算法
数据结构
数组
二分法
非递归
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
if (target < nums[0] || target > nums[nums.length - 1]) {
return -1;
}
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
return mid;
} else if (target < nums[mid]) {
right = mid - 1;
} else if (target > nums[mid]) {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
递归
package javasuanfa;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
int target = 3;
System.out.println(search(nums, target,0,nums.length-1));
}
public static int search(int[] nums, int target, int left, int right) {
if (target < nums[0] || target > nums[nums.length - 1]) {
return -1;
}
left = 0;
right = nums.length - 1;
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (target < nums[mid]) {
return search(nums, target, left, mid - 1);
}
else if (target > nums[mid]) {
return search(nums, target, mid + 1, right);
}
else {
return mid;
}
}
}
双指针
删除数组元素
class Solution {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
int slowp=0;
for(int fastp=0;fastp<nums.length;fastp++){
if(nums[fastp]!=val){
nums[slowp++]=nums[fastp];
}
}
return slowp;
}
}
有序数组平方
class Solution {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
int[] result =new int[nums.length];
int left=0;
int right=nums.length-1;
for(int k=nums.length-1;k>=0;k--){
int lsquare=nums[left]*nums[left];
int rqsuare=nums[right]*nums[right];
if(rqsuare>lsquare) {
result[k] = rqsuare;
right--;
}
else {
result[k]=lsquare;
left++;
}
}
return result;
}
}
滑动窗口(长度最小子数组)
class Solution {
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
int left = 0;
int sum = 0;
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int right = 0; right < nums.length; right++) {
sum += nums[right];
while (sum >= target) {
result = Math.min(result, right - left + 1);
sum -= nums[left++];
}
}
return result == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : result;
}
}
螺旋矩阵
class Solution {
public int[][] generate
Matrix(int n) {
int[][] result = new int[n][n];
//填充数字
int insert=1;
//循环次数
int loop = n / 2;
//偏移量
int offset=0;
//起始位置
int StartX = 0;
int StartY = 0;
//坐标
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
//中间
int mid=n/2;
while (loop>0){
x=StartX;
y=StartY;
//上行
for(;x<n-offset-1;x++){
result[y][x]=insert++;
}
//右列
for (;y<n-offset-1;y++){
result[y][x]=insert++;
}
//下列
for(;x>StartX;x--){
result[y][x]=insert++;
}
//左列
for (;y>StartY;y--){
result[y][x]=insert++;
}
loop--;
offset++;
StartX++;
StartY++;
}
if(n%2==1)result[mid][mid]=insert;
if(n==1)result[0][0]=1;
return result;
}
}
广义表
1. 广义表的定义
广义表(Lists,又称列表)是线性表的推广。即广义表中放松对表元素的原子限制,容许它们具有其自身结构。
广义表是n(n≥0)个元素a1,a2,…,ai,…,an的有限序列。
其中:
①ai--或者是原子或者是一个广义表。
②广义表通常记作:
Ls=( a1,a2,…,ai,…,an)。
③Ls是广义表的名字,n为它的长度。
④若ai是广义表,则称它为Ls的子表。
注意:
①广义表通常用圆括号括起来,用逗号分隔其中的元素。
②为了区分原子和广义表,书写时用大写字母表示广义表,用小写字母表示原子。
③若广义表Ls非空(n≥1),则al是LS的表头,其余元素组成的表(a1,a2,…,an)称为Ls的表。
④广义表是递归定义的。
2. 广义表的表示
(1)广义表常用表示
① E=()
E是一个空表,其长度为0。
② L=(a,b)
L是长度为2的广义表,它的两个元素都是原子,因此它是一个线性表
③ A=(x,L)=(x,(a,b))
A是长度为2的广义表,第一个元素是原子x,第二个元素是子表L。
④ B=(A,y)=((x,(a,b)),y)
B是长度为2的广义表,第一个元素是子表A,第二个元素是原子y。
⑤ C=(A,B)=((x,(a,b)),((x,(a,b)),y))
C的长度为2,两个元素都是子表。
⑥ D=(a,D)=(a,(a,(a,(…))))
D的长度为2,第一个元素是原子,第二个元素是D自身,展开后它是一个无限的广义表。
(2)广义表的深度
一个表的"深度"是指表展开后所含括号的层数。
【例】表L、A、B、C的深度为分别为1、2、3、4,表D的深度为∞。
(3)带名字的广义表表示
如果规定任何表都是有名字的,为了既表明每个表的名字,又说明它的组成,则可以在每个表的前面冠以该表的名字,于是上例中的各表又可以写成:
①E()
②L(a,b)
③A(x,L(a,b))
④B(A(x,L(a,b)),y)
⑤C(A(x,l(a,b)),B(A(x,L(a,b)),y))
⑥D(a,D(a,D(…)))
(4)广义表的图形表示
①图中的分支结点对应广义表
②非分支结点一般是原子
③但空表对应的也是非分支结点。
【例】下图给出了几个广义表的图形表示

图 广义表的图形表示
3. 广义表的操作
广义表的基本操作主要有以下5种:
(1)GetHead(L):求广义表的表头操作。如果广义表是空表,返回NULL,否则返回指向表头结点的指针。
(2)GetTail(L):求广义表的表尾操作。如果广义表是空表,返回NULL,否则返回指向表尾结点的指针。
(3)GListLength(L):返回广义表的长度操作。如果广义表是空表,则返回0,否则返回广义表的长度。
(4)GListDepth(L):求广义表的深度操作。深度就是广义表中括号嵌套的层数。空表返回1,否则返回表的深度。
(5)CopyGList(&T,L):广义表的复制操作。由广义表L复制得到广义表T。复制成功返回1,否则返回0。
广义表中的每个元素可以用一个结点表示,表中有两类结点:原子结点和子表结点。广义表可以分解为表头和表尾,一个表头和一个表尾可以确定一个广义表。因此,一个表结点一般由三个域组成:标志域、指向表头的指针域和指向表尾的指针域。一个原子结点一般由两个域组成:标志域和值域。4. 广义表的运算
在此,只讨论广义表的两个特殊的基本运算:取表头head(Ls)和取表尾tail(Ls)。
根据表头、表尾的定义可知:任何一个非空广义表的表头是表中第一个元素,它可以是原子,也可以是子表,而其表尾必定是子表。
【例】
head(L)=a, tail(L)=(b)
head(B)=A, tail(B)=(y)
由于tail(L)是非空表,可继续分解得到:
head(tail(L))=b, tail(tail(L))=()
对非空表A和(y),也可继续分解。
注意:广义表()和(())不同。前者是长度为0的空表,对其不能做求表头和表尾的运算;而后者是长度为l的非空表(只不过该表中惟一的一个元素是空表),对其可进行分解,得到的表头和表尾均是空表()。
表
- iterator迭代器
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_29689343/article/details/113832455
SeqList
操作合集
完整代码
#include "SeqList.h"
#include "stdlib.h" //realloc
#include "String" //string
#include "assert.h" //assert
#include "iostream" //cout
using namespace std;
//初始化操作
int SeqList:: InitList(SeqList& L) {
L.elem = new int[LIST_INIT_SIZE];
L.length = 0;
L.listsize = LIST_INIT_SIZE;
return OK;
}
//增加存储容量
int SeqList:: addlistsize(SeqList& L, int n) {
int* newbase = (int*)realloc(L.elem, (L.listsize + n * LISTINCREMENT) * sizeof(int));
if (!newbase)exit(OVERFLOW);
L.elem = newbase;
L.listsize += n * LISTINCREMENT;//增加储存容量
return OK;
}
//结构销毁操作
int SeqList:: DestroyList(SeqList& L) {
delete[] L.elem;
L.elem = NULL;
L.length = 0;
L.listsize = 0;
return OK;
}
//引用型操作
bool SeqList::ListEmpty(SeqList L) {
return L.length == 0;
}
int SeqList::ListLength(SeqList L) {
assert(L.elem != NULL);
cout << "顺序表长度:" << L.length<<endl;
return L.length;
}
//求前驱
int SeqList::PriorElem(SeqList L, int cur_e, int& pre_e) {
assert(L.elem != NULL);
if (LocateElem(L, cur_e) <= 0) {
cout << "该元素无前驱" << endl;
return ERROR;
}
pre_e = L.elem[LocateElem(L, cur_e) - 1];
cout << "元素"<<cur_e<<"的前驱:" << pre_e << endl;
return OK;
}
//求后驱
int SeqList::NextElem(SeqList L, int cur_e, int& next_e) {
assert(L.elem != NULL);
if (LocateElem(L, cur_e) >= L.length - 1) {
cout << "该元素无后驱" << endl;
return ERROR;
}
next_e = L.elem[LocateElem(L, cur_e) + 1];
cout << "元素" << cur_e << "的后驱:" << next_e << endl;
return OK;
}
//获取第i个元素的值返回于e
int SeqList::GetElem(SeqList L, int i, int& e) {
assert(L.elem != NULL);
if (i < 0 || i > L.length ) {
cout << "越界" << endl;
return ERROR;
}
e = L.elem[i - 1];
return OK;
}
//定位元素
int SeqList::LocateElem(SeqList L, int e) {
assert(L.elem != NULL);
for (int i = 0; i < L.length; ++i) {
if (L.elem[i] == e) {
cout << "元素" << e << "的位置:" << i<<endl;
return i;
}
}
cout << "该表内无" << e << "元素" << endl;
return ERROR;
}
//遍历打印
int SeqList::ListTraverse(SeqList L) {
assert(L.elem != NULL);
if (L.length == 0)cout << "该顺序表内无元素" << endl;
cout << "L内元素为:" ;
for (int i = 0; i < L.length; ++i) {
cout << L.elem[i] << " " ;
}
cout << endl;
return OK;
}
//置空
int SeqList:: ClearList(SeqList& L) {
delete[] L.elem;
InitList(L);
return OK;
}
//改变i位置的值
int SeqList::PutElem(SeqList& L, int i, int e) {
assert(L.elem != NULL);
if (i < 0 || i > L.length - 1) {
cout << "越界" << endl;
return ERROR;
}
L.elem[i] = e;
return OK;
}
//在第i个元素之前插入
int SeqList::ListInsert(SeqList& L, int i, int e) {
assert(L.elem != NULL);
if (i < 1 || i > L.length + 1) {
cout << "插入位置越界" << endl;
return ERROR;
}
if (L.length >= L.listsize) {//存储空间已满
addlistsize(L, 1);//增加存储10Datatype容量
}
for (int j = L.length - 1; j >= i - 1; --j)
L.elem[j + 1] = L.elem[j];
L.elem[i - 1] = e;
L.length++;
return OK;
}
//删除i个元素
int SeqList::ListDelete(SeqList& L, int i, int &e) {
assert(L.elem != NULL);
if (i < 1 || i > L.length) {
cout << "删除元素越界" << endl;
return ERROR;
}
e = L.elem[i];
for (; i < L.length-1; ++i)
L.elem[i] = L.elem[i+1];
L.length--;
return OK;
}
//尾插
int SeqList::SeqListPushBack(SeqList &L, int x) {
assert(&L);
//L.ListInsert(L,L.length+1,x); 调用插入函数
L.elem[L.length] = x;
L.length++;
return OK;
}
//尾删
int SeqList::SeqListPopBack(SeqList &L) {
assert(&L);
int e;
L.ListDelete(L,L.length-1,e);
return e;
}
//测试
int SeqList:: Test() {
SeqList s;
s.InitList(s);//初始化
s.SeqListPushBack(s, 1); //尾插
s.SeqListPushBack(s, 2);
s.SeqListPushBack(s, 3);
s.ListInsert(s, 4, 4); //指定插入
s.ListTraverse(s); //遍历
int e = 2, cure_e = 2;
s.LocateElem(s, e);//获取e元素的位置
s.GetElem(s, 3, e);//获取第三个元素的值
s.PriorElem(s, cure_e, e);//求前驱
s.NextElem(s, cure_e, e);//求后驱
s.ListLength(s); //顺序表长度
s.PutElem(s, 2, 5);//改变第三个元素的值
s.SeqListPopBack(s); //尾删
s.ListTraverse(s); //遍历
s.ListLength(s);
s.ClearList(s); //置空
s.ListTraverse(s);
s.DestroyList(s); //销毁
s.ListTraverse(s);
return OK;
}
函数列举
初始化操作
int SeqList:: InitList(SeqList& L) {
L.elem = new int[LIST_INIT_SIZE];
L.length = 0;
L.listsize = LIST_INIT_SIZE;
return OK;
}
增加存储容量
int SeqList:: addlistsize(SeqList& L, int n) {
int* newbase = (int*)realloc(L.elem, (L.listsize + n * LISTINCREMENT) * sizeof(int));
if (!newbase)exit(OVERFLOW);
L.elem = newbase;
L.listsize += n * LISTINCREMENT;//增加储存容量
return OK;
}
结构销毁操作
int SeqList:: DestroyList(SeqList& L) {
delete[] L.elem;
L.elem = NULL;
L.length = 0;
L.listsize = 0;
return OK;
}
判空
bool SeqList::ListEmpty(SeqList L) {
return L.length == 0;
}
求长
int SeqList::ListLength(SeqList L) {
assert(L.elem != NULL);
cout << "顺序表长度:" << L.length<<endl;
return L.length;
}
求前驱
int SeqList::PriorElem(SeqList L, int cur_e, int& pre_e) {
assert(L.elem != NULL);
if (LocateElem(L, cur_e) <= 0) {
cout << "该元素无前驱" << endl;
return ERROR;
}
pre_e = L.elem[LocateElem(L, cur_e) - 1];
cout << "元素"<<cur_e<<"的前驱:" << pre_e << endl;
return OK;
}
求后驱
int SeqList::NextElem(SeqList L, int cur_e, int& next_e) {
assert(L.elem != NULL);
if (LocateElem(L, cur_e) >= L.length - 1) {
cout << "该元素无后驱" << endl;
return ERROR;
}
next_e = L.elem[LocateElem(L, cur_e) + 1];
cout << "元素" << cur_e << "的后驱:" << next_e << endl;
return OK;
}
获取第i个元素的值返回于e
int SeqList::GetElem(SeqList L, int i, int& e) {
assert(L.elem != NULL);
if (i < 0 || i > L.length ) {
cout << "越界" << endl;
return ERROR;
}
e = L.elem[i - 1];
return OK;
}
定位元素
int SeqList::LocateElem(SeqList L, int e) {
assert(L.elem != NULL);
for (int i = 0; i < L.length; ++i) {
if (L.elem[i] == e) {
cout << "元素" << e << "的位置:" << i<<endl;
return i;
}
}
cout << "该表内无" << e << "元素" << endl;
return ERROR;
}
遍历打印
int SeqList::ListTraverse(SeqList L) {
assert(L.elem != NULL);
if (L.length == 0)cout << "该顺序表内无元素" << endl;
cout << "L内元素为:" ;
for (int i = 0; i < L.length; ++i) {
cout << L.elem[i] << " " ;
}
cout << endl;
return OK;
}
置空
int SeqList:: ClearList(SeqList& L) {
delete[] L.elem;
InitList(L);
return OK;
}
改变i位置的值
int SeqList::PutElem(SeqList& L, int i, int e) {
assert(L.elem != NULL);
if (i < 0 || i > L.length - 1) {
cout << "越界" << endl;
return ERROR;
}
L.elem[i] = e;
return OK;
}
在第i个元素之前插入
int SeqList::ListInsert(SeqList& L, int i, int e) {
assert(L.elem != NULL);
if (i < 1 || i > L.length + 1) {
cout << "插入位置越界" << endl;
return ERROR;
}
if (L.length >= L.listsize) {//存储空间已满
addlistsize(L, 1);//增加存储10Datatype容量
}
for (int j = L.length - 1; j >= i - 1; --j)
L.elem[j + 1] = L.elem[j];
L.elem[i - 1] = e;
L.length++;
return OK;
}
删除i个元素
int SeqList::ListDelete(SeqList& L, int i, int &e) {
assert(L.elem != NULL);
if (i < 1 || i > L.length) {
cout << "删除元素越界" << endl;
return ERROR;
}
e = L.elem[i];
for (; i < L.length-1; ++i)
L.elem[i] = L.elem[i+1];
L.length--;
return OK;
}
尾插
int SeqList::SeqListPushBack(SeqList &L, int x) {
assert(&L);
//L.ListInsert(L,L.length+1,x); 调用插入函数
L.elem[L.length] = x;
L.length++;
return OK;
}
置空
int SeqList:: ClearList(SeqList& L) {
delete[] L.elem;
InitList(L);
return OK;
}
尾删
int SeqList::SeqListPopBack(SeqList &L) {
assert(&L);
int e;
L.ListDelete(L,L.length-1,e);
return e;
}
LinkedList
操作合集
#include "ListNode.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
ListNode::ListNode()
{
this->val =0;
this->next =nullptr;
}
ListNode::ListNode(int val, ListNode* next)
{
this->val = val;
this->next = next;
}
ListNode::ListNode(int val)
{
this->val = val;
}
ListNode::ListNode( ListNode* next)
{
this->next = next;
}
int ListNode::Val()
{
return val;
}
//初始化
ListNode* ListNode::initList(ListNode* head,int a[],int n) {
int inputnum;
int i=0;
ListNode* node;
ListNode* nodetemp;
head = nullptr;
nodetemp = nullptr;
while (n--) {
inputnum=a[i];
i++;
node = new ListNode;
node->val = inputnum;
if (head == nullptr) {
head = node;
}
else
{
nodetemp->next = node;
}
nodetemp = node;
nodetemp->next = nullptr;
}
return head;
}
//创建
ListNode* ListNode::CreatList(ListNode* head,int n) {
cout << "input:";
int inputnum;
ListNode* node;
ListNode* nodetemp;
head = nullptr;
nodetemp = nullptr;
while (n--) {
cin >> inputnum;
node = new ListNode;
node->val = inputnum;
if (head == nullptr) {
head = node;
}
else
{
nodetemp->next = node;
}
nodetemp = node;
nodetemp->next = nullptr;
}
return head;
}
//遍历
int ListNode::ListTravel(ListNode* head) {
cout << "链表元素依次为:" ;
ListNode* curnode=new ListNode();
curnode = head;
while (curnode != nullptr) {
cout << curnode->val<<" ";
curnode = curnode->next;
}
return OK;
}
//翻转链表(双指针)
