.发布题目集1~3的总结性Blog
前言:
1.知识点:
1.java中的基础程序语法
2.数据的输入与输出;
3.java中变量的构造;
4.java中运算符的使用
5.类的构造方法、方法的调用、参数传递、对象的构造与使用;
6.Java中的控制流程(循环结构、控制结构等;
7.学习编写结构清晰、逻辑正确、功能完善的java代码;
8.java方法(Method);
2.题量以及难度:
- 第一次题集总量略多但单题难度不高都是比较基础的题目代码行数都不高;
- 第二次题集数量中等但题目难度偏高要灵活构造类方法;
- 第三次题集数量是最少的题集但单题难度过高需要灵活掌握类的使用以及封装的思想以及正则表达式的灵活运用;
设计与分析:
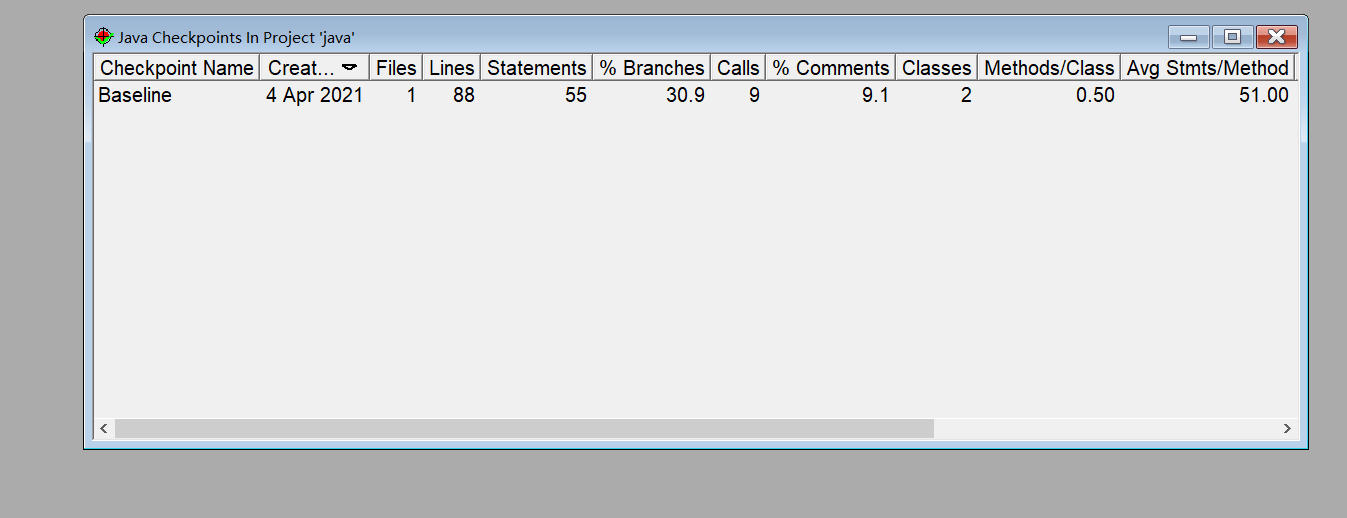
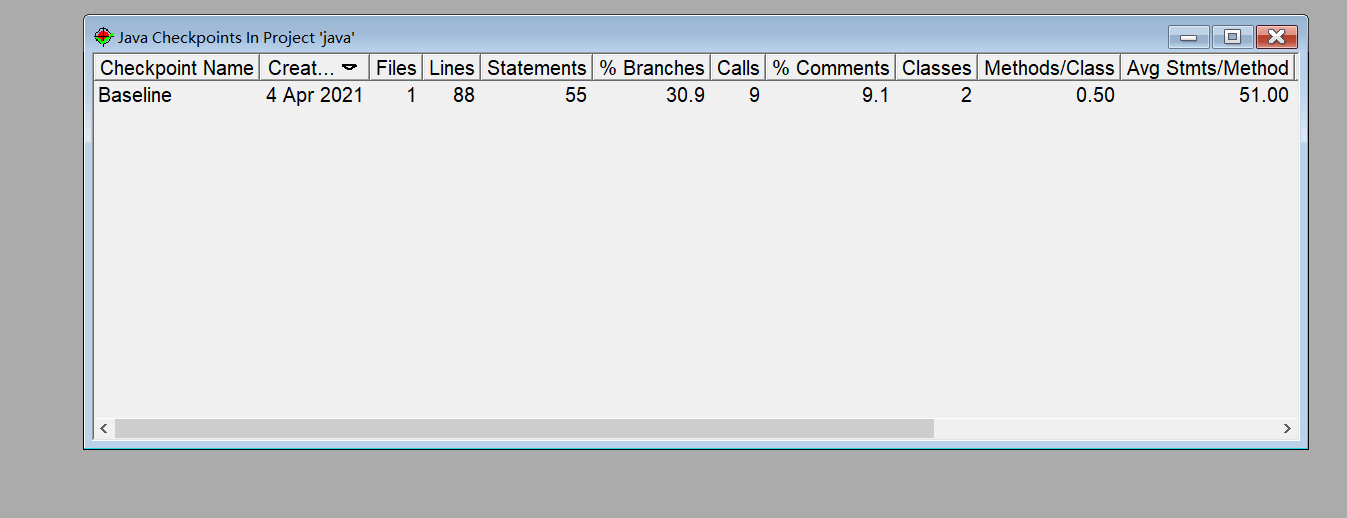
题集1的7-8生成分析报告
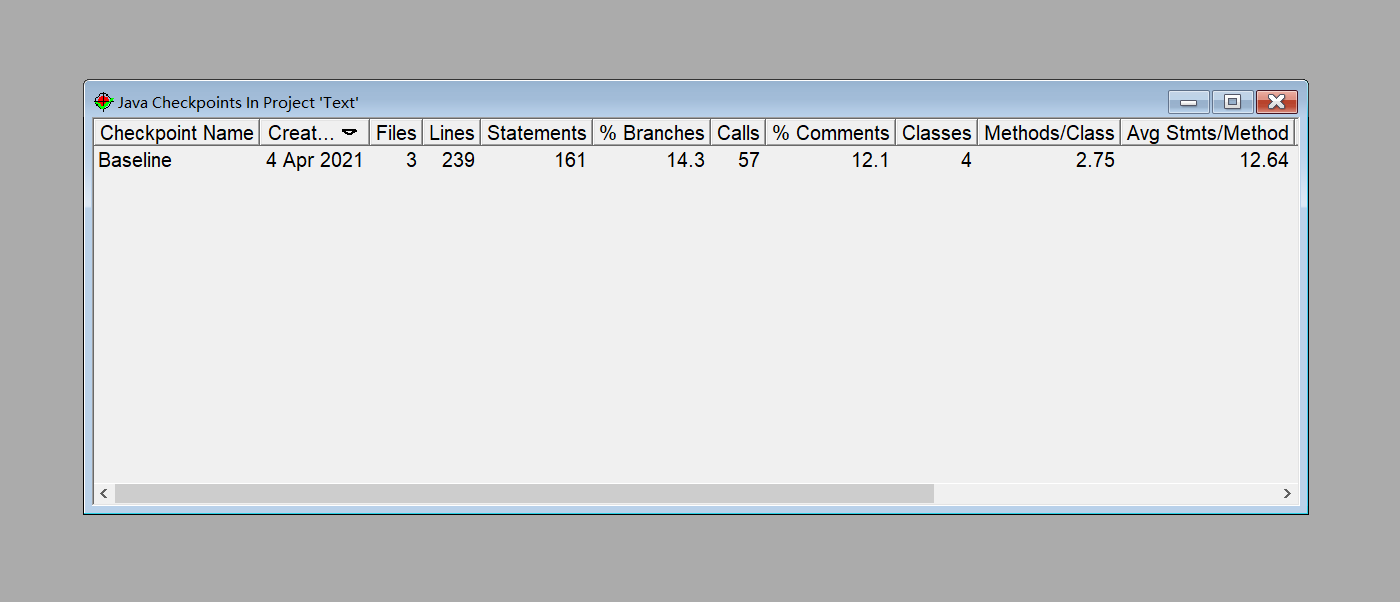
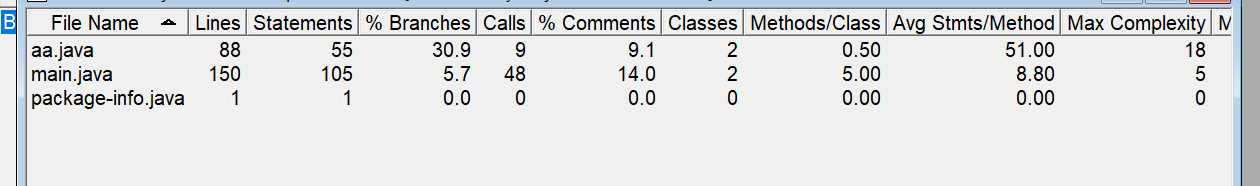
题集2中的7-4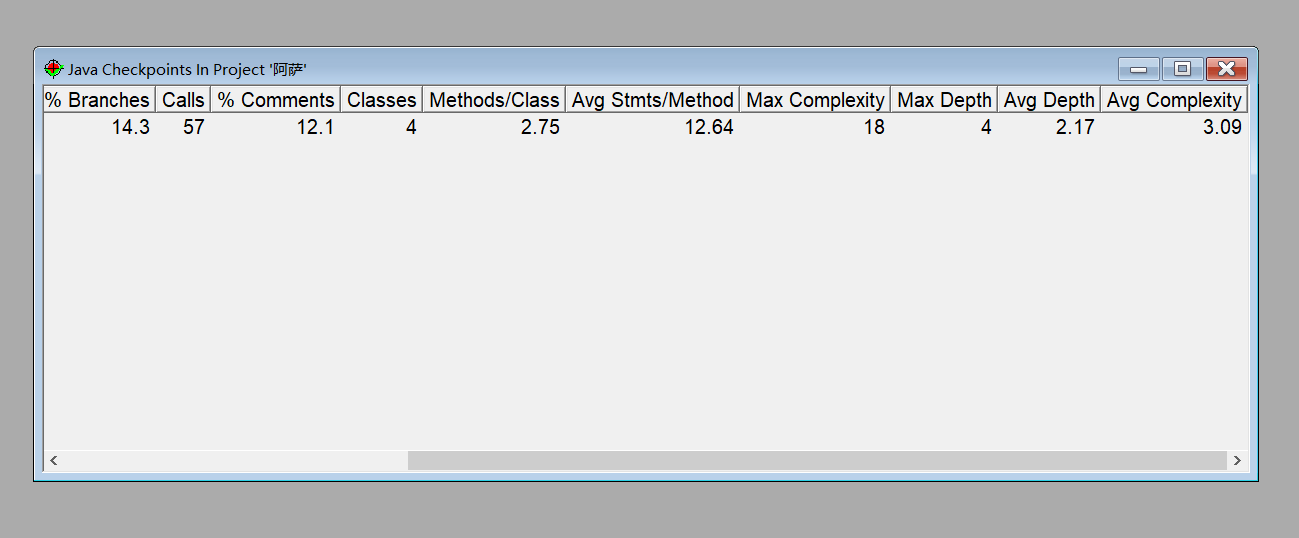
题集2中的7-5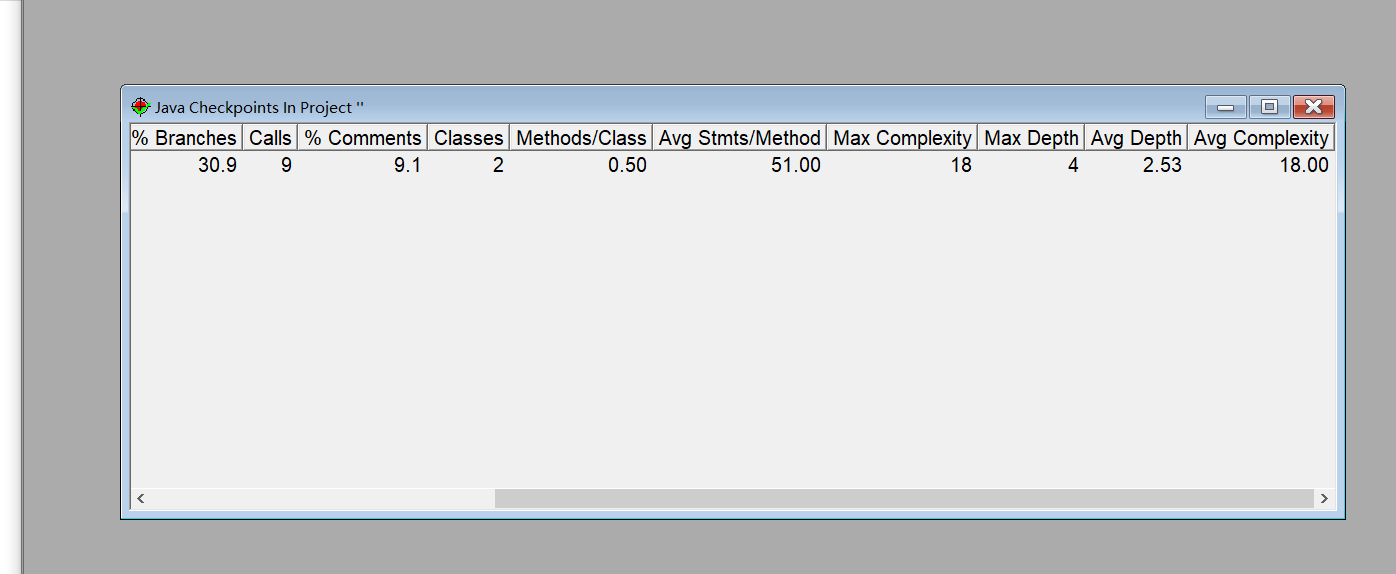
题集3中的7-2
采坑心得:
题集 1 的7- 8
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
float a= input.nextFloat();
float b= input.nextFloat();
float c= input.nextFloat();
if((a>=1)&&(a<=200)&&(b>=1)&&(b<=200)&&(c>=1)&&(c<=200))
{
if(a+b>c&&a+c>b&&c+b>a)
{
if(a==b&&b==c)
{
System.out.println("Equilateral triangle");
}
else if(a==b||a==c||b==c)
{
if(a*a+b*b==c*c||a*a+c*c==b*b||b*b+c*c==a*a)
{
System.out.println("Isosceles right-angled triangle");
}
System.out.println("Isosceles triangle");
}
else if((a*a+b*b==c*c)||(a*a+c*c==b*b)||(c*c+b*b==a*a))
{
System.out.println("Right-angled triangle");
}
else
{
System.out.println("General triangle");
}
}
else
{
System.out.println("Not a triangle");
}
}
else
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
}
其中数据合法(及可构造成为三角形的数据)以及对于多个隐含条件的逻辑关系可以合理安排以及对于多种三角形的类型需要注意逻辑关系很容易有逻辑漏洞其余并不过多问题。
7-2 合并两个有序数组为新的有序数组
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int x=input.nextInt();
int[]a=new int[x];
for(int i=0;i<x;i++)
a[i]=input.nextInt();
int y=input.nextInt();
int[]b=new int[y];
for(int i=0;i<y;i++)
b[i]=input.nextInt();
int lena = a.length;
int lenb = b.length;
int[] c = new int[lena + lenb];
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
