实验四
实验四
实验任务一
代码
GradeCalc.cpp
#include <algorithm>
#include <array>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <numeric>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include "GradeCalc.hpp"
GradeCalc::GradeCalc(const std::string &cname):course_name{cname},is_dirty{true} {
counts.fill(0);
rates.fill(0);
}
void GradeCalc::input(int n) {
if(n <= 0) {
std::cerr << "输入的成绩数量无效! 请输入一个大于0的整数\n";
std::exit(1);
}
grades.reserve(n);
int grade;
for(int i = 0; i < n;) {
std::cin >> grade;
if(grade < 0 || grade > 100) {
std::cerr << "输入的成绩无效! 请输入一个[0,100]的整数\n";
continue;
}
grades.push_back(grade);
++i;
}
is_dirty = true; // 标记成绩已改变,需要重新计算统计信息
}
void GradeCalc::output() const {
for(auto grade: grades)
std::cout << grade << ' ';
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void GradeCalc::sort(bool ascending) {
if(ascending)
std::sort(grades.begin(), grades.end());
else
std::sort(grades.begin(), grades.end(), std::greater<int>());
}
int GradeCalc::min() const {
if(grades.empty())
return -1;
auto it = std::min_element(grades.begin(), grades.end());
return *it;
}
int GradeCalc::max() const {
if(grades.empty())
return -1;
auto it = std::max_element(grades.begin(), grades.end());
return *it;
}
double GradeCalc::average() const {
if(grades.empty())
return 0.0;
double avg = std::accumulate(grades.begin(), grades.end(), 0.0)/grades.size();
return avg;
}
void GradeCalc::info() {
if(is_dirty)
compute();
std::cout << "锟轿筹拷锟斤拷锟斤拷:\t" << course_name << std::endl;
std::cout << "平锟斤拷锟斤拷:\t" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << average() << std::endl;
std::cout << "锟斤拷叻锟?:\t" << max() << std::endl;
std::cout << "锟斤拷头锟?:\t" << min() << std::endl;
const std::array<std::string, 5> grade_range{"[0, 60) ",
"[60, 70)",
"[70, 80)",
"[80, 90)",
"[90, 100]"};
for(int i = static_cast<int>(grade_range.size())-1; i >= 0; --i)
std::cout << grade_range[i] << "\t: " << counts[i] << "锟斤拷\t"
<< std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << rates[i]*100 << "%\n";
}
void GradeCalc::compute() {
if(grades.empty())
return;
counts.fill(0);
rates.fill(0.0);
// 统锟狡革拷锟斤拷锟斤拷锟斤拷锟斤拷锟斤拷
for(auto grade:grades) {
if(grade < 60)
++counts[0]; // [0, 60)
else if (grade < 70)
++counts[1]; // [60, 70)
else if (grade < 80)
++counts[2]; // [70, 80)
else if (grade < 90)
++counts[3]; // [80, 90)
else
++counts[4]; // [90, 100]
}
// 统锟狡革拷锟斤拷锟斤拷锟轿憋拷锟斤拷
for(size_t i = 0; i < rates.size(); ++i)
rates[i] = counts[i] * 1.0 / grades.size();
is_dirty = false; // 标记成绩已改变,需要重新计算统计信息
}
GradeCalc.hpp
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <array>
#include <string>
class GradeCalc {
public:
GradeCalc(const std::string &cname);
void input(int n); // 录入n个成绩
void output() const; // 输出成绩
void sort(bool ascending = false); // 排序 (默认降序)
int min() const; // 返回最低分(如成绩未录入,返回-1)
int max() const; // 返回最高分 (如成绩未录入,返回-1)
double average() const; // 返回平均分 (如成绩未录入,返回0.0)
void info(); // 输出课程成绩信息
