目录
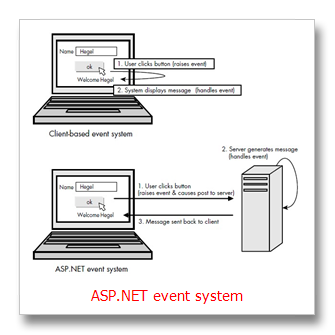
ASP.NET的事件模式(ASP.NET Event Model)
事件处理器(event handler):event handler 用来决定当一个事件被激发是的处理方式,比如当用户点击鼠标或者是用户从一个下拉列表中选中某个选项等等。
在.NET Framework中, 所有的事件处理器都有一个特定的方法签名(method signature)—也就是说方法的返回类型(return type)和参数(parameters)。事件处理器都是void方法,它接收两个参数:一个对象参数(object parameter)和事件声明参数(EventArgs parameter)。对象参数指激发事件的对象。例如:如果你在不同的控件使用相同的event handler,对象参数将用来判断是哪个控件激发了该事件。EventArgs parameter包含说明特定事件的信息。例如:ImageClickEventArgs parameter包含用户点击某个图片的位置信息(x和y坐标)。ASP.NET的事件处理过程不同于一般Windows应用程序在于事件的激发是发生在客户端,然后传输到服务器端进行处理。
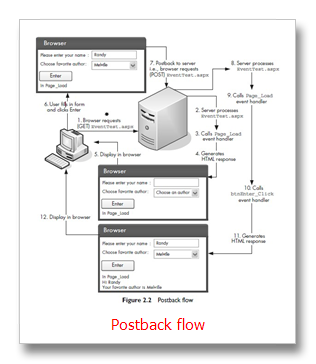
回传(Postback)
postback: is the process by which the browser posts information
back to itself (i.e., posts information back to the server by requesting the same page). Postback in ASP.NET only occurs within Web Forms (i.e., within a form element with runat=server), and only server controls postback information to the server. Each cycle in which information is displayed and then posted back to the server is sometimes also called a round trip.
Page and Control Events
View State and Control State
It is a specially encoded string that is used to retain page and form information between requests and is stored within a hidden HTML <input> element. All page elements not posted back via the standard HTTP POST mechanism are stored within this string.
Page Lifecycle
Page and control events occur in a certain order, which is called the page lifecycle.
Cross-Page Posting
ASP.NET Code Compilation
The Page Class
Request: The Request property of the Page class returns an HttpRequest object. This HttpRequest represents the HTTP values sent by the browser with its request. It contains members for retrieving query string or form parameters, cookie data, as well as information about the requesting browser.
HttpRequest class
Response: The HttpResponse class represents the server’s HTTP response to the current request.
HttpResponse
Server: The Server property of the Page class returns an HttpServerUtility object.
HttpServerUtility class
Response.Redirect Versus Server.Transfer
两种方法都是重新定向到指定的页面,前者要形成一个客户端到服务器的响应Round trip,因此客户端的浏览器地址栏会出现更新;后者允许较快,因为它是直接加载请求的页面,因此不存在浏览器地址栏的更新,
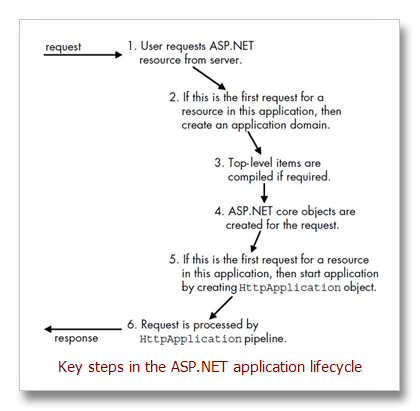
ASP.NET Application Lifecycle
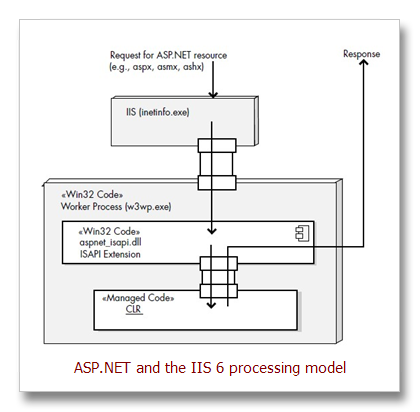
1、User Requests ASP.NET Resource from Server
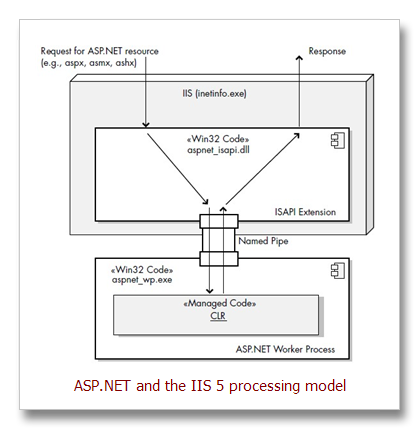
An ISAPI extension is a Windows DLL that can be directly invoked by
a URL and that interacts and works with a request to a Web server; for ASP.NET,
the extension is aspnet_isapi.dll. An ISAPI filter, on the other hand, is a
Windows DLL that modifies the incoming and outgoing data stream to and from
IIS; for ASP.NET, the filter is aspnet_filter.dll, and is used only to preprocess
cookieless session state.