while (i < lena && j < lenb) {
if (a[i] < b[j])
c[k++] = a[i++];
else
c[k++] = b[j++];
}
while (i < lena)
c[k++] = a[i++];
while (j < lenb)
c[k++] = b[j++];
for (int m = 0; m < c.length; m++)
System.out.print(c[m]+" ");
}
}
对输入的数据进行冒泡排序即可还有就是对于数据输出的格式需要注意以及对于需要多调试几次。
题集2中的7-4
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = input.nextInt();
int month = input.nextInt();
int day = input.nextInt();
int days=checkInputValidity(year, month, day);
if(days==1)
{
int[] aa=new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
if(isLeapYear(year))
aa[2] = 29;
int a = 0,b = 0,c = 0;
if(checkInputValidity(year,month,day)==1) {
if(month==12) {
if(day==aa[month]) {
a = year+1;
b = 1;
c = 1;}
if(day>0&&day<aa[month])
{a = year;
b = month;
c =day +1;
}
}
if(month<12) {
if(day==aa[month]) {
a = year;
b = month + 1;
c = 1;}
if(day>0&&day<aa[month])
{a = year;
b = month;
c = day+1;
}
}
System.out.println("Next date is:"+a+"-"+b+"-"+c);
}
}
else
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) {
boolean isLeapYear = (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 !=0 )||year % 400 == 0;
return isLeapYear;
}
public static int checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day)
{
int a=0;
int[] mon1=new int[]{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int[] mon2=new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
if(year>=1820&&year<=2020)
{
if(month>0&&month<=12)
{
if(isLeapYear(year))
{
if(day<=mon1[month]&&day>0)
a=1;
}
else
{
if(day<=mon2[month]&&day>0)
a=1;
}
}
}
return a;
}
}
要求:Main类中必须含有如下方法,签名如下:
public static void main(String[] args);//主方法
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) ;//判断year是否为闰年,返回boolean类型
public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day);//判断输入日期是否合法,返回布尔值
public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day) ; //求输入日期的下一天
