手撕算法
数组
-
- 索引为数字,存放出现次数。
-
- 数组往右递增,往下递增。可从右上角遍历,过大往左,过小往下,溢出报错,找到返回。
-
- 迭代优于递归。
-
- 首先判断是否为没有旋转的数组,最左<最右
- 循环中依次判断找到的情况,无法应用二分查找的情况,排除递增序列的情况。
-
-
注意n很大的情况。
-
利用递归全排列的方式,输出时考虑前面的0不显示。
-
-
- 维护两个指针,前偶后奇则调换。
-
- 外圈打印的条件:start*2<min(row,col)
- 从左往右不约束
- 从上往下需要2行:start<end_y
- 从右往左需要满足2列:start<end_y&&start<end_x
- 从下往上需要3行:start<end_y-1&&start<end_x
-
partition思想找出中位数,或记录出现次数。
-
topK问题。
public class TopK { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer[] arr = {3,2,5,8,71,3,69,5,4,9,82,5,55,96,485,357}; System.out.println(top(Arrays.asList(arr),5)); } public static <T extends Comparable<T>> List<T> top(List<T> list, int top){ if (list == null){ throw new RuntimeException("list is null!"); } PriorityQueue<T> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(top); list.forEach(t -> { if (queue.size() < top){ queue.add(t); }else if (queue.peek().compareTo(t) < 0){ queue.poll(); queue.add(t); } }); LinkedList<T> arr = new LinkedList<>(); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ arr.addFirst(queue.poll()); } return arr; } } -
维护一个最小堆和最大堆,数目之差不能超过1,最小堆的所有数据要大于最大堆。
class MedianFinder { //最小堆 Queue<Integer> min_queue; //最大堆 Queue<Integer> max_queue; /** initialize your data structure here. */ public MedianFinder() { this.min_queue=new PriorityQueue<>((o1,o2)->o1-o2); this.max_queue=new PriorityQueue<>((o1,o2)->o2-o1); } public void addNum(int num) { if(min_queue.size()==max_queue.size()){ //插入小顶堆 if(min_queue.isEmpty()||num>=max_queue.peek()){ min_queue.offer(num); }else{ min_queue.offer(max_queue.poll()); max_queue.offer(num); } }else{ //插入大顶堆 if(num<=min_queue.peek()){ max_queue.offer(num); }else{ max_queue.offer(min_queue.poll()); min_queue.offer(num); } } } public double findMedian() { if(min_queue.size()==max_queue.size()){ return ((double)min_queue.peek()+(double)max_queue.peek())/2; }else{ return (double)min_queue.peek(); } } } /** * Your MedianFinder object will be instantiated and called as such: * MedianFinder obj = new MedianFinder(); * obj.addNum(num); * double param_2 = obj.findMedian(); */ -
分析数字1的出现规律。
-
0123456789101112131415...y
-
数组类型必须为封装类型,重写Comparator中的compare方法。class Solution { public String minNumber(int[] nums) { String[] strs = new String[nums.length]; for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { strs[i] = String.valueOf(nums[i]); } Arrays.sort(strs, new Comparator<String>() { @Override public int compare(String o1, String o2) { String o12 = o1 + o2; String o21 = o2 + o1; for (int i = 0; i < o12.length(); i++) { if (o12.charAt(i) != o21.charAt(i)) { return o12.charAt(i) - o21.charAt(i); } } return 0; } }); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); for (String s : strs) { sb.append(s); } return sb.toString(); } } -
滑动窗口,Set维护不重复的字符
class Solution { public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) { if(s.length()<2){ return s.length(); } int i=0; int j=0; Set<Character> set=new HashSet<Character>(); int max=0; while(j<s.length()){ if(!set.contains(s.charAt(j))){ max=Math.max(max,j-i+1); set.add(s.charAt(j)); j++; }else{ set.remove(s.charAt(i)); i++; } } return max; } } -
创建数组保存已有的丑树,空间换时间
-
归并排序(较难)
-
二分查找的判定条件
