redis缓存淘汰策略--主动淘汰
2020-11-10 07:57 虎背熊腰 阅读(461) 评论(0) 收藏 举报文章摘要:
redis 作为一个高性能key-value 数据库,当内存不足是必然需要执行数据淘汰策略,本文只分析主动淘汰策略,讨论的版本是redis3.0
配置参数和相关数据结构:
maxmemory_policy 设置淘汰策略取值如下:
1、volatile-lru:从已设置过期时间的数据集(server.db[i].expires)中挑选最近最少使用的数据淘汰
2、volatile-ttl:从已设置过期时间的数据集(server.db[i].expires)中挑选将要过期的数据淘汰
3、volatile-random:从已设置过期时间的数据集(server.db[i].expires)中任意选择数据淘汰
4、allkeys-lru:从数据集(server.db[i].dict)中挑选最近最少使用的数据淘汰
5、allkeys-random:从数据集(server.db[i].dict)中任意选择数据淘汰
6、no-enviction(驱逐):禁止驱逐数据
maxmemory_samples 随机采样数量默认5
redisObj结构体
redis的key固定用一种数据结构来表达就够了,这就是动态字符串sds。
而value则比较复杂,为了在同一个dict内能够存储不同类型的value,这就需要一个通用的数据结构,这个通用的数据结构就是robj
typedef struct redisObject {
unsigned type:4;
unsigned encoding:4;
unsigned lru:LRU_BITS; /* LRU time (relative to global lru_clock) or
* LFU data (least significant 8 bits frequency
* and most significant 16 bits access time). */
int refcount;
void *ptr;
} robj;
其中lru:LRU_BITS就是用来实现lru和lfu等淘汰策略关键点之一
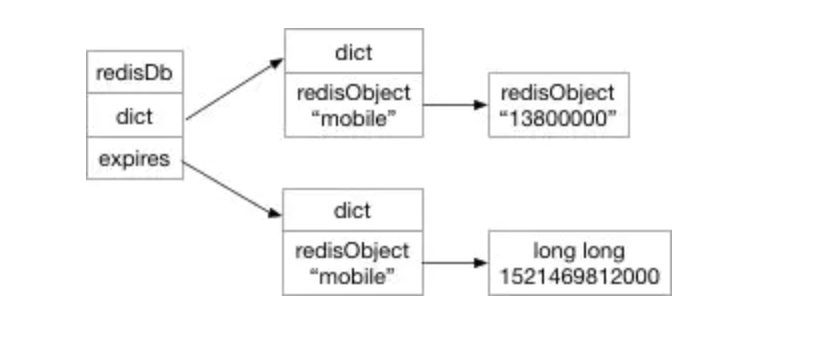
expires 链表
在 redisDb 中使用了 dict *expires,来存储过期时间的。其中 key 指向了 keyspace 中的 key(c 语言中的指针),
value 是一个 long long 类型的时间戳,标定这个 key 过期的时间点,单位是毫秒
主体执行流程(以volatile-lru为例)
1:服务初始化执行init调用evictionPoolAlloc 初始化lru pool (size = 16数组) 2:判断是否需要缓存淘汰策略 3:执行 freeMemoryIfNeeded 4:循环16个db,每个db选择maxmemory_samples个元素,根据idea(空闲时间)执行插入排序放入db lru pool中 5:删除lru pool中最末尾的元素 6:重复操作直到满足需求内存
代码详解执行流程(以volatile-lru为例)
初始化全局lru pool
initServer(){
evictionPoolAlloc(); /* Initialize the LRU keys pool. */
}
void evictionPoolAlloc(void) {
struct evictionPoolEntry *ep;
int j;
ep = zmalloc(sizeof(*ep)*EVPOOL_SIZE);
for (j = 0; j < EVPOOL_SIZE; j++) {
ep[j].idle = 0;
ep[j].key = NULL;
ep[j].cached = sdsnewlen(NULL,EVPOOL_CACHED_SDS_SIZE);
ep[j].dbid = 0;
}
EvictionPoolLRU = ep;//size = 16 的数组
}
//判断是否需要执行淘汰策略,需要执行则会进入freeMemoryIfNeeded函数
freeMemoryIfNeeded() {
while (mem_freed < mem_tofree) {
//循环释放直到满足需求内存
struct evictionPoolEntry *pool = EvictionPoolLRU;//这是一个全局引用
.....