再判断下一天中如果是本月的最后一天或者是润年中的闰月的最后一天需要跳月在这里需要较多的篇幅去编写以及调试还有就是调试上容易出现逻辑错误
题集2中的7-5- import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); boolean f=true; int y=0,m=0,d=0,n=0; if (sc.hasNextInt()) y= sc.nextInt(); else f=false; if (sc.hasNextInt()) m= sc.nextInt(); else f=false; if (sc.hasNextInt()) d= sc.nextInt(); else f=false; if (sc.hasNextInt()) n= sc.nextInt(); else f=false; if (checkInputValidity(y,m,d,n)&&f){ nextDate(y,m,d,n); }else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) { boolean ret=false; if ((year%100!=0&&year%4==0)||(year%400==0)){ ret=true; } return ret; } public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day,int n){ boolean ret=false; int[] mm={31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; if (isLeapYear(year))mm[1]=29; if ((year>=1820&&year<=2020)&&(month>=1&&month<=12)&&(day>=1&&day<=mm[month-1])){//此处的month-1用来判断不同年份的不同月份的数据是否合法 ret=true; } return ret; } public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day,int n) { int[] mm={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; if (isLeapYear(year))mm[2]=29; day-=n; if (n>0){ while (day<=0){ month--; if (month==0){//这边因为是mm有0的索引,因此要提前判断是否等于0 month+=12; year--; } day+=mm[month]; } }else if (n<0){ while (day>mm[month]) { day-=mm[month]; month++; if (month==13){ month-=12; year++; } } } System.out.printf("%d days ago is:%d-%d-%d\n",n,year,month,day); } }
其中与上一题中的下一天无过多删改就是下n天在数据的运算中更为复杂
题集2中的7-3
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
Main ljy = new Main();
int year = input.nextInt();
int month = input.nextInt();
int day = input.nextInt();
int days = numOfDays(year,month ,day);
if(format(year,month,day)==1) {
if(ljy.isLeapYear(year)) {
System.out.println(year+" is a leap year.");
