vuex
状态管理
组件之间传值
父给子传
- 父组件
- 子组件
- props 接收
props: {
name: {
type: String,
required: true
}
}
- props 接收
子给父传
-
父组件
<number :num="number" @change="handelChange">
<number :num="number" @change="count = $event"> -
子组件
<a @click="handleAdd" href="javascript:void(0)">+// data props: { num: { type: Number, default: 1 } } // methods handleAdd() { this.count++ // 触发事件 this.$emit('change', this.count) }
兄弟组件传值 (Event bus)
- 参考链接
使用步骤
把 Foo.vue 中的 count 值传递给 Bar.vue
事件类似于方法,属于某个对象,要在同一个对象上触发和注册事件。所以创建一个负责通信的对象
-
创建 eventBus.js ,存储一个负责通信的 Vue 的实例(让搜有组件都能够使用)
import Vue from 'vue'
// 负责通信的 vue
const vue = new Vue()
export default vue -
在 Foo.vue 中触发事件
import eventHub from '@/eventHub'
……
// 合适的时机,触发事件
eventHub.$emit('change', this.count) -
在 Bar.vue 中注册事件
import eventHub from '@/eventHub'
……
created () {
eventHub.$on('change', (c) => {
this.num = c
})
}
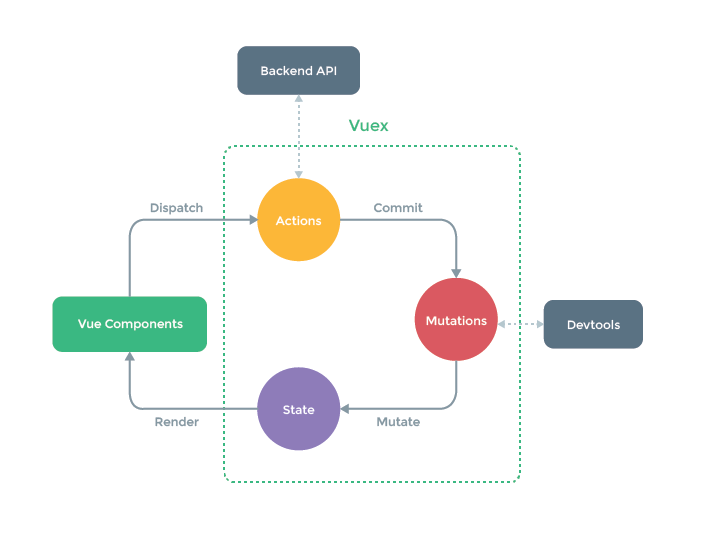
Vuex
Vuex 介绍
- 参考链接
- 如果项目比较复杂用过去的组件传值方式就比较困难(注意:小项目使用组件传值的方式没有问题)
- Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式
- 采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态
- Vuex 也集成到 Vue 的官方调试工具 devtools ,提供了:time-travel 调试、状态快照等功能
- vuex 管理状态,依然是响应式的
Vuex 快速体验
- 每一个 Vuex 应用的核心就是 store(仓库)
- “store”基本上就是一个容器,它包含着你的应用中大部分的状态 (state)
- Vuex 的状态存储是响应式的
- 你不能直接改变 store 中的状态
安装 Vuex
npm i vuex
创建仓库 Store
-
创建 Store src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutation: {
setCount (state) {
state.count++
}
}
})
export default store -
Vue 实例中配置 Store
// 注册 store
import store from './store'new Vue({ // 配置 store store, render: h => h(App) }).$mount('#app') -
组件中使用状态数据
// 使用 state 中的数据
{{ this.$store.state.count }}
// 调用 mutation 修改 state
this.$store.commit('setState') -
注意
- 通过提交 mutation 的方式,修改 state 状态
- 通过 devtools 追踪到状态的变化
核心概念
State
- Vuex 使用单一状态树,用一个对象就包含了全部的应用层级状态
- 使用计算属性简化组件中访问 State
// 在组件中
computed: {
count () {
return this.$store.state.count
}
}
// 使用 {{ count }}
Getter
- 如果对某个状态值进行计算的结果在多个组件中都需要使用,此时在多个组件中定义计算属性会变得重复
- Vuex 允许我们在 store 中定义“getter”(可以认为是 store 的计算属性)
- 定义 getter
// stote/index.js 中
getters: {
reverseMsg (state) {
return state.msg.split('').reverse().join('')
}
} - 组件中使用 getter {{ $store.getters.reverseMsg }}
- 定义 getter
Mutation
-
更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态的唯一方法是提交 mutation
-
Vuex 中的 mutation 非常类似于事件:每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的 事件类型 (type) 和 一个 回调函数 (handler)
-
回调函数会接受 state 作为第一个参数
- 定义 mutation
// stote/index.js 中
mutations: {
increment (state) { //increment就是时间类型
// 变更状态
state.count++
}
} - 组件中使用
this.$store.commit('setCount')
- 定义 mutation
-
提交载荷 (Payload)
- 向 store.commit 传入额外的参数,即 mutation 的 载荷(payload):
mutations: {
// n 即是载荷
increment (state, n) {
state.count += n
}
}
// 在组件中
this.$store.commit('increment', 10) - 在大多数情况下,载荷应该是一个对象,这样可以包含多个字段并且记录的 mutation 会更易读:
mutations: {
increment (state, payload) {
state.count += payload.amount
}
}
// 在组件中调用
this.$store.commit('increment', {
amount: 10
})
- 向 store.commit 传入额外的参数,即 mutation 的 载荷(payload):
-
对象方式的提交
-
提交 mutation 的另一种方式是直接使用包含 type 属性的对象:
// 组件中的调用
store.commit({
// mutation的名字
type: 'increment',
amount: 10
})
-
-
使用常量替代 Mutation 事件类型
-
注意
- Mutation 中的操作都是同步的 ,为了让 devtools 能够跟踪 state 的变化
- 如果想要做异步操作更新 state ,需要使用 Action
