Java集合,概念及一般代码操作
集合
常用集合的分类:
Collection 接口的接口 对象的集合(单列集合)
├——-List 接口:元素按进入先后有序保存,可重复
│—————-├ LinkedList 接口实现类, 链表, 插入删除, 没有同步, 线程不安全
│—————-├ ArrayList 接口实现类, 数组, 随机访问, 没有同步, 线程不安全
│—————-└ Vector 接口实现类 数组, 同步, 线程安全
│ ———————-└ Stack 是Vector类的实现类
└——-Set 接口: 仅接收一次,不可重复,并做内部排序
├—————-└HashSet 使用hash表(数组)存储元素
│————————└ LinkedHashSet 链表维护元素的插入次序
└ —————-TreeSet 底层实现为二叉树,元素排好序
Map 接口 键值对的集合 (双列集合)
├———Hashtable 接口实现类, 同步, 线程安全
├———HashMap 接口实现类 ,没有同步, 线程不安全-
│—————–├ LinkedHashMap 双向链表和哈希表实现
│—————–└ WeakHashMap
├ ——–TreeMap 红黑树对所有的key进行排序
└———IdentifyHashMap
Collection
java.util.Collection 是集合工具类,用来对集合的操作。部分操作如下
public static <T> bollean addAll(Collection<T> c,T... elements);//添加多个元素
public static <T> void shuffle(List<T> l);//打乱元素顺序
public static <T> void sort(List<T> l)//将集合中元素按照默认规则排序
List
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E>
特点
-
有序的集合,存储元素和去除的元素顺序是一致的
-
有索引,包含了一些带索引的方法
-
允许存储重复的元素
ArrayList
特点
-
适合查询,不适合增删改
-
线程不安全
List接口中带索引的方法(特有):
-
-public void void add(int index, E element): 将指定元素,添加到指定位置上
-
-public E set(int index, E element): 用指定元素替换集合中指定位置的元素,返回值的更新前元素
-
-public E get (int inde): 返回集合中指定位置的元素
-
-public E remove (int inde): 移除集合中指定位置的元素,返回的是被移除的元素
一般操作
public void test01() {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("a");
list.add("c");
list.add("d");
list.add("g");
list.add("a");
// 添加
list.add(3, "lkl");
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println("=========");
// 移除
String remove = list.remove(2);
System.out.println("被移除的元素是:" + remove);
System.out.println(list);
// 替换
String hzy = list.set(3, "hzy");
System.out.println("被替换的元素" + hzy);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println("遍历=========");
System.out.println("增强for循环遍历=========");
// 遍历
// 增强for循环
for (String s : list) {
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("一般for循环=========");
// 一般for循环
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); ++i) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
System.out.println("迭代器=========");
// 迭代器
Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
LinkedList
List接口的链接列表实现。实现所有可选的列表操作,并且允许所有元素(包括null)。除了实现List接口外,LinkedList类还为在列表的开头及结尾get、remove和insert元素提供了统一的命名方法。这些操作允许将链接列表用作堆栈、队列[双端队列。
特点
-
有很多操作首尾元素的方法
-
底层是链表:增删改快,查询慢
-
线程不安全
注意:使用linkedList的话,不能使用多态,因为它有很多特有的方法
一般方法
public void addFirst(E e) 将制定的元素插入此列表的开头
public void addLast(E e) 将制定的元素插入此列表的结尾
public E pop( )从此列表所表示的堆栈处弹出一个元素。
public void push(E e )从此列表所表示的堆栈处弹出一个元素。
public E removeFirst () 移除并返回此列表的第一个元素。
public E removeLast () 移除并返回此列表的最后一个元素。
// LinkedList 主要方法
Vector
public class Vector<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, Serializable
Vector 类可以实现可增长的对象数组。与数组一样,它包含可以使用整数索引进行访问的组件。但是,Vector 的大小可以根据需要增大或缩小,以适应创建 Vector 后进行添加或移除项的操作。
-
单线程、速度慢
set
java.util.Set接口 extends Collection接口
特点
-
不允许存储重复的元素
-
没有索引,没有带索引的方法,也不能用普通的for循环遍历
-
根据hashcode() 和 equals()方法 共同判断是否重复
hashSet
-
基于 HashMap 来实现的,是一个不允许有重复元素的集合。
-
允许有 null 值。
-
是无序的,即不会记录插入的顺序。
-
不是线程安全的。
-
HashSet 实现了 Set 接口。
一般代码
// 去重操作 HashSet 需要重写hashCode() 和 equals()方法
treeSet
-
有序
一般操作
// TreeSet
学生类
package com.pojo;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
/**
* @author 刘凯丽
* @createTime 2021/4/18 21:27
* @projectName javase-study
* @className Student.java
* @description TODO
*/
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private String name;
private int age;
LinkedHashSet
java.util.LinkedHashSet extends HashSet集合
特点:
底层是一个哈希表(数组+链表/红黑树)+链表;多了一条链表
保证其中元素是有序的
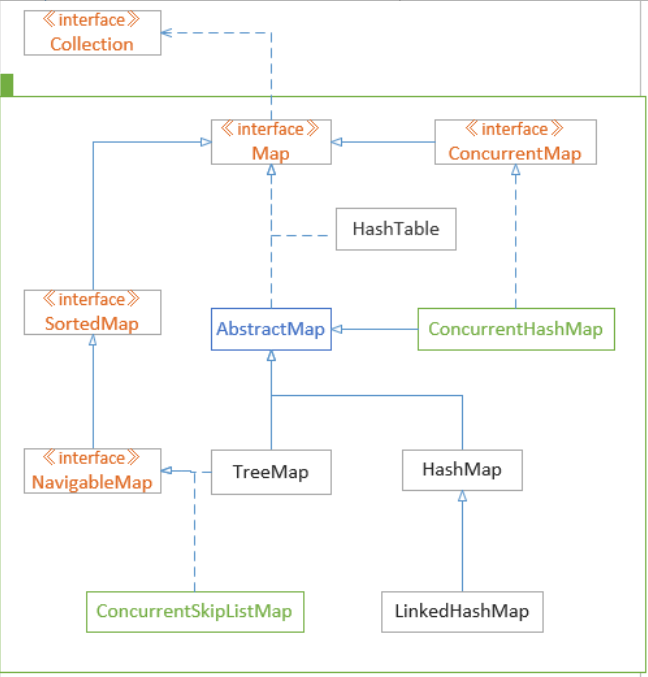
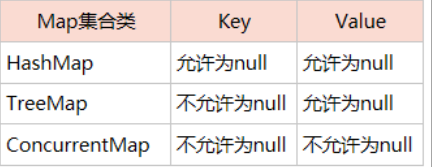
Map


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号