ListNode* ListNode::reverseList_1(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* temp; //保存cur下一个节点
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* pre = NULL;
while (cur) {
temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
//翻转链表(递归)
ListNode* ListNode::reverseList_2(ListNode* head) {
return reverse(NULL, head);
}
ListNode* ListNode::reverse(ListNode* pre, ListNode* cur) {
if (cur == NULL)return pre;
ListNode* temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
return reverse(cur, pre);
}
//链表左右两两交换
ListNode* ListNode::swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummtyHead = new ListNode(0);//虚拟头节点
dummtyHead->next = head;
ListNode* cur = dummtyHead;
while (cur->next != NULL && cur->next->next != NULL) {
ListNode* tmp = cur->next;//记录临时节点
ListNode* tmp1 = cur->next->next->next;//记录临时节点
cur->next = cur->next->next->next;//第一步
cur->next->next = tmp;//第二步
cur->next->next->next = tmp1;//第三步
cur = cur->next->next;//cur向后移动两位,准备下一轮交换
}
return dummtyHead->next;
}
//链表长度
int ListNode::ListLength(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* cur = head;
int n = 0;
while (cur->next != NULL) {
cur = cur->next;
n++;
}
return n;
}
//删除倒数第N个
ListNode* ListNode::deletebehindN(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* cur = head;
int length = ListLength(head);
for (int i = 0; i < length - n; i++) {
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = cur->next->next;
return head;
}
//删除倒数第N个(双指针)
ListNode* ListNode::removeNthfromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode* fast = dummyHead;
ListNode* slow = dummyHead;
while (n-- && fast != nullptr) {
fast = fast->next;
}
fast = fast->next;//再往前走一步,让slow指向删除节点前一个
while (fast != nullptr) {
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
slow->next = slow->next->next;
return dummyHead->next;
}
//判断是否有环
ListNode* ListNode::ifcircle(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* fast;
ListNode* slow;
int count = 0;
fast = slow = head;
while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if (fast == slow) {
ListNode* index1;
ListNode* index2;
index1 = head;
index2 = fast;
while (index1 != index2) {
count++;
index1 = index1->next;
index2 = index2->next;
}
return index2;
}
}
return NULL;
}
//相交节点
ListNode* ListNode::getIntersectionNode(ListNode* headA, ListNode* headB) {
ListNode* curA = headA;
ListNode* curB = headB;
int lenA = 0, lenB = 0;
while (curA != NULL) {
lenA++;
curA = curA->next;
}
while (curB != NULL) {
lenB++;
curB = curB->next;
}
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
if (lenB > lenA) {
int i = lenB - lenA;
while (i--)
{
curB = curB->next;
}
}
else
{
int i = lenA - lenB;
while (i--)
{
curA = curA->next;
}
}
while (curA != curB) { //地址相等
curA = curA->next;
curB = curB->next;
}
return curA;
}
函数列举
初始化
ListNode* ListNode::initList(ListNode* head,int a[],int n) {
int inputnum;
int i=0;
ListNode* node;
ListNode* nodetemp;
head = nullptr;
nodetemp = nullptr;
while (n--) {
inputnum=a[i];
i++;
node = new ListNode;
node->val = inputnum;
if (head == nullptr) {
head = node;
}
else
{
nodetemp->next = node;
}
nodetemp = node;
nodetemp->next = nullptr;
}
return head;
}
创建
ListNode* ListNode::CreatList(ListNode* head,int n) {
cout << "input:";
int inputnum;
ListNode* node;
ListNode* nodetemp;
head = nullptr;
nodetemp = nullptr;
while (n--) {
cin >> inputnum;
node = new ListNode;
node->val = inputnum;
if (head == nullptr) {
head = node;
}
else
{
nodetemp->next = node;
}
nodetemp = node;
nodetemp->next = nullptr;
}
return head;
}
遍历
int ListNode::ListTravel(ListNode* head) {
cout << "链表元素依次为:" ;
ListNode* curnode=new ListNode();
curnode = head;
while (curnode != nullptr) {
cout << curnode->val<<" ";
curnode = curnode->next;
}
return OK;
}
翻转链表(双指针)
ListNode* ListNode::reverseList_1(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* temp; //保存cur下一个节点
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* pre = NULL;
while (cur) {
temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
翻转链表(递归)
ListNode* ListNode::reverseList_2(ListNode* head) {
return reverse(NULL, head);
}
ListNode* ListNode::reverse(ListNode* pre, ListNode* cur) {
if (cur == NULL)return pre;
ListNode* temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
return reverse(cur, pre);
}
链表左右两两交换
ListNode* ListNode::swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummtyHead = new ListNode(0);//虚拟头节点
dummtyHead->next = head;
ListNode* cur = dummtyHead;
while (cur->next != NULL && cur->next->next != NULL) {
ListNode* tmp = cur->next;//记录临时节点
ListNode* tmp1 = cur->next->next->next;//记录临时节点
cur->next = cur->next->next->next;//第一步
cur->next->next = tmp;//第二步
cur->next->next->next = tmp1;//第三步
cur = cur->next->next;//cur向后移动两位,准备下一轮交换
}
return dummtyHead->next;
}
链表长度
int ListNode::ListLength(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* cur = head;
int n = 0;
while (cur->next != NULL) {
cur = cur->next;
n++;
}
return n;
}
删除倒数第N个
ListNode* ListNode::deletebehindN(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* cur = head;
int length = ListLength(head);
for (int i = 0; i < length - n; i++) {
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = cur->next->next;
return head;
}
删除倒数第N个(双指针)
ListNode* ListNode::removeNthfromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode* fast = dummyHead;
ListNode* slow = dummyHead;
while (n-- && fast != nullptr) {
fast = fast->next;
}
fast = fast->next;//再往前走一步,让slow指向删除节点前一个
while (fast != nullptr) {
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
slow->next = slow->next->next;
return dummyHead->next;
}
判断是否有环
ListNode* ListNode::ifcircle(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* fast;
ListNode* slow;
int count = 0;
fast = slow = head;
while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if (fast == slow) {
ListNode* index1;
ListNode* index2;
index1 = head;
index2 = fast;
while (index1 != index2) {
count++;
index1 = index1->next;
index2 = index2->next;
}
return index2;
}
}
return NULL;
}
相交节点
ListNode* ListNode::getIntersectionNode(ListNode* headA, ListNode* headB) {
ListNode* curA = headA;
ListNode* curB = headB;
int lenA = 0, lenB = 0;
while (curA != NULL) {
lenA++;
curA = curA->next;
}
while (curB != NULL) {
lenB++;
curB = curB->next;
}
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
if (lenB > lenA) {
int i = lenB - lenA;
while (i--)
{
curB = curB->next;
}
}
else
{
int i = lenA - lenB;
while (i--)
{
curA = curA->next;
}
}
while (curA != curB) { //地址相等
curA = curA->next;
curB = curB->next;
}
return curA;
}
移除列表元素(JAVA)
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
while (head != null && head.val == val) {
head = head.next;
}
// 已经为null,提前退出
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
// 已确定当前head.val != val
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == val) {
pre.next = cur.next;
} else {
pre = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return head;
}
设计链表(JAVA)
//单链表
class LinkedNode {
int val;
LinkedNode next;
LinkedNode(){}
LinkedNode(int val) {
this.val=val;
}
}
class MyLinkedList {
int size;
LinkedNode head;
public MyLinkedList() {
size = 0;
head = new LinkedNode(0);
}
public int get(int index) {
if(index>=size){
return -1;
}
if(index<0){
index=0;
}
LinkedNode pre=head;
for(int i =0;i<=index;i++){
pre=pre.next;
}
return pre.val;
}
public void addAtHead(int val) {
addAtIndex(0, val);
}
public void addAtTail(int val) {
addAtIndex(size, val);
}
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if (index > size) {
return;
}
if (index < 0) {
index = 0;
}
size++;
LinkedNode pre = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
LinkedNode toAdd = new LinkedNode(val);
toAdd.next = pre.next;
pre.next = toAdd;
}
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if (index >= size) {
return;
}
if (index < 0) {
index = 0;
}
size--;
LinkedNode pre=head;
for(int i=0;i<index;i++){
pre=pre.next;
}
pre.next=pre.next.next;
}
public void overTurn() {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode temp = null;
while (cur != null) {
temp = cur.next;//保存下一节点
cur.next = prev;//连接上一节点
prev = cur;//保存当前节点
cur = temp;//切换节点
}
head.next= prev;
ListNode newnode =head;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
newnode=newnode.next;
}
newnode.next=null;
}
public void reverseList(ListNode Start,ListNode End) {
head.next = reverse(Start,End );
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode prev, ListNode cur) {
if (cur == null) {
return prev;
}
ListNode temp = null;
temp = cur.next;// 先保存下一个节点
cur.next = prev;// 反转
// 更新prev、cur位置
// prev = cur;
// cur = temp;
return reverse(cur, temp);
}
}
结构体定义
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "stdio.h"
#include "cstdlib"
#define OK 1;
#define ERROR -1;
#define LIST_INIT_SIZE 100
#define LISTINCREMENT 10
typedef char ElemType;
typedef int Status;
typedef struct LNode {//单链表
ElemType data; //数据
struct LNode* next; //下一指针
}LNode, * LinkList;
typedef struct DuLNode {//双向链表
ElemType data;
struct DuLNode* prior;
struct DuLNode* next;
}DuLNode, * DiLinkList;
typedef struct SeqList {
int* elem;//线性表首地址
int length;//长度
int listsize = LIST_INIT_SIZE;//当前分配的存储空间
};
表的初始化,不带头节点,内置,顺序
LinkList CreatSlist()
{
LinkList head = NULL;
for (int i = 5; i >= 1; i--)
{
LinkList newhead = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
newhead->data = i;
newhead->next = head;
head = newhead;
}
return head;
}
顺序创建,输入,n
void CreatListno(LinkList& L, int n) {
L = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
L->next = NULL;
LinkList nL = L;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
LinkList p = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
scanf("%d", &p->data);
p->next = nL->next;
nL->next = p;
nL = p;
}
}
逆序创建输入单链表,n
void CreateList(LinkList& L, int n) {
L = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
L->next = NULL;
for (int i = n; i > 0; i--) {
LinkList p = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
scanf("%d", & p->data);
p->next = L->next;
L->next = p;
}
}
遍历
void travel(LinkList L) {
LinkList p = L->next;
if (!p)printf("空表");
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%c ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
打印输出
void print(LinkList P)
{
while (P != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", P->data);
P = P->next;
}
printf("\n");
return;
}
取第i个结点元素
Status GetElem(LinkList L,int i,ElemType &e) {
LinkList p = L->next;
int j = i;
while (p && j < i) {
p = p->next;
++j;
}
if (!p || j > i)return ERROR;
e = p->data;
return OK;
}
在第i个元素之前插入
Status ListInsert(LinkList &L,int i,ElemType e) {
LinkList p = L;
int j = i;
while (p && j < i-1) {
p = p->next;
++j;
}
if (!p || j < i - 1) {
return ERROR;
}
LinkList q = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
q->data = e;
q->next = p->next;
p->next = q;
return OK;
}
删除data值为x的结点
void ListDel_X(LinkList& L, int x) {
if (L->next == NULL) {
printf("空表无法删除\n");
return;
}
LinkList p = L->next, pre_p = L;
int flag = 0;
while (p) {
if (p->data == x) {
pre_p->next = p->next;
free(p);
p = pre_p->next;
//p=p->next;
//pre_p->next=p;
flag = 1;
}
else {
pre_p = p;
p = p->next;
}
}
flag == 1 ? printf("已删除\n") : printf("无此元素\n");
}
删除data值为x的直接前驱结点
void ListDel_Xpre(LinkList& L, int x) {
if (L->next == NULL) {
printf("空表无法删除\n");
return;
}
LinkList p = L->next, pre_p = L;
if (p->data == x)
printf("首元素无前驱无法执行操作\n");
p = p->next;
int flag = 0;
while (p) {
if (p->data == x) {
pre_p->next = p;
p = pre_p->next->next;
//p=p->next;
//pre_p->next=p;
flag = 1;
}
else {
pre_p = pre_p->next;
p = p->next;
}
}
flag == 1 ? printf("已删除直接前驱\n") : printf("无此元素\n");
}
删除第i个结点
Status ListDelete(LinkList& L, int i, ElemType e) {
LinkList p = L;
int j = i;
while (p->next && j < i - 1) {
p = p->next;
++j;
}
if (!p->next || j > i - 1)return ERROR;
p->next = p->next->next;
return OK;
}
删除最小元素结点
Status DelMinNode(LinkList& head) {
LinkList p = head->next, pre = head;
LinkList minp=NULL, minpre=NULL;
ElemType min = p->data;
while (p != NULL) {
if (p->data < pre->data) {
min = p->data;
minp = p;
minpre = pre;
}
pre = p;
p = p->next;
}
minpre->next = minp->next;
free(minp);
return OK;
}
改造单向循环链表
Status linklist_cycle(LNode* head) {
LNode* p = head;
if (!p)return ERROR;
while (p->next != NULL)//时间复杂度为O(n)为链表长度
p = p->next;
p->next = head;
return OK;
}
连接循环链表
Status merge(LNode *L1,LNode *L2) {
LNode* p = L1, * q = L2;
while (p->next != L1)p = p->next;
while (q->next != L2)q = q->next;
q->next = L1;
p->next = L2;
return OK;
}
顺序表逆置最小辅助空间(顺序表)
Status Invert_seqList(SeqList &L) {
ElemType temp;
for (int i = 0; i < L.length / 2; i++) {
temp = L.elem[i];
L.elem[i] = L.elem[L.length - i - 1];
