MySQL-08-索引
11、6.7
1、索引
1、什么是索引及其作用?
像是一个目录,用于加速查找的速度
作用:1.约束 2、加速查找
2、索引原理
索引的本质是一张表,也就是我们创建索引相当于创建一个目录,也就是牺牲了存储空间加速了查找
底层实现:
-
哈希算法:根据要建索引的那一列,通过哈希算法计算出特定位置,然后存储原本表数据行的位置
进行查找, 是无序的,对于单个查找很快,范围查找很慢
-
B树:大多数也都是用B树的,性质像二叉搜索树,查的很快,复杂度,logn,n为树高
3、索引分类
-
普通索引
定义:
create index 索引名 on 表名(列名) -
主键索引
-
唯一索引
定义:
create unique index 索引名 on 表名(列名) -
组合索引
定义:
create index 索引名 on 表名(列名1,列名2···)联合唯一索引 :
create unique index 索引名 on 表名(列名1,列名2···)
**另外创建索引还可以指定列的长度create unique index 索引名 on 表名(列名1(20)):表示列1的钱20个字符 **,一般我们在有相同数的时候使用,比如说列1后面全是 @qq.com,这样不能与其他行区分开来,加上也没用浪费空间!
2、索引补充
不是真正的索引
-
覆盖索引
比如 A 表中id 为索引, 我们select idfrom A where id = 7; 一句话就是我们查索引,映射的列也是索引,这样MySQL会直接去索引的那个数据结构中寻找,而不会去原表中找,速度很快。
-
索引合并
就是两个索引都被命中, A表中(id, name)是两个索引, 我们select * from A where id = “?” and name = “?”; 这种情况就是索引合并
索引合并的效率 < 组合索引:因为回去两个数据结构中查询,估计会慢点!
-
最左前缀原则
在组合索引的前提下
比如说我们有一个组合索引, create index name_email on student(name, email)
此时我们想命中索引就要遵循这个最左前缀原则:
select * from student where name ="??" 可以命中
select * from student where email = “?” 不能命中
select * from student where name ="??" and email = “?” 可命中
-
命中索引
几种常见不不能命中索引的例子
-
避免使用 like 模糊查询
我们实际开发中一般为了效率会多建一张表
![]()
-
避免使用函数
例如 select * from A where reverse(name) = “bingbing”;
这样也不会走索引,正确的做法是在java程序中反转bingbing
3、 最左前缀原则
上面说过
4、影响效率的:避免使用 select * 和count(*) 换成count(1)
5、- or 假设表中索引是 nid 和 email
select * from tb1 where nid = 1 or name = 'seven@live.com';
特别的:当or条件中有未建立索引的列才失效,以下会走索引
select * from tb1 where nid = 1 or name = 'seven';
select * from tb1 where nid = 1 or name = 'seven@live.com' and email = 'alex'
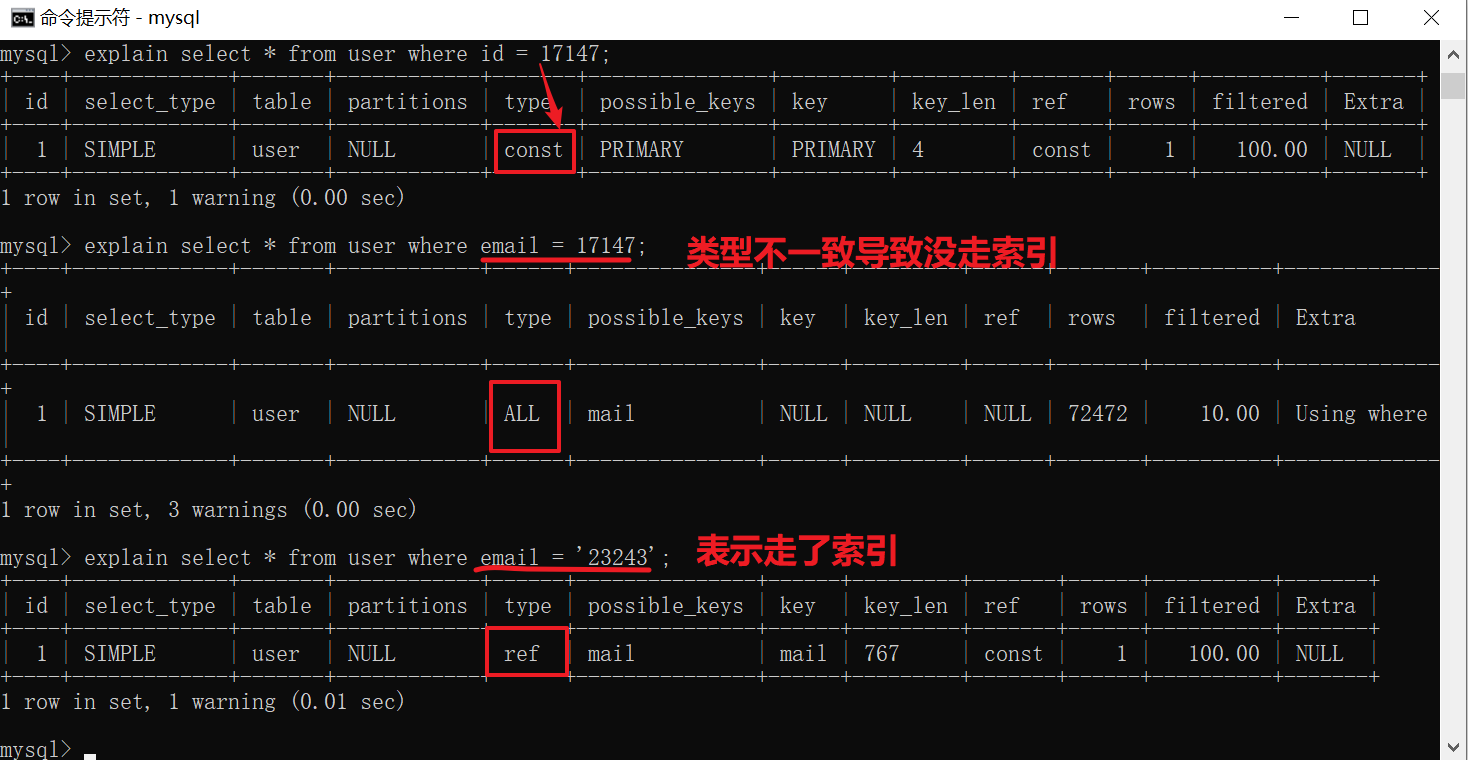
6、类型不一致
如果列是字符串类型,传入条件是必须用引号引起来,不然不走索引
select * from tb1 where email = 999;
7、!=
select * from tb1 where email != 'alex'