private:
void compute(); // 成绩统计
private:
std::string course_name; // 课程名
std::vector<int> grades; // 课程成绩
std::array<int, 5> counts; // 保存各分数段人数([0, 60), [60, 70), [70, 80), [80, 90), [90, 100]
std::array<double, 5> rates; // 保存各分数段人数占比
bool is_dirty; // 脏标记,记录是否成绩信息有变更
};
task1.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "GradeCalc.hpp"
void test() {
GradeCalc c1("OOP");
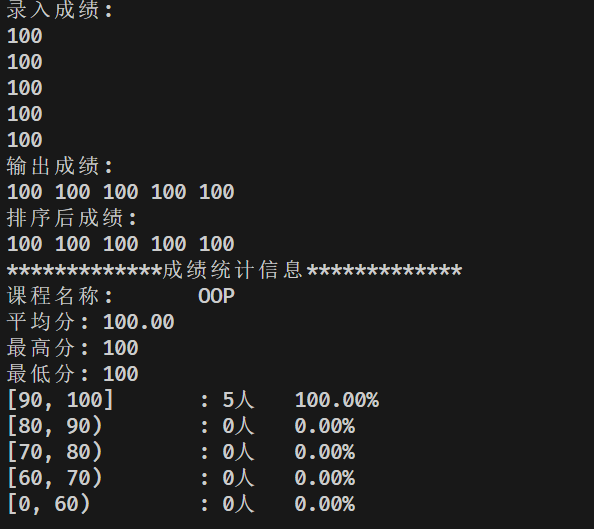
std::cout << "录入成绩:\n";
c1.input(5);
std::cout << "输出成绩:\n";
c1.output();
std::cout << "排序后成绩:\n";
c1.sort(); c1.output();
std::cout << "*************成绩统计信息*************\n";
c1.info();
}
int main() {
test();
}
运行结果截图
回答问题
问题1:组合关系识别
在GradeCalc类声明中,体现"组合"关系的成员声明有:
std::string course_name; - 被组合对象:存储课程名称的字符串对象
std::vector
std::array<int, 5> counts; - 被组合对象:存储各分数段人数统计的固定数组
std::array<double, 5> rates; - 被组合对象:存储各分数段占比的固定数组
bool is_dirty; - 被组合对象:标记成绩数据是否已变更需要重新计算
问题2:接口暴露理解
c
Apply
GradeCalc c("OOP");
c.inupt(5); // 不合法:拼写错误,应该是input不是inupt
c.push_back(97); // 不合法:GradeCalc类没有push_back方法
不合法的原因:
c.inupt(5); - 方法名拼写错误,应该是input(5)
c.push_back(97); - GradeCalc类没有提供push_back方法,grades是私有成员,不能直接通过push_back添加成绩
问题3:架构设计分析
(1)连续打印3次统计信息,compute会被调用1次。is_dirty标记的作用:第一次调用info()时会调用compute()并将is_dirty设为false,后续两次调用info()时由于is_dirty为false,不会再次调用compute()。
(2)不需要更改compute调用位置。因为update_grade()会修改成绩数据,只需要在update_grade()中将is_dirty设为true即可,下次调用info()时会自动重新计算。
问题4:功能扩展设计
要增加"中位数"统计,不新增数据成员可以在compute()函数中添加计算逻辑:
cpp
Apply
void GradeCalc::compute() {
// ... 原有代码 ...
// 计算中位数
double median = 0.0;
if (!grades.empty()) {
std::vector<int> sorted_grades = grades;
std::sort(sorted_grades.begin(), sorted_grades.end());
size_t n = sorted_grades.size();
if (n % 2 == 0)
median = (sorted_grades[n/2-1] + sorted_grades[n/2]) / 2.0;
else
median = sorted_grades[n/2];
}
is_dirty = false;
}
问题5:数据状态管理
compute中不能去掉这两行。如果去掉,在以下使用场景会引发统计错误:
当成绩数据被修改(如调用input()添加新成绩或sort()改变成绩顺序)后再次调用info()时,由于is_dirty为true会调用compute(),但如果没有counts.fill(0); rates.fill(0);这两行,counts和rates数组会保留上次的统计结果,导致统计结果累加错误。
问题6:内存管理理解
(1)对程序功能没有影响。去掉grades.reserve(n);后程序仍能正常编译运行,功能不受影响。
(2)对性能有影响。去掉后会导致vector在添加元素时可能需要多次重新分配内存和复制元素,降低性能。
实验任务二
代码
GradeCalc.cpp
#include <algorithm>
#include <array>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <numeric>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include "GradeCalc.hpp"
GradeCalc::GradeCalc(const std::string &cname): course_name{cname}, is_dirty{true}{
counts.fill(0);
rates.fill(0);
}
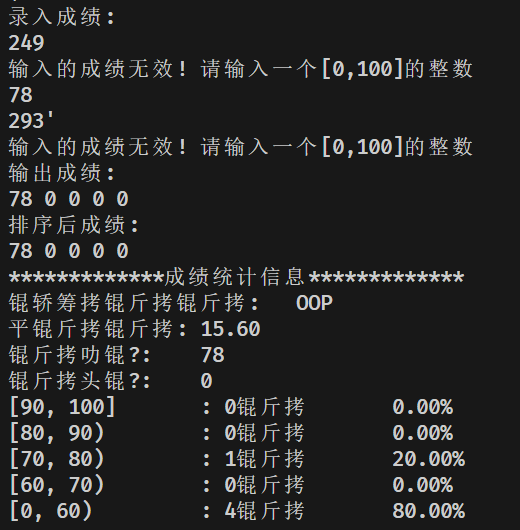
void GradeCalc::input(int n) {
if(n < 0) {
std::cerr << "无效输入! 人数不能为负数\n";
return;
}
this->reserve(n);
int grade;
for(int i = 0; i < n;) {
std::cin >> grade;
if(grade < 0 || grade > 100) {
std::cerr << "无效输入! 分数须在[0,100]\n";
continue;
}
this->push_back(grade);
++i;
}
is_dirty = true;
}
void GradeCalc::output() const {
for(auto grade: *this)
std::cout << grade << ' ';
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void GradeCalc::sort(bool ascending) {