L.elem[L.length - i - 1] = temp;
}
return OK;
}
逆置算法(三辅助)
Status invent(LinkList &head){
LinkList p, q, r;
if (!head->next)return ERROR;
p = head->next;
q = p->next;
p->next = NULL;
while (q) {
r = q;
q = q->next;
head->next = r;
r->next = p;
p = r;
}
}
头插法
LinkList reserve(LinkList &head) {
LinkList temp=NULL, phead=NULL;
while (head != NULL) {
temp = head;
head = head->next;
temp->next = phead;
phead = temp;
}
return phead;
}
就地逆置
LinkList reverse_2(LinkList& head) {
LinkList p = NULL,q = NULL;
p = head;
q = head->next;
while (q != NULL) {
p->next = q->next;
q->next = head;
head = q;
q = p->next;
}
p = NULL;
return head;
}
判断回文
Status ifPalin(){
char c;
int flag = 1;
LinkList L1,L2;
L1 = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
L2 = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
L1->next = NULL;
L2->next = NULL;
LinkList nL1= L1,nL2=L2;
LinkList p= (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
LinkList q = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
while ((c=getchar())!='@')
{
//顺序
p = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
p->data = c;
p->next = nL1->next;
nL1->next = p;
nL1 = p;
//逆序
q = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
q->data = c;
q->next = nL2->next;
nL2->next = q;
}
nL1 = L1->next;
nL2 = L2->next;
while (nL1!=NULL)
{
if (nL1->data == nL2->data) { nL1 = nL1->next; nL2 = nL2->next; }
else
{
printf("bu是");
return 0;
}
}
printf("是");
return 1;
}
栈
理论
底层容器:缺省情况下deque(双向队列)/list/vector
std::stack<int, std::vector<int> > third; // 使用vector为底层容器的栈
std::queue<int, std::list<int>> third; // 定义以list为底层容器的队列
标准栈操作
push(x) -- 将一个元素放入队列的尾部。
pop() -- 从队列首部移除元素。
peek() -- 返回队列首部的元素。
empty() -- 返回队列是否为空。
操作合集(用stackr容器)
class Solution {
public:
struct abb {
int data;
}abb;
private: string s;
public:
//有效的括号
bool isValid(string s) {
if (s.size() % 2 != 0)return false;//为奇数一定不匹配
stack<char> st;
cout << st.empty();
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
if (s[i] == '(')st.push(')');
else if (s[i] == '{')st.push('}');
else if (s[i] == '[')st.push(']');
else if (st.empty() || st.top() != s[i])return false;
else st.pop();
}
return st.empty();
}
//删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
string removeDuplicates(string S) {
stack<char> st;
for (char s : S) {
if (st.empty() || s != st.top()) {
st.push(s);
}
else
{
st.pop();
}
}
string result = "";
while (!st.empty()) {
result += st.top();
st.pop();
}
reverse(result.begin(), result.end());
return result;
}
//逆波兰表达式求值
int evalRPN(vector<string> &s) {
stack<int> st;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
int num1 = st.top();
st.pop();
int num2 = st.top();
st.pop();
if (s[i] == "+" || s[i] == "-" || s[i] == "*" || s[i] == "/") {
if (s[i] == "+")st.push(num1 + num2);
if (s[i] == "-")st.push(num1 - num2);
if (s[i] == "*")st.push(num1 * num2);
if (s[i] =="/")st.push(num1 / num2);
}
else {
st.push(stoi(s[i]));
}
}
int result = st.top();
st.pop();
return result;
}
};
操作合集(自定义结构体)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cstdlib>//malloc
#define OK 1
#define ERROR -1
#define STACK_INIT_SIZE 100 //初始分配空间
#define STACKINCREMENT 10 //分配增量
typedef int ElemType;
typedef int Status;
//栈的链式实现
typedef struct SNode{
ElemType data;
struct SNode* next;
}SNode,*StackPtr;
typedef struct {
StackPtr top;//栈顶指针
int count; //元素数
}LinkStack;
Status InitStackLink(LinkStack &S) {
S.top = NULL;
S.count = 0;
return OK;
}
Status GetTopLink(LinkStack S,ElemType &e) {
printf("COUNT:%d\n",S.count);
if (S.count == 0)return ERROR;
e = S.top->data;
printf("gettop:%d",e);
return OK;
}
Status PopLink(LinkStack &S,ElemType &e) {
if (S.count == 0)return ERROR;
e = S.top->data;
S.top = S.top->next;
S.count--;
return OK;
}
Status PushLink(LinkStack& S, ElemType e) {
SNode* p = (StackPtr)malloc(sizeof(SNode));
if (!p)printf("ERROR\n");
p->data = e;
p->next = S.top;
S.top = p;
printf("push:%d\n",S.top->data);
S.count++;
return OK;
}
//栈的顺序实现
typedef struct {
ElemType* base;//存储空间基址
ElemType* top;//栈顶指针
int StackSize;//已分配空间
}SqStack;
//初始化操作
Status InitStack(SqStack &S) {
S.base = (ElemType*)malloc(STACK_INIT_SIZE*sizeof(ElemType));
if (!S.base) { exit(OVERFLOW); }
S.top = S.base;
S.StackSize = STACK_INIT_SIZE;
return OK;
}
//取栈顶元素
Status GetTop(SqStack S) {
if (S.top == S.base)return ERROR;
return *(S.top-1);
}
//进栈
Status Push(SqStack& S, ElemType e) {
if (S.top - S.base >= S.StackSize) {
S.base = (ElemType*)realloc(S.base, S.StackSize+STACKINCREMENT * sizeof(ElemType));
if (!S.base)exit(OVERFLOW);
S.top = S.base + S.StackSize;
S.StackSize += STACKINCREMENT;
}
*(S.top++) = e;
return OK;
}
//出栈
Status Pop(SqStack& S, ElemType& e) {
if (S.top == S.base)return ERROR;
e = *(--S.top);
return OK;
}
//判断栈空
bool StackEmpty(SqStack S) {
if (S.base == S.top)return true;
else
{
return false;
}
}
//进制转换 不断取模入栈,num=num/n
void conversion(int num,int n,ElemType &e) {
ElemType temp;
SqStack S;
int flag = 1;
while (num) {
Push(S, num % n);
num = num / n;
}
while (!StackEmpty(S)) {
Pop(S, temp);
if (flag)flag = 0;
else
{
e = temp * 10 + temp;
}
printf("&d", temp);
}
printf("\n");
printf("%d", e);
}
//判断是否为运算符,是运算符返回1,若不是返回0
int In(char c)
{
switch (c) {
case '+':
case '-':
case '*':
case '/':
case '(':
case ')':
case '=':
return 1;
default:
return 0;
}
}
//判断是否为数,是运算符返回1,若不是返回0
int InNum(char c)
{
if (c >= 48 && c <= 57)return 1;
else
{
return 0;
}
}
//比较优先级
char Precede(char operate1, char operate2)
{
int i, j;
char pre[7][7] = {// + - * / ( ) =
{'>','>','<','<','<','>','>'},
{'>','>','<','<','<','>','>'},
{'>','>','>','>','<','>','>'},
{'>','>','>','>','<','>','>'},
{'<','<','<','<','<','=','0'},
{'>','>','>','>','0','>','>'},
{'<','<','<','<','<','0','='} };
switch (operate1) {
case '+': i = 0; break;
case '-': i = 1; break;
case '*': i = 2; break;
case '/': i = 3; break;
case '(': i = 4; break;
case ')': i = 5; break;
case '=': i = 6; break;
}
switch (operate2) {
case '+': j = 0; break;
case '-': j = 1; break;
case '*': j = 2; break;
case '/': j = 3; break;
case '(': j = 4; break;
case ')': j = 5; break;
case '=': j = 6; break;
}
return(pre[i][j]);
}
//操作
int Operate(int a, char operate, int b)
{
int result;
switch (operate) {
case'+':return a + b;
case'-':return a - b;
case'*':return a * b;
case'/': //判断除数是否为0,若除数为零返回错误提示
if (b != 0)
return a / b;
else
{
printf("0不能作为被除数!\n");
exit(1);
}
}
}
//数学表达式求值
ElemType EvaluateExpressione(char content[]) {
SqStack OPTR;//运算符栈
SqStack OPND;//运算数栈;
InitStack(OPTR);
InitStack(OPND);
Push(OPTR, '=');
int temp;
int e;//存放pop操作符
int a,b;//pop操作数
int x, y;//存放数
char ch;//读取内容字符
int i = 0;//表达式数组下标
ch = content[i];
while (ch != '=' || GetTop(OPTR) != '=') {
if (InNum(ch)) {//是操作数
x = ch - '0';
Push(OPND, x);
y = x;
ch = content[++i];//读取下一位字符并将指针向后偏移一位
while (InNum(ch))
{
x = ch - '0';
y = 10 * y + x;
Pop(OPND, a);
Push(OPND, y);
ch = content[++i];//读取下一位字符并将指针向后偏移一位
}
}
else if(In(ch)) {//操作符
switch (Precede(GetTop(OPTR), ch))//比较ch的与OPTR栈顶元素的优先级
{
case'<':
Push(OPTR, ch);
ch = content[++i]; //读取下一位字符并将指针向后偏移一位
break;
case'>':
Pop(OPTR, e);
Pop(OPND, a);
Pop(OPND, b);
Push(OPND, Operate(b,e,a));
break;
case'=':
Pop(OPTR,temp);
ch =content[++i]; //读取下一位字符并将指针向后偏移一位
break;
}
}
else
{
printf("输入包含无效字符!");
exit(1);
}
}
return GetTop(OPND);
}
//数学表达式求值
ElemType EvaluateExpressione2( ) {
SqStack OPTR;//运算符栈
SqStack OPND;//运算数栈;
InitStack(OPTR);
InitStack(OPND);
Push(OPTR, '=');
int a, b, e,x;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch != '=' || GetTop(OPTR) != '=') {
if (!In(ch)) {//是操作数
Push(OPND,ch);
printf("操作数");
ch = getchar();
}
else {//操作符
switch (Precede(GetTop(OPTR), ch))//比较ch的与OPTR栈顶元素的优先级
{
case'<':
Push(OPTR, ch);
ch = getchar();
break;
case'>':
Pop(OPTR, e);
Pop(OPND, a);
Pop(OPND, b);
Push(OPND, Operate(b, e, a));
break;
case'=':
Pop(OPTR, x);
ch = getchar();
break;
}
}
}
return GetTop(OPND);
}
Status main() {
char content[100]; //定义一个字符数组用于存储表达式
int result;
int i = 0;
do {
i = 0;
printf("请输入表达且以=结束:\n");
do {
content[i++] = getchar();
} while (content[i - 1] != '=');
result = EvaluateExpressione(content);
printf("%d\n", result);
getchar();
printf("请按回车以继续,若结束请输入!");
} while (getchar() != '!');
return 0;
}
Pair数据类型
1.1 pair类型概述
pair的功能就像它的名字一样,pair将一对值组合成一个值,这一对值可以具有不同的数据类型,两个值可以分别用pair的两个公有函数first和second访问。
pair类所在的头文件与命名函数是:
#include <utility>
1.2 pair对象基本定义
pair是一种模板类型,其中包含两个数据值,两个数据的类型可以不同,基本的定义如下:
pair<int, string> a;
表示a中有两个类型,第一个元素是int型的,第二个元素是string类型的,如果创建pair的时候没有对其进行初始化,则调用默认构造函数对其初始化。
pair<string, string> a("James", "Joy");
也可以像上面一样在定义的时候直接对其初始化。
由于pair类型的使用比较繁琐,因为如果要定义多个形同的pair类型的时候,可以时候typedef简化声明:
typedef pair<string, string> author;
author pro("May", "Lily");
author joye("James", "Joyce");
1.3 pair对象访问
对于pair类,由于它只有两个元素,分别名为first和second,因此直接使用普通的点操作符即可访问其成员
pair<string, string> a("Lily", "Poly");
string name;
name = pair.second;
1.4 生成新的pair对象
可以使用make_pair对已存在的两个数据构造一个新的pair类型:
int a = 8;
string m = "James";
pair<int, string> newone;
newone = make_pair(a, m);
队列
操作合集
class Myqueue { //实现单调队列(从大到小)滑动窗口最大值
public:
deque<int> que;
//弹出前检查是否为空且弹出元素是否为front元素
void pop(int value) {
if (!que.empty() && value == que.front()) {
que.pop_front();
7h77777777777777777777777777
}
void push(int value) {
while (!que.empty() && value > que.back()) {
que.pop_back();
}
que.push_back(value);
}
int front() {
return que.front();
}
vector<int> maxSlidingwindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
Myqueue que;
vector<int> result;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
que.push(nums[i]);
}
result.push_back(que.front());
for (int i = k; i < nums.size(); i++) {
que.pop(nums[i - k]);
que.push(nums[i]);
result.push_back(que.front());
}
return result;
}
};
class priqueue {//前k个高频元素(优先级队列)
public:
// 小顶堆
class mycomparison {
public:
bool operator()(const pair<int, int>& lhs, const pair<int, int>& rhs) {
return lhs.second > rhs.second;
}
};
vector<int> topKFrequent(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
// 要统计元素出现频率
unordered_map<int, int> map; // map<nums[i],对应出现的次数>
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
map[nums[i]]++;
}
// 对频率排序
// 定义一个小顶堆,大小为k
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, mycomparison> pri_que;
// 用固定大小为k的小顶堆,扫面所有频率的数值
for (unordered_map<int, int>::iterator it = map.begin(); it != map.end(); it++) {
pri_que.push(*it);
if (pri_que.size() > k) { // 如果堆的大小大于了K,则队列弹出,保证堆的大小一直为k
pri_que.pop();
}
}
// 找出前K个高频元素,因为小顶堆先弹出的是最小的,所以倒序来输出到数组
vector<int> result(k);
for (int i = k - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
result[i] = pri_que.top().first;
pri_que.pop();
}
return result;
}
};
函数列举
滑动窗口最大值
class Myqueue { //实现单调队列(从大到小)滑动窗口最大值
public:
deque<int> que;
//弹出前检查是否为空且弹出元素是否为front元素
void pop(int value) {
if (!que.empty() && value == que.front()) {
que.pop_front();
7h77777777777777777777777777
}
void push(int value) {
while (!que.empty() && value > que.back()) {
que.pop_back();
}
que.push_back(value);
}
int front() {
return que.front();
}
vector<int> maxSlidingwindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
Myqueue que;
vector<int> result;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
que.push(nums[i]);
}
result.push_back(que.front());
for (int i = k; i < nums.size(); i++) {
que.pop(nums[i - k]);
que.push(nums[i]);
result.push_back(que.front());
}
return result;
}
};
前k个高频元素(优先级队列)
class priqueue {
public:
// 小顶堆
class mycomparison {
public:
bool operator()(const pair<int, int>& lhs, const pair<int, int>& rhs) {
return lhs.second > rhs.second;
}
};
vector<int> topKFrequent(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
// 要统计元素出现频率
unordered_map<int, int> map; // map<nums[i],对应出现的次数>
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
map[nums[i]]++;
}
// 对频率排序
// 定义一个小顶堆,大小为k
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, mycomparison> pri_que;
// 用固定大小为k的小顶堆,扫面所有频率的数值
for (unordered_map<int, int>::iterator it = map.begin(); it != map.end(); it++) {
pri_que.push(*it);
if (pri_que.size() > k) { // 如果堆的大小大于了K,则队列弹出,保证堆的大小一直为k
pri_que.pop();
}
}
// 找出前K个高频元素,因为小顶堆先弹出的是最小的,所以倒序来输出到数组
vector<int> result(k);
for (int i = k - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
result[i] = pri_que.top().first;
pri_que.pop();
}
return result;
}
};
树
任务点
- 二叉树
- 二叉搜索树
- avl树
- 红黑树
树的定义和基本术语
-
树的定义:n(n≥0)个结点的有限集。在任一棵非空树中:
- 有且仅有一个特定称为根的结点
- n>1时,其余结点可分为m(m>0)个互不相交的有限集T1,T2,…,Tm,Ti称为树的子树。
- 树的性质:
- 递归性
- 层次性
- 树的基本术语:
- 树的结点:数据元素及若干指向其子树的分支
- 结点的度:结点拥有的子树的个数
- 树的度:树中所以结点的度的最大值
- 叶子结点(终端结点):树中所以结点的度的最大值
- 分支结点(非终端结点):度大于0的结点
- 孩子:结点的子树的根
- 双亲:B是A的孩子,则A是B的双亲
- 兄弟:同一双亲的孩子互称兄弟
- 堂兄弟:双亲在同一层的结点
- 祖先:从根到该节点所经分支上的所有结点
- 子孙:以某结点为根的子树中的任一结点都是该结点的子孙
- 结点的层次:从根结点算起,根为第一层,它的孩子为第二层...