Action
Action 类似于 mutation,不同在于:
-
Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态
-
Action 可以包含任意异步操作
- store 中
// Action 函数接受一个与 store 实例具有相同方法和属性的 context 对象
// context.commit() / context.state
increment (context) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('increment')
}, 1000)
} - 组件中调用,Action 通过 store.dispatch 方法触发:
this.$store.dispatch('increment')
- store 中
-
以载荷方式分发
// 以载荷形式分发
store.dispatch('increment', {
amount: 10
})// 以对象形式分发 store.dispatch({ type: 'increment', amount: 10 })
辅助函数
mapState
-
可以使用 mapState 简化生成计算属性
// 在组件中
import { mapState } from 'vuex'computed: mapState({
// msg: function (state) {
// return state.msg
// }
// msg: (state) => state.msg,
// 可以重新命名
message: 'msg'
}) -
当映射的计算属性的名称与 state 的子节点名称相同时,我们也可以给 mapState 传一个字符串数组。
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
computed: mapState(['msg'])
-
如果组件中有自己的计算属性,这个时候 mapState 要配合对象展开运算符 — 推荐
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
computed: {
localComputed () { /* ... */ },
// 使用对象展开运算符将此对象混入到外部对象中
...mapState({
// ...
})
}
mapGetter
-
mapGetters 辅助函数仅仅是将 store 中的 getter 映射到局部计算属性:
// 在组件中
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'computed: {
// 使用对象展开运算符将 getter 混入 computed 对象中
...mapGetters([
'reverseMsg',
'anotherGetter',
// ...
])
} -
如果你想将一个 getter 属性另取一个名字,使用对象形式:
// 在组件中
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'computed: {
// 使用对象展开运算符将 getter 混入 computed 对象中
...mapGetters({
rmsg: 'reverseMsg',
anotherGetter: 'anotherGetter'
})
}
mapMutation
-
注意 mutation 映射的是方法 methods
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapMutations([
'increment', // 将this.increment()映射为this.$store.commit('increment')// `mapMutations` 也支持载荷: 'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('incrementBy', amount)` ]), ...mapMutations({ add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')` }) }}
mapAction
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapActions([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
// `mapActions` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapActions({
add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
})
}
}
Module
- 由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象
- Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)
- 每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter
基本演示
// store/index.js 中
const moduleA = {
state: {
acount: 1
},
mutations: {
setACount (state) {
state.acount++
}
},
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA
}
})
// 组件中使用模块A
// 访问状态
this.$store.state.a.acount // -> moduleA 的状态
// 提交 commit
this.$store.commit('setACount')
命名空间
// 创建 store/modules/moduleA.js
export default {
// 开启命名空间
namespaced: true,
state: {
acount: 10
},
mutations: {
setACount (state) {
state.acount++
}
}
}
// 组件中使用
computed: {
// 映射命名空间下的状态数据
...mapState({
acount: state => state.moduleA.acount,
bcount: state => state.moduleB.bcount,
})
// ...mapState('moduleB', ['bcount']),
// ...mapState('moduleA', ['acount'])
},
methods: {
// 调用 this['moduleB/setBCount']()
...mapMutations(['moduleB/setBCount'], ['moduleA/setACount']),
// 调用 this.setBCount()
// ...mapMutations('moduleB', ['setBCount']),
}
官方示例




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号