Kubernetes Declarative Deployment
应用系统在代码迭代升级时,在发布时经常面临的问题就是,新 / 老业务的并存,或者是版本切换等问题
- 在发布时多个版本并存的问题
- 如果不能接受多个版本并存,需要关闭旧版本,停机切换到新版本,带来的问题就是增加更多的资源
Declarative Deployment
在kubernetes环境中,在发布部署有发如下几种部署策略
- RollingUpdate(滚动更新)
- Fixed Deployment(固定部署)
- Blue-Green Release(蓝绿发布)
- Canary Release(金丝雀发布)
RollingUpdate
在kubernetes中,Pod的更新是通过Deployment的概念实现的,Deployment在后端创建一个支持标签集的副本集合,即ReplicaSet
Deployment有支持二种更新策略RollingUpdate & Recreate
- 配置
# A rolling update Deployment apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: random-generator spec: # More than 1 replica is required for a rolling update replicas: 3 strategy: type: RollingUpdate rollingUpdate: # Number of Pods which can be run temporarily in addition the replicas # specified during an updated # (so it could 4 in our case at max) maxSurge: 1 # Number of Pods which can be unavaiable during the update. Here it could # be that only 2 Pods are running at a time during the update maxUnavailable: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: random-generator template: metadata: labels: app: random-generator spec: containers: - image: k8spatterns/random-generator:1.0 name: random-generator env: - name: PATTERN value: Declarative Deployment ports: - containerPort: 8080 protocol: TCP # Readiness probes are very important for a RollingUpdate to work properly, # so don't forget them livenessProbe: httpGet: path: /actuator/health port: 8080 initialDelaySeconds: 15 readinessProbe: exec: command: [ "stat", "/opt/random-generator-ready" ]
-