ASP.NET worker process (aspnet_wp.exe), which then takes over and controls the execution of the request. This worker process is a small Win32 executable that loads and hosts the CLR. Generally, there is only one instance of this process running on the machine; that is, all future requests are routed through this one worker process (see Figure 2.15). However, if there are multiple CPUs on the Web server, each CPU can run a separate single worker process.
IIS 6 generic worker process (named w3wp.exe)
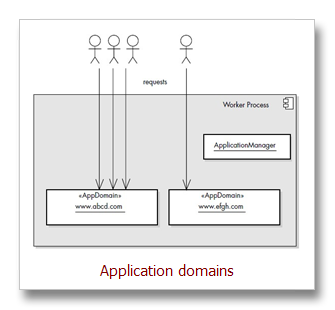
2、If First Request for Any Resource in Application, Create Application Domain
服务器可以同时容纳多个应用程序。每一个应用程序都是以虚拟目录或网站根目录的形式存在。一旦应用程序获得请求消息,ApplicationManager类激活、初始化开始管理整个应用程序的生命周期,并创建一个AppDomain类的application domain
3、Top-Level Items Are Compiled If Required
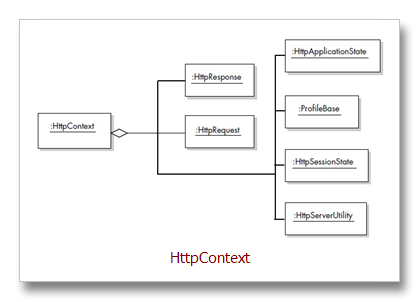
4、ASP.NET Core Objects Are Created for the Request
HttpContext, which represents the context of the current request, and which creates and wraps (i.e., provides programmatic access via properties to) the other core objects for processing a request, namely the HttpRequest, HttpResponse, Cache, HttpApplicationState, HttpSessionState, HttpServerUtility, ProfileBase, and TraceContext objects
HttpRequest class contains all the information about the current request, such as the requesting browser type, cookies for this site contained on the client, and any GET/POST parameter values being sent to the server. The HttpResponse class encapsulates all the HTTP response information sent from an
ASP.NET operation back to the browser, such as the rendered output (HTML),
cookies, and HTTP header information.
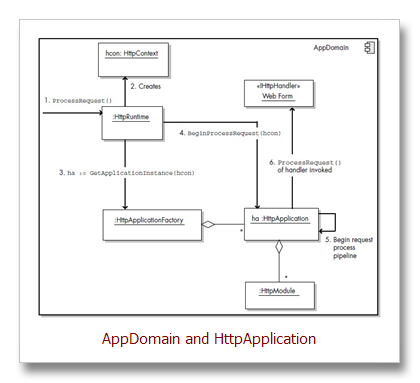
5、Assign HttpApplication Object to Request
An HTTP module is an object that is used for every request made to an application.
ASP.NET HTTP modules are similar to ISAPI filters in that they run for all requests. However,
they are written in managed code and are fully integrated with the lifecycle of an
ASP.NET application. HTTP modules can also be reused across applications. HTTP
modules are thus used to examine incoming requests, take actions based on the
request, and examine the outbound response and modify it, if necessary.
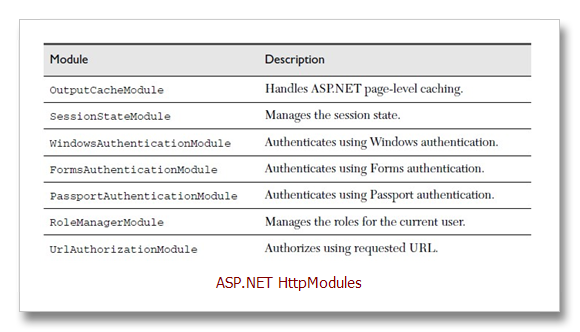
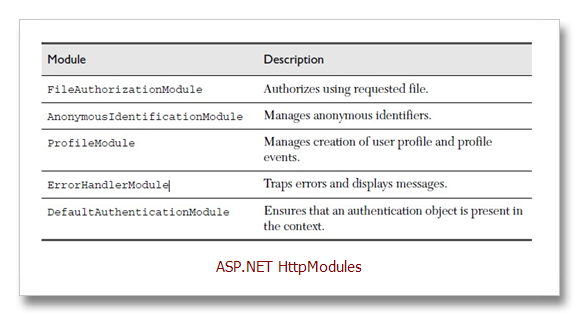
ASP.NET uses modules to implement a variety of application features. Some of
the built-in modules help implement caching, security authentication, session state services, role management, permissions for accessing URLs and files, as well as error handling (see Table 2.8). Modules can consume application events and can raise events that can be handled in the Global.asax file.