- 树的深度:树中结点的最大层次树数
- 路径的长:从结点n1到nk的路径的长为路径上的边的条数
- 深度:对任意结点ni,ni的深度为从根到ni的唯一路径的长
- 高:从ni到一片树叶的最长路径的长
- 有序树:树中结点的各子树从左到右有次序(不能互换)
- 无序树:树中结点的各子树从左到右无次序(能互换)
- 森林:m(m>=0)棵互不相交的树的集合
二叉树的性质
- 在二叉树的第i层上至多有2^(i-1)^个结点
- 深度为K的二叉树至多有2^K^-1个结点
- 任意一棵二叉树,终端结点数为n0,度为2的结点数为n2,则n0=n2+1
- 任意一课树,结点总数N,分支总数B,则N=B+1=n0+n1+n2....
- 有n个结点的完全二叉树的深度为[log~2~^n^]+1(下取整)
- 按层序遍历二叉树有
- 若i=1,无双亲;若i>1,其双亲是[i/2](下取整)
-
若2i>n,为叶子结点;否则,其左孩子为2i
-
若2i+1>n,无右孩子;否则,其右孩子为2i+1
二叉树的种类
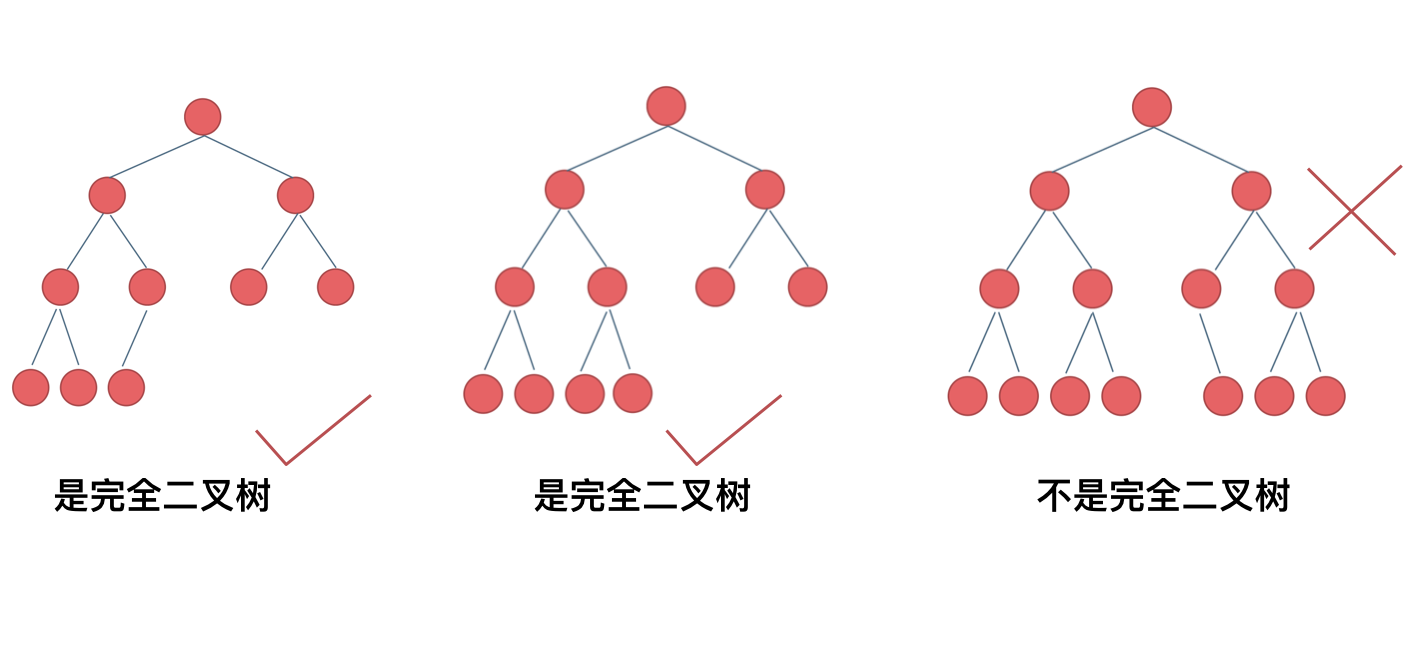
满二叉树
满二叉树:如果一棵二叉树只有度为0的结点和度为2的结点,并且度为0的结点在同一层上,则这棵二叉树为满二叉树。
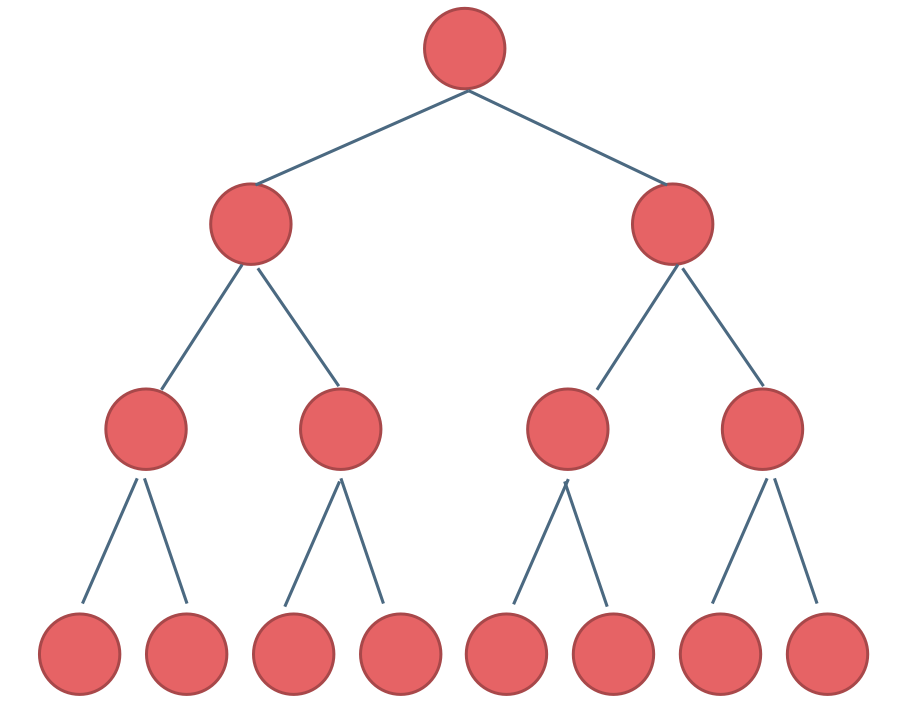
完全二叉树
在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2(h-1) 个节点。
优先级队列其实是一个堆,堆就是一棵完全二叉树,同时保证父子节点的顺序关系。
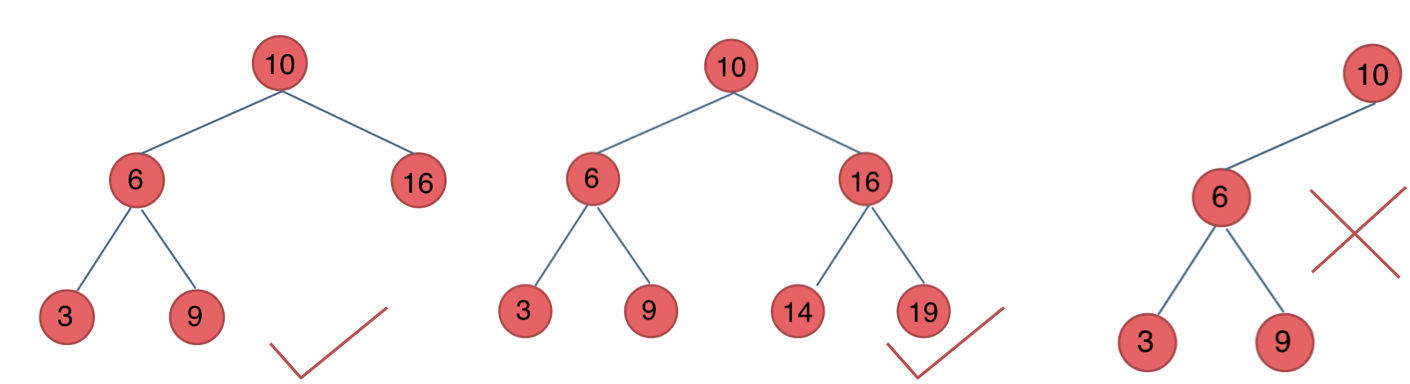
二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树是一个有序树。
- 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
- 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
- 它的左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树
平衡二叉搜索树
平衡二叉搜索树:又被称为AVL(Adelson-Velsky and Landis)树,且具有以下性质:它是一棵空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树
二叉树算法
二叉树结点实现(存储结构)
顺序存储
#define MAX_TREE_SIZE 100
typedef TElemType SqBTree[MAX_TREE_SIZE];
SqBTree bt;
缺点:浪费空间,始于满/完全二叉树(要把空结点也表示出来)
链式存储
二叉
-
含有n个结点的二叉链表有n+1个空链域
-
c
typedef struct BiTNode{
ElemType val;
struct BiTNode *lchild,*rchild;
}BiTNode,*BiTree;
- c++
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
- java
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
三叉
- c
typedef struct ThiTNode{
TElemType val;
struct ThiTNode *lchild,*rchild,*parent;
}ThiTNode,*ThiTree;
遍历二叉树
遍历方式
- 二叉树主要有两种遍历方式:
- 深度优先遍历:先往深走,遇到叶子节点再往回走。
- 广度优先遍历:一层一层的去遍历。
- 深度优先遍历
- 前序遍历(递归法,迭代法)
- 中序遍历(递归法,迭代法)
- 后序遍历(递归法,迭代法)
- 广度优先遍历
- 层次遍历(迭代法)
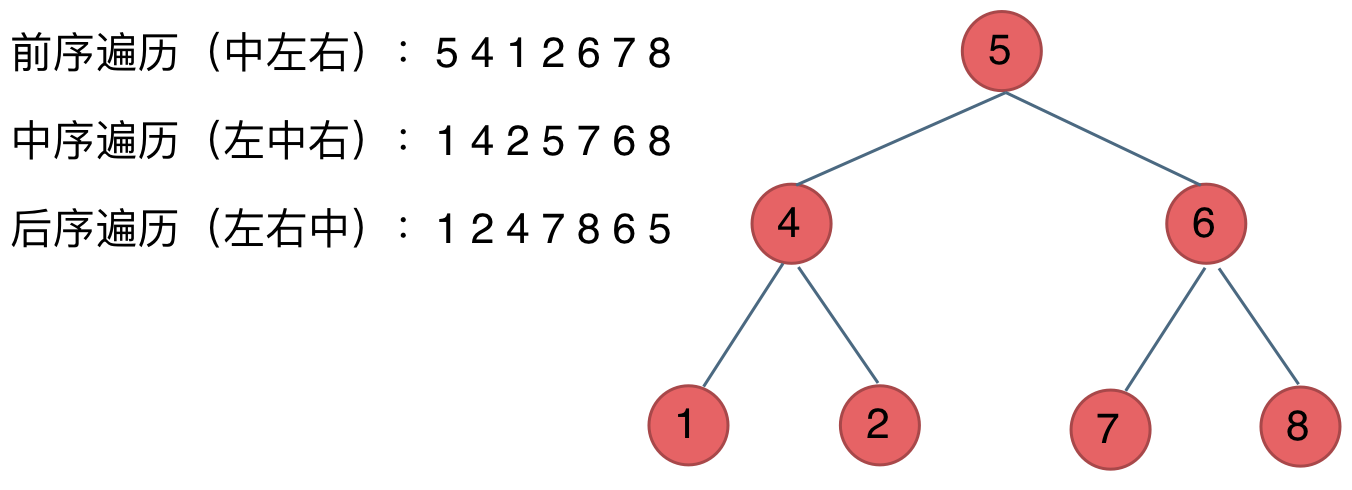
- 前中后指中间结点的遍历顺序
- 前序遍历:中左右
- 中序遍历:左中右
- 后序遍历:左右中
算法实现
递归遍历
- 确定递归函数的参数和返回值: 确定哪些参数是递归的过程中需要处理的,那么就在递归函数里加上这个参数, 并且还要明确每次递归的返回值是什么进而确定递归函数的返回类型。
- 确定终止条件: 写完了递归算法, 运行的时候,经常会遇到栈溢出的错误,就是没写终止条件或者终止条件写的不对,操作系统也是用一个栈的结构来保存每一层递归的信息,如果递归没有终止,操作系统的内存栈必然就会溢出。
- 确定单层递归的逻辑: 确定每一层递归需要处理的信息。在这里也就会重复调用自己来实现递归的过程。
- c++
void PreTravesal(TreeNode* cur,vector<int>& result){ if(cur==NULL) return;//终止条件 result.push(cur->val); PreTravesal(cur->lchild,result);//左孩子 PreTravesal(cur->rchild,result);//右孩子 } void InTravesal(TreeNode* cur,vector<int>& result){ if(cur==NULL) return;//终止条件 PreTravesal(cur->lchild,result);//左孩子 result.push(cur->val); PreTravesal(cur->rchild,result);//右孩子 } void PostTravesal(TreeNode* cur,vector<int>& result){ if(cur==NULL) return;//终止条件 PreTravesal(cur->lchild,result);//左孩子 PreTravesal(cur->rchild,result);//右孩子 result.push(cur->val); }- c
Status PreTraversal(BiTree T,Status(* Visit)(TElemType e)) { if (T) { if (Visit(T->data)) if (PreTraversal(T->lchild, Visit)) if (PreTraversal(T->rchild, Visit)) return OK; return ERROR;//防止Visit()返回0 } else { return OK; } return OK; } Status InTraversal(BiTree T, Status(*Visit)(TElemType e)) { if (T) { if (InTraversal(T->lchild, Visit)) if (Visit(T->data)) if (InTraversal(T->rchild, Visit)) return OK; return ERROR;//防止Visit()返回0 } else { return OK; } return OK; } Status PostTraversal(BiTree T, Status(*Visit)(TElemType e)) { if (T) { if (PostTraversal(T->lchild, Visit)) if (PostTraversal(T->rchild, Visit)) if (Visit(T->data)) return OK; return ERROR;//防止Visit()返回0 } else { return OK; } return OK; }迭代遍历
- 迭代遍历(非统一)
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { stack<TreeNode*> st; vector<int> result; if (root == NULL) return result; st.push(root); while (!st.empty()) { TreeNode* node = st.top(); // 中 st.pop(); result.push_back(node->val); if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右(空节点不入栈) if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左(空节点不入栈) } return result; } vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { vector<int> result; stack<TreeNode*> st; TreeNode* cur = root; while (cur != NULL || !st.empty()) { if (cur != NULL) { // 指针来访问节点,访问到最底层 st.push(cur); // 将访问的节点放进栈 cur = cur->left; // 左 } else { cur = st.top(); // 从栈里弹出的数据,就是要处理的数据(放进result数组里的数据) st.pop(); result.push_back(cur->val); // 中 cur = cur->right; // 右 } } return result; } vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { stack<TreeNode*> st; vector<int> result; if (root == NULL) return result; st.push(root); while (!st.empty()) { TreeNode* node = st.top(); st.pop(); result.push_back(node->val); if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 相对于前序遍历,这更改一下入栈顺序 (空节点不入栈) if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 空节点不入栈 } reverse(result.begin(), result.end()); // 将结果反转之后就是左右中的顺序了 return result; }- 迭代遍历(统一)
vector<int> preorderTraversalT(TreeNode* root) { vector<int> result; stack<TreeNode*> st; if (root != NULL) st.push(root); while (!st.empty()) { TreeNode* node = st.top(); if (node != NULL) { st.pop(); if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右 if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左 st.push(node); // 中 st.push(NULL); } else { st.pop(); node = st.top(); st.pop(); result.push_back(node->val); } } return result; } vector<int> inorderTraversalT(TreeNode* root) { vector<int> result; stack<TreeNode*> st; if (root != NULL) st.push(root); while (!st.empty()) { TreeNode* node = st.top(); if (node != NULL) { st.pop(); // 将该节点弹出,避免重复操作,下面再将右中左节点添加到栈中 if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 添加右节点(空节点不入栈) st.push(node); // 添加中节点 st.push(NULL); // 中节点访问过,但是还没有处理,加入空节点做为标记。 if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 添加左节点(空节点不入栈) } else { // 只有遇到空节点的时候,才将下一个节点放进结果集 st.pop(); // 将空节点弹出 node = st.top(); // 重新取出栈中元素 st.pop(); result.push_back(node->val); // 加入到结果集 } } return result; } vector<int> postorderTraversalT(TreeNode* root) { vector<int> result; stack<TreeNode*> st; if (root != NULL) st.push(root); while (!st.empty()) { TreeNode* node = st.top(); if (node != NULL) { st.pop(); st.push(node); // 中 st.push(NULL); if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右 if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左 } else { st.pop(); node = st.top(); st.pop(); result.push_back(node->val); } } return result; }层序遍历
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) { queue<TreeNode*> que; if (root != NULL) que.push(root); vector<vector<int>> result; while (!que.empty()) { int size = que.size(); vector<int> vec; // 这里一定要使用固定大小size,不要使用que.size(),因为que.size是不断变化的 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { TreeNode* node = que.front(); que.pop(); vec.push_back(node->val); if (node->left) que.push(node->left); if (node->right) que.push(node->right); } result.push_back(vec); } return result; } }; # 递归法 class Solution { public: void order(TreeNode* cur, vector<vector<int>>& result, int depth) { if (cur == nullptr) return; if (result.size() == depth) result.push_back(vector<int>()); result[depth].push_back(cur->val); order(cur->left, result, depth + 1); order(cur->right, result, depth + 1); } vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) { vector<vector<int>> result; int depth = 0; order(root, result, depth); return result; } };创建二叉树
//先序 Status PreCreateBiTree(BiTree &T){ char ch; scanf("%c",&ch); if(ch=='')T=NULL; else{ if(!(T=(BiTnode*)malloc(sizeof(TNode)))) exit(OVERFLOW); T->data=ch;//中 PreCreateBiTree(T->lchild);//左 PreCreateBiTree(T->rchild);//右 } return OK; }翻转二叉树
void invertTree(TreeNode* root){ if(root==NULL) return; swap(root->lchild,root->rchild); invertTree(root->lchild); invertTree(root->rchild); } void swap(TreeNode* lchild,TreeNode* rchild){ TreeNode* temp; temp=lchild; lchild=rchild; rchild=temp; }对称二叉树
bool compare(TreeNode* L,TreeNode* R){ //都空 if(L==NULL&&R==NULL) return true; //左空右不空 else if(L==NULL&&R!=NULL) return false; //右空左不空 else if(R==NULL&&L!=NULL) return false; //左右不空且不等 else if(L!=R) return false; //接下来就是左右都有值且相等 bool l=compare(L->lchild,R->rchild);//左子树:左 ;右子树:右 bool r=compare(L->rchild,R->lchild);//左子树:右 ;右子树:左 bool isSame=l&&r; //中 return isSame; } bool isduic(TreeNode* root){ if(root==NULL) return true; return compare(root->lchild,root->rchild); }统计叶子结点个数
Status CountLeaf(BiTree T,int& count){ if(T){ if((T->lchild==NULL)&&(T->rchild==NULL)){count++;return OK;} CountLeaf(T->lchild,count); //访问左 CountLeaf(T->rchild,count); //访问右 }else return ERROR; }求二叉树的深度
int Depth(BiTree T){ int d=0,dl=0,dr=0; if(!T) d=0; else{ dl=Depth(T->lchild); dr=Depth(T->rchild); d=1+max(dl,dr); } return d; }求二叉树的最小深度
int getDepth(TreeNode* node) { if (node == NULL) return 0; int leftDepth = getDepth(node->left); // 左 int rightDepth = getDepth(node->right); // 右 // 中 // 当一个左子树为空,右不为空,这时并不是最低点 if (node->left == NULL && node->right != NULL) { return 1 + rightDepth; } // 当一个右子树为空,左不为空,这时并不是最低点 if (node->left != NULL && node->right == NULL) { return 1 + leftDepth; } int result = 1 + min(leftDepth, rightDepth); return result; }求完全二叉树结点个数
普通二叉树逻辑,按后序遍历
int getNodesNum(TreeNode* T){ int n,ln,rn; if(!T) return 0; else{ ln=getNodesNum(T->lchild); rn=getNodesNum(T->rchild); n=ln+rn+1; return n; } }int getNodesNum(TreeNode* T,int &count){ if(T){ count++; getNodesNum(T->lchild,count); getNodesNum(R->lchild,count); } }完全二叉树逻辑,求每个子树的满二叉树
int getNodesNum(TreeNode*T){ if(!T)return 0; int ldeep=0,rdeep=0; TreeNode* lt=T->lchild; TreeNode* rt=T->rchild; while(lt){ lt=lt->lchild; ldeep++; } while(rt){ rt=rt->rchild; rdeep++; } if(ldeep==rdeep){ return (2<<ldeep)-1; } return getNodesNum(T->lchild)+getNodesNum(T->rchild)+1; }判断平衡二叉树
int getHeight(TreeNode* T){ if(!T)return 0; int leftHeight=getHeight(T->lchild); if(leftHeight==-1)return -1; int rightHeight=getHeight(T->rchild); if(rightHeight==-1)return -1; return abs(leftHeight-rightHeight)>1?-1: 1+max(leftHeight,rightHeight); } Boolean ifph(TreeNode* T){ return getHeight(T)==-1?false : true; }求根节点到叶子节点的所有路径
class Solution{ private: void traversal(TreeNode* T,vector<int>& path,vector<string>& result){ path.push_back(T->val); if(T->lchild==NULL&&T->rchild==NULL){ string spath; for(int i=0;i<path.size()-1;i++){ spath=path[i].toString(); spath+="->"; } spath+=path[path.szie()-1]; reslut.push_back(spath); return; } if(T->lchild){ Traversal(T->lchild,path,reslut); path.pop_back(); } if(T->rchild){ Traversal(T->rchild,path,reslut); path.pop_back(); } } public: vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* T){ vector<string> result; vector<int> path; if(T==NULL)return result; traversal(T,path,result); return result; } }左叶子之和