**特别的:如果是主键,则还是会走索引**
select * from tb1 where nid != 123
- select * from tb1 where email > 'alex'
8、 >
特别的:如果是主键或索引是整数类型,则还是会走索引
select * from tb1 where nid > 123
select * from tb1 where num > 123
9、order by
select name from tb1 order by email desc;
当根据索引排序时候,**选择的映射如果不是索引,则不走索引**
特别的:如果对主键排序,则还是走索引:
select * from tb1 order by nid desc;
- 速度检测
以实际为标准
但是有时候sql语句执行时间太长,所以我们需要使用explain来预估执行时间
1、语法
expalain select * from user where id > 1
这里并不会真正的执行sql语句,而是解释分析sql,但是不一定准确
- 解析时间分类
解释理论正确,也有例外:select * from user limit 1;是all 但是很快
| 类型 | 速度 |
|---|---|
| all | 全表查询,速度最慢 |
| index | 去索引表中全表扫描,也慢 |
| ref | 普通索引 |
| const | 主键索引 |
执行计划:让mysql预估执行操作(一般正确)
all < index < range < index_merge < ref_or_null < ref < eq_ref < system/const
id,email
慢:
select * from userinfo3 where name='alex'
explain select * from userinfo3 where name='alex'
type: ALL(全表扫描)
select * from userinfo3 limit 1;
快:
select * from userinfo3 where email='alex'
type: const(走索引)
DBA工作慢日志配置
4. DBA工作
慢日志
- 执行时间 > 10
- 未命中索引
- 日志文件路径
配置:
- 内存
show variables like '%query%'
set global 变量名 = 值 //设置慢日志开启或者关闭
- 配置文件
mysqld --defaults-file='E:\wupeiqi\mysql-5.7.16-winx64\mysql-5.7.16-winx64\my-default.ini'
my.conf内容:
slow_query_log = ON
slow_query_log_file = D:/....
注意:修改配置文件之后,需要重启服务
分页查询优化
普通的分页查询会默认扫描全表,速度很慢

select * from user limit 60000, 10;
-
优化思路1
select * from user where id in (select id from user limit 60000, 10);
不会快很多因为还是会在索引表中扫描全部
-
优化2
思路就是:我们每页都有一个最大的页码max 和最小的min,
下一页就是:id > max limit 每页显示的条数
上一页就是:id < min limit 10 order by id desc; 倒序一下
下n也就是: 必须要嵌套一层查询
select * from user where id in (select B.id from ( (select N.id from (select id from user where id > 60000 limit 30) as N order by N.id desc limit 10) ) as B);



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号