剑指Offer算法题
一、链表
1、从尾到头打印链表
问题:输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)。
输入:head = [1,3,2] 输出:[2,3,1]
解法:使用栈先进后出
class Solution { public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) { //将链表数据依次放到栈中 Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<ListNode>(); ListNode p= head; while (p!= null) { stack.push(p); p= p.next; } //将栈中的数弹出放到数组中 int size = stack.size(); int[] print = new int[size]; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { print[i] = stack.pop().val; } return print; } }
2、删除链表的节点
问题:给定单向链表的头指针和一个要删除的节点的值,定义一个函数删除该节点。返回删除后的链表的头节点。
输入: head = [4,5,1,9], val = 5
输出: [4,1,9]
class Solution { public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) { //删除时添加dummy头节点,方便修改头节点 ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1); dummy.next=head; ListNode p=dummy; //找到值为val的节点 while(p.next.val!=val){ p=p.next; } //执行删除操作 p.next=p.next.next; //返回dummy的下个节点 return dummy.next; } }
3、链表中倒数第k个节点
问题:输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个节点。
输入:给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 k = 2.
输出:返回链表 4->5.
class Solution { public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) { ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; //先让快指针fast前进k步 while (fast != null && k > 0) { fast = fast.next; k--; } //快慢指针同时前进n-k,慢指针的位置即倒数k的位置 while (fast != null) { fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } return slow; } }
4、链表中环的入口位置
问题:
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 从链表的头节点开始沿着 next 指针进入环的第一个节点为环的入口节点。如果链表无环,则返回 null。

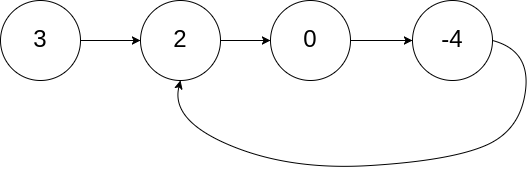
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
解法:使用双指针

public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) { ListNode fast = head, slow = head; while (true) { if (fast == null || fast.next == null) return null; //快指针每次走两步,慢指针每次走一步 fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; //当快慢指针相遇时,退出循环 if (fast == slow) break; } //令指针从头开始走,当两个指针相遇时即环的入口 fast = head; while (slow != fast) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; } return fast; } }
5、反转链表
给定单链表的头节点 head ,请反转链表,并返回反转后的链表的头节点。
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
解法一:迭代、多指针
class Solution { public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { ListNode prev = null; ListNode curr = head; while (curr != null) { //先保存当前节点的下个节点 ListNode next = curr.next; //将当前节点的next指向上一节点 curr.next = prev; //移动pre到curr prev = curr; //移动curr到下个节点 curr = next; } return prev; } }
解法二:递归
class Solution { public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null) { return head; } //设置新的头节点为反转后的链表 ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next); //修改一下节点的next为当前节点 head.next.next = head; //将当前节点的next置为null head.next = null; //返回最后一个节点为新的链表头节点 return newHead; } }
6、合并两个排序的链表
问题:输入两个递增排序的链表,合并这两个链表并使新链表中的节点仍然是递增排序的。
输入:1->2->4, 1->3->4
输出:1->1->2->3->4->4
解法一:迭代
class Solution { public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0), cur = dummy; while(l1 != null && l2 != null) { //当l1的值比较小,curr的next指向l1 if(l1.val < l2.val) { cur.next = l1; l1 = l1.next; } //当l2的值比较小,curr的next指向l2 else { cur.next = l2; l2 = l2.next; } cur = cur.next; } //将curr的next指向当前不为空的链表 cur.next = l1 != null ? l1 : l2; return dummy.next; } }
解法二:递归
class Solution { public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { //当l1为空,直接返回l2链表 if(l1 == null) { return l2; } if(l2 == null) { return l1; } //如果l1的值比较小,则设置l1的next为l1.next和l2中更小的那个节点 if(l1.val < l2.val) { l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2); return l1; } else { l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next); return l2; } } }
7、复杂链表的复制
问题:请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。