class Solution{ int leftCount(TreeNod *T){ if(!T)return 0; int left=0; if(T->left&&!T->left->left&&!T->right->right){//是左叶子 int left= T->left->val; }else if(T->left){ int left= leftCount(T->left); } int right= leftCount(T->right); return left+right; } } class Solution { public: int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) { if (root == NULL) return 0; if (root->left == NULL && root->right== NULL) return 0; int leftValue = sumOfLeftLeaves(root->left); // 左 if (root->left && !root->left->left && !root->left->right) { // 左子树就是一个左叶子的情况 leftValue = root->left->val; } int rightValue = sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right); // 右 int sum = leftValue + rightValue; // 中 return sum; } };求树最左边的值
递归法
class Solution{ public: int maxDepth=INT_MIN; int result; void travesal(TreeNode* T,int depth){ if(T->left==NULL&&T->right==NULL){ if(depth>maxDepth){ result=T->val; maxDepth=depth; } return; } if(T->left){ travesal(T->left,depth+1);//隐藏回溯 } if(T->left){ travesal(T->left,depth+1);//隐藏回溯 } return; } int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* T){ travesal(T,0); return result; } }迭代层序遍历
class Solution{ public: int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* T){ queue<TreeNode*>que; for(roo!=NULL)que.push(T); int reuslt=0; while(!qy=ue.empty()){ int size=que,size(); for(int i=0;i>size;i++){ TreeNode* node=que.front(); que.pop(); if(i==0)result=node->val; if(node->left)que.push(node->left); if(node->right)que.push(node->right); } } return result; } }AVL树
AVL定义
AVL树是带有平衡条件的二叉查找树,即每一个结点的左右子树的高度最多差1的二叉查找树(空树高定义为-1)
AVL具体算法
结点声明
struct AvlNode { ElemType element; AvlNode *left; AvlNode *right; int height; AvlNode(const ElemType &element,AvlNode *lt,AvlNode *rt,int h=0):element(element),left(lt),right(rt),height(h) };返回结点高度
int height(AvlNode *t)const { return t==NULL ? -1:t->height; }单旋转
void rotateWithLeftChild(AvlNode *k2){ }图
图的定义和术语
图G是由一个顶点集V和一个边集E构成的数据结构。 记为二元组形式: G= (V, E) 其中: V是由顶点构成的非空有限集合, 记为:V={V0, V1, V2, …Vn-1} E是由V中顶点的对偶构成的有限集合, 记为:E={(V0, V2), (V3, V4), … },若E为空,则图中只有顶 点而没有边。 有向图 弧、弧尾或初始点、弧头或终端点 无向图的定义和术语 子图: G =(V, E),G’= (V’, E’),若V’ V,E’ E,G’是G的子图 邻接点: 如果边(v, v’)∈E,v和v’互为邻接点 依附(相关联): 边(v,v’)依附于顶点v和v’。 顶点v的度: 和v相关联的边的数目。记为TD(v) 有向图的定义和术语 邻接到:弧<v,v’> ∈E,称v邻接到v’,v’邻接自v 顶点v的入度:以顶点v为头的弧的数目,记为ID(v) 顶点v的出度:以顶点v为尾的弧的数目,记为OD(v) 顶点v的度:TD(v)= ID(v)+ OD(v) 一个有n个顶点和e条边或弧的图,满足:e=sum(TD(v))/2 路径、回路和路径长度 在无向图G中,若存在一个顶点序列(Vp , Vi1 , Vi2 , … , Vin , Vq), 使(Vp, Vi1),(Vi1, Vi2),…,(Vin, Vq)均为图G的边,则该称顶点 的序列为顶点Vp到顶点Vq的路径。若G是有向图,则路径是有向 的。 路径长度定义为路径上的边数或者弧的数目。 若一条路径中不出现重复顶点,则称此路径为简单路径。 若一条路径的起点和终点相同(Vp=Vq)称为回路或环。 除了起点和终点相同外,其余顶点不相同的回路,称为简单回 路或简单环。 无向图的连通性 连通:顶点v至v’ 之间有路径存在。 连通图:无向图 G 的任意两点之间都连通。 连通分量:无向图的极大连通子图。 有向图的连通性 连通:顶点v至v’ 之间有路径存在。 强连通图:有向图G的任意两点之间都连通。 强连通分量:有向图的极大连通子图。 无向图的生成树 无向图生成树:图的极小连通子图。包含图的n个结点和n-1条边 1、一棵有n个顶点的生成树有且仅有n-1条边 2、一个无向图有n个顶点和小于n-1条边,是非连通图 3、一个无向图有多于n-1条边,必有环 有向图的生成森林 有向树:如果一个有向图恰有一个顶点入度为0,其余顶点入度 均为1,则是有向树。 有向图的生成森林:由若干有向树组成,含有图中全部顶点,但 只有足以构成若干棵不相交的有向树的弧。 完全图 在图G中: 若G为无向图,任意两个顶点之间都有一条边,称G为无向完全图。顶点数为n,无向完全图的边数:e=n(n-1)/2 若G为有向图,任意两个顶点之间都有弧,称G为有向完全图。顶点数为n,有向完全图的弧数:e=n(n-1) 稀疏图(sparse graph):有很少条边或弧(e<nlog2n)的图。 稠密图(dense graph):有很多条边或弧(e>nlog2n)的图。 边或弧的权值(weight):与弧或边相关的数。可以表示从一个顶点到另一个顶点的距离、花费的代价、所需的时间等。 网络(network):带权的图称之为网络。图的存储结构
数组(邻接矩阵)表示法
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20 typedef enum {DG,DN,UDG,UDN} GraphKind typedef struct ArcCell{ int adj; }ArcCell,AdjMatrix[MAX_VERTEX_NUM][MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; typedef struct { int vex[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; AdjMatrix arcs; int vexnum,arcnum; GraphKind kind; }邻接表
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20 typedef int infoType; typedef struct ArcNode{ int adjvex; //邻接下标,当前表结点 struct ArcNode *nextrac;//下一邻接结点 infoType info;//边权值 }ArcNode; typedef struct VNode{ ArcNode *firstarc; int data;//有关信息 }VNode,AdjList[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; typedef struct { AdjList vertices;//头结点数组 int vexnum,arcnum; int kind; }ALGraph;构造无向图UDG(邻接矩阵)
void creatUDG(MGraph &G){ int a,b; int i,j; scanf("%d,%d",&G.vexnum,&G.arcnum);//读入顶点、边数 for(int i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++>)scanf("%d",&G.vex[i]);//构造顶点数组 for(int i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++) for(int j=0;j<G.vexnum;i++>) G.vertices[i][j]={0,NULL}; for(int k=0;k<G.arcnum;k++){ scanf("%d,%d",&a,&b); i=LocateVex(G,a); j=LocateVex(G,b); G.arcs[i][j].adj=1; G.arcs[i][j].adj=G.arcs[j][i]; } }构造无向图UDG(邻接表)
void creatNG(ALGraph &G){ scanf("%d,%d",&G.vexnum,&G.arcnum);//读入顶点、边数 for(int i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++){//读入顶点值 scanf("%d",&G.vertices[i].data); G.vertices[i].firstarc=NULL; } for(i=0;i<G.arcnum;i++){ int a,b; scanf("%d,%d",&a,&b); p=(ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); q=(ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); p->adjvex=a;q->adjvex=b; p->nextarc=G.vertices[b].firstrac;G.vertices[b].firstrac=p;//<b,a> q->nextarc=G.vertices[a].firstrac;G.vertices[a].firstrac=q;//<a,b> } }遍历
深度优先遍历时间复杂度分析
当用邻接表时,时间复杂度O(n+e),遍历所有顶点O(n),查找所有顶点的邻接点O(e)
当用邻接矩阵时,时间复杂度O(nn),遍历所有顶点O(n),查找一个顶点的邻接点O(n),查找所有顶点的邻接点O(nn)深度优先搜索(递归)
Boolean visited[MAX];//是否已被访问 Status(*VisitFunc)(int v); void DFSTraverse(Graph G,Status(*Visit)(int v)){ VisitFunc=Visit; for(int v=0;v<G.vexnum;++v) visited[v]=FLASE; for(int v=0;v<G.vexnum;++v) if(!visited[v])DFS(G,v); } void DFS(){ visited[v]=TRUE;VisitFunc(v); for(w=FirstAdjVex(G,v);w;w=NextAdjVex(G,v,w)) if(!visited[w])DFS(G,w); } Boolean visited[MAX]; Status (*VisitFunc)(int v); void DFSTraverse(Graph G,Status(*Vistit)(int v)){ VisitFunc=Visit; for(int i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++)visited[i]=false; for(int i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++){ if(!visited[i])GFS(G,v); } } void GFS(Graph G,int v){ visited[v]=true; VisitedFunc(v);//访问 for(int w=FirstAdjVex(G,v);w;w=NextAdjVex(G,v,w)){ if(!visited[w])GFS(G,v); } } int FirstAdjVex(Graph G,int v){ return G.vertices[v].firstarc->adjvex; } int NextAdjVex(Graph G,int v,int w){ p=(ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); p=G.vertices[v].firstarc; while(p->adjvex!=w){ p=p->nextarc; } return p->nextarc->adjvex; }深度优先遍历(非递归)
Boolean visited[MAX]; void GFS(Graph p,Status(*Visit)(int v)){ for(int i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++)visited[i]=false; int p=0; cur=(ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); cur=G.vertices[0].firstarc; Stack<int> s; Visit(p); visited[p]=true; s.push(p); while(!s.empty()){ for(p=cur->adjvex;visited[p]&&cur!=null;cur=cur->nextarc,p=cur->adjvex){} if(cur==NULL){ s.pop(); cur=G.vertices[s.top()].firstarc; continue; } Visit(p); visited[p]=true; s.push(p); cur=G.vertices[p].firsttarc; } } void DFStraverse(Graph G,Status(*Visit)(int v)){ for(int v=0;v<G.vexnum;v++)visited[v]=false; stack<int> s; int u,w; for(v=0;v<G.vexnum;v++){ if(!visited[v]){ Visit(v);visited[v]=true;s.push(v); while(!s.empty()){ for(w=FirstAdjVex(G,u);w;w=NextAdjVex(G,u,w)){ if(!visited[u]){ Visit(v);visited[v]=true;s.push(v); break; } } if(!w){s.pop();} } } } }广度优先时间复杂度分析
图的遍历本质上都是对每个顶点查找邻接点的过程,所以时间复杂度同深度遍历
广度优先遍历
void BFStraverse(Graph G,Status(*Visit)(int v)){ for(int v=0;v<G.vexnum;v++)visited[v]=false; InitQueue(Q); int u,w; for(v=0;v<G.vexnum;v++){ if(!visited[v]){ Visit(v);visited[v]=true;EnQueue(Q,v); while(!QueueEmpty(Q)){ DeQueue(Q,u); for(w=FirstAdjVex(G,u);w;w=NextAdjVex(G,u,w)){ if(!visited[u]){ Visit(v);visited[v]=true;EnQueue(Q,v); } } } } } }求无向图连通分支数量
int count(Graph G){ for(int i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++){ if(visited[i]==0){ k++; DFS(G,visit); } } return k; }最小生成树
Prim算法
struct{ vertexType adjvex;//顶点下标 int lowcost;//最小权值 }closedge[MAXA]; void MiniSpanTree(MGrap G,VexType u){ int k=LocateVex(u); for(int i=0;i<vexnum;i++){ if(i!=k) closedge[i]={k,G.arcs[k][i].adj}; } closege[k].lowcost=0;//以0判断是否纳入 for(int i=1;i<vexnum;i++){ k=Mini(closedge);//找到与以纳入顶点的最路径 printf("%c->%c",closedge[k].adjvex,G.vex[k])//输出一条边 closedge[k].lowcost=0;//纳入 for(int j=0;j<vexnum;j++){//更新closedge if(G.arcs[k][j].adj<closedge[j].lowcost) closedge[j]={G.vex[k],G.arcs[k][j].adj}; } } }kruscal算法
void kruskal(Edge E[],int n,int e) { int i,j,m1,m2,sn1,sn2,k,sum=0; int vset[n+1]; for(i=1;i<=n;i++) //初始化辅助数组 vset[i]=i; k=1;//表示当前构造最小生成树的第k条边,初值为1 j=0;//E(边集)中边的下标,初值为0 while(k<e)//生成的边数小于e时继续循环 { m1=E[j].vex1; m2=E[j].vex2;//取一条边的两个邻接点 sn1=vset[m1]; sn2=vset[m2]; //分别得到两个顶点所属的集合编号 if(sn1!=sn2)//两顶点分属于不同的集合,该边是最小生成树的一条边 {//防止出现闭合回路 printf("V%d-V%d=%d\n",m1,m2,E[j].weight); sum+=E[j].weight; k++; //生成边数增加 if(k>=n) break; for(i=1;i<=n;i++) //两个集合统一编号 if (vset[i]==sn2) //集合编号为sn2的改为sn1 vset[i]=sn1; } j++;//扫描下一条边 } printf("最小权值之和=%d\n",sum); }AOV 网络和拓扑排序
定义
偏序:若集合 X 上的关系R是传递的、自反的、反对称的,
则称R是集合X上的偏序关系。指集合中部分成员之间可比较。全序:若关系R 是集合 X 上的偏序关系,如果对于每个x,y属
于X,必有xRy 或yRx ,则称R是集合X上的全序关系。指集
合中全部成员之间可比较。拓扑排序:由一个集合上的一个偏序得到该集合上的一个全
序的操作。这个全序被称为拓扑有序。AOV(Activity On Vertices)网:有向图表示工程,顶点表示活动,
有向边<vi,vj>表示活动vi必须先于活动vj进行,其中vi是vj的直接前驱,
vj是vi的直接后继。若从顶点vi到vk有一条路径,则vi是vk的前驱、vk是vi的后继。在AOV网中,不应该出现有向环。
AOV网中检测环的办法:对有向图构造其顶点的拓扑排
序序列,若网中所有顶点都在它的拓扑有序序列中,则不
存在环。(对一个无向图来说,可以用深度优先遍历,若
遇到回边,则必定存在环)算法实现
Status TopologicalSort(ALGraph G){ int Indegree[MAX]; stack<int> S; FindeIndegree(G,Indegree);//计算各结点的入度 for(int i=0,i<G.vexnum;i++){ if(!Indegree[i])push(S,i); } int count=0; p=(ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); while(!empty(S)){ pop(S,k);printf("%d",G.vertices[k].adjvex);count++; for(p=G.vertices[k].firstarc;p;p=p->nextarc){ int q=p->adjvex; if(!(--Indegree[q]))push(S,q); } } if(count<G,vexnum)return ERROR; return OK; }AOV-网 关键路径
AOE-网(Active On Edge):在带权的有向无环图中,顶点表示事件,弧表示工程的一个活动,弧上权值表示活动持续的时间。用来估算工程完成时间。源点:入度为0的顶点。汇点:出度为0的顶点。
路径长度:AOE网中路径上各活动持续时间之和。