if(ascending)
std::sort(this->begin(), this->end());
else
std::sort(this->begin(), this->end(), std::greater<int>());
}
int GradeCalc::min() const {
if(this->empty())
return -1;
return *std::min_element(this->begin(), this->end());
}
int GradeCalc::max() const {
if(this->empty())
return -1;
return *std::max_element(this->begin(), this->end());
}
double GradeCalc::average() const {
if(this->empty())
return 0.0;
double avg = std::accumulate(this->begin(), this->end(), 0.0) / this->size();
return avg;
}
void GradeCalc::info() {
if(is_dirty)
compute();
std::cout << "课程名称:\t" << course_name << std::endl;
std::cout << "平均分:\t" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << average() << std::endl;
std::cout << "最高分:\t" << max() << std::endl;
std::cout << "最低分:\t" << min() << std::endl;
const std::array<std::string, 5> grade_range{"[0, 60) ",
"[60, 70)",
"[70, 80)",
"[80, 90)",
"[90, 100]"};
for(int i = static_cast<int>(grade_range.size())-1; i >= 0; --i)
std::cout << grade_range[i] << "\t: " << counts[i] << "人\t"
<< std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << rates[i]*100 << "%\n";
}
void GradeCalc::compute() {
if(this->empty())
return;
counts.fill(0);
rates.fill(0);
// 统计各分数段人数
for(int grade: *this) {
if(grade < 60)
++counts[0]; // [0, 60)
else if (grade < 70)
++counts[1]; // [60, 70)
else if (grade < 80)
++counts[2]; // [70, 80)
else if (grade < 90)
++counts[3]; // [80, 90)
else
++counts[4]; // [90, 100]
}
// 统计各分数段比例
for(size_t i = 0; i < rates.size(); ++i)
rates[i] = counts[i] * 1.0 / this->size();
is_dirty = false;
}
GradeCalc.hpp
#pragma once
#include <array>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
class GradeCalc: private std::vector<int> {
public:
GradeCalc(const std::string &cname);
void input(int n); // 录入n个成绩
void output() const; // 输出成绩
void sort(bool ascending = false); // 排序 (默认降序)
int min() const; // 返回最低分
int max() const; // 返回最高分
double average() const; // 返回平均分
void info(); // 输出成绩统计信息
private:
void compute(); // 计算成绩统计信息
private:
std::string course_name; // 课程名
std::array<int, 5> counts; // 保存各分数段人数([0, 60), [60, 70), [70, 80), [80, 90), [90, 100]
std::array<double, 5> rates; // 保存各分数段占比
bool is_dirty; // 脏标记,记录是否成绩信息有变更
};
task2.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "GradeCalc.hpp"
void test() {
GradeCalc c1("OOP");
std::cout << "录入成绩:\n";
c1.input(5);
std::cout << "输出成绩:\n";
c1.output();
std::cout << "排序后成绩:\n";
c1.sort(); c1.output();
std::cout << "*************成绩统计信息*************\n";
c1.info();
}
int main() {
test();
}
运行结果截图

回答问题
问题1:继承关系识别
cpp
Apply
class GradeCalc: private std::vector
这行代码体现了GradeCalc类私有继承自std::vector
的继承关系。
问题2:接口暴露理解
当前继承方式下,基类vector
的接口不会自动成为GradeCalc的公有接口,因为使用的是私有继承。
在test模块中的使用:
c
Apply
GradeCalc c("OOP");
c.input(5); // 合法:input是GradeCalc的公有方法
c.push_back(97); // 不合法:push_back是vector的方法,但私有继承使其无法在类外访问