更新过程需要满足以下公式
其中x代表线上可用实例,如下
2 ≤ x ≤ 4 (2 小于等于 x 小于等于4)
在整个更新过程不会出现宕机
![]()
- 优点
- deployment是Kubernetes的资源对象,其状态完全由Kubernetes内部控制,整个更新过程都是发生服务端,无需与客户端交互
- deployment是一个可执行的对象,在部署生产环境之前,可以在其它环境进行测试与验证
- 更新的整个过程会被记录下来并标记版本号,并支持回滚、暂停
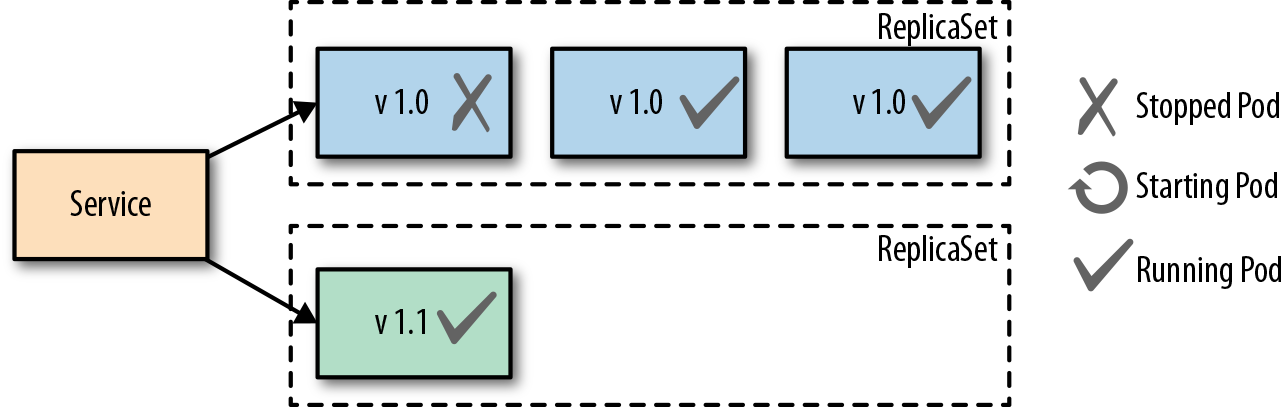
fixed update
RollingUpdate的策略在发布时可以规避掉0停机,但是缺点就是在整个过程中会存在线上环境会存在二个版本在运行,可以对于一些消费场景可能会有问题
什么是kubernetes的fixedupdate
Kubernetes的Recreate策略,在更新过程中首先会kill掉线上环境正在运行的实例,当旧的实例结束后,同时启动新的实例
在整个更新过程中会短暂停机,意味着线上环境短暂不能提供服务
Blue-Green Release
原理
- 使用最新的版本的容器(称之为绿色)用来创建第二个deployment,但是不会马上对外提供服务,在此时原有蓝色的实例还在线上环境运行
- 确保绿色实例完全Ok的状态下,且可以处理业务请求,将流量从蓝色实例切换到绿色实例上。Kubernetes是通过service lable,就是标签选择器选择了绿色的Pod进行新老切换的
- 在观察并确认绿色Pod可以正常响应新请求,开始终结或者移除蓝色的Pod,并释放资源

总结
蓝绿发布优势在于,同一时间只有一个版本提供线上环境服务
蓝绿发布劣势在于,在发布过程中,需要二倍的资源进行更新
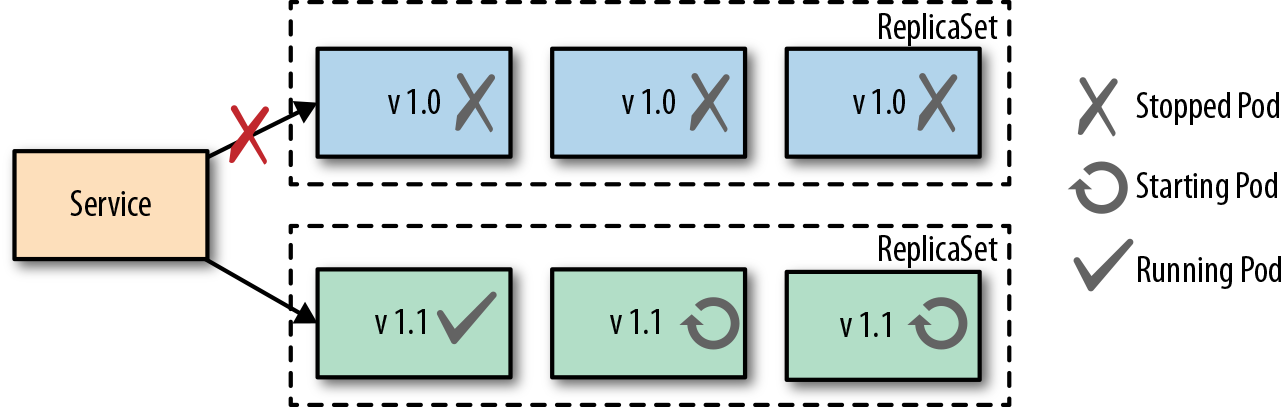
Canary Release
金丝雀发布,与上面不同之处是它是平滑地部署到生产环境,这种方法只是将新实例替换一部分老的实例,因此可以把风险控制的更低,如果有问题可以迅速恢复,不会大面积受到影响,
等到对新版本的代码进行一段时间的验证,即可以把其它剩余逐渐更新
在Kubernetes中,金丝雀发布的实现发布,为新版本的代码是创建一个新的deployment,并且制定适应的label,然后再新的deployment的加入到前端service资源中,实际上service后端有二种Pod(新的与旧的)
具体操作方式如下
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/deployment/#canary-deployment
https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/manage-deployment/#canary-deployments
https://github.com/kelseyhightower/talks/tree/master/kubecon-eu-2016/demo#deploy-a-canary
总结
下图展示了deployment和发布策略,并图解在更新过程中Pod实例变化







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号