-
一个数只出现1次,其他数出现2次
数组异或的结果。
两个数各出现1次,其他数出现2次
数组异或的某位为1,根据该位拆分数组2份(两个出现一次的数分组)
public int[] singleNumbers(int[] nums) { int res = 0; for (int num : nums) { res ^= num; } //得到res的最后一个1所在的位置,根据该位置区分 res = res - (res & (res - 1)); List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>(); List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>(); for (int num : nums) { if ((num & res) == 0) { list1.add(num); } else { list2.add(num); } } int[] ans = new int[2]; for (int num : list1) { ans[0] ^= num; } for (int num : list2) { ans[1] ^= num; } return ans; }一个数出现1次,其他数出现3次
将所有数的二进制的每一位相加,能被3整除,该位就是0,否则为1,状态机
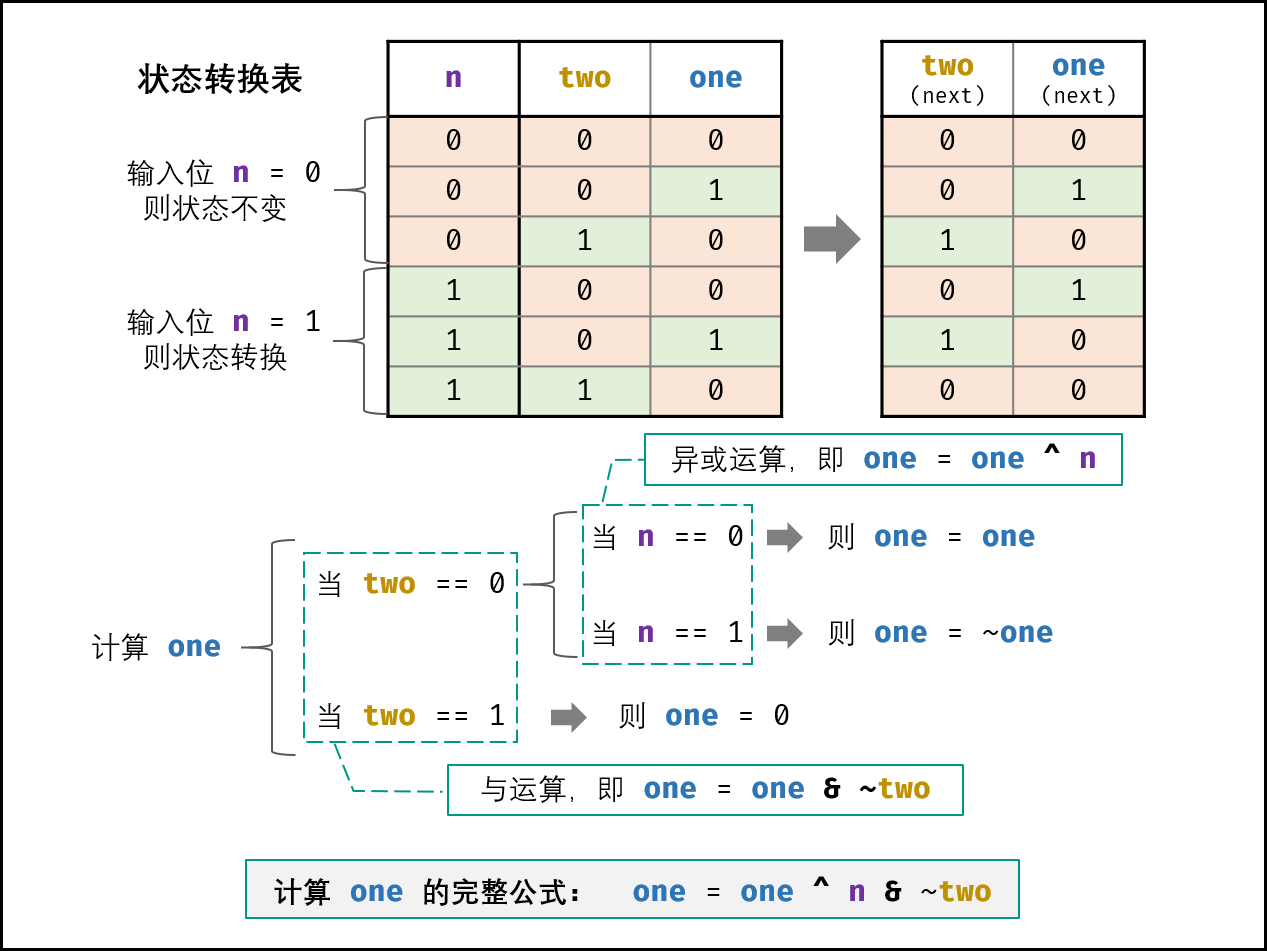
class Solution { //(另非)与(自异) public int singleNumber(int[] nums) { int i=0; int j=0; //另一位是1,该位不能为1 //该位不考虑进位的加法(异或) for(int n:nums){ i=(~j)&(i^n); j=(~i)&(j^n); } return i; } } -
双指针,一个从前往后,一个从后往前
-
翻转前n个+翻转后面部分+翻转整个字符串=左旋n位
-
public class QuickSort{ public void quickSort(int[] nums,int head,int tail){ int i=head; int j=tail; int index=nums[i]; while(i<j){ while(i<j&&nums[j]>=index){ j--; } if(i<j){ nums[i++]=nums[j]; } while(i<j&&nums[i]<index){ i++; } if(i<j){ nums[j--]=nums[i]; } nums[i]=index; quickSort(nums,head,i-1); quickSort(nums,i+1,tail); } } } -
public class MergeSort { private static void mergeSort(int[] arrays, int head, int tail) { if (head < tail) { int mid = (head + tail) / 2; mergeSort(arrays, head, mid); mergeSort(arrays, mid + 1, tail); merge(arrays, head, mid, tail); } } private static void merge(int[] arrays, int head, int mid, int tail) { int[] new_arrays = new int[tail - head + 1]; int i = head; int j = mid + 1; int index = 0; while (i <= mid && j <= tail) { if (arrays[i] <= arrays[j]) { new_arrays[index] = arrays[i]; i++; } else { new_arrays[index] = arrays[j]; j++; } index++; } while (i <= mid) { new_arrays[index++] = arrays[i++]; } while (j <= tail) { new_arrays[index++] = arrays[j++]; } for (int k = head; k <= tail; k++) { arrays[k] = new_arrays[k - head]; } } }
字符串
-
空格替换为较长的字符串,从尾到头复制。
-
字符的出现次数HashMap
链表
-
利用栈(也可反转)。
-
下一个节点的值拷贝,该节点指向下下个。
-
1、快慢指针判断是否有环。2、得到环中节点数目。3、指针2移动节点数目,同时移动直至相遇则是入口节点。
-
class Solution { public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { if(head==null||head.next==null) return head; ListNode cur= reverseList(head.next); head.next.next=head; head.next=null; return cur; } } -
public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { if(headA==null||headB==null){ return null; } //用栈的思想,从后往前比较 Stack<ListNode> stack1=new Stack<>(); Stack<ListNode> stack2=new Stack<>(); while(headA!=null){ stack1.push(headA); headA=headA.next; } while(headB!=null){ stack2.push(headB); headB=headB.next; } ListNode cur=null; while((!stack1.isEmpty())&&(!stack2.isEmpty())&&(stack1.peek()==stack2.peek())){ cur=stack1.pop(); stack2.pop(); } return cur; } }
二叉树
-
public class PreorderTraversal { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); TreeNode cur = root; while (!stack.isEmpty() || cur != null) { while (cur != null) { //先序cur的值 list.add(cur.val); stack.push(cur); cur = cur.left; } cur = stack.pop(); //中序 cur = cur.right; } return list; } } -