原因:私有继承使得基类的所有成员在派生类中都成为私有成员,外部代码无法直接访问。
问题3:数据访问差异
问题1:继承关系识别
cpp
Apply
class GradeCalc: private std::vector
这行代码体现了GradeCalc类私有继承自std::vector
的继承关系。
问题2:接口暴露理解
当前继承方式下,基类vector
的接口不会自动成为GradeCalc的公有接口,因为使用的是私有继承。
在test模块中的使用:
c
Apply
GradeCalc c("OOP");
c.input(5); // 合法:input是GradeCalc的公有方法
c.push_back(97); // 不合法:push_back是vector的方法,但私有继承使其无法在类外访问
原因:私有继承使得基类的所有成员在派生类中都成为私有成员,外部代码无法直接访问。
问题3:数据访问差异
cpp
Apply
// 组合方式
for(auto grade: grades) // 通过成员对象grades访问数据
// 继承方式
for(int grade: *this) // 通过继承的基类接口直接访问数据(将自身当作vector使用)
封装差异:
组合方式:数据访问需要通过成员对象grades,封装性更好,外部代码无法直接访问内部数据
继承方式:可以直接使用*this当作vector使用,数据访问更直接但封装性较弱
问题4:组合 vs. 继承方案选择
结论:组合方案更适合成绩计算这个问题场景。
理由:成绩计算类与vector之间是"has-a"(有一个)关系而非"is-a"(是一个)关系。GradeCalc"有一个"成绩列表,而不是GradeCalc"是一个"vector。组合方式提供了更好的封装性,可以更好地控制接口暴露,符合面向对象设计的"优先使用组合"原则。
实验任务三
代码
demo3.cpp
#include <string>
#include "Graph.hpp"
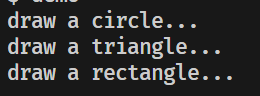
void test() {
Canvas canvas;
canvas.add("circle");
canvas.add("triangle");
canvas.add("rectangle");
canvas.paint();
}
int main() {
test();
}
Graph.hpp
#include <algorithm>
#include <cctype>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "Graph.hpp"
// Circle类实现
void Circle::draw() { std::cout << "draw a circle...\n"; }
// Triangle类实现
void Triangle::draw() { std::cout << "draw a triangle...\n"; }
// Rectangle类实现
void Rectangle::draw() { std::cout << "draw a rectangle...\n"; }
// Canvas类实现
void Canvas::add(const std::string& type) {
Graph* g = make_graph(type);
if (g)
graphs.push_back(g);
}
void Canvas::paint() const {
for (Graph* g : graphs)
g->draw();
}
Canvas::~Canvas() {
for (Graph* g : graphs)
delete g;
}
// 工具函数实现
// 字符串 → 枚举转换
GraphType str_to_GraphType(const std::string& s) {
std::string t = s;
std::transform(s.begin(), s.end(), t.begin(),
[](unsigned char c) { return std::tolower(c);});
if (t == "circle")
return GraphType::circle;
if (t == "triangle")
return GraphType::triangle;
if (t == "rectangle")
return GraphType::rectangle;
return GraphType::circle; // 缺省返回
}
// 创建图形,返回堆对象指针
Graph* make_graph(const std::string& type) {
switch (str_to_GraphType(type)) {
case GraphType::circle: return new Circle;
case GraphType::triangle: return new Triangle;
case GraphType::rectangle: return new Rectangle;
default: return nullptr;
}
}
Graph.hpp
#pragma once
#include <string>
#include <vector>
enum class GraphType {circle, triangle, rectangle};
// Graph类定义
class Graph {
public:
virtual void draw() {}
virtual ~Graph() = default;
};
// Circle类声明
class Circle : public Graph {
public:
void draw();
};
// Triangle类声明
class Triangle : public Graph {
public:
void draw();
};
// Rectangle类声明
class Rectangle : public Graph {
public:
void draw();
};
// Canvas类声明
class Canvas {
public:
void add(const std::string& type); // 根据字符串添加图形
void paint() const; // 使用统一接口绘制所有图形
~Canvas(); // 手动释放资源
private:
std::vector<Graph*> graphs;
};
// 4. 工具函数
GraphType str_to_GraphType(const std::string& s); // 字符串转枚举类型
