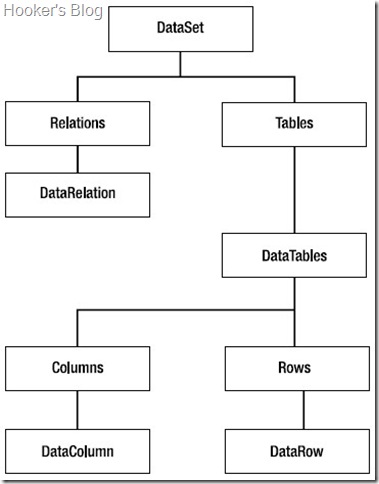
DataSet architecture
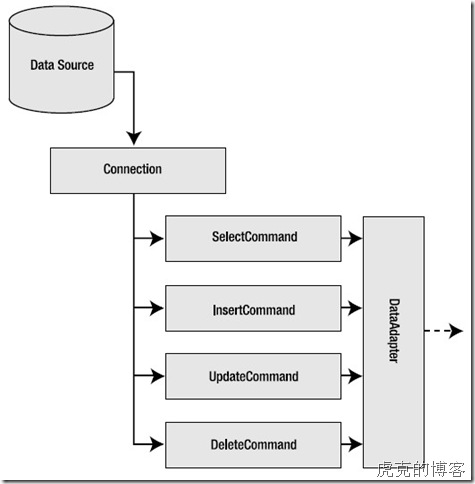
DataAdapter architecture
ADO.NET模式的两种数据连接模式
• Connected data access
执行步骤如下
1. Establish a connection with the database.
2. Fetch a set of records in a cursor.
3. Work with the fetched data (perform read, modify, and delete operations or even calculations).
4. Update the database, if there are any changes.
5. Close the database connection.
适合使用的情景
• You are developing applications that are online all the time. For example, in a ticket reservation
application it is necessary that you work with the latest data from the database.
In such cases, connected data access becomes necessary.
• You want to avoid the overhead of using offline data. When you use queries directly
against a database, naturally they bypass any of the intermediate layers that are involved
in disconnected data-access techniques. For example, suppose that you wish to display a
simple employee listing to the end user. This task does not involve any processing as such.
Using connected data access in such cases will of course give the best performance.
• You need a cursor model for some reason.
示例代码
1: protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
2: {3: SqlConnection cnn = new SqlConnection(@"data source=.;initial catalog=northwind;integrated security=true");
4: SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand();
5: cmd.Connection = cnn; 6: cmd.CommandType = CommandType.Text;7: cmd.CommandText = TextBox1.Text + " FOR XML AUTO";
8: cnn.Open();9: //Connected Data Access关键代码
10: XmlReader reader = cmd.ExecuteXmlReader();11: StreamWriter writer = File.CreateText(@"\temp.xml");
12: writer.Write("<root>");
13: while (reader.Read())
14: { 15: writer.Write(reader.ReadOuterXml()); 16: }17: writer.Write("</root>");
18: writer.Close(); 19: reader.Close(); 20: cnn.Close(); 21: Process.Start(@"\temp.xml");
22: }
<%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeFile="Default6.aspx.cs" Inherits="Default6" %><!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<div>
Execute Select Query:
<asp:TextBox ID="TextBox1" runat="server" Height="21px" Width="371px"></asp:TextBox>
<br />
<asp:Button ID="Button1" runat="server" Text="Execute" OnClick="Button1_Click" />
<br />
Result XML File:</div>
<asp:TextBox ID="TextBox2" runat="server" Height="253px" TextMode="MultiLine" Width="508px"></asp:TextBox>
</form>
</body>
</html>
• Disconnected data access
执行步骤
1. Establish a connection with the database.
2. Fetch the data that you require and store it in some offline medium.
3. Close the database connection.
4. Work with the fetched data (perform read, modify, and delete operations or even
calculations).
5. Again, open a database connection if you wish to update the changes made to the data
back to the database.
