使用DDD模式实现简单API(8/6)
处理领域事件(补充)
介绍
上一篇文章中讲述了发布和处理领域事件,这篇文章将结合“盒子模式”(“盒子模式”是一种方案,当程序与外部的组件或服务交互时,保证程序的信息一定能到成功传递到目标,但是可能发生重复传递)对事件的处理进行优化,将数据以结构化的方式在事务边界内在系统内传递。
系统的深度
在进入正题之前,先分析下我对深度系统和浅系统的看法
浅系统
通常情况下,浅系统表现为,当完成一个事件后,就没有后续动作了。
一个典型的浅系统包含大量的增删改查操作,大部分的操作与页面展示的数据相关,包含少量的业务的逻辑。有时,这样的系统也可以称之为数据库浏览器。
其他能够标明一个浅系统的特征是系统的需求分析,如果通过页面原型就可以描述系统的功能和实现,没有潜在的业务逻辑和定义,那就说明是一个浅系统。
从DDD的角度来说,浅系统通常表现为:集成根内的命令执行时,触发了一个事件,然后就没有后续了。没有事件订阅者,没有处理程序,没有工作流,没有与其他上下文的通信也没有第3方的系统,如下图:
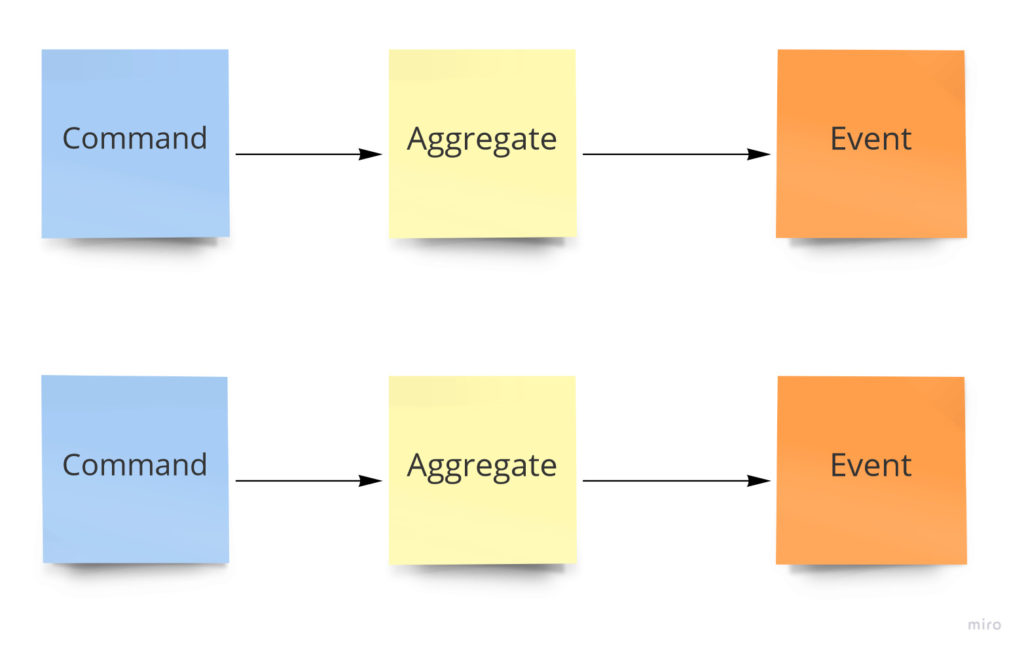
触发动作,执行请求,保存数据-流程结束。在这种情况下,不需要采用DDD模式,简单的设计模式就足以胜任。
深系统
深系统与浅系统完全相反