System.out.println(year+"-"+month+"-"+day+" is "+ljy.getWhatDay(days)+".");
}
else {
System.out.println(year+" is not a leap year.");
System.out.println(year+"-"+month+"-"+day+" is "+ljy.getWhatDay(days)+".");
}
}
else System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) {
boolean isLeapYear = (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 !=0 )||year % 400 == 0;
return isLeapYear;
}
public static int numOfDays(int year,int month ,int day) {
int days=0;
int i ;
int []aa = new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
for(i=1;i<year;i++){
if(i%4==0&&i%100!=0||i%400==0) {
days+=366;}
else
days+=365;
}
if((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 !=0 )||year % 400 == 0)
aa[2]=29;
for(i = 1;i<month;i++){
days+=aa[i];}
days+=day;
return days;
}
public static String getWhatDay(int days) {
if(days%7==0) {
return "Sunday";
}
else if(days%7==1) {
return "Monday";
}
else if(days%7==2) {
return "Tuesday";
}
else if(days%7==3) {
return "Wednesday";
}
else if(days%7==4) {
return "Thursday";
}
else if(days%7==5) {
return "Friday";
}
else
return "Saturday";
}
public static int format(int year,int month,int day)
{
int Format=0;
int[] mon1=new int[]{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int[] mon2=new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
if(year>=1820&&year<=2020)
{
if(month>0&&month<=12)
{
if(isLeapYear(year))
{
if(day<=mon1[month]&&day>0)
Format=1;
}
else
{
if(day<=mon2[month]&&day>0)
Format=1;
}
}
}
return Format;
}
}
在是周几的逻辑上要反复推敲以及对于闰年闰月的逻辑调用
题集3中的7-1
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int id=input.nextInt();
double balance=input.nextDouble();
double annualInterestRate=input.nextDouble();
double m1=input.nextDouble();
double m2=input.nextDouble();
Account s1=new Account();
s1.setId(id);
s1.setBalance(balance);