6. Update the database, if there are any changes.
7. Close the database connection.
适合使用的情景
• Your application data can be updated in batches.
• Your application does not need up-to-the minute data from the database.
• You want to pass data across multiple layers of your system.
• You want to pass data from your application to another application.
• Your application data is generated programmatically and is not coming from any
data source.
示例代码
<%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeFile="DataSetXML.aspx.cs" Inherits="DataSetXML" %><!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<div>
Employee ID:
<asp:DropDownList ID="ddlID" runat="server" Height="27px" Width="198px" AutoPostBack="True"
OnSelectedIndexChanged="ddlID_SelectedIndexChanged">
</asp:DropDownList>
<br />
First Name:
<asp:TextBox ID="txtFirstName" runat="server" Height="23px" Width="200px"></asp:TextBox>
<br />
Last Name:
<asp:TextBox ID="txtLastName" runat="server" Height="25px" Width="200px"></asp:TextBox>
<br />
Home Phone:
<asp:TextBox ID="txtPhone" runat="server" Height="23px" Width="204px"></asp:TextBox>
<br />
Notes:
<br />
<asp:TextBox ID="txtNotes" runat="server" Height="174px" TextMode="MultiLine" Width="421px"></asp:TextBox>
<br />
<asp:Button ID="btnInsert" runat="server" Text="Insert" OnClick="btnInsert_Click" />
<asp:Button ID="btnUpdate" runat="server" Text="Update" OnClick="btnUpdate_Click" />
<asp:Button ID="btnDelete" runat="server" Text="Delete" OnClick="btnDelete_Click" />
<asp:Button ID="btnSave" runat="server" Text="Save" Height="26px" Width="59px" OnClick="btnSave_Click" />
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
1: using System;
2: using System.Data;
3: using System.Data.SqlClient;
4: 5: public partial class DataSetXML : System.Web.UI.Page
6: {7: string strConn = @"data source=.;initial catalog=northwind;integrated security=true";
8: DataSet ds = new DataSet();
9: SqlDataAdapter da = new SqlDataAdapter();
10: SqlConnection cnn;11: protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
12: {13: cnn = new SqlConnection(strConn);
14: SqlCommand cmdEmployees = new SqlCommand();
15: cmdEmployees.CommandText = "SELECT * FROM employees";
16: cmdEmployees.Connection = cnn; 17: da.SelectCommand = cmdEmployees;18: da.Fill(ds, "Employees");
19: FillEmployees(); 20: }21: private void FillEmployees()
22: {23: if (!IsPostBack)
24: { 25: ddlID.Items.Clear(); 26: }27: foreach (DataRow row in ds.Tables["Employees"].Rows)
28: {29: if (row.RowState != DataRowState.Deleted)
30: { 31: ddlID.Items.Add(row["EmployeeID"].ToString());
32: } 33: } 34: }35: protected void ddlID_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
36: { 37: string id = ddlID.SelectedItem.ToString();
38: DataRow[] rows = ds.Tables["Employees"].Select("EmployeeID=" + id);
39: txtFirstName.Text = rows[0]["firstname"].ToString();
40: txtLastName.Text = rows[0]["lastname"].ToString();
41: txtPhone.Text = rows[0]["homephone"].ToString();
42: txtNotes.Text = rows[0]["notes"].ToString();
43: }44: protected void btnInsert_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
45: {46: DataRow row = ds.Tables["Employees"].NewRow();
47: row["employeeid"] = ddlID.Text;
48: row["firstname"] = txtFirstName.Text;
49: row["lastname"] = txtLastName.Text;
50: row["homephone"] = txtPhone.Text;
51: row["notes"] = txtNotes.Text;