//接下来获取bestkey
for (i = 0; i < server.dbnum; i++) {
dict = server.maxmemary_policy & MAMMEMARY_FLAG_ALLKEYS ? db->dict ? db->expire;
//循环16个db找出符合条件的写入lru pool 全局对象
evictionPoolPopulate(dict);//EVPOOL_SIZE 默认16
}
//从redis evictionPool 中选择bestkey,就是队列尾部的元素
for (k = EVPOOL_SIZE-1; k >= 0; k--) {
.......
bestkey = ...
}
//删除bestkey
if (server.lazyfree_lazy_eviction)
dbAsyncDelete(db,keyobj);
else
dbSyncDelete(db,keyobj);
mem_freed++;
}
}
evictionPoolPopulate()
{
count = dictGetSomeKeys(sampledict,samples,server.maxmemory_samples);
for (j = 0; j < count; j++) {
unsigned long long idle;
sds key;
robj *o;
dictEntry *de;
de = samples[j];
key = dictGetKey(de);
/* If the dictionary we are sampling from is not the main
* dictionary (but the expires one) we need to lookup the key
* again in the key dictionary to obtain the value object. */
if (server.maxmemory_policy != MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_TTL) {
if (sampledict != keydict) de = dictFind(keydict, key);
o = dictGetVal(de);
}
/* Calculate the idle time according to the policy. This is called
* idle just because the code initially handled LRU, but is in fact
* just a score where an higher score means better candidate. */
if (server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LRU) {
idle = estimateObjectIdleTime(o);//过期时间
} else if (server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LFU) {
/* When we use an LRU policy, we sort the keys by idle time
* so that we expire keys starting from greater idle time.
* However when the policy is an LFU one, we have a frequency
* estimation, and we want to evict keys with lower frequency
* first. So inside the pool we put objects using the inverted
* frequency subtracting the actual frequency to the maximum
* frequency of 255. */
idle = 255-LFUDecrAndReturn(o);
} else if (server.maxmemory_policy == MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_TTL) {
/* In this case the sooner the expire the better. */
idle = ULLONG_MAX - (long)dictGetVal(de);
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown eviction policy in evictionPoolPopulate()");
}
/* Insert the element inside the pool.
* First, find the first empty bucket or the first populated
* bucket that has an idle time smaller than our idle time. */
k = 0;
//插入排序
while (k < EVPOOL_SIZE &&
pool[k].key &&
pool[k].idle < idle) k++;
if (k == 0 && pool[EVPOOL_SIZE-1].key != NULL) {
/* Can't insert if the element is < the worst element we have
* and there are no empty buckets. */
continue;
} else if (k < EVPOOL_SIZE && pool[k].key == NULL) {
/* Inserting into empty position. No setup needed before insert. */
} else {
/* Inserting in the middle. Now k points to the first element
* greater than the element to insert. */
if (pool[EVPOOL_SIZE-1].key == NULL) {
/* Free space on the right? Insert at k shifting
* all the elements from k to end to the right. */
/* Save SDS before overwriting. */
sds cached = pool[EVPOOL_SIZE-1].cached;
memmove(pool+k+1,pool+k,
sizeof(pool[0])*(EVPOOL_SIZE-k-1));
pool[k].cached = cached;
} else {
//已经没有空间了,往前移剔除第一个元素 memmove系统函数 ,插入到k-1
/* No free space on right? Insert at k-1 */
k--;
/* Shift all elements on the left of k (included) to the
* left, so we discard the element with smaller idle time. */
sds cached = pool[0].cached; /* Save SDS before overwriting. */
if (pool[0].key != pool[0].cached) sdsfree(pool[0].key);
memmove(pool,pool+1,sizeof(pool[0])*k);
pool[k].cached = cached;
}
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号