s1.setAnnualInterestRate(annualInterestRate);
s1.withDraw(m1);
s1.deposit(m2);
System.out.println("The Account'balance:"+String.format("%.2f",s1.getBalance()));
System.out.println("The Monthly interest:"+String.format("%.2f",s1.getMonthlyInterestRate()));
System.out.println("The Account'dateCreated:2020-07-31");
}
}
class Account
{
private int id;
private double balance;
private double annualInterestRate;
public int getId(){
return id;
}
public void setId(int id){
this.id = id;
}
public double getBalance(){
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(double balance){
this.balance = balance;
}
public double getAnnualInterestRate(){
return this.annualInterestRate;
}
public void setAnnualInterestRate(double annualInterestRate ){
this.annualInterestRate = annualInterestRate;
}
public double getMonthlyInterestRate(){
return balance*(annualInterestRate / 1200);
}
public void withDraw(double money){
if(balance >= money&&money>=0){
balance -= money;
}
else
System.out.println("WithDraw Amount Wrong");
}
public void deposit(double money){
if(money >= 0&&money<=20000){
balance += money;
}
else
System.out.println("Deposit Amount Wrong");
}
}
设计一个名称为Account的类,具体包括:
- id:账号,私有属性,整型,默认值为0;
- balance:余额,私有属性,实型,默认值为0;
- annualInterestRate:当前利率,私有属性,实型,默认值为0,假设所有帐户均有相同的利率;
- dateCreated:账户开户时间,私有属性,LocalDate类型,默认为2020年7月31日;
- 一个能创建默认账户的无参构造方法;
- 一个能创建带特定id和初始余额的账户的构造方法;
- id、balance、annualInterstRate的getter及setter方法;
- dateCreated的getter方法;
- 一个名为getMonthlyInterestRate()的方法返回月利率(月利率计算公式:余额*(年利率/1200));
- 一个名为withDraw的方法从账户提取特定数额,当提取数额大于余额或为负数系统返回
WithDraw Amount Wrong提示; - 一个名为deposit的方法向账户存储特定数额,当存储数额大于20000元或为负数系统返回
Deposit Amount Wrong提示。
在Account 这个类中的方法中需要多个数据进行调用最后是在数据输出时返回月利息以及余额时需要格式化输出String.format("%.2f",s1.getBalance())以及String.format("%.2f",s1.getMonthlyInterestRate())
(Java中强大的format)