关键路径:路径长度最长的路径。设活动ai在有向无环图G的有向边<j,k>上:
事件vj的最早发生时间ve(j):从源点v0到vj的最长路径长度。
ve(0)=0;
ve(j)=从源点到顶点j的最长的路径长度。
ve(k)=Max{ve(j)+dut(<j,k>)}事件vj的最迟开始时间vl(j):保证汇点vn-1在ve(n-1)时刻完成的前提下,事件vj最迟允许开始的时间。
vl(n-1) = ve(n-1)=从源点到汇点的最长路径长度;
vl(k)=从汇点到顶点k的最短的路径长度。
vl(j)=Min{vl(k)-dut(<j,k>)}设活动ai在有向边<j,k>上,有:
活动ai的最早开始时间e(i):从源点v0到vj的最长路径长度。
e(i)= ve(j);活动ai的最迟开始时间l(i):是不推迟工程完成的前提下,该活动允许的最迟开始时间。
l(i)=vl(k)-dut(<j,k>)活动ai时间余量:l(i)-e(i)
关键活动:满足l(i)=e(i)的活动。关键路径上的活动都是关键活动。
int ve[MAX]; int vl[MAX]; Status TopologicalSort(ALGraph G,stack T){ int Indegree[MAX]; stack<int> S; FindeIndegree(G,Indegree);//计算各结点的入度 for(int i=0,i<G.vexnum;i++){ if(!Indegree[i])push(S,i); ve[i]=0; } int count=0; p=(ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); while(!empty(S)){ pop(S,k);push(T,k);printf("%d",G.vertices[k].adjvex);count++; for(p=G.vertices[k].firstarc;p;p=p->nextarc){ int q=p->adjvex; if(!(--Indegree[q]))push(S,q); if(ve[k]+*(p->info)>ve[q])ve[q]=ve[k]+*(p->info); } } if(count<G,vexnum)return ERROR; return OK; } Status CriticalPath(ALGraph G){ stack<int> T; int i=0; if(!TopologicalSort(Graph G,stack T)) return ERROR;//判断是否有环且求ve for(int i=0,i<G.vexnum;i++){ vl[i]=ve[G.vexnum-1]; } while(!empty(T)){//求vl pop(T,i); for(p=G.vertices[i].firstarc;p;p=p->nextarc){ int j=p->adjvex; if(vl[i]>vl[j]-*(p->info))vl[i]=ve[j]-*(p->info); } } for(int i=0,i<G.vexnum;i++){//对每一个弧判断是否是关键路径/活动 for(p=G.vertices[i].firstarc;p;p=p->nextarc){ int k=p->adjvex; int e=ve[i]; int l=vl[k]-*(p->info); if(e==l)printf("%d;%d;%d",i,k,*(p->info)); } } }最短路径
Dijkstra算法
用于求源点到其余顶点的最短路径void ShortPath(MGraph G,int v0,PathMatrix &P,ShortPathTable &D){ bool final[MAX]; int v; for(int v=0;v<G.vexnum;v++){ final[v]=false; D[v]=G.arcs[v0][v];//所有顶点初始化 for(int w=0;w<G.vexnum;w++)P[v][w]=false;//初始化P数组 if(D[v]<INFINITY)P[v][v0]=P[v][v]=true;//将与v0有直接路径的顶点更改p } D[v0]=0;fina[v0]=true;P[v0][v0]=true;//处理v0 for(int i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++){//进行n-1次 min=INFINITY; for(int w=0;w<G.vexnum;w++){ if(!final[w]) if(D[w]<min){v=w;min=D[w];} } if(min<INFINITY){ final[v]=true; for(int v=0;v<G.vexnum;v++){ if(!final[v]&&(min+G.arcs[w][v])<D[v]){ D[v]=min+G.arcs[w][v]; P[v][w]=P[v][w]=true; } } } } }Floyd算法
用于求点到点的最短路径#define INFINITY 999 void ShortPath(MGraph G,PathMatrix &P[],DistanceMatrix &D){ for(int v=0;v<G.vexnum;v++) for(int w=0;w<G.vexnum;w++){ D[v][w]=G.arcs[v][w]; for(int u=0;u<G.vexnum;u++)P[v][w][u]=0; if(D[v][w]<INFINITY)P[v][w][v]=P[v][w][w]=true; } for(int u=0;u<G.vexnum;u++) for(int v=0;v<vexnum;v++) for(int w=0;w<vexnum;w++){ if(D[v][w]>D[v][u]+D[u][w]){ D[v][w]=D[v][u]+D[u][w]; for(int i=0;i<G.vexnum;G++){ P[v][w][i]=p[v][u][i]||p[u][w][i]; } } } } #define INFINITY 999 void ShortPath(MGraph G,PathMatrix &P[],DistanceMatrix &D){ for(int v=0;v<G.vexnum;v++) for(int w=0;w<G.vexnum;w++){ D[v][w]=G.arcs[v][w];//初始化D for(int u=0;u<G.vexnum;u++)P[v][w][u]=false;//初始化P if(D[v][w]<INFINITY)P=[v][w][v]=P[v][w][w]=true;//有直接路径v->w } for(int u=0;u<G.vexnum;u++) for(int v=0;v<G.vexnum;v++) for(int w=0;w<G.vexnum;w++){ if(D[v][u]+D[u][w]<D[v][w]){ D[v][w]=D[v][u]+D[u][w]; for(int i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++){ P[v][w][i]=P[v][u][i]||P[u][w][i];//把从v->w的最短路径上经过的点全置为true } } } }#include<stdio.h> #include<cstdlib> #include<stack> #include<queue> using namespace std; #define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20 typedef int Status; typedef struct ArcNode { int adjvex; //邻接下标,当前表结点 struct ArcNode* nextarc;//下一邻接结点 int info;//边权值 }ArcNode; typedef struct VNode { ArcNode* firstarc; int data;//有关信息 }VNode, AdjList[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; typedef struct { AdjList vertices;//头结点数组 int vexnum, arcnum; int kind; }ALGraph; bool visited[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; //创建邻接表图 void creatNG(ALGraph& G) { int a, b; ArcNode* p, *q; printf("input顶点,边数:"); scanf_s("%d,%d", &G.vexnum, &G.arcnum);//读入顶点、边数 for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++) {//读入顶点值 printf("输入第%d个顶点值:",i); scanf_s("%d",&G.vertices[i].data); ArcNode* p = (ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); G.vertices[i].firstarc = p; p->adjvex = -1; } for (int i = 0; i < G.arcnum; i++) { printf("输入第i条边:"); scanf_s("%d,%d", &a, &b); p = (ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); q = (ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); p->adjvex = a; q->adjvex = b; p->nextarc = G.vertices[b].firstarc; G.vertices[b].firstarc = p;//<b,a> q->nextarc = G.vertices[a].firstarc; G.vertices[a].firstarc = q;//<a,b> } } int visit(int v) { printf("%d ",v); return 0; } int FirstAdjVex(ALGraph G, int v) { return G.vertices[v].firstarc->adjvex; } int NextAdjVex(ALGraph G, int v, int w) { ArcNode* p; p = (ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); p = G.vertices[v].firstarc; while (p->adjvex != w) { p = p->nextarc; } return p->nextarc->adjvex; } //深度优先 void DFStraverse(ALGraph G, Status(*Visit)(int v)) { for (int v = 0; v < G.vexnum; v++)visited[v] = false; stack<int> s; int u, w; for (int v = 0; v < G.vexnum; v++) { if (!visited[v]) { Visit(v); visited[v] = true; s.push(v); while (!s.empty()) { v=s.top(); s.pop(); for (w = FirstAdjVex(G, v); w!=-1; w = NextAdjVex(G, v, w)) { if (!visited[w]) { Visit(w); visited[w] = true; s.push(w); break; } } //if (w!=-1) { s.pop(); } } } } } //广度 void BFStraverse(ALGraph G, Status(*Visit)(int v)) { for (int v = 0; v < G.vexnum; v++)visited[v] = false; queue<int> Q; int u, w; for (int v = 0; v < G.vexnum; v++) { if (!visited[v]) { Visit(v); visited[v] = true; Q.push(v); while (!Q.empty()) { u = Q.front(); Q.pop(); for (w = FirstAdjVex(G, u); w != -1; w = NextAdjVex(G, u, w)) { if (!visited[w]) { Visit(w); visited[w] = true; Q.push(w); } } } } } } int main() { ALGraph G; creatNG(G); DFStraverse(G, visit); printf("\n"); BFStraverse(G, visit); }算法
查找
定义
查找表(Search Table) :由同一类型的数据元素(或记录)构成的集合。 对查找表经常进行的操作: 1)查询某个“特定的”数据元素是否在查找表中; 2)检索某个“特定的”数据元素的各种属性; 3)在查找表中插入一个数据元素; 4)从查找表中删去某个数据元素。 静态查找表(Static Search Table) : 仅作上述1)和2)操作的查找表 动态查找表(Dynamic Search Table):作上述1)、2)、3)、4)操作的查找表 关键字(Key):数据元素中某个数据项的值,用以标识一个数据元素 主关键字(Primary Key):可以唯一标识一个记录的关键字 次关键字(Secondary Key):用以识别若干记录的关键字 平均查找长度 查找算法的性能分析:通常以关键字和给定值进行比较的记录个数的平均值为衡量算法好坏的依据. 平均查找长度(Average Search Length):查找算法在查找成功时平均查找长度和查找不成功时平均查找长度之和。 查找成功的平均查找长度:为确定记录在查找表中的位 置,需和给定值进行比较的关键字个数的期望值, 令: Pi:查找表中第i个记录的概率 Ci:找到表中其关键字与给定值相等的第i个记录时,和给定值比较过的关键字的个数. ASL(SS)=NUM(PiCi); 查找不成功平均查找长度:查找不成功时和给定值进行比较 的关键字个数的期望值称为查找不成功时平均查找长度。顺序表的查找
代码实现
int Search_Seq( SSTable ST, KeyType key ) { ST.elem[0]. key = key;//哨兵 for ( i = ST.length ; ! EQ(ST.elem[i]. key, key ) ; - - i ); return i; } // Search_Seq性能分析
等概率下查找成功的平均查找长度:$P_{i}=\frac{1}{n}$
$C_{i}=n-i+1$
$$ASL_{SS}=\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^{n}(n-i+1)=\frac{n+1}{2}$$等概率下查找不成功的平均查找长度(假定查找成功和查找不 成功的可能性相同,对每个记录的查找概率也相同):$P_{i}=\frac{1}{2}$
$C_{i}=n+1$
$$ASL_{SF}=\frac{1}{2}*(n+1)=\frac{n+1}{2}$$
平均查找长度:
$$ASL=\frac{n+1}{4}+\frac{n+1}{2}=\frac{3}{4}(n+1)$$有序表的二分查找
代码实现
int Search_Bin ( SSTable ST, KeyType key ) { low = 1 ; high = ST.length ; while ( low <= high ) { mid = ( low + high ) / 2 ; if ( EQ(ST.elem[mid]. key, key ) ) return mid ; else if ( LT( key , ST.elem[mid]. key ) ) high = mid -1 ; else low = mid + 1; } return 0 ; } // Search_Bin性能分析
一般情况下,表长为n的折半查找的判定树的深度和含有n个
结点的完全二叉树的深度相同,设$n=2^{h}-1$且查找概率相等
(1/n),则折半查找成功的平均查找长度
$$ASL_{SS}=\frac{1}{n}\sum_{j=1}{h}j*2=\frac{n+1}{n}\log_{2}{(n+1)}-1$$分块有序的查找(索引顺序表的查找)
定义
顺序表+索引表组成
索引表按关键字有序,可用二分或顺序查找
性能分析
长度为n的表平均分成n块,每块含有s个记录
$ASL_{bs}=L_{b}+L_{s}$
$L_{b}$:索引表确定所在块的平均查找长度
$L_{s}$:块中查找元素的平均查找长度
$ASL_{bs}=L_{b}+L_{s}=b\sum_{j=1}{b}j+s\sum_{j=1}j=\frac{b+1}{2}+\frac{s+1}{2}$二叉查找树(二叉排序树)
定义
二叉排序树(二叉查找树)(Binary Sort Tree, BST):空树或具
有下列性质的二叉树:
根的左子树若非空,则左子树上的所有结点的关键字值均小于根结点的值。
根的右子树若非空,则右子树上的所有结点的关键字值均大于根结点的值。
它的左右子树同样是二叉排序树。中序遍历二叉排序树可得到一个关键字的有序序列
算法实现
1.查找Status Search(BiTree T,KeyType key){ if(T==NULL||EQ(key,T->data.key))return T; else if(LT(key,T->data.key)) return Search(T->left,key); else return Search(T->right,key); }2.插入
改进查找算法Status Search(BiTree T,KeyType key,BiTree f,BiTree &p){ if(!T){p=f; return false;} else if(EQ(kEY,T->data.key)){p=T;return true;} else if(LT(key,T->data.key))return Search(T->left,key,T,p); else return Search(T->right,key,T,p); }Status Insert(BiTree &T,Element e){ Bitree p; if(!Search(Bitree T,e.key,NULL,p)){//查询失败 Bitree s=(BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode)); s->data=e;s->left=s->right=NULL; if(!p)T=s;//插入结点是根结点 else if(LT(e.key,p->data.key)) p->left=s; else p->right=s; return true; } reutrn false; }3.删除
Status DeleteBST(BSTree &T,int key){ if(!T)return FALSE;//空树 else{ if(EQ(key,T->data)) return Delete(T); else if(LT(key,T->data)){ return DeleteBST(T->lchild,key); } else return DeleteBST(T->rchild,key); } } Status Delete(BSTree &p){ BSTree q=(BSTree)malloc(szieof(BiTNode)) if(!p->rchild){ q=p;p=p->lchild;free(q); }else if(!p->lchild){ q=p;p=p->rchild;free(q); }else{ q=p; s=p->lchild; while(s->rchild){//找左子树最大值 q=s; s=s->rchild; } p->data=s->data;//取左子树最大值 if(q!=p)q->rchild=s->lchild;//悬挂最大值的左子树 else q->lchild=s->lchild; free(s); } }性能分析
最坏情况:单支树,深度为n,$ASL_(ss)=\frac{n+1}{2}$
最好情况:折半查找判定树,深度为n,$ASL_(ss)$与$log_(2)^(n)$成正比哈希表
排序
插入排序
直接插入排序(基于顺序查找)
介绍
稳定排序
从未排序中依次取出元素与已排序的元素依次比较并插入到合适位置
缺点:大量数据时,比较和移动操作过多
优点:容易实现,适用于基本有序
时间复杂度
$$O(n^{2})$$
最好情况:比较n-1,移动0
最坏情况:比较$\sum_{i=2}{n}i=\frac{(n+2)(n-1)}{2}$,移动$\sum_{i=2}(i+1)=\frac{(n+4)(n-1)}{2}$
代码void InsertionSort(SqLiist &L){ for(i=2;i<=L.length;i++){ if(LT(L.r[i].key,L.r[i-1].key)){ L.r[0]=L.r[i];//监视哨 L.r[i]=L.r[i-1]; for(int j=i-2;LT(L.r[0].key,L.r[j].key);--j) L.r[j+1]=L.r[j];//比监事哨大的一律右移动 L.r[j+1]=L.r[0]; } } } void InsertionSort(SqLit & L){ for(int i=2;i<=L.length;++i){ if(LT(L.r[i].key,L.r[i-1].key)){ L.r[0]=L.r[i]; //复制为监视哨 L.r[i]=L.r[i-1]; for(int j=i-2;LT(L.r[0].key,L.r[j].key);--j) L.r[j+1]=L.r[j]; L.r[j+1]=L.r[0]; } } }折半插入排序(基于折半查找)
介绍
稳定
把直接插入排序比较代码替换为折半查找插入位置
时间复杂度
$$O(n^{2})
仅仅优化了比较次数