public class PostorderTraversal { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { LinkedList<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>(); LinkedList<Integer> output = new LinkedList<>(); if (root == null) { return output; } stack.add(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = stack.pollLast(); output.addFirst(node.val); if (node.left != null) { stack.add(node.left); } if (node.right != null) { stack.add(node.right); } } return output; } } -
根据前序遍历和中序遍历构造二叉树。
-
递归遍历二叉树,判断树A中以R为根节点的树是否与树B具有相同的数据结构。
class Solution { public boolean isSubStructure(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) { if(B==null||A==null){ return false; } //A为根节点与B相等 if(isEqual(A,B)){ return true; } //A的左右子树是否包含B return isSub(A.left, B)||isSub(A.right,B); } private boolean isSub(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) { if(B==null){ return true; } if(A==null){ return false; } //A为根节点与B相等 if(isEqual(A,B)){ return true; } //A的左右子树是否包含B return isSub(A.left, B)||isSub(A.right,B); } private boolean isEqual(TreeNode A, TreeNode B){ if(B==null){ return true; } if(A==null){ return false; } if(A.val!=B.val){ return false; } return isEqual(A.left,B.left)&&isEqual(A.right,B.right); } } -
public class MirrorTree { public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) { //空节点直接返回 if(root==null){ return root; } //交换左右节点 TreeNode temp = root.left; root.left = root.right; root.right = temp; //左右节点分别镜像 mirrorTree(root.left); mirrorTree(root.right); } } -
public class IsSymmetric { public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) { return isSym(root,root); } private boolean isSym(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2){ //节点均为空 if(root1==null && root2==null){ return true; } //节点只有一个为空 if(root1==null || root2==null){ return false; } //对称点的取值不相等 if(root1.val != root2.val){ return false; } return isSym(root1.left,root2.right) && isSym(root1.right,root2.left); } } /** 非递归实现*/ public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) { //队列 Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); if (root == null) return true; //左子节点和右子节点同时入队 queue.add(root.left); queue.add(root.right); //如果队列不为空就继续循环 while (!queue.isEmpty()) { //每两个出队 TreeNode left = queue.poll(), right = queue.poll(); //如果都为空继续循环 if (left == null && right == null) continue; //如果一个为空一个不为空,说明不是对称的,直接返回false if (left == null ^ right == null) return false; //如果这两个值不相同,也不是对称的,直接返回false if (left.val != right.val) return false; //这里要记住入队的顺序,他会每两个两个的出队。 //左子节点的左子节点和右子节点的右子节点同时 //入队,因为他俩会同时比较。 //左子节点的右子节点和右子节点的左子节点同时入队, //因为他俩会同时比较 queue.add(left.left); queue.add(right.right); queue.add(left.right); queue.add(right.left); } return true; } -
- 队列
-
- 从根节点到叶节点形成一条路径。
-
root节点的左边为左子树的最右节点,右边为右子树的最左节点。
public class TreeToDoublyList { public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) { if (root == null) { return null; } solve(root); Node l = root; Node r = root; while (l.left != null) { l = l.left; } while (r.right != null) { r = r.right; } l.left = r; r.right = l; return l; } private void solve(Node root) { if (root.left != null) { solve(root.left); Node left = findLeftMax(root.left); root.left = left; left.right = root; } if (root.right != null) { solve(root.right); Node right = findeRightMin(root.right); root.right = right; right.left = root; } } private Node findeRightMin(Node right) { if (right.left == null) { return right; } return findeRightMin(right.left); } private Node findLeftMax(Node left) { if (left.right == null) { return left; } return findLeftMax(left.right); } } -