Graph* make_graph(const std::string& type); // 创建图形,返回堆对象指针
运行结果截图
回答问题
问题1:对象关系识别
(1)组合关系的成员声明代码行:
cpp
Apply
std::vector<Graph*> graphs;
被组合对象功能:存储指向各种图形对象的指针,管理画布上的所有图形。
(2)继承关系的类声明代码行:
问题2:多态机制观察
(1)如果Graph中的draw未声明成虚函数,Canvas::paint()中g->draw()将只会调用Graph基类的draw()函数,输出为空,无法实现多态效果,无法根据实际对象类型调用相应的绘制函数。
(2)如果std::vector<Graph*>改成std::vector
(3)如果~Graph()未声明成虚函数,当通过基类指针删除派生类对象时,只会调用基类的析构函数,不会调用派生类的析构函数,可能导致派生类中分配的资源无法正确释放,造成内存泄漏。
问题3:扩展性思考
要新增星形Star,需要在以下文件做改动:
Graph.hpp:
在enum class GraphType中添加star
新增class Star : public Graph类声明
在str_to_GraphType函数声明中添加星形处理
Graph.cpp:
实现Star::draw()函数
在str_to_GraphType函数中添加星形字符串转换
在make_graph函数的switch语句中添加case GraphType:⭐ return new Star;
问题4:资源管理
(1)make_graph返回的对象在Canvas析构函数中被释放。具体流程:make_graph在堆上创建对象→Canvas::add将其指针存入vector→Canvas析构函数遍历vector并delete所有指针。
(2)使用原始指针管理内存的利弊:
优点:灵活、效率高、直接控制内存
缺点:需要手动管理内存,容易出现内存泄漏或重复删除;异常安全性差;代码可维护性较低
实验任务四
代码
Toy.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
class ToyFactory;
class Toy{
public:
Toy(const std::string& name, int type, int number);
~Toy();
std::string get_name() const;
int get_type() const;
int get_number() const;
void set_is_sold(bool is_sold);
std::string get_seller_name() const;
void set_seller_name(const std::string& seller_name);
void set_factory(ToyFactory* factory);
private:
std::string name;
int type;
bool is_sold;
std::string seller_name;
int number;
ToyFactory* factory;
};
class ToyFactory{
public:
ToyFactory(std::vector<int> product_types);
~ToyFactory();
Toy* create_toy(const std::string& name, int type, int number);
std::string get_seller_name(Toy* toy) const;
void product_toys(int type, int num);
void sell_toy(int toy_type, const std::string& seller_name, int num);
void add_type(int type);
int toy_count(int type) const;
int total_toy_count() const;
private:
bool is_sold(Toy* toy) const;
std::vector<Toy*> sold_toys;
std::vector<Toy*> unsold_toys;
std::vector<Toy*> toys;
std::map<int, int> type_count;
};
ToyFactory.cpp
#include "Toy.hpp"
#include<vector>
#include<map>
void ToyFactory::add_type(int type) {
if(type_count.find(type) != type_count.end()){
std::cout << "Type " << type << " already exists in the factory" << std::endl;
return;
}
type_count[type] = 0;
std::cout << "Successfully added " << type << " to the factory" << std::endl;
}
ToyFactory::ToyFactory(std::vector<int> product_types) {
for(auto type: product_types)
add_type(type);
}
ToyFactory::~ToyFactory() {
for(auto toy: toys)
delete toy;
for(auto toy: sold_toys)
delete toy;
for(auto toy: unsold_toys)
delete toy;
}
Toy* ToyFactory::create_toy(const std::string& name, int type, int number) {
Toy* toy = new Toy(name, type, number);
toy->set_factory(this);
return toy;
}
std::string ToyFactory::get_seller_name(Toy* toy) const {
for(auto _toy: sold_toys){
if(_toy->get_number() == toy->get_number()){
return _toy->get_seller_name();
}
}
std::cout << "Toy " << toy->get_number() << " has not been sold yet" << std::endl;