题集3中的7-2
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = input.nextInt();
int month = input.nextInt();
int day = input.nextInt();
Date s1=new Date();
s1.setYear(year);
s1.setMonth(month);
s1.setDay(day);
if(s1.checkInputValidity(year, month, day)==1)
{
int[] aa=new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
if(s1.isLeapYear(year))
aa[2] = 29;
int a = 0,b = 0,c = 0;
if(s1.checkInputValidity(year,month,day)==1) {
if(month==12) {
if(day==aa[month]) {
a = year+1;
b = 1;
c = 1;}
if(day>0&&day<aa[month])
{a = year;
b = month;
c =day +1;
}
}
if(month<12) {
if(day==aa[month]) {
a = year;
b = month + 1;
c = 1;}
if(day>0&&day<aa[month])
{a = year;
b = month;
c = day+1;
}
}
System.out.println("Next day is:"+a+"-"+b+"-"+c);
}
}
else
System.out.println("Date Format is Wrong");
}
}
class Date
{
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
private int days=checkInputValidity(year, month, day);
public void setYear(int year){
this.year = year;
}
public double getYear(){
return year;
}
public void setMonth(int month){
this.month = month;
}
public double getMonth(){
return month;
}
public void setDay(int day){
this.days = day;
}
public double getDay(){
return day;
}
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) {
boolean isLeapYear = (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 !=0 )||year % 400 == 0;
return isLeapYear;
}
public static int checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day)
{
int a=0;
int[] mon1=new int[]{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int[] mon2=new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
if(year>=1820&&year<=2020)
{
if(month>0&&month<=12)
{
if(isLeapYear(year))
{
if(day<=mon1[month]&&day>0)
a=1;
}
else
{
if(day<=mon2[month]&&day>0)
a=1;
}
}
}
return a;
}
}
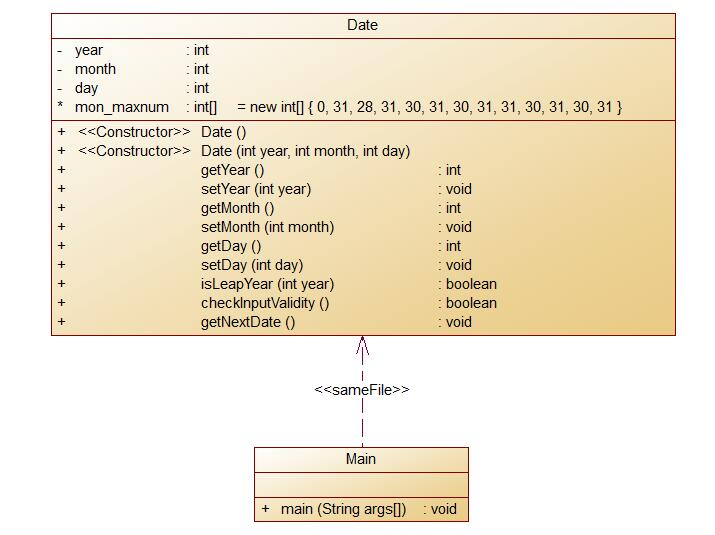
