通过注解实现IOC
实现实体类
package com.zhongge.entity;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @ClassName User
* @Description TODO
* @Author zhongge
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Component("user01")
public class User {
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", address=" + address +
'}';
}
@Value("李华")
private String name;
@Resource
private Address address;
}
package com.zhongge.entity;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @ClassName Address
* @Description TODO
* @Author zhongge
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Component
public class Address {
public String getLoc() {
return loc;
}
public void setLoc(String loc) {
this.loc = loc;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address{" +
"loc='" + loc + '\'' +
'}';
}
@Value("毕节")
private String loc;
public Address(String loc) {
this.loc = loc;
}
public Address() {
}
}
测试结果
package com.zhongge.test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
/**
* @ClassName Main
* @Description TODO
* @Author zhongge
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//通过注解获取IOC容器
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("com.zhongge.entity");
//通过IOC容器获取对象
System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("user01"));
}
}
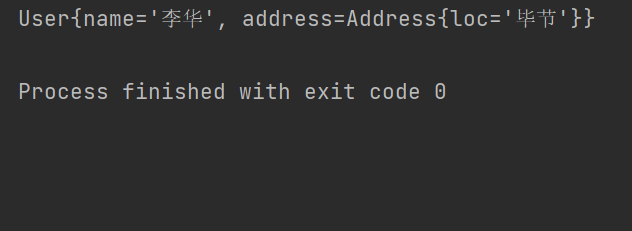
结果:
补充知识
要通过注解实现 Spring IOC,需遵循以下核心步骤,结合注解扫描、Bean 标记和依赖注入来完成容器管理:
一、核心注解说明
Spring 提供了一系列注解来替代 XML 配置,实现“零 XML”式 IOC:
| 注解 | 作用 |
|---|---|
@Component |
通用组件注解,标记类为 Spring 管理的 Bean(可用于任何层)。 |
@Service |
语义化注解,专用于业务逻辑层(Service 层),功能同 @Component。 |
@Repository |
语义化注解,专用于数据访问层(DAO 层),功能同 @Component。 |
@Controller |
语义化注解,专用于控制层(如 SpringMVC 的 Controller)。 |
@Autowired |
自动依赖注入,按类型匹配 Bean(可结合 @Qualifier 按名称匹配)。 |
二、步骤 1:开启注解扫描(替代 XML 的 <context:component-scan>)
在 Spring 配置类中用 @ComponentScan 指定需要扫描的包(若用 XML 则需配置 <context:component-scan>)。
方式 1:纯注解配置(推荐 Spring Boot)
@Configuration // 标记为 Spring 配置类
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.zhongge") // 扫描指定包及其子包下的注解
public class AppConfig {
// 无需额外配置,注解扫描由 @ComponentScan 完成
}
方式 2:XML 配置(兼容传统 Spring)
若仍需保留 XML,在 applicationContext.xml 中添加:
<!-- 开启注解扫描,Spring 会自动处理 @Component/@Service 等注解 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zhongge"/>
三、步骤 2:用注解标记 Bean(替代 XML 的 <bean> 标签)
将需要由 Spring 管理的类用 @Component/@Service/@Repository/@Controller 标记。
以你之前的 Address 和 Student 为例:
// com.zhongge.entity.Address
@Component // 标记为 Spring Bean(也可用 @Service/@Repository 等,语义化可选)
public class Address {
private String loc;
// Getter/Setter/toString 略
}
// com.zhongge.entity.Student
@Component
public class Student {
@Autowired // 自动注入 Address 类型的 Bean
private Address address;
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
// 构造器/Setter/toString 略
}
四、步骤 3:依赖注入(用 @Autowired 替代 XML 的 <property>/<constructor-arg>)
@Autowired 支持字段注入、构造器注入、Setter 注入三种方式,推荐构造器注入(更符合 Spring 官方推荐)。
1. 字段注入(最简单,直接在属性上标记)
@Component
public class Student {
@Autowired // 直接注入 Address 类型的 Bean
private Address address;
// 其他属性略...
}
2. 构造器注入(Spring 推荐,更利于依赖检查)
@Component
public class Student {
private final Address address;
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
@Autowired // 构造器上标记,Spring 会自动传入 Address Bean
public Student(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
// Setter/toString 略...
}
3. Setter 注入(需提供 Setter 方法)
@Component
public class Student {
private Address address;
// 其他属性略...
@Autowired // 在 Setter 方法上标记
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
五、测试注解版 IOC(编写 Main 类)
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 加载注解配置类(或 XML 配置)
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
// 或加载 XML:new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Student student = context.getBean(Student.class);
System.out.println(student); // 应输出包含 Address 的 Student 对象
}
}
六、进阶:多 Bean 冲突时的处理
若同一接口有多个实现类(如 Address 有子类 HomeAddress 和 SchoolAddress),需结合 @Qualifier 按名称注入:
// 多个 Address 实现类
@Component("homeAddress")
public class HomeAddress extends Address { ... }
@Component("schoolAddress")
public class SchoolAddress extends Address { ... }
// Student 中指定注入名称
@Component
public class Student {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("homeAddress") // 明确注入名称为 "homeAddress" 的 Bean
private Address address;
// ...
}
七、注解 vs XML:优缺点对比
| 方式 | 优点 | 缺点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 注解 | 简洁、无 XML 冗余、开发效率高 | 配置与代码耦合(需修改类) | 大多数场景,尤其是 Spring Boot 项目 |
| XML | 配置与代码分离、便于统一管理 | 冗余代码多、维护成本高 | 需频繁修改配置(如环境切换)、旧项目兼容 |
而且注解一次只可以实现一个类
通过注解实现 IOC 后,Spring 会自动扫描、创建 Bean 并完成依赖注入,大幅简化了配置流程。如果你的项目是 Spring Boot,只需在主类上加 @SpringBootApplication(内部包含 @ComponentScan),即可零配置实现 IOC。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号