return "";
}
void ToyFactory::product_toys(int type, int num) {
if(type_count.find(type) == type_count.end())
return;
for(int i = 0; i < num; ++i){
type_count[type] += 1;
Toy* toy = this->create_toy(std::to_string(type)+"toyname" + std::to_string(type_count[type]), type, type_count[type]);
toys.push_back(toy);
unsold_toys.push_back(toy);
}
std::cout << "Successfully produced " << num << " " << type << " toys" << std::endl;
}
int ToyFactory::toy_count(int type) const {
if(type_count.find(type) == type_count.end())
return -1;
return type_count.at(type);
}
int ToyFactory::total_toy_count() const {
int total = 0;
for(auto count: type_count)
total += count.second;
return total;
}
void ToyFactory::sell_toy(int toy_type, const std::string& seller_name, int num) {
if(type_count.find(toy_type) == type_count.end())
return;
if(type_count[toy_type] < num){
std::cout << "Not enough " << toy_type << " toys to sell" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Producing " << num - type_count[toy_type] << " more " << toy_type << " toys" << std::endl;
product_toys(toy_type, num - type_count[toy_type]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < num; ++i){
for(auto toy: unsold_toys){
if(toy->get_type() == toy_type){
toy->set_seller_name(seller_name);
toy->set_is_sold(true);
sold_toys.push_back(toy);
unsold_toys.erase(std::remove(unsold_toys.begin(), unsold_toys.end(), toy), unsold_toys.end());
break;
}
}
}
std::cout << "Successfully sold " << num << " " << toy_type << " toys to " << seller_name << std::endl;
}
Toy.cpp
#include "Toy.hpp"
void Toy::set_is_sold(bool is_sold) {
this->is_sold = is_sold;
}
Toy::Toy(const std::string& name, int type, int number):name{name},type{type},number{number} {
is_sold = false;
}
Toy::~Toy() {}
std::string Toy::get_name() const {
return name;
}
int Toy::get_type() const {
return type;
}
int Toy::get_number() const {
return number;
}
void Toy::set_seller_name(const std::string& seller_name) {
this->seller_name = seller_name;
}
std::string Toy::get_seller_name() const {
return seller_name;
}
void Toy::set_factory(ToyFactory* factory) {
this->factory = factory;
}
task4.cpp
#include "Toy.hpp"
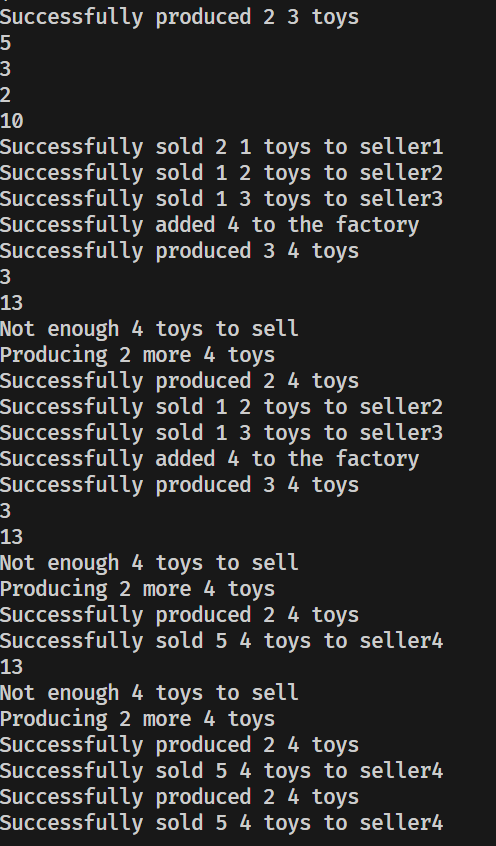
int main(){
ToyFactory factory({1, 2, 3});
factory.product_toys(1, 5);
factory.product_toys(2, 3);
factory.product_toys(3, 2);
std::cout << factory.toy_count(1) << std::endl;
std::cout << factory.toy_count(2) << std::endl;
std::cout << factory.toy_count(3) << std::endl;
std::cout << factory.total_toy_count() << std::endl;
factory.sell_toy(1, "seller1", 2);
factory.sell_toy(2, "seller2", 1);
factory.sell_toy(3, "seller3", 1);
factory.add_type(4);
factory.product_toys(4, 3);
std::cout << factory.toy_count(4) << std::endl;
std::cout << factory.total_toy_count() << std::endl;
factory.sell_toy(4, "seller4", 5);
return 0;
}
运行结果截图


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号