此题与题集2中的7-4问题基本一样用的多久就是要体现类的封装getter 以及settter的使用(而我们在设置变量的属性时,我们通常会对数据进行封装,这样就可以增加了数据访问限制,增加了程序可维护性。而实现方法就是:用private去修饰一个变量,然后再用setter方法去设置该变量的值,然后在用getter方法去调用该变量的值。)
题集3中的7-3
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
String str=input.nextLine();
char[]s=str.toCharArray();
str=str.replaceAll(" ","");
if("+".equals(s[0]))
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else
{
Pattern r=Pattern.compile("(([-|+]?)[1-9][0-9]*)([(*x^-)|(*x^)]?)([0-9]*)");
Pattern l=Pattern.compile("[0-9]*");
Matcher m=r.matcher(str);
Matcher k=l.matcher(str);
if(m.matches())
{
if(!k.matches())
{
while(m.find())
{
Matcher p=l.matcher(m.group());
if(p.matches())
{
}
}
}
else
System.out.println("0");
}
else
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
}
这道题还有很多部分没有完成只有对输入数据是否合法运用正则表达式的判断进行了部分操作将输入的数据进行比对数字+“x“(0/1)(
(([-|+]?)[1-9][0-9]*)([(*x^-)|(*x^)]?)([0-9]*))
求导应继续使用类的封装创建一个新的类新的方法进行对yi元多项式进行求导;
改进建议:
- 在定义常量时,一定要确定的定义一个不变量;
- 不要旧语法困扰你,遇到了,就查查别纠结;
- 编程命名的规范性。代码除了给机器看,也要给人看。要写能够结构清晰,命名规范;
- 在类的封装上要合理规范化;
- 对于正则表达式的调试要加强(搞懂正则表达式的语法及其灵活调用);
总结:
- 通过实验提高了自己找错以及调试代码的能力,类的调用以及对于类的传参有了一个更清楚的认识以及java面向对象编程的思想;
- 希望在题集结束后选择性公布正确代码;
- 多了解Java中的自带函数;
- 多总结并理解方法的构造;灵活运用java中类的封装(将类的某些信息隐藏在类的内部,不允许外部程序直接访问,而是通过该类提供的方法来对隐藏的信息进行操作和访问。)注意内部类对象的创建。只有是成员内部类创建内部类对象时候才需要通过外部类对象来创建。其他都是可以直接创建的。当外部类和内部类变量重名的话,想要调用外部变量。成员内部类需要(类名.this.变量名)。静态内部类需要是(类名.变量名)
- 学会了正则表达式的基本语法灵活调用还是需要时间去掌握的 部分(
1. . 和 \
. 在正则表达式中表示任意一个字符\ 在正则表达式当中表示转义字符,比如.在正则表达式当中表示任意一个字符,要是单纯的想要表达一个.的时候,就需
要用到\转义字符来表示, \. 在java程序当中\也是被认为特殊字符,也需要进行转义,应该用\\.
2.字符集合[]
)
[] 用来描述一个单一的字符,方括号内部可以定义这个字符的内容,也可以描述一个范围
[abc] abc中的任意一个字符
[a-z] 小写字母当中a-z的任意一个单词
[A-Z] 大写字母当中A-Z中的任意一个单词
[0-9] 数字0-9中的任意一个数字
[a-zA-Z0-9] a-zA-z0-9中的任意一个字符
[a-z&&[^bc]] a-z中除了bc以外的任意一个字母


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号