代码void BiInsertionSort(SqList &L){ for(int i=2;i<L.length;i++){ L.r[0]=L.r[i]; low=1;high=i-1; while(low<=high){ m=(low+high)/2; if(LT(L.r[0].key,L.r[m],key)){ high=m-1; }else low=m+1; } for(int j=i-1;j>=high+1;j--) L.r[j+1]=L.r[j];//后移数据 L.r[high+1]=L.r[0];//插入 } }希尔排序(基于逐趟缩小增量)
介绍
不稳定
使用增量进行直接插入排序
时间复杂度
在$O(nlog_{2}{n})$与$O(n)$之间
代码void ShellSort (SqList &L, int dlta[], int t) { // 增量为dlta[]的希尔排序 for (k=0; k<t; ++t) ShellInsert(L, dlta[k]); //一趟增量为dlta[k]的插入排序 } // ShellSort void ShellInsert ( SqList &L, int dk ) { for ( i=dk+1; i<=L.length; ++i ) if (LT( L.r[i].key,L.r[i-dk].key)) { L.r[0] = L.r[i]; // 暂存在r[0] for (j=i-dk; j>0&& LT(L.r[0].key,L.r[j].key); j-=dk) L.r[j+dk] = L.r[j]; // 记录后移,查找插入位置 L.r[j+dk] = L.r[0]; // 插入 } // if } // ShellInsert冒泡排序
介绍
稳定
对n个数进行n-1趟排序,每次冒泡最大值
时间复杂度
$O(n^{2})$
最坏比较$\sum_{i=n}^{2}(i-1)=\frac{n(n-1)}{2}$
最坏移动$3\sum_{i=n}^{2}(i-1)=\frac{3n(n-1)}{2}$
代码void bubble_sort(int arr[], int size) { int i = 0; int change = 1;//交换标志 for (i = 0,change=1; i < size - 1&&change; i++) { change = 0; int j = 0; for (j = 0; j < size - i - 1; j++) { if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) { int temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j + 1]; arr[j + 1] = temp; change = 1; } } printf("第%d趟交换结果:",i+1); for (int k = 0; k < size; k++) { printf("%d ", arr[k]); } printf("\n"); } }快速排序
介绍
稳定
首先选一个枢值(即比较的基准),通过一趟排序将待排序记录分割成独立的两部分前一部分记录的关键码均小于或等于枢值,后一部分记录的关键码均大于或等于枢值,然后分别对这两部分重复上述方法,直到整个序列有序。
时间复杂度
平均时间复杂度=最好时间复杂度=$O(nlog_{2}^{n})$
最坏时间复杂度$O(n^{2})$(当序列有序时,退化为冒泡排序)
代码int Partition (SqList& L, int low, int high) { L.r[0]=L.r[low]; pivotkey = L.r[low].key; while (low<high) { while (low<high && L.r[high].key>=pivotkey) --high; L.r[low]=L.r[high]; while (low<high && L.r[low].key<=pivotkey) ++low; L.r[high]=L.r[low]; } L.r[low]=L.r[0]; return low; // 返回枢轴所在位置 } // Partition void QSort (SqList &L, int low, int high) { // 对记录序列R[s..t]进行快速排序 if (low < high) { // 长度大于1 pivotloc = Partition(L, low, high); // 对 R[s..t] 进行一次划分 QSort(L, low, pivotloc-1); // 对低子序列递归排序,pivotloc是枢轴位置 QSort(L, pivotloc+1, high); // 对高子序列递归排序 } } // QSort void QuickSort( SqList & L) { // 对顺序表进行快速排序 QSort(L, 1, L.length); } // QuickSort选择排序
简单选择排序
介绍
从无序序列中选出最小记录插入到有序序列
时间复杂度
$O(n^{2})$
比较总次数$\sum_{i=1}^{n-1}(n-i)=\frac{n(n-1)}{2}$
代码void SelectSort (SqList &L) { // 对记录序列R[1..n]作简单选择排序。 for (i=1; i<L.length; ++i) { // 选择第 i 小的记录,并交换到位 j = SelectMinKey(L, i); // 在 R[i..n] 中选择关键字最小的记录 if (i!=j) L.r[i]←→L.r[j]; // 与第 i 个记录交换 } } // SelectSort堆排序
介绍
不稳定
大根堆/小根堆:完全二叉树中所有非终端结点的值均不小于(或不大于)其左、右孩子结点的值。
若在输出堆顶的最小(大)值之后,使得剩余n-1个元素的序列重又建成一个堆,则得到 n个元素中的次小(大)值。此反复执行,便能得到一个有序序列,这个过程称之为堆排序。
复杂度
时间复杂度$O(nlog_{2}^{n})$
空间复杂度$O(1)$归并排序
基数排序
复杂度总结
选择排序不稳定
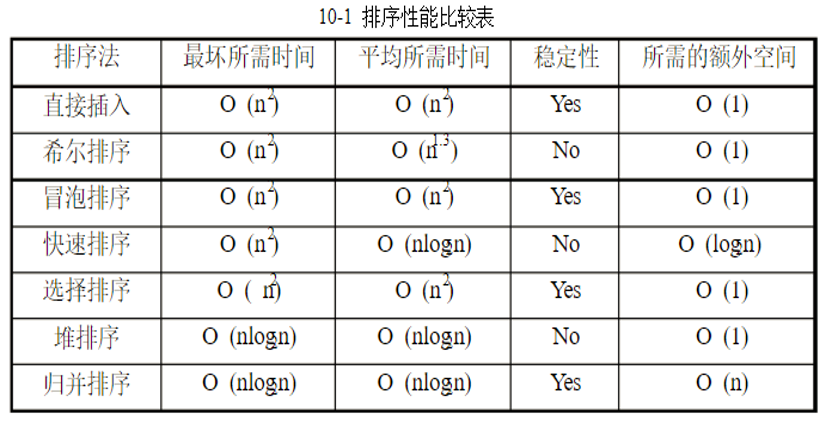
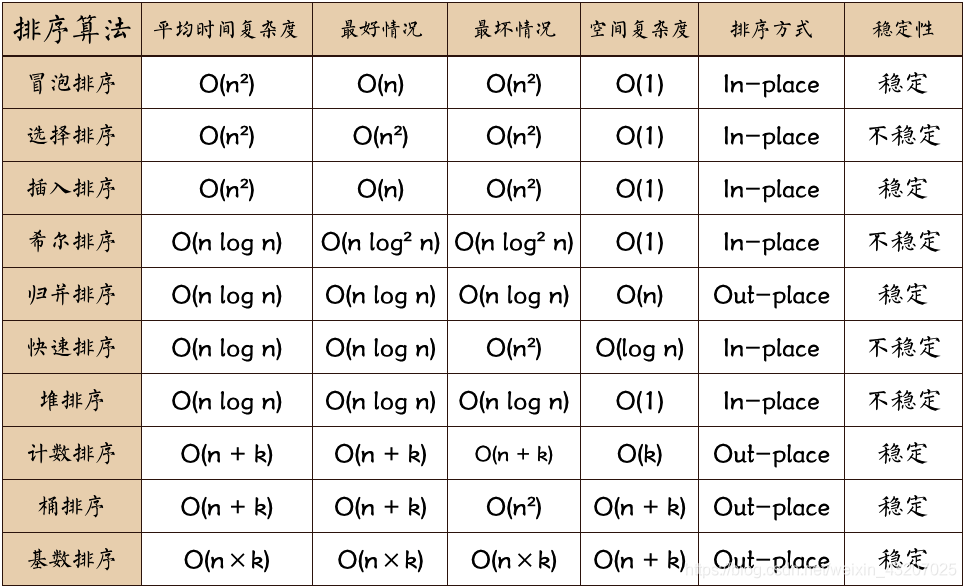
基础算法
埃及分数
#include<stdio.h> int main() { int a,b,c,d,e; printf("分子,分母"); scanf("%d,%d",&a,&b); printf("%d/%d=",a,b); do { c=b/a; e=c+1; printf("1/%d+",e); a=a*e-b; b=b*e; }while(a!=1&&b%a!=0); if(a!=1&&b%a==0) printf("1/%d",b/a); else printf("1/%d",b/a); return 0; }五个莫尼森数
#include<stdio.h> #include<math.h> int main() { int m,p=2,a=1,t,i,b,x; while(a<=5) { m=pow(2.0,p)-1; for(t=2;t<m;t++) if(m%t==0)break; if(m==t) { a++; printf("%d\n",m); } do { p++; for(x=2;x<p;x++) if(p%x==0)continue; }while(p!=x); } return 0; } /*t = 0; while ( t == 0 ) { p++; for ( t = 1, j = 2; t && j <= sqrt( p ); j++ ) if ( p % j == 0 ) t = 0; } */输出星号
# #include <stdio.h> int main() {int i,j,k; for (i=0;i<=3;i++) {for (j=0;j<=2-i;j++) printf(" "); for (k=0;k<=2*i;k++) printf("*"); printf("\n"); } for (i=0;i<=2;i++) {for (j=0;j<=i;j++) printf(" "); for (k=0;k<=4-2*i;k++) printf("*"); printf("\n"); } return 0; }分解质因数
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int n, i; scanf( "%d", &n ); printf( "%d=", n ); for ( i = 2; i <= n; i++ ) while ( n != i ) { if ( n % i == 0 ) { printf( "%d*", i ); n = n / i; } else break; } printf( "%d", n ); }完数
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int i,j,sum=0; for(i=2;i<=1000;i++) { for(j=1;j<i;j++) { if(i%j==0) sum+=j; } if(sum==i) { printf("%d=1",sum); for(j=2;j<i;j++) { if(i%j==0) printf("+%d",j); } } if(sum==i){ printf("\n"); } sum=0; } return 0; }质数
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int i,j,n=0; for(i=100;i<=200;i++) { for(j=2;j<i;j++) { if(i%j==0) break; } if(j==i) { printf("%d ",i); n++; if(n%10==0) printf("\n"); } } return 0; }公约数,公倍数
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int m,n,r,x,t; while(2) { printf("输入两个正整数:"); scanf("%d,%d",&n,&m); if(n<m) {x=n; n=m; m=x; }t=n*m; while(m!=0) { r=n%m; n=m; m=r; } printf("最大公约数为:%d\n",n); printf("最小公倍数为:%d\n",t/n); } return 0; } #include<stdio.h> int main() { int m,n,i,x; scanf("%d,%d",&m,&n); /* for(i=m;i>0;i--) if(m%i==0&&n%i==0) {printf("max公约数:%d\nmin公倍数:%d",i,m*n/i); break; } */ x=m*n; while(i!=0) {i=m%n; m=n; n=i; } printf("max公约数:%d\nmin公倍数:%d",m,x/m); return 0; }分解质因子式
#include<stdio.h> #include<math.h> int main(void){ int i,j; long int m, n; int count; int isPrime,flag; isPrime = 1; flag = 0; scanf("%ld",&n); printf("%ld=",n); m = sqrt(n); for(i = 2; i <= m;i++){ if(n%i == 0){ //printf("%d",i); isPrime = 0; count = 1; n = n / i; while(n%i == 0){ n = n / i; count++; } if(flag) printf("*"); else flag = 1; if(count == 1) printf("%d",i); else printf("%d^%d",i,count); } } if(isPrime) printf("%d",n); return 0; }统计单词个数
#include<stdio.h> int main() { char string[81]; int i,sum=0,word=0; char c; gets(string); for(i=0;(c=string[i]!='\0';i++) if(c=='')word=0; else if(word==0){ word=1; num++; } printf("There are %d words in this line.\n",sum); retun 0; }数字变字符
#include<stdio.h> int main() { return 0; }public class VedioExtractSpeech { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("toChinese:"+toChinese("1230456")); System.out.println("toChinese2:"+toChinese2("1230456")); } private static String toChinese(String str) { String[] s1 = { "零", "一", "二", "三", "四", "五", "六", "七", "八", "九" }; String[] s2 = { "十", "百", "千", "万", "十", "百", "千", "亿", "十", "百", "千" }; String result = ""; int n = str.length(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { int num = str.charAt(i) - '0'; if (i != n - 1 && num != 0) { result += s1[num] + s2[n - 2 - i]; } else { result += s1[num]; } } return result; } private static String toChinese2(String str) { String[] s2 = {"零", "一", "二", "三", "四", "五", "六", "七", "八", "九"}; StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer(); for (char c : str.toCharArray()) { sb.append(s2[Integer.parseInt(String.valueOf(c))]); } return sb.toString(); } }取每一位数字
int a = 456789 5:a//10000%10二分法循环
int search(int* nums, int numsSize, int target){ int low=0 , high=numsSize-1; int half=(low+high)/2; while (low<=high){ half = (low + high) / 2; if (nums[half]==target) break; if (nums[half]>target){ high=half-1; continue; } if (nums[half]<target){ low=half+1; continue; } } if(nums[half]==target){ return half; } else return -1; }package javasuanfa; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; int target = 3; System.out.println(search(nums, target)); } public static int search(int[] nums, int target) { if (target < nums[0] || target > nums[nums.length - 1]) { return -1; } int left = 0; int right = nums.length - 1; while (left <= right) { int mid = (left + right) / 2; if (nums[mid] == target) { return mid; } else if (target < nums[mid]) { right = mid - 1; } else if (target > nums[mid]) { left = mid + 1; } } return -1; } }package javasuanfa; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; int target = 3; System.out.println(search(nums, target,0,nums.length-1)); } public static int search(int[] nums, int target, int left, int right) { if (target < nums[0] || target > nums[nums.length - 1]) { return -1; } left = 0; right = nums.length - 1; int mid = (left + right) / 2; if (target < nums[mid]) { return search(nums, target, left, mid - 1); } else if (target > nums[mid]) { return search(nums, target, mid + 1, right); } else { return mid; } } }排序算法
打擂台
#include<stdio.h> int main() { int a[3][4]={{0,1,2,3},{4,5,6,7},{8,9,10,11}},t,x,y,max,row,colum; max=a[0][0]; for(x=0;x<=2;x++) {for(y=0;y<=3;y++) if(a[x][y]>max) { max=a[x][y]; row=x; colum=y; } else { row=0; colum=0; } } printf("max=%d\nrow=%d\ncolum=%d\n",max,row+1,colum+1); return 0; }冒泡排序
c语言
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include <stdio.h> void bubble_sort(int arr[], int size) { int i = 0; int change = 1;//交换标志 for (i = 0,change=1; i < size - 1&&change; i++) { change = 0; int j = 0; for (j = 0; j < size - i - 1; j++) { if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) { int temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j + 1]; arr[j + 1] = temp; change = 1; } } printf("第%d趟交换结果:",i+1); for (int k = 0; k < size; k++) { printf("%d ", arr[k]); } printf("\n"); } } int main() { int size = 0; printf("输入数组大小size:"); scanf("%d", & size); int arr[100]; int i = 0; printf("输入要升序排序的数组:"); for (i = 0; i < size; i++) { scanf("%d",&arr[i]); } printf("排序前:"); for (i = 0; i < size; i++) { printf("%d ", arr[i]); } printf("\n"); bubble_sort(arr, size); // 冒泡排序函数 printf("排序后:"); for (i = 0; i < size; i++) { printf("%d ", arr[i]); } return 0; }#include<stdio.h> int main() { int a[10],t,i,n; printf("input10nums:"); for(i=0;i<=9;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]); for(n=0;n<=8;n++)//8=N-2 { for(i=0;i<=8-n;i++)//8-n=N-2-n {if(a[i]>a[i+1]) {t=a[i]; a[i]=a[i+1]; a[i+1]=t; } } } for(i=0;i<=9;i++) printf("%d\n",a[i]); return 0; }

java
public class Main{ public static void main(String []args){ int arry[]={3,2,5,6,8,7}; Main sorter=new Main(); sorter.sort(arry); } public void sort(int[] array){ for(int i = 0;i<array.length-1;i++){ for(int k = 0;k<array.length-1-i;k++){ if(array[k]>array[k+1]){ int temp=array[k]; array[k]=array[k+1]; array[k+1]=temp; } } } showArray(array); } public void showArray(int[] aray){ for(int x:aray){ System.out.print(x ); } } }链表冒泡排序