HTTP handlers, All HTTP handlers implement the IHttpHandler or the IHttpAsyncHandler interface. All Web Forms are in fact HTTP handlers because their base class (the Page class) implements IHttpHandler.
6、Process Request Using HttpApplication Pipeline
After the HttpApplication object has been initialized and retrieved, the request
can finally be processed. The request is processed in a certain specific order, and for
this reason, it is called a pipeline. This request pipeline mainly consists of triggered
events. The majority of these events are handled by the HttpApplicaton object,
whereas others are handled by the various HTTP modules or by the HTTP handler
defined for the requested file type. The steps in the pipeline are as follows.
1. Validate the request.
The request information sent by the browser is initially preprocessed to
verify that it contains nothing potentially dangerous in terms of security.
2. Perform URL mapping if necessary.
The Web.config file allows you to map a URL that is displayed to users to a
URL that exists in your Web application. This mapping occurs here.
3. BeginRequest event triggered.
This event indicates the creation of any given new request. This event is
always raised and is always the first event to occur during the processing of a
request.
4. AuthenticateRequest event triggered.
This event is triggered when the authentication mechanism configured (in
the Web.config file) has authenticated (i.e., established the identity of) the
user of the current request.
5. PostAuthenticateRequest event triggered.
This event is triggered after the AuthenticateRequest event has
occurred (that is, after the identity of the user has been established).
6. AuthorizeRequest event triggered.
This event occurs when ASP.NET has authorized the current request.
7. PostAuthorizeRequest event triggered.
This event is triggered after the AuthorizeRequest event has
occurred (that is, after the request has been authorized).
8. ResolveRequestCache event triggered.
When this event occurs, any HTTP caching modules can serve requests
from the cache, bypassing execution of the rest of this pipeline.
9. PostResolveRequestCache event triggered.
This event is triggered after the request cache has been processed.
10. Based on the filename extension of the requested resource, the appropriate
HTTP handler is instantiated.
11. PostMapRequestHandler event triggered.
This event is triggered after the current request has been mapped to the
appropriate HTTP handler.
12. AcquireRequestState event triggered.
This event is triggered when the current state (for example, session state)
that is associated with the current request is acquired from the ASP.NET
runtime.
13. PostAcquireRequestState event triggered.
This event is triggered after the state for the current request is acquired.
14. PreRequestHandlerExecute event triggered.
This event is triggered just before the HTTP handler executes.
15. Call the ProcessRequest method of the HTTP handler class.
The ProcessRequest method enables processing of the requests by the
HTTP handler. For Web Forms, this method is defined in the base Page
class. In other words, it is during this event that the Web Form executes. The
page lifecycle, as shown in Figure 2.8, can be inserted here.
16. PostRequestHandlerExecute event triggered.
This event is triggered after the HTTP handler class has finished executing
the ProcessRequest method.
17. ReleaseRequestState event triggered.
This event is triggered after the application is finished with the request. This
event tells any state HTTP modules to save the current state data.
18. PostReleaseRequestState event triggered.
This event is triggered after the request state has been saved.
19. Perform response filtering if specified.
The HttpResponse object has a Filter property that allows a filter to be
wrapped around the output sent to the HTTP response stream.
20. UpdateRequestCache event triggered.
When this event is triggered, any HTTP caching modules can store
responses that will be used to serve subsequent requests from the cache.
21. PostUpdateRequestCache event triggered.
This event is triggered after the request cache has been updated.
22. EndRequest event triggered.
This event is triggered to indicate that the HTTP request pipeline chain is
finished.
关键概念
• Application class/file
• Application domain
• Application lifecycle
• Application pool
• Application restart
• Control state
• Cross-page posting
• Delegate
• Event handler
• HTTP handler
• HTTP module
• HttpApplication pipeline
• ISAPI extension
• ISAPI filter
• Page events
• Page lifecycle
• Partial class
• Postback
• Round trip
• View state
• Worker process
• XML documentation comments




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号