多进程拷贝--mmap实现
多进程拷贝的的方式有多种,内存映射便是其中一种实现方法,不废话了。
*************************************************************************************
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
char *p;
unsigned char *src,*dst;
int fd1,fd2;
int i,n = atoi(argv[3]);
int size;
int blocksize;
pid_t pid;
struct stat sta;
fd1 = open(argv[1],O_RDONLY);
//fd1 = open("wegbk.txt",O_RDONLY);
if(fd1 < 0)
{
perror("open src failed.");
exit(1);
}
fd2 = open(argv[2],O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0664);
//fd2 = open("t.txt",O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0664);
if(fd2 < 0)
{
perror("open dst failed.");
close(fd1);
exit(1);
}
if(fstat(fd1,&sta))
{
perror("Stat file error.");
close(fd1);
close(fd2);
exit(1);
}
//printf("*****src file size = %d***\n",sta.st_size);
//将目标文件扩展为源文件大小
size = sta.st_size;
ftruncate(fd2,size);
blocksize = size/n;
src = (unsigned char*)mmap(NULL,size,PROT_READ,MAP_SHARED,fd1,0);
if(src == MAP_FAILED)
{
perror("map src error.");
close(fd1);
close(fd2);
exit(1);
}
dst = (char*)mmap(NULL,sta.st_size,PROT_WRITE,MAP_SHARED,fd2,0);
if(dst == MAP_FAILED)
{
perror("map dst error.");
close(fd1);
close(fd2);
exit(1);
}
close(fd1);
close(fd2);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
pid = fork();
if(pid<0)
{
perror("fork error.");
exit(1);
}
else if(pid == 0)
break;
}
if(i<n)
{
//printf("%dth child\n",i+1);
int k;
if(i == (n-1)) //千万注意不能写成=,否则会搞死你的
blocksize += (size%n);
char buf[blocksize];
src += (blocksize*i);
dst += (blocksize*i);
printf("%dth Chlild copying----start addr src=%u,dst = %u\n",i+1,src,dst);
memcpy(buf,src,blocksize);
memcpy(dst,buf,blocksize);
printf("%dth Chlild copy done.\n",i+1);
}
else
{
//In parent
//sleep(2);
int j;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
waitpid(-1, NULL, WNOHANG);
}
munmap(src,sta.st_size);
munmap(dst,sta.st_size);
return 0;
}
return 0;
}
*************************************************************************************
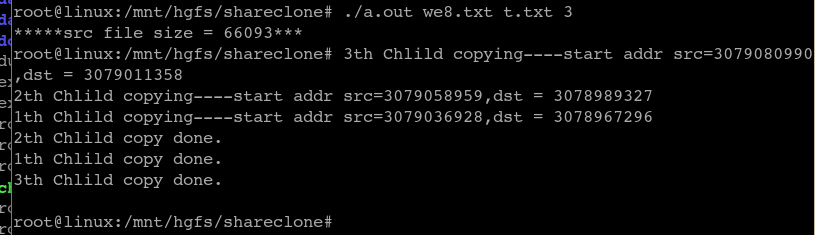
执行结果:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号