二叉树是数据结构中的非常重要的概念;对初学者来讲这是数据结构的承上启下部分。
看二叉树有一段时间了,这里做一个相应的总结。
需要掌握的术语:
度:1.结点的度:子树个数;
2. 树的度:结点度的最大值;
叶子 :度==0的结点;(终端结点)
分支:度!=0的结点;(非终端结点)
孩子:某结点的子树的根节点;
双亲:与孩子对应;
兄弟:同样双亲;
路径长度:经过的边数;
祖先:直系关联的上层;
子孙:与祖先对应;
有序树:交换各结点位置树发生变化;
无序树:反之;
------------------------------------------------------
二叉树的递归建树过程:(前序建树)

Node *Bitree::Creat(Node *p) { DataType ch; cin>>ch; if(ch!='#') p=NULL; else { p=new Node; p->A=ch; p->Left=Creat(p->Left); p->Right=Creat(p->Right); } Root=p; return p; }
二叉树的递归遍历操作:(依旧用前序为例)

1 void *Bitree::Print(Node *p) 2 { 3 if(p==NULL) 4 return; 5 cout<<p->A<<' '; 6 Print(p->Left); 7 Print(p->Right); 8 return; 9 }
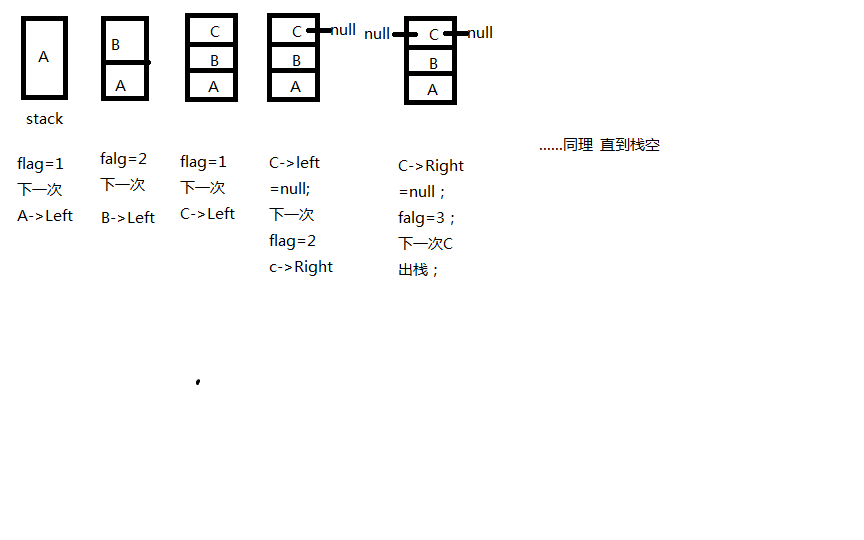
二叉树非递归建树过程:
方法:
用栈来控制进出;
然后当flag==1;表示需要建立栈顶元素的左孩子;
flag==2;表示需要建立栈顶元素的右孩子;
flag==3;表示右孩子建立完成需要出栈;
假设:ABC###D##

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #ifndef BITREE 4 #define BITREE 5 typedef char DataType; 6 struct Node 7 { 8 DataType A; 9 Node *Left,*Right; 10 }; 11 class Bitree 12 { 13 Node *Root; 14 public: 15 Bitree(){Root=NULL;} 16 void Creat(); 17 void Remove(); 18 void Sort(); 19 void Print(Node *p)const; 20 Node *GetRoot(); 21 }; 22 void Bitree::Creat() 23 { 24 Node *stack[100];int top=-1; 25 char ch; 26 cin>>ch; 27 int flag=1; 28 if(ch=='#') 29 return; 30 Root=new Node; 31 Root->A=ch; 32 Root->Left=NULL; 33 Root->Right=NULL; 34 35 stack[++top]=Root; 36 while(top!=-1) 37 { 38 Node *p; 39 40 41 if(flag==1) 42 { 43 cin>>ch; 44 if(ch=='#') 45 { 46 flag=2; 47 } 48 else 49 { 50 p=new Node; 51 p->A=ch; 52 p->Left=NULL; 53 p->Right=NULL; 54 stack[top]->Left=p; 55 stack[++top]=p; 56 flag=1; 57 } 58 } 59 else if(flag==2) 60 { 61 cin>>ch; 62 if(ch=='#') 63 { 64 flag=3; 65 } 66 else 67 { 68 p=new Node; 69 p->A=ch; 70 p->Left=NULL; 71 p->Right=NULL; 72 stack[top]->Right=p; 73 stack[++top]=p; 74 flag=1; 75 } 76 } 77 else if(flag==3) 78 { 79 Node *temp; 80 temp = stack[top--]; 81 while (top >= 0 && stack[top]->Right == temp) 82 --top; 83 flag=2; 84 } 85 } 86 } 87 void Bitree::Print(Node *p)const 88 { 89 if(p==NULL) 90 return; 91 cout<<p->A<<' '; 92 Print(p->Left); 93 Print(p->Right); 94 return; 95 } 96 Node *Bitree::GetRoot() 97 { 98 return Root; 99 } 100 #endif 101 int main() 102 { 103 Bitree B; 104 B.Creat(); 105 B.Print(B.GetRoot()); 106 }
二叉树的递归求深度
int Bitree::Depth(Node *p) { if(p==NULL) { return 0; } int left=1; int right=1; left+=Depth(p->Left); right+=Depth(p->Right); return left>right?left:right; }
二叉树的非递归求深度
方法:层序遍历每一层Depth++即可;
int TreeDepth(TreeNode* pRoot) { queue<TreeNode*> q; if(!pRoot) return 0; q.push(pRoot); int level=0; while(!q.empty()){ int len=q.size(); level++; while(len--){ TreeNode* tem=q.front(); q.pop(); if(tem->left) q.push(tem->left); if(tem->right) q.push(tem->right); } } return level; }
二叉树前序遍历非递归写法;
void Bitree::PreOrder(Node *p) { Node *stack[100]; int top=-1; while(p!=NULL&&top!=-1) { while(p!=NULL) { cout<<p->A; stack[++top]=p; p=p->Left; } if(top!=-1) { p=stack[top--]; p=p->Right; } } }
二叉树删除子树;
方法:
先找到删除子树的双亲,然后双亲结点赋空;把子树的每一个地址前序遍历入栈;
对每一个地址进行delete;
二叉树层序遍历递归队列写法:

1 //递归写法 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 #include<queue> 5 struct Node 6 { 7 struct Node *Left,*Right; 8 char data; 9 }; 10 class Bitree 11 { 12 queue<Node *> s; 13 Node *root; 14 public: 15 Bitree(){root=NULL;} 16 Node *Create(Node *); 17 void Print(Node *); 18 Node *Getroot(); 19 void CCC(); 20 }; 21 Node *Bitree::Create(Node *p) 22 { 23 char ch; 24 cin>>ch; 25 if(ch=='#') 26 p=NULL; 27 else 28 { 29 p=new Node; 30 p->data=ch; 31 p->Left=Create(p->Left); 32 p->Right=Create(p->Right); 33 34 } 35 root=p; 36 return p; 37 } 38 void Bitree::Print(Node *p) 39 { 40 cout<<p->data<<' '; 41 if(p->Left!=NULL) 42 s.push(p->Left); 43 if(p->Right!=NULL) 44 s.push(p->Right); 45 s.pop(); 46 if(!s.empty()) 47 Print(s.front()); 48 } 49 void Bitree::CCC() 50 { 51 s.push(root); 52 Print(s.front()); 53 } 54 Node * Bitree::Getroot() 55 { 56 return root; 57 } 58 int main() 59 { 60 Bitree l; 61 l.Create(l.Getroot()); 62 l.CCC(); 63 }
二叉树层序遍历递归用深度求:

1 //递归写法 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<queue> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 struct Node 7 { 8 char A; 9 Node *Left,*Right; 10 }; 11 class Bitree 12 { 13 Node *Root; 14 queue<Node *> Dui; 15 public: 16 Bitree(){Root=NULL;}; 17 Node *Create(Node *); 18 int Depth(Node* pRoot);//计算二叉树深度; 19 void Print(Node *p,int level); 20 void ARR(Node *p); 21 Node * Back(); 22 }; 23 Node *Bitree::Create(Node *p) 24 { 25 char ch; 26 cin>>ch; 27 if(ch=='#') 28 p=NULL; 29 else 30 { 31 p=new Node ; 32 p->A=ch; 33 p->Left=Create(p->Left); 34 p->Right=Create(p->Right); 35 } 36 Root=p; 37 return p; 38 } 39 Node * Bitree::Back() 40 { 41 return Root; 42 } 43 void Bitree::Print(Node *p,int level) 44 { 45 if(p==NULL||level<1) 46 return; 47 else if(level==1) 48 { 49 cout<<p->A<<' '; 50 return; 51 } 52 Print(p->Left,level-1); 53 Print(p->Right,level-1); 54 55 } 56 void Bitree::ARR(Node *p) 57 { 58 if(p==NULL) 59 return; 60 int depth=Depth(p); 61 62 int i; 63 for(i=1;i<=depth;i++) 64 { 65 Print(p,i); 66 67 } 68 69 } 70 int Bitree::Depth(Node* pRoot)//计算二叉树深度 71 { 72 if(pRoot==NULL)//如果pRoot为NULL,则深度为0,这也是递归的返回条件 73 return 0; 74 //如果pRoot不为NULL,那么深度至少为1,所以left和right=1 75 int left=1; 76 int right=1; 77 left+=Depth(pRoot->Left);//求出左子树的深度 78 right+=Depth(pRoot->Right);//求出右子树深度 79 80 return left>right?left:right;//返回深度较大的那一个 81 } 82 int main() 83 { 84 Bitree T; 85 T.Create(T.Back()); 86 T.ARR(T.Back()); 87 return 0; 88 }
判断完全二叉树的方法:
在队列里遍历,空树也存;
然后判断队列书否为空;
bool Bitree::Complete(Node *p) { s.push(p); while((p=s.front())!=NULL) { s.pop(); s.push(p->left); s.push(p->right); } while(!s.empty()) { p=s.front(); s.pop(); if(p!=NULL) { return false; } } return true; }
求二叉树宽度;

1 void Bitree::Print(Node *p) 2 { 3 if(p==NULL) 4 { 5 cout<<0; 6 return; 7 } 8 int Lastwidth=0; 9 int MaxWidth=0; 10 s.push(Root); 11 p=Root; 12 MaxWidth=s.size(); 13 while(!s.empty()) 14 { 15 Lastwidth=s.size(); 16 while(Lastwidth!=0) 17 { 18 p=s.front(); 19 s.pop(); 20 if(p->Left!=NULL) 21 s.push(p->Left); 22 if(p->Right!=NULL) 23 s.push(p->Right); 24 Lastwidth--; 25 } 26 MaxWidth=MaxWidth>s.size()?MaxWidth:s.size(); 27 } 28 cout<<MaxWidth; 29 return; 30 }
----------- 一剑天涯-------------




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号