深系统是被设计为处理一个大的、复杂的领域内业务的系统。如果领域业务复杂,相应的领域模型也会较为复杂。当然,领域模型应该尽可能的简化,但是不能失去它在给定上下文中代表的概念和需要处理的业务逻辑。
我们不会仅仅通过一个页面原型来描述一个深系统,因为内部的业务逻辑很复杂。保存和读取数据仅仅是系统的动作之一,其它动作包括:
- 与其它系统通信
- 复杂的数据处理
- 调用系统内的其他组件
从DDD的角度来看,在上下文发生的事情将会多得多,集成根可能会发布多个领域事件,对于一个事件,可能存在多个处理器来相应不同的行为。它可能是与外部的系统进行通信或者是调用另外一个集成根的命令,同时又会发布出新的事件形成新的调用链。如下图:
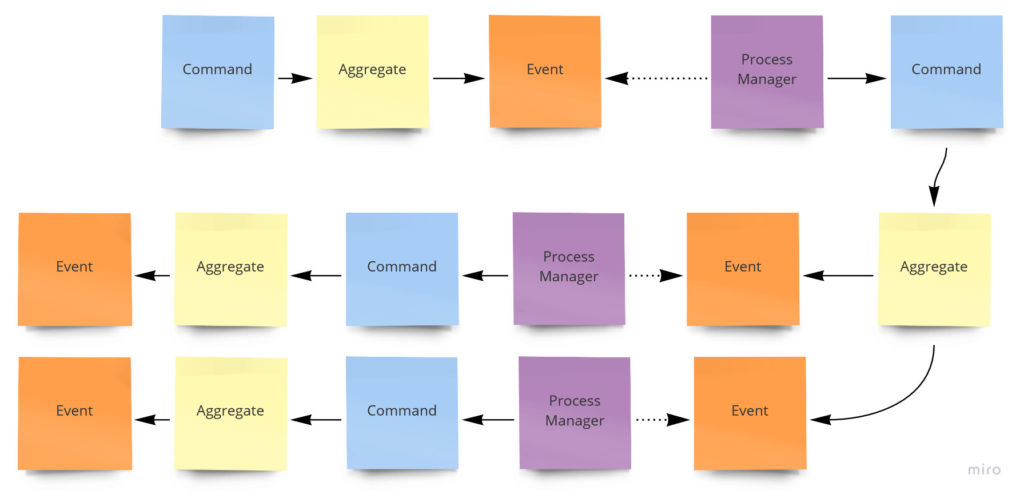
问题
在上一篇文章中呈现的领域事件处理非常简单,它不支持集成根之间的互相调用和事件的再发布,换句话说,它不支持复杂的工作流和数据处理。只有命令-集成根-领域事件-处理器这样的单一工作流。
实际的情况下,则必须考虑复杂业务。假设一个顾客下订单之后:
- 一封确认邮件需要发送给客户进行确认
- 支付请求应该被创建
- 关于支付详情的邮件需要发送给客户
这些需求如下图所示:
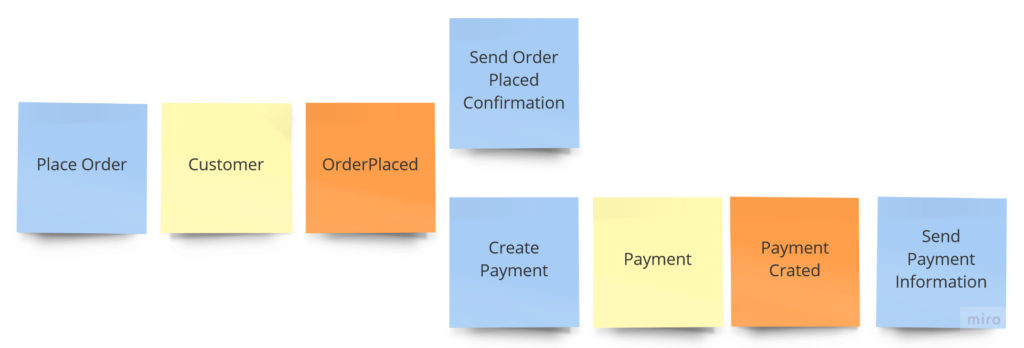
我们假设下订单和支付的创建动作需要在一个事务内,如果事务成功,我们需要发送2封邮件-关于下订单和支付。如何实现这样的场景呢?