#include <stdio.h> #include <malloc.h> #define LEN sizeof(struct student) struct student {long num; int score; struct student *next; }; struct student lista,listb; int n,sum=0; int main() {struct student *creat(void); struct student *insert(struct student *,struct student *); void print(struct student *); struct student *px(struct student *abh,int sum); struct student *ahead,*bhead,*abh; printf("input list a:\n"); ahead=creat(); sum=sum+n; printf("input list b:\n"); bhead=creat(); sum=sum+n; abh=insert(ahead,bhead); abh=px(abh,sum); print(abh); return 0; } struct student *creat(void) //建立链表函数 {struct student *p1,*p2,*head; n=0; p1=p2=(struct student *)malloc(LEN); printf("input number & scores of student:\n"); printf("if number is 0,stop inputing.\n"); scanf("%ld,%d",&p1->num,&p1->score); head=NULL; while(p1->num !=0) {n=n+1; if (n==1) head=p1; else p2->next=p1; p2=p1; p1=(struct student *)malloc(LEN); scanf("%ld,%d",&p1->num,&p1->score); } p2->next=NULL; return(head); } /* struct student *insert(struct student *ah,struct student *bh) //插入函数 {struct student * pa1,* pa2,* pb1,* pb2; pa2=pa1=ah; pb2=pb1=bh; do {while((pb1->num>pa1->num) && (pa1->next !=NULL)) {pa2=pa1; pa1=pa1->next; } if (pb1->num <= pa1->num) {if (ah==pa1) ah=pb1; else pa2->next=pb1; pb1=pb1->next; pb2->next=pa1; pa2=pb2; pb2=pb1; } }while ((pa1->next!=NULL) || (pa1==NULL && pb1!=NULL)); if ((pb1!=NULL) && (pb1->num>pa1->num) && (pa1->next==NULL)) pa1->next=pb1; return(ah); } */ struct student *insert(struct student *ah,struct student *bh) { struct student *pnew; pnew=ah; while(pnew->next!=NULL) { pnew=pnew->next; } pnew->next=bh; return(ah); } struct student *px(struct student *abh,int sum) { struct student *p,*p1,*p2,*p2pre; p=NULL; p1=p2=p2pre=abh; int count=1; while(count<sum) { p1=p2=p2pre=abh; while(p1->next!=NULL) { p2pre=p2; p2=p1; p1=p1->next; if((p1->num)<(p2->num)) { if(abh==p2)abh=p1; else p2pre->next=p1; p2->next=p1->next; p1->next=p2; } } count++; } return abh; } void print(struct student *head) //输出函数 {struct student *p; printf("There are %d records: \n",sum); p=head; if (p !=NULL) do {printf("%ld %d\n",p->num,p->score); p=p->next; }while (p !=NULL); }快速排序
c语言
#include<stdio.h> void quicksort(int arry[],int L,int R) { if(L>=R) return ; int left=L,right=R; int pivot=arry[L]; while(left<right) { while(left<right&&arry[right]>=pivot) {right--; } //if(left<right) arry[left]=arry[right]; while(left<right&&arry[left]<=pivot) {left++; } //if(left<right) arry[right]=arry[left]; //if(left>=right) //arry[left]=pivot; } arry[left]=pivot; quicksort(arry,L,right-1); quicksort(arry,right+1,R); } int main() { int arry[9]; int i,j; for(i=0;i<9;i++) {printf("%dth:",i+1); scanf("%d",&arry[i]); } quicksort(arry,0,8); for(j=0;j<9;j++) {printf("%d ",arry[j]); } return 0; }反转排序
java
public class Main{ public static void main(String []args){ int arry[]={3,2,5,6,8,7}; Main sorter=new Main(); sorter.sort(arry); } public void sort(int[] array){ int temp; int len=array.length; for(int i = 0;i<len/2;i++){ temp=array[i]; array[i]=array[len-1-i]; array[len-1-i]=temp; } showArray(array); } public void showArray(int[] aray){ for(int x:aray){ System.out.print(x ); } } }链表快速排序
#include <stdio.h> #include <malloc.h> #define LEN sizeof(struct student) struct student { int num; int score; struct student* next; }; struct student lista, listb; int n, sum = 0; int main() { struct student* creat(void); struct student* insert(struct student*, struct student*); void print(struct student*); struct student* bianli(struct student* abh); void px(struct student* abh, struct student* abe); void swapnode(struct student* i, struct student* j); struct student* ahead, * bhead, * abh,*abe; printf("input list a:\n"); ahead = creat(); sum = sum + n; printf("input list b:\n"); bhead = creat(); sum = sum + n; abh = insert(ahead, bhead); abe = bianli(abh); px(abh, abe); print(abh); return 0; } struct student* creat(void) //建立链表函数 { struct student* p1, * p2, * head; n = 0; p1 = p2 = (struct student*)malloc(LEN); printf("input number & scores of student:\n"); printf("if number is 0,stop inputing.\n"); scanf("%ld,%d", &p1->num, &p1->score); head = NULL; while (p1->num != 0) { n = n + 1; if (n == 1) head = p1; else p2->next = p1; p2 = p1; p1 = (struct student*)malloc(LEN); scanf("%ld,%d", &p1->num, &p1->score); } p2->next = NULL; return(head); } /* struct student *insert(struct student *ah,struct student *bh) //插入函数 {struct student * pa1,* pa2,* pb1,* pb2; pa2=pa1=ah; pb2=pb1=bh; do {while((pb1->num>pa1->num) && (pa1->next !=NULL)) {pa2=pa1; pa1=pa1->next; } if (pb1->num <= pa1->num) {if (ah==pa1) ah=pb1; else pa2->next=pb1; pb1=pb1->next; pb2->next=pa1; pa2=pb2; pb2=pb1; } }while ((pa1->next!=NULL) || (pa1==NULL && pb1!=NULL)); if ((pb1!=NULL) && (pb1->num>pa1->num) && (pa1->next==NULL)) pa1->next=pb1; return(ah); } */ struct student* insert(struct student* ah, struct student* bh) { struct student* pnew; pnew = ah; while (pnew->next != NULL) { pnew = pnew->next; } pnew->next = bh; return(ah); } /*struct student* px(struct student* abh, int sum) { struct student* p, * p1, * p2, * p2pre; p = NULL; p1 = p2 = p2pre = abh; int count = 1; while (count < sum) { p1 = p2 = p2pre = abh; while (p1->next != NULL) { p2pre = p2; p2 = p1; p1 = p1->next; if ((p1->num) < (p2->num)) { if (abh == p2)abh = p1; else p2pre->next = p1; p2->next = p1->next; p1->next = p2; } } count++; } return abh; }*/ struct student* bianli(struct student* abh) { struct student* abe; abe = abh; while (abe->next != NULL) { abe = abe->next; } return abe; } void px(struct student* abh, struct student* abe) { if ((abe == abh) || (abh->next == NULL) || (abh == NULL)) return ; void swapnode(struct student* i, struct student* j); struct student* ipre, * i, * j; int pivot; ipre = abh; j=i = abh->next; pivot = abh->num; while (j != NULL) { if (j->num < pivot) { swapnode(i, j); ipre=i; i=i->next; } j=j->next; } swapnode(abh, ipre); px(abh, ipre); px(i, abe); return ; } void swapnode(struct student* i, struct student* j) { int a, b; a = i->num; i->num = j->num; j->num = a; b = i->score; i->score = j->score; j->score = b; } void print(struct student* head) //输出函数 { struct student* p; printf("There are %d records: \n", sum); p = head; if (p != NULL) do { printf("%ld %d\n", p->num, p->score); p = p->next; } while (p != NULL); }简单插入排序
希尔排序法
选择法排序
c语言
#include<stdio.h> int main() { int i,j,k,n,m,max,t; //scanf("%d",&n); int a[]={1,2,5,9,5}; int len = sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0]); // for(k=0;k<=len;k++) //scanf("%d",a[k]); for(j=0;j<len-1;j++) {max=a[j]; for(i=j+1;i<=len;i++) if(a[i]>max) { max=a[i]; t=a[j]; a[j]=a[i]; a[i]=t; } } for(k=0;k<=len-1;k++) printf("%d",a[k]) ; return 0; }java
public class Main{ public static void main(String []args){ int arry[]={3,2,5,6,8,7}; Main sorter=new Main(); sorter.sort(arry); } public void sort(int[] array){ int index; for(int i = 1;i<array.length;i++){ index=0; for(int k = 1;k<=array.length-i;k++){ if(array[k]>array[index]){ index=k; } } int temp=array[array.length-i]; array[array.length-i]=array[index]; array[index]=temp; } showArray(array); } public void showArray(int[] aray){ for(int x:aray){ System.out.print(x ); } } }堆排序法
双指针
删除数组元素
Int return() { Int slowp=0; Int fastp=0; For(fastp=0;fastp<=numszie;fastp++) { If(nums[fastp]!=val) Nums[slowp++]=nums[fastp]; } Return slowp; }public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) { int slowp=0; for(int fastp=0;fastp<nums.length;fastp++){ if(nums[fastp]!=val){ nums[slowp++]=nums[fastp]; } } return slowp; }数组平方排序
/** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ int* sortedSquares(int* nums, int numsSize, int* returnSize){ *returnSize=numsSize; int k; int left=0; int right=numsSize-1; int* result=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * numsSize); for(k=numsSize-1;k>=0;k--){ int lsquare=nums[left]*nums[left]; int rsquare=nums[right]*nums[right]; if(rsquare>lsquare){ result[k]=rsquare; right--; } else{ result[k]=lsquare; left++; } } return result; }public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) { int[] result =new int[nums.length]; int left=0; int right=nums.length-1; for(int k=nums.length-1;k>=0;k--){ int lsquare=nums[left]*nums[left]; int rqsuare=nums[right]*nums[right]; if(rqsuare>lsquare) { result[k] = rqsuare; right--; } else { result[k]=lsquare; left++; } } return result; }滑动窗口
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) { int left = 0; int sum = 0; int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (int right = 0; right < nums.length; right++) { sum += nums[right]; while (sum >= target) { result = Math.min(result, right - left + 1); sum -= nums[left++]; } } return result == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : result; }迷宫
/* * To change this template, choose Tools | Templates * and open the template in the editor. */ package migong; /** * * @author Administrator */ public class Main { /** * @param args the command line arguments */ public static void main(String[] args) { //绘制迷宫 int[][] map = new int[8][7]; //最上与最下s for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) { map[0][i] = 1; map[7][i] = 1; } //最左与最右 for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { map[i][0] = 1; map[i][6] = 1; } //额外 map[3][1] = map[3][2] = 1; map[4][2] = map[5][2] = map[6][2] = 1; map[4][4] = map[5][4] = map[6][4] = 1; System.out.println("当前地图======"); for (int i = 0; i < map.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < map[i].length; j++) { System.out.print(map[i][j] + ""); } System.out.println(); } //找路 T t1 = new T(); t1.findway(map, 1, 1); System.out.println("\n======找路的情况如下======"); for (int i = 0; i < map.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < map[i].length; j++) { System.out.print(map[i][j] + ""); } System.out.println(); } } } class T { //初始位置(1,1) // 0表示可以走 1 表示障碍物 2表示可以走(通路)3走过但是死路 public boolean findway(int[][] map, int i, int j) { if (map[6][5] == 2) {//找到 return true; } else { if (map[i][j] == 0) {//可以走没走过 map[i][j] = 2; if (findway(map, i + 1, j)) { return true; } else if (findway(map, i, j + 1)) { return true; } else if (findway(map, i - 1, j)) { return true; } else if (findway(map, i, j - 1)) { return true; } else { map[i][j] = 3; return false; } } else { return false; } } } }s
- 层次遍历(迭代法)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号