适配器设计模式实战2
一.目的
结合源码来深入理解适配器模式,本文通过java.sql的源码来讲解适配器模式的思想
适配器模式介绍可参考 适配器模式实战1
二.业务场景介绍
在编写服务端代码时,我们需要使用数据库,而数据库种类繁多,最常用的关系型数据库mysql,oracle等,不同的数据库由不同的组织和公司开发,所以api不可能完全做的一样,而jdk为了适配不同类型的数据库,提供了Driver接口和DriverManager类,为我们执行数据库业务提供了同一的接口.
三.角色划分
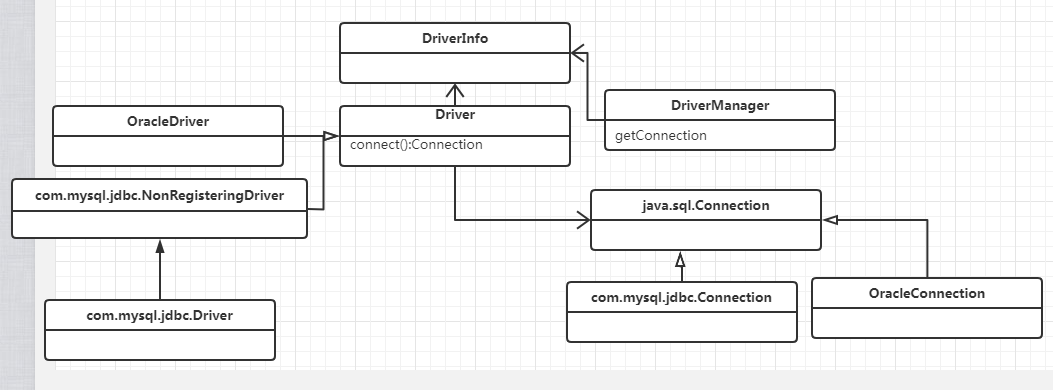
四.具体代码
java.sql.Driver代码
public interface Driver {
Connection connect(String url, java.util.Properties info)
throws SQLException;
boolean acceptsURL(String url) throws SQLException;
DriverPropertyInfo[] getPropertyInfo(String url, java.util.Properties info)
throws SQLException;
int getMajorVersion();
int getMinorVersion();
boolean jdbcCompliant();
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
}
com.mysql.jdbc.NonRegisteringDriver 代码
public class NonRegisteringDriver implements Driver{
//...
public Connection connect(String url, Properties info) throws SQLException {
if (url != null) {
if (StringUtils.startsWithIgnoreCase(url, "jdbc:mysql:loadbalance://")) {
return this.connectLoadBalanced(url, info);
}
if (StringUtils.startsWithIgnoreCase(url, "jdbc:mysql:replication://")) {
return this.connectReplicationConnection(url, info);
}
}
Properties props = null;
if ((props = this.parseURL(url, info)) == null) {
return null;
} else if (!"1".equals(props.getProperty("NUM_HOSTS"))) {
return this.connectFailover(url, info);
} else {
try {
com.mysql.jdbc.Connection newConn = ConnectionImpl.getInstance(this.host(props), this.port(props), props, this.database(props), url);
return newConn;
} catch (SQLException var6) {
throw var6;
} catch (Exception var7) {
SQLException sqlEx = SQLError.createSQLException(Messages.getString("NonRegisteringDriver.17") + var7.toString() + Messages.getString("NonRegisteringDriver.18"), "08001", (ExceptionInterceptor)null);
sqlEx.initCause(var7);
throw sqlEx;
}
}
}
//...
}
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
public class Driver extends NonRegisteringDriver implements java.sql.Driver {
public Driver() throws SQLException {
}
static {
try {
DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
} catch (SQLException var1) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");
}
}
}
当调用Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver") 时,该驱动会被注册到DriverManager里
OracleDriver
public class OracleDriver implements Driver{
//...
public Connection connect(String var1, Properties var2) throws SQLException{
//...
}
//...
}
public interface Connection extends Wrapper, AutoCloseable{
Statement createStatement() throws SQLException;
PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException;
CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql) throws SQLException;
String nativeSQL(String sql) throws SQLException;
void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException;
boolean getAutoCommit() throws SQLException;
void commit() throws SQLException;
void rollback() throws SQLException;
void close() throws SQLException;
boolean isClosed() throws SQLException;
//.....
}
com.mysql.jdbc.Connection
public interface Connection extends java.sql.Connection, ConnectionProperties{
//....
}
oracle.jdbc.OracleConnection
public interface OracleConnection extends Connection{
//...
}
oracle.jdbc.OracleConnectionWrapper
public class OracleConnectionWrapper implements OracleConnection{
//...
}
五.具体调用
//首先建立驱动 oracle
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
//mysql
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.driver");
//数据库不同,接口都通用一个
//驱动成功后进行连接
conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
//准备SQL语句
PreparedStatement pStatement = connection.prepareStatement(query);
//执行SQL语句
ResultSet resultSet = pStatement.executeQuery();
六.总结
由此可见,jdbc采用了接口适配的思想,为我们调用数据库提供了同一接口,而不用管具体不同类型数据库的内部实现,既方便了调用,也方便了用配置文档类配置数据库相关信息


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号