广度优先搜索
广度优先搜索概念可自行查阅
用二叉树的层序遍历会容易理解很多,如图
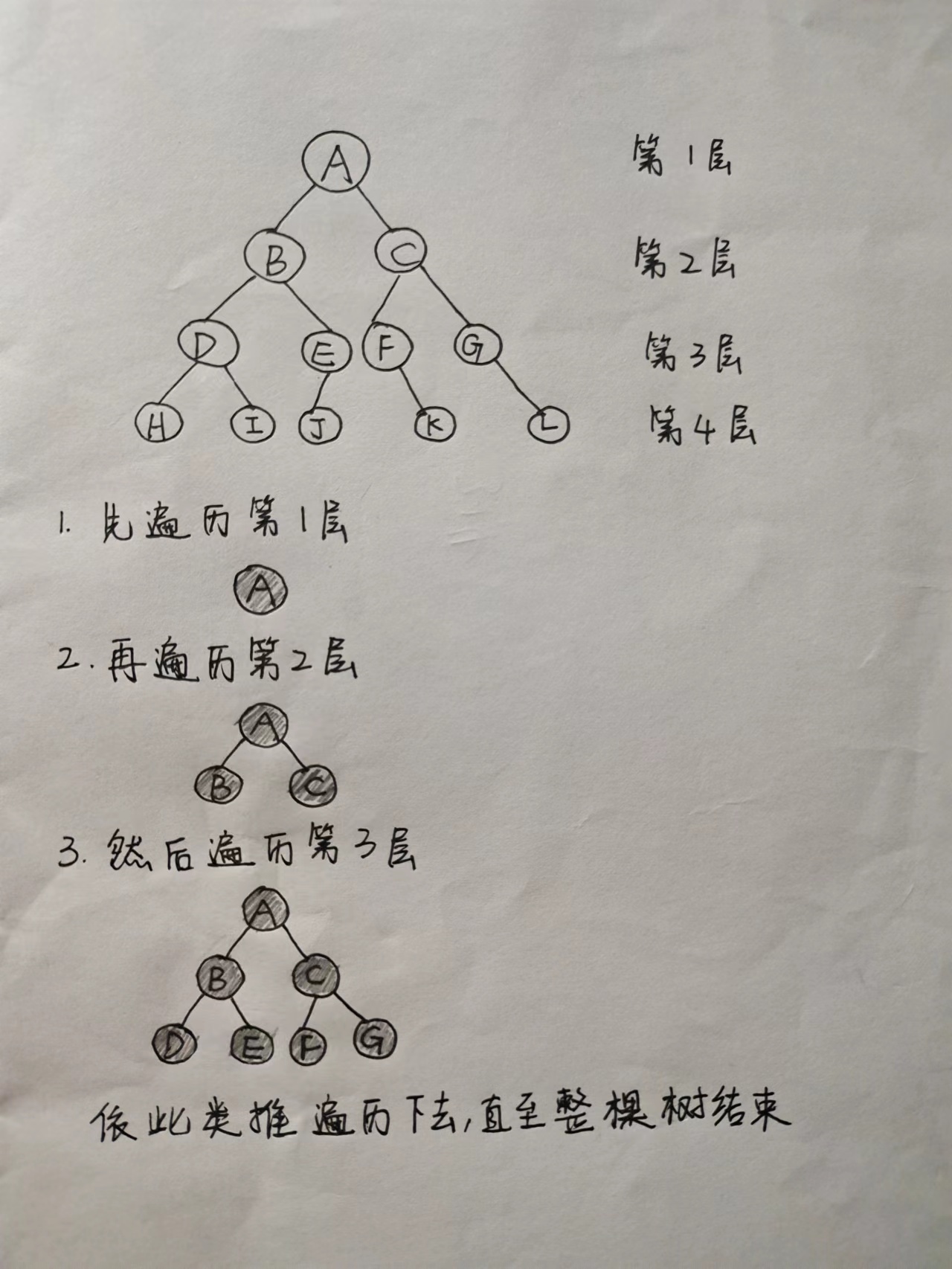
层序遍历怎么实现呢 要用到队列(先进先出):

这个题的一个难点就是你要把每一层的元素分开,一个一维数组里放一层元素,在C语言写法里可以设一个last参数记录上一层遍历结束时的rear值,这样last与front之差即上一层元素的个数
c++写法就简单一些,上一层元素个数即队列的大小
c
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * struct TreeNode *left; 6 * struct TreeNode *right; 7 * }; 8 */ 9 10 11 /** 12 * Return an array of arrays of size *returnSize. 13 * The sizes of the arrays are returned as *returnColumnSizes array. 14 * Note: Both returned array and *columnSizes array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). 15 */ 16 int** levelOrder(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){ 17 *returnSize = 0; 18 if(root == NULL) 19 return NULL; 20 int** res = malloc(sizeof(int *)*2000); 21 *returnColumnSizes = malloc(sizeof(int )*2000); 22 struct TreeNode* queue[2000]; 23 int rear = 0,front = 0; 24 queue[rear ++] = root; 25 while(front < rear){ 26 int last = rear; 27 int col = 0; 28 res[*returnSize] = malloc(sizeof(int )*(last - front)); 29 struct TreeNode* cur; 30 for(;front < last;){ //可以改为while(front < last),emm...我个人更喜欢for循环 因为时间效率高一点 31 cur = queue[front ++]; 32 res[(*returnSize)][col ++] = cur -> val; 33 if(cur -> left) 34 queue[rear ++] = cur -> left; 35 if(cur -> right) 36 queue[rear ++] = cur -> right; 37 38 } 39 (*returnColumnSizes)[(*returnSize)++] = col; 40 } 41 return res; 42 }
c++
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 8 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 9 * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} 10 * }; 11 */ 12 class Solution { 13 public: 14 vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) { 15 vector<vector<int> > res; 16 if(! root) 17 return res; 18 queue<TreeNode*> q; 19 q.push(root); 20 while(!q.empty()){ 21 res.push_back(vector<int>()); 22 int col = q.size(); 23 for(int i = 0;i < col;i ++){ 24 auto cur = q.front(); 25 q.pop(); 26 res.back().push_back(cur -> val); 27 if(cur -> left) 28 q.push(cur -> left); 29 if(cur -> right) 30 q.push(cur -> right); 31 } 32 } 33 return res; 34 } 35 };
