case 1:
fmt.Println("relocate file")
case 2:
fmt.Println("EXEC (executable file) ")
case 3:
fmt.Println("Shared objective file")
case 4:
fmt.Println("Core file")
default:
fmt.Println("Error")
}
//5.machine
fmt.Print(" Machine: ")
switch filedata[elf.EI_NIDENT+2] {
case byte(elf.EM_386):
fmt.Println("Inter 83086")
case byte(elf.EM_ARM):
fmt.Println("ARM")
case byte(elf.EM_X86_64):
fmt.Println("AMD X86-64 arrchitecture")
default:
fmt.Printf("Error")
}
....
}
3、ELF文件加载过程
关于ELF加载过程可以查看源码:https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v6.0.11/source/fs/binfmt_elf.c
ELF程序执行时,代码和数据必须在内存,因此同windows下Exe文件的加载执行过程类似,需要先申请一定的内存空间、映射elf文件到内存、修改CPU的指令指针寄存器为程序的入口开始执行代码。不同点在于进行内存映射、创建进程的具体实现上存在差异,但是整个逻辑上相似。
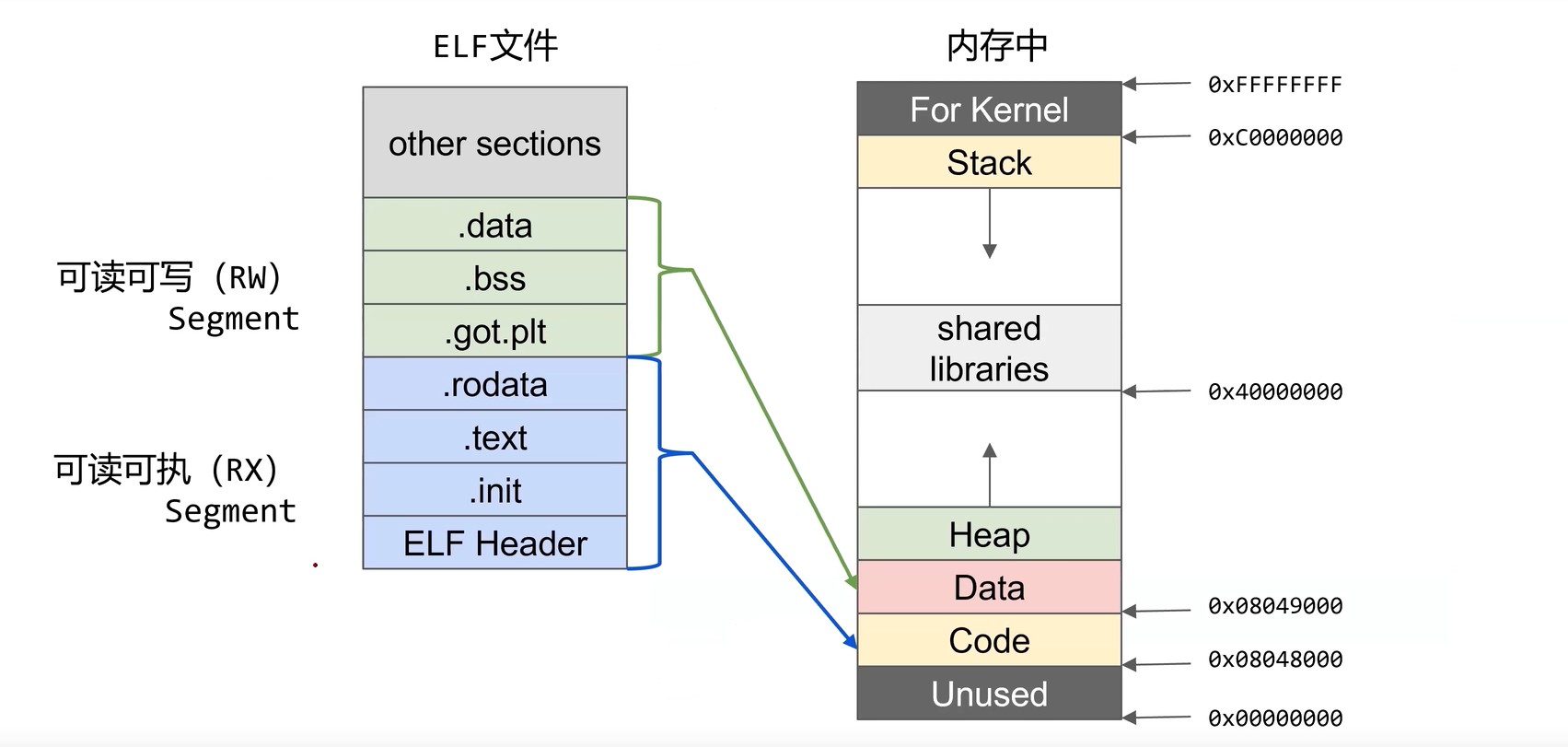
Linux 提供三种方式来加载可执行程序:
- load_binary: 通过读存放在可执行文件中的信息为当前进程建立一个新的执行环境
- load_shlib: 用于动态的把一个共享库捆绑到一个已经在运行的进程, 这是由uselib()系统调用激活的
- core_dump: 在名为core的文件中, 存放当前进程的执行上下文. 这个文件通常是在进程接收到一个缺省操作为”dump”的信号时被创建的, 其格式取决于被执行程序的可执行类型
3.1 Shell执行命令的完整周期
1、当Shell执行一个程序时,父Shell进程生成一个子shell进程(父进程的复制),子shell进程通过系统调用execve启动加器;/linux/v4.20.17/source/fs/exec.c
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(execve,
const char __user *, filename,
const char __user *const __user *, argv,
const char __user *const __user *, envp)
{
return do_execve(getname(filename), argv, envp);
}
2、在内核中真正执行execv()/execve()的是do_execve(),该函数首先打开映像文件,并从目标文件头部读取若干字节(即ELF头部大小),然后调用search_binary_handler。这里需要注意的是函数参数bprm, 其类型为linux_binprm结构体。linux内核对所支持的每种可执行的程序类型都有个struct linux_binfmt来记录程序信息。这是一种可执行文件类型的注册机制:所有注册的的linux_binfmt对象都处于一个链表中(全局链表变量 formats),通过registre_fmt()注册一种linux_binfmt新类型。系统初始化时为每个编译进内核的可执行格式都执行registre_fmt()函数。当我们执行一个可执行程序的时候, 内核会list_for_each_entry遍历所有注册的linux_binfmt对象, 对其调用load_binrary方法来尝试加载, 直到加载成功为止(前面介绍的search_binary_handler() 函数)。
ELF文件格式注册的linux_binfmt结构对象elf_format。
int search_binary_handler(struct linux_binprm *bprm)
{
bool need_retry = IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_MODULES);
struct linux_binfmt *fmt;