输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
解法:回溯 + 哈希表
class Solution { Map<Node, Node> cachedNode = new HashMap<Node, Node>(); public Node copyRandomList(Node head) { if (head == null) { return null; } //当缓存中没有当前节点 if (!cachedNode.containsKey(head)) { //先创建新节点 Node headNew = new Node(head.val); //把当前节点和新节点的映射关系放到缓存中 cachedNode.put(head, headNew); //新节点的next和random都通过递归从缓存获取 headNew.next = copyRandomList(head.next); headNew.random = copyRandomList(head.random); } return cachedNode.get(head); } }
8、两个链表的第一个公共节点
问题:输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共节点。

输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
解法一:哈希集合
public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { Set<ListNode> visited = new HashSet<ListNode>(); //先遍历链表A,把节点放入set中 ListNode p = headA; while (p != null) { visited.add(p); p = p.next; } //再遍历链表B p = headB; while (p != null) { //当集合中存在当前节点,该节点即为两个链表首次相交的节点 if (visited.contains(p)) { return p; } p = p.next; } return null; } }
解法二:双指针
public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { if (headA == null || headB == null) { return null; } //pA和pB先后遍历两个链表,pA先从链表A的头节点开始走 ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB; //当pA和pB相等,即相交的节点 while (pA != pB) { //当pA为空时,继续遍历链表B pA = pA != null ? pA.next : headB; pB = pB != null ? pB.next : headA; } return pA; } }
二、数组
1、数组中重复的数字
找出数组中重复的数字。在一个长度为 n 的数组 nums 里的所有数字都在 0~n-1 的范围内。数组中某些数字是重复的,但不知道有几个数字重复了,也不知道每个数字重复了几次。请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字。
输入:[2, 3, 1, 0, 2, 5, 3]
输出:2 或 3
解法一:哈希集合
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) { Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(); for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { //判断当前元素是否已经存在 if (set.contains(nums[i])) { return nums[i]; } set.add(nums[i]); } return -1; }
解法二:将元素i放到i位置
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) { for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { //判断索引i是否等于索引i位置的值,例如索引2的值也为2 while (i != nums[i]) { //判断索引nums[i]是否等于索引nums[i]位置的值,是的话说明该位置已经交换完毕了,存在重复值 if (nums[i] == nums[nums[i]]) { return nums[i]; } //交换nums[i]和索引nums[i]上的值 int tmp = nums[nums[i]]; nums[nums[i]] = nums[i]; nums[i] = tmp; } } //没有找到重复数字 return -1; }
2、二维数组中的查找
问题:在一个 n * m 的二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个高效的函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
现有矩阵 matrix 如下,给定 target = 5,返回 true。
[
[1, 4, 7, 11, 15],
[2, 5, 8, 12, 19],
[3, 6, 9, 16, 22],
[10, 13, 14, 17, 24],
[18, 21, 23, 26, 30]
]
解法:从右上角开始搜索
class Solution { public boolean findNumberIn2DArray(int[][] matrix, int target) { if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) { return false; } int rows = matrix.length, columns = matrix[0].length; //从右上角开始搜索,能保证每次判断只需往一个方向移动 int row = 0, column = columns - 1; //当走到数组尽头表示没找到 while (row < rows && column >= 0) { int num = matrix[row][column]; //找到查找的数 if (num == target) { return true; //如果当前值比目标值大,则向左移动 } else if (num > target) { column--; //如果当前值比目标值小,则向下移动 } else { row++; } } return false; } }
3、旋转数组的最小数字
问题:
把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。
给你一个可能存在 重复 元素值的数组 numbers ,它原来是一个升序排列的数组,并按上述情形进行了一次旋转。请返回旋转数组的最小元素。例如,数组 [3,4,5,1,2] 为 [1,2,3,4,5] 的一次旋转,该数组的最小值为1。
输入:[3,4,5,1,2]
输出:1
解法:二分法
class Solution { //正常递增时,左边数字一定小于右边,如果存在某个数比有右边的数大,说明这段区间存在旋转数字 public int minArray(int[] numbers) { int l = 0, r = numbers.length - 1; while (l < r) { int mid = (l + r) / 2; //当中点值比右边界值大,说明最小值在右边区间 if (numbers[mid] > numbers[r]) l = mid + 1; //当中点值比右边界值小,说明最小值在左边区间 else if (numbers[mid] < numbers[r]) r = m; //如果中点值与右边界值相等,则区间想左移动 else r--; } //左右相等时,返回的为最小值 return numbers[l]; } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号