用'$'表示空节点。
-
二叉搜索树,先遍历右子树,再遍历根节点,最后遍历左节点
class Solution { private static int n; private static int res; public int kthLargest(TreeNode root, int k) { n=k; find(root); return res; } public void find(TreeNode root){ if(root==null){ return; } find(root.right); if(n<=0){ return; } if(--n==0){ res=root.val; return; } find(root.left); } } -
1+max(左子树的深度,右子树的深度)
public class MaxDepth { public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { return (root != null)? (1+Math.max(maxDepth(root.left),maxDepth(root.right))) : 0; } } -
public class IsBalanced { public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) { return recur(root) != -1; } //返回root的高度 public int recur(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } int left = recur(root.left); int right = recur(root.right); if (left == -1 || right == -1) { return -1; } if (Math.abs(left - right) < 2) { return 1 + Math.max(left, right); } return -1; } } -
class Solution { TreeNode node=null; public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { dfs(root,p,q); return node; } public boolean dfs(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q){ if(root==null){ return false; } boolean lson=dfs(root.left,p,q); boolean rson=dfs(root.right,p,q); //左子树和右子树都有节点 if(lson&&rson){ node=root; } //本身为节点且左子树或右子树有节点 if((root.val==p.val||root.val==q.val)&&(lson||rson)){ node=root; } return lson||rson||root.val==p.val||root.val==q.val; } }
堆栈
-
栈2不为空直接弹出,否则栈1压入栈2再弹出。
-
队列头维护最大值的索引,有更大值或者超过滑动窗口宽度后弹出后面的数。
class Solution { public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) { if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) { return new int[0]; } int[] res = new int[nums.length - k + 1]; //queue存放索引 Deque<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>(); for(int i = 0, j = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { //不为空,且超过长度则队列poll if(!queue.isEmpty() && i - queue.peek() >= k) { queue.poll(); } //加入新的数,poll出比它小的数 while(!queue.isEmpty() && nums[i] > nums[queue.peekLast()]) { queue.pollLast(); } //offer相当于add,不会抛出异常而是返回错误 queue.offer(i); //赋滑动窗口的最大值 if(i >= k - 1) { res[j++] = nums[queue.peek()]; } } return res; } }
动态规划
-
长度不小于5时,尽可能多剪长度为3的绳子。
- 绳子长度>1,至少剪成两段,答案需要取模 1e9+7(1000000007
class Solution { public int cuttingRope(int n) { //n<4,切出长度为1 return n<4?n-1:(int)cut(n); } public long cut(long n) { //n=4为本身,否则n-3 return n<=4?n:(cut(n-3)*3)%1000000007; } } -
class Solution { public double myPow(double x, int n) { return n<0?1/p(x,-n):p(x,n); } public double p(double x, int n){ if(n==0){ return 1; } if(n==2){ return x*x; } return n%2==0?p(p(x,n/2),2):p(p(x,n/2),2)*x; } } -
class Solution { public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) { if(nums.length==0){ return 0; } int[] res=new int[nums.length]; res[0]=nums[0]; int max=res[0]; for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++){ res[i]=Math.max(nums[i],nums[i]+res[i-1]); max=Math.max(max,res[i]); } return max; } } -