int retval;
/* This allows 4 levels of binfmt rewrites before failing hard. */
if (bprm->recursion_depth > 5)
return -ELOOP;
retval = security_bprm_check(bprm);
if (retval)
return retval;
retval = -ENOENT;
retry:
read_lock(&binfmt_lock);
list_for_each_entry(fmt, &formats, lh) {
if (!try_module_get(fmt->module))
continue;
read_unlock(&binfmt_lock);
bprm->recursion_depth++;
retval = fmt->load_binary(bprm);
read_lock(&binfmt_lock);
put_binfmt(fmt);
bprm->recursion_depth--;
if (retval < 0 && !bprm->mm) {
/* we got to flush_old_exec() and failed after it */
read_unlock(&binfmt_lock);
force_sigsegv(SIGSEGV, current);
return retval;
}
if (retval != -ENOEXEC || !bprm->file) {
read_unlock(&binfmt_lock);
return retval;
}
}
read_unlock(&binfmt_lock);
if (need_retry) {
if (printable(bprm->buf[0]) && printable(bprm->buf[1]) &&
printable(bprm->buf[2]) && printable(bprm->buf[3]))
return retval;
if (request_module("binfmt-%04x", *(ushort *)(bprm->buf + 2)) < 0)
return retval;
need_retry = false;
goto retry;
}
return retval;
}
3、search_binary_handler函数遍历format格式,对于linux下的elf格式的可执行文件而言,会找到elf_format,调用其load_binary函数,对elf类型而言,则调用load_elf_binary。
static struct linux_binfmt elf_format = {
.module = THIS_MODULE,
.load_binary = load_elf_binary, //处理函数
.load_shlib = load_elf_library,
.core_dump = elf_core_dump,
.min_coredump = ELF_EXEC_PAGESIZE,
};
4、load_elf_binary函数加载和启动ELF程序。具体代码位于文件:/source/fs/binfmt_elf.c。该函数主要完成以下工作来加载elf文件:
- 填充并检查目标程序ELF头部
- 调用 load_elf_phdrs加载目标程序的程序头部
- 如果需要动态链接,则寻找和处理解释器段
- 装入程序的segment
- 填写程序入口
- 调用create_elf_tables填写目标文件的参数环境变量等信息
- start_thread进入新程序的入口
参考资料:
https://blog.csdn.net/gatieme/article/details/51628257
https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.20.17/source/fs/binfmt_elf.c#L690
https://blog.csdn.net/conansonic/article/details/53740670
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/147322084
https://www.bookstack.cn/read/gctt-godoc/Source-debug-elf-elf.md


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号