1. 说明
/*
* 定义 :
* def mapPartitions[U: ClassTag](
* f: Iterator[T] => Iterator[U],
* preservesPartitioning: Boolean = false): RDD[U]
* 功能 :
* 1. 以分区为单位,对rdd的元素做一些处理(转换、过滤、排序、聚合)
* 2. 将待处理的数据以分区为单位发送到计算节点进行处理,这里的处理是指可以进行任意的处理,哪怕是过滤数据
* 3. 获取每个分区的迭代器,在函数中通过这个分区的迭代器对整个分区的数据进行操作
* 4. 传入一个迭代器,返回一个迭代器
* note :
* 1. 会将整个分区的数据都加载到内存处理,如果不及时释放 可能会造成内存溢出
* */
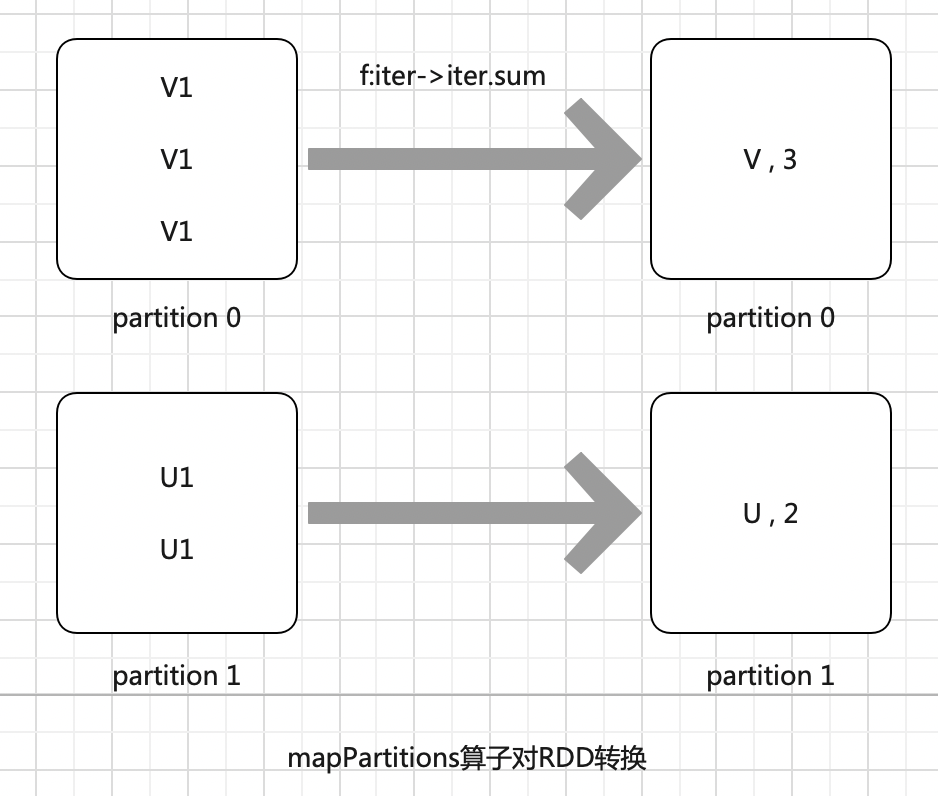
//1. mapPartitons
object mapPartitionsTest extends App {
val sparkconf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("mapPartitionsTest")
val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(sparkconf)
val rdd: RDD[Int] = sc.makeRDD(List(1, -2, 3, 14, 1, -10, -100), 2)
// 对rdd 做绝对值转换
private val absRdd: RDD[Int] = rdd.mapPartitions(
iter => {
val list = iter.toList
println("处理分区 :" + list.mkString(","))
list.iterator
}
)
println(s"rdd1 :${absRdd.collect().mkString(",")}")
sc.stop()
}
2. map 和 mapPartitons 的区别
//1. 处理数据角度
map :
输入: 处理的数据单位 是Rdd的元素(一个一个元素处理)
输出: 处理后Rdd元素的数据类型
mapPartitons :
输入: 处理的数据单位 是Rdd的分区数据的迭代器(批处理)
输出: 处理后的迭代器
//2. 功能角度
map : 只是对元素(类型或值)的转换,元素个数不会改变
mapPartitons : 对rdd分区做转换(传入一个迭代器,返回一个迭代器),分区个数不会改变,元素个数可能会被改变
//3. 性能角度
map : 同一分区串行处理,效率低 (每条数据调用 cleanF,调用完后会释放内存)
mapPartitons : 批量处理,效率高
note : 由于将 分区内数据都读取到内存,当数据量过大时,可能造成内存溢
//4. 使用角度
map : cleanF 逻辑简单(没有有io连接),分数数据量大
mapPartitons : cleanF 逻辑复杂(有io连接,如 数据库、网络TCP、文件流,减少创建、关闭连接次数,来提高效率),分数数量小
//5. 源码角度
def map[U: ClassTag](f: T => U): RDD[U] = withScope {
val cleanF = sc.clean(f) //闭包清除
new MapPartitionsRDD[U, T](this, (_, _, iter) => iter.map(cleanF))
}
iter.map(cleanF) 遍历分区数据,并对每条数据调用 cleanF (Task内每条数据都会调用 cleanF)
def mapPartitions[U: ClassTag](
f: Iterator[T] => Iterator[U],
preservesPartitioning: Boolean = false): RDD[U] = withScope {
val cleanedF = sc.clean(f) //闭包清除
new MapPartitionsRDD(
this,
(_: TaskContext, _: Int, iter: Iterator[T]) => cleanedF(iter),
preservesPartitioning)
}
cleanedF(iter) 将整个分区数据作为参数,每个分区只调用一次 cleanedF (Task内只会调用一次 cleanF)
3. 需求 : 分别计算分区内 最大值
object mapPartitionsTestByMax extends App {
val sparkconf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("mapPartitionsTest")
val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(sparkconf)
val rdd: RDD[Int] = sc.makeRDD(List(1, -2, 3, 14, 1, -10, -100), 2)
// 获取每个分区内的最大值
// note : f: Iterator[T] => Iterator[U]
private val maxRdd: RDD[Int] = rdd.mapPartitions(
iter => List(iter.max).iterator //获取 iter内最大值,再将最大值转为List,iterator
)
println(s"rdd1 :${maxRdd.collect().mkString(",")}")
sc.stop()
}
4. 需求 : 分区内排序
object mapPartitionsTestBySort extends App {
val sparkconf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("mapPartitionsTest")
val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(sparkconf)
val rdd: RDD[Int] = sc.makeRDD(List(1, -2, 3, 14, 1, -10, -100, 8), 2)
// 分区内排序
// note : f: Iterator[T] => Iterator[U]
private val sortRdd: RDD[Int] = rdd.mapPartitions(
iter => iter.toList.sorted.iterator
)
println(s"rdd1 :${sortRdd.collect().mkString(",")}")
sc.stop()
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号