手撕异常
1.异常体系结构
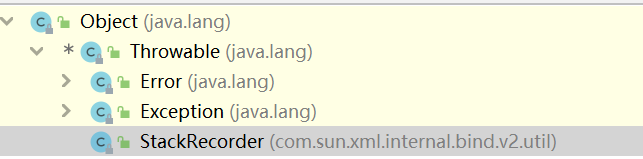
ThrowableThe {@code Throwable} class is the superclass of all errors and exceptions in the Java language.ErrorAn {@code Error} is a subclass of {@code Throwable} that indicates serious problems that a reasonable application should not try to catch.Most such errors are abnormal conditions.常见Error:ExceptionThe class {@code Exception} and its subclasses are a form of {@code Throwable} that indicates conditions that a reasonable applicationmight want to catch.常见Exception:运行时异常编译时异常2.处理异常主要分成两种 抛出异常、抓住异常①抛出异常:(手动抛出)
public static void test1() {
int j = 0;
if(j == 0){
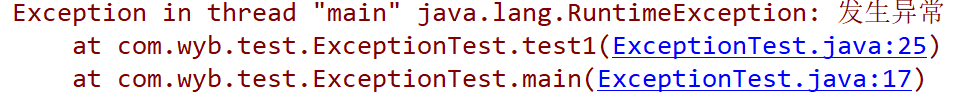
throw new RuntimeException("发生异常");
}
}(自动抛出)
public static void test1() {
int i = 10;
int j = 0;
System.out.println(i/j);
}②抓住异常 分为try-catch-finally、throwstry-catch-finally 为真正处理异常 实例:
public static void test1() {
int i = 10;
int j = 0;
try {
System.out.println(i/j);
} catch (Exception e) {
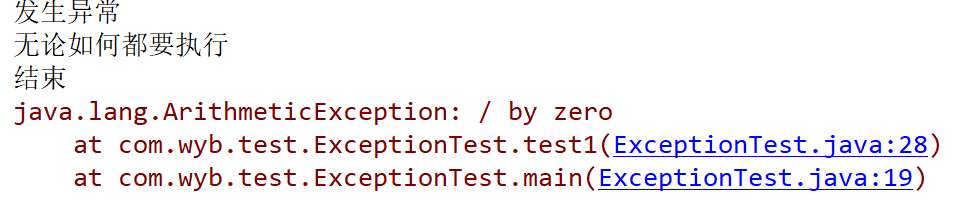
System.out.println("发生异常");
e.printStackTrace();//显示发生异常的路径
} finally {
System.out.println("无论如何都要执行");
}
System.out.println("结束");
}上图为控制台运行打印输出结果throws:往外层方法调用者抛,该方式并没有真正处理异常,只不过将异常抛给了方法的调用者,但是最终无论如何都需要处理,否则就直接暴露异常
//在外层用 try-catch-finally 处理了异常,不影响后序代码的执行,如果在外部同样还是往外抛,那么在发生异常时就程序结束了
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
test1();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//由于try catch 处理了异常,所以继续执行
}
public static void test1() throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(1000);
//如果发生异常,下面的代码不在执行
}3.开发细节当子类重写父类某一方法时,子类抛出异常不能大于父类抛出的异常Talk is cheap! Show me your Code!父类
public class Person {
public void testException() throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}子类
public class SubPerson extends Person {
//重写父类testExeption()方法
@Override
public void testException() throws InterruptedException {
}
}以上是正常情况,即子类重写父类testException()方法时,抛出的异常并未大于父类的异常。
但是当子类的抛出的异常类型大于父类的异常类型时,编译器直接显示错误。
原因:造成这一现象的原因因为倘若真的可以让子类抛出的异常类型大于父类的异常类型,考虑这种情况 Person person = new SubPerson(),此时根据编译看左运行看右的原则,编译时testException()的所能抛出的异常类型为父类该方法抛出的类型,然而运行时子类的重写该方法时抛出的异常类型大于
实际所能接受的异常类型,这样必然会造成异常不能有效处理。
由此引发的一种极端情况,倘若父类没有设置throws,那么子类重写该方法时,子类只能手动在内部使用try-catchthrow 和 throws区别:throw 表示抛出一个异常类的对象,生成异常对象的过程。声明在方法体内。throws 属于异常处理的一种方式,声明在方法的声明处。4.自定义异常
//1.继承于现的异常结构:RuntimeException 、Exception
public class MyException extends RuntimeException {
//2.提供全局常量:serialVersionUID
static final long serialVersionUID = -7034897190745766939L;
//3.提供重载的构造器
public MyException() {
super();
}
public MyException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public MyException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public MyException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
protected MyException(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) {
super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace);
}
}一般来讲,自定义异常主要是根据不同的业务情况,能够给出更加细致的异常提示,帮助更好的解决bug
try {
int i = 10/0;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new MyException("数学异常!");
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号