蓝桥杯 跳马
1.可以把这个题抽象为一棵树,(a,b)为根节点,因为马的下一步有八个位置,把这八个位置里可到达的点当根节点的子节点,令根节点那层为第0层,所以此时子节点这层就是第一层,然后把第一层的每个子节点当根节点,找出第二层的所有子节点对每一层以此类推
2.然后你会发现目标点(c,d)在哪一层 马就需要跳几步,比如目标点就是在根节点处那么马就需要跳0步,在第一层就跳一步。所以我们只需找到目标点在哪一层,即对树进行层序遍历
3.树的层序遍历可以用队列来实现
c
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int next[8][2]={-2,-1,-2,1,-1,-2,-1,2,1,-2,1,2,2,-1,2,1}; int visited[9][9]; int queue[64]; int bfs(int a,int b,int c,int d) { int i,rear=0,front=0; visited[a][b]=1; queue[rear++]=a*8+b; int last,rank=0,flag=0; while(front<rear) { int last=rear; rank++; while(front<last) { int cur=queue[front++]; int row=cur/8,col=cur%8; for(i=0;i<8;i++) { int px=row+next[i][0]; int py=col+next[i][1]; if(px==c&&py==d) return rank; if(px>=1&&px<=8&&py>=1&&py<=8&&visited[px][py]==0) { queue[rear++]=px*8+py; visited[px][py]=1; } } } } return -1; } int main() { int a,b,c,d,cnt; scanf("%d%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c,&d); if(a==c&&b==d) cnt=0; else cnt=bfs(a,b,c,d); printf("%d",cnt); return 0; }
c++
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> using namespace std; int next[8][2]={-2,-1,-2,1,-1,-2,-1,2,1,-2,1,2,2,-1,2,1}; int visited[9][9]; int bfs(int a,int b,int c,int d){ visited[a][b] = 1; queue<int> q; q.push(a * 8 + b); int row = 0; while(!q.empty()){ int s = q.size(); row ++; for(int j = 0;j < s;j ++){ int cur = q.front(); q.pop(); int x = cur / 8,y = cur % 8; for(int i = 0;i < 8;i ++){ int px = x + next[i][0]; int py = y + next[i][1]; if(px == c && py == d) return row; if(px > 0 && px <= 8 && py > 0 && py <= 8 && visited[px][py] == 0){ visited[px][py] = 1; q.push(px * 8 + py); } } } } return -1; } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int a,b,c,d; cin >> a >> b >> c >> d; if(a == c && b == d) cout << 0; else cout << bfs(a,b,c,d); return 0; }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号