52: ds.Tables["Employees"].Rows.Add(row);
53: FillEmployees(); 54: }55: protected void btnUpdate_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
56: {57: if (ddlID.SelectedItem == null)
58: {59: Response.Write("Please select Employee ID!");
60: return;
61: } 62: string id = ddlID.SelectedItem.ToString();
63: DataRow[] rows = ds.Tables["Employees"].Select("EmployeeID=" + id);
64: rows[0].BeginEdit();65: rows[0]["firstname"] = txtFirstName.Text;
66: rows[0]["lastname"] = txtLastName.Text;
67: rows[0]["homephone"] = txtPhone.Text;
68: rows[0]["notes"] = txtNotes.Text;
69: rows[0].EndEdit(); 70: }71: protected void btnDelete_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
72: {73: if (ddlID.SelectedItem == null)
74: {75: Response.Write("Please select Employee ID!");
76: return;
77: }78: string id = ddlID.SelectedItem.ToString();
79: DataRow[] rows = ds.Tables["Employees"].Select("EmployeeID=" + id);
80: rows[0].Delete(); 81: FillEmployees(); 82: }83: protected void btnSave_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
84: {85: SqlCommand cmdInsert = new SqlCommand();
86: SqlCommand cmdUpdate = new SqlCommand();
87: SqlCommand cmdDelete = new SqlCommand();
88: cmdInsert.Connection = cnn; 89: cmdUpdate.Connection = cnn; 90: cmdDelete.Connection = cnn;91: cmdInsert.CommandText = "INSERT INTO employees(firstname,lastname,homephone,notes) VALUES(@fname,@lname,@phone,@notes)";
92: cmdUpdate.CommandText = "UPDATE employees SET firstname=@fname,lastname=@lname,homephone=@phone WHERE employeeid=@empid";
93: cmdDelete.CommandText = "DELETE FROM employees WHERE employeeid=@empid";
94: SqlParameter[] pInsert = new SqlParameter[4];
95: pInsert[0] = new SqlParameter("@fname", SqlDbType.VarChar);
96: pInsert[0].SourceColumn = "firstname";
97: pInsert[1] = new SqlParameter("@lname", SqlDbType.VarChar);
98: pInsert[1].SourceColumn = "lastname";
99: pInsert[2] = new SqlParameter("@phone", SqlDbType.VarChar);
100: pInsert[2].SourceColumn = "homephone";
101: pInsert[3] = new SqlParameter("@notes", SqlDbType.VarChar);
102: pInsert[3].SourceColumn = "notes";
103: foreach (SqlParameter p in pInsert)
104: { 105: cmdInsert.Parameters.Add(p); 106: }107: SqlParameter[] pUpdate = new SqlParameter[5];
108: pUpdate[0] = new SqlParameter("@fname", SqlDbType.VarChar);
109: pUpdate[0].SourceColumn = "firstname";
110: pUpdate[1] = new SqlParameter("@lname", SqlDbType.VarChar);
111: pUpdate[1].SourceColumn = "lastname";
112: pUpdate[2] = new SqlParameter("@phone", SqlDbType.VarChar);
113: pUpdate[2].SourceColumn = "homephone";
114: pUpdate[3] = new SqlParameter("@notes", SqlDbType.VarChar);
115: pUpdate[3].SourceColumn = "notes";
116: pUpdate[4] = new SqlParameter("@empid", SqlDbType.VarChar);
117: pUpdate[4].SourceColumn = "employeeid";
118: foreach (SqlParameter p in pUpdate)
119: { 120: cmdUpdate.Parameters.Add(p); 121: }122: SqlParameter[] pDelete = new SqlParameter[1];
123: pDelete[0] = new SqlParameter("@empid", SqlDbType.VarChar);
124: pDelete[0].SourceColumn = "employeeid";
125: foreach (SqlParameter p in pDelete)
126: { 127: cmdDelete.Parameters.Add(p); 128: } 129: da.InsertCommand = cmdInsert; 130: da.UpdateCommand = cmdUpdate; 131: da.DeleteCommand = cmdDelete;132: da.Update(ds, "Employees");
133: ds.AcceptChanges(); 134: } 135: }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号