f(i)=f(i+1)+g(i,i+1)*f(i+2) -
棋盘的左上角到达右下角
得到礼物的价值最多。
-
class Solution { public int trap(int[] height) { int len=height.length; if(len<=2){ return 0; } int[] left=new int[len]; int[] right=new int[len]; //根据左边界,该位置能存储的最大水量 for(int i=1;i<len-1;i++){ left[i]=Math.max(left[i-1],height[i-1]); } //根据右边界,该位置能存储的最大水量 for(int i=len-2;i>0;i--){ right[i]=Math.max(right[i+1],height[i+1]); } int sum=0; for(int i=1;i<len;i++){ sum+=Math.max(Math.min(left[i],right[i])-height[i],0); } return sum; } }
位运算
-
n&(n-1):去除最右边的1。
抽象建模能力
-
//构造二维数组,用n-1的骰子数量求n的骰子数量 class Solution { //骰子的面 private static final int count = 6; public double[] twoSum(int n) { double[][] res = new double[n][n * count]; for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { res[0][i] = 1; } for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { for (int j = i - 1; j < (i+1) * count; j++) { for (int k = Math.max(0, j - 6); k < j; k++) { res[i][j] += res[i - 1][k]; } } } double[] t_res = new double[n * count - n + 1]; for (int i = 0; i < n * count - n + 1; i++) { t_res[i] = res[n - 1][i + n - 1]; } double sum = Arrays.stream(res[n - 1]).sum(); for (int i = 0; i < n * count - n + 1; i++) { t_res[i] /= sum; } return t_res; } } -
class Solution { public boolean isStraight(int[] nums) { Arrays.sort(nums); //能补的个数 int res=0; //需要补的个数 int len=0; //不为0且重复的情况 for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++){ if(nums[i-1]!=0&&nums[i]==nums[i-1]){ return false; } } for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){ if(nums[i]==0){ res++; } //不为0的个数之间需要添加的数 else if(i>0&&nums[i-1]!=0){ len+=nums[i]-nums[i-1]-1; } } return res>=len; } } -
0,1,2,...n-1的n个数从0开始数m个就删除一个,求最后剩下的数字
public int lastRemaining(int n,int m){ if(n<1||m<1){ return -1; } int last=0; for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){ last=(last+m)%i; } retrun last; } -
状态机
-
class Solution { public int add(int a, int b) { int num1;//保存相加位 int num2;//保存进位 do{ num1=a^b; num2=(a&b)<<1; a=num1; b=num2; } while(b!=0);//没有进位 return a; } } -
class Solution { public int[] constructArr(int[] a) { int len=a.length; if(len==0){ return a; } int[] left=new int[len]; int[] right=new int[len]; left[0]=1; right[0]=1; for(int i=1;i<len;i++){ left[i]=left[i-1]*a[i-1]; right[i]=right[i-1]*a[len-i]; } int[] res=new int[len]; for(int i=0;i<len;i++){ res[i]=left[i]*right[len-1-i]; } return res; } } -
public class LRUCache { LRU cache; public LRUCache(int capacity) { this.cache = new LRU(capacity); } class LRU extends LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> { int capacity; public LRU(int capacity) { super(capacity, 0.75f, true); this.capacity = capacity; } public boolean removeEldestEntry(HashMap.Entry entry) { return this.size() > capacity; } } public int get(int key) { if (cache.containsKey(key)) { return cache.get(key); } return -1; } public void put(int key, int value) { cache.put(key, value); } }

 剑指OFFER习题及部分解答,仅作参考。
剑指OFFER习题及部分解答,仅作参考。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号