方案
首先,最重要的是我们需要记住事务的边界,我们做出一下规定:
- 命令处理器定义事务的边界。事务在命令处理器被调用时开始,在命令处理器提交时结束。
- 同时被调用的命令处理器都处在同一个事务内
- 如果想要执行事务之外的内容,我们需要创建一个基于领域事件的公共事件,我称之为领域事件通知,一些人称为公共事件,但是概念是一样的
其次,何时发布和处理领域事件,每个集成根的方法执行完成时都可能创建事件,所以:
- 在每个命令执行时(提交事务之前)
- 每个事件处理之后(不提交事务)
第三个要考虑的是领域通知的执行,我们需要在事务之外处理它们,这里就引入了“盒子模式”的概念。
实现
我们首先想到的是在每个命令处理的结尾发布事件并提交事务,在领域事件处理的结尾只发布事件。但是有一种更为优雅的方式-使用装饰器模式。装饰器模式允许我们将业务逻辑包裹在一段基础代码中,类似于切面编程和.Net Core中间件。
我们需要两个装饰器,第一个用于命令处理器:
public class DomainEventsDispatcherCommandHandlerDecorator<T> : IRequestHandler<T, Unit> where T:IRequest
{
private readonly IRequestHandler<T, Unit> _decorated;
private readonly IUnitOfWork _unitOfWork;
public DomainEventsDispatcherCommandHandlerDecorator(
IRequestHandler<T, Unit> decorated,
IUnitOfWork unitOfWork)
{
_decorated = decorated;
_unitOfWork = unitOfWork;
}
public async Task<Unit> Handle(T command, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
await this._decorated.Handle(command, cancellationToken);
await this._unitOfWork.CommitAsync(cancellationToken);
return Unit.Value;
}
}
在第16行,执行了被装饰的命令的方法,在第18行,执行了UnitOfWork的提交动作。UoW发布了领域事件,然后提交了事务。
public class UnitOfWork : IUnitOfWork
{
private readonly OrdersContext _ordersContext;
private readonly IDomainEventsDispatcher _domainEventsDispatcher;
public UnitOfWork(
OrdersContext ordersContext,
IDomainEventsDispatcher domainEventsDispatcher)
{
this._ordersContext = ordersContext;
this._domainEventsDispatcher = domainEventsDispatcher;
}
public async Task<int> CommitAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken = default(CancellationToken))
{
await this._domainEventsDispatcher.DispatchEventsAsync();
return await this._ordersContext.SaveChangesAsync(cancellationToken);
}
}
根据上面提出的要求,我们需要第二个装饰器来处理领域事件,这个装饰器只会发布领域事件,不会提交数据库事务。
public class DomainEventsDispatcherNotificationHandlerDecorator<T> : INotificationHandler<T> where T : INotification
{
private readonly INotificationHandler<T> _decorated;
private readonly IDomainEventsDispatcher _domainEventsDispatcher;
public DomainEventsDispatcherNotificationHandlerDecorator(
IDomainEventsDispatcher domainEventsDispatcher,
INotificationHandler<T> decorated)
{
_domainEventsDispatcher = domainEventsDispatcher;
_decorated = decorated;
}
public async Task Handle(T notification, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
await this._decorated.Handle(notification, cancellationToken);
await this._domainEventsDispatcher.DispatchEventsAsync();
}
}
最后,需要在IOC容器中配置装饰器(Autofac的例子)
builder.RegisterGenericDecorator(
typeof(DomainEventsDispatcherNotificationHandlerDecorator<>),
typeof(INotificationHandler<>));
builder.RegisterGenericDecorator(
typeof(DomainEventsDispatcherCommandHandlerDecorator<>),
typeof(IRequestHandler<,>));
添加领域通知到盒子
为了处理事务之外的基于领域事件的通知,我们需要采用盒子模式。
var domainEventNotifications = new List<IDomainEventNotification<IDomainEvent>>();
foreach (var domainEvent in domainEvents)
{
Type domainEvenNotificationType = typeof(IDomainEventNotification<>);
var domainNotificationWithGenericType = domainEvenNotificationType.MakeGenericType(domainEvent.GetType());
var domainNotification = _scope.ResolveOptional(domainNotificationWithGenericType, new List<Parameter>
{
new NamedParameter("domainEvent", domainEvent)
});
if (domainNotification != null)
{
domainEventNotifications.Add(domainNotification as SeedWork.IDomainEventNotification<IDomainEvent>);
}
}
domainEntities
.ForEach(entity => entity.Entity.ClearDomainEvents());
var tasks = domainEvents
.Select(async (domainEvent) =>
{
await _mediator.Publish(domainEvent);
});
await Task.WhenAll(tasks);
foreach (var domainEventNotification in domainEventNotifications)
{
string type = domainEventNotification.GetType().FullName;
var data = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(domainEventNotification);
OutboxMessage outboxMessage = new OutboxMessage(
domainEventNotification.DomainEvent.OccurredOn,
type,
data);
this._ordersContext.OutboxMessages.Add(outboxMessage);
}
注:通知的存储在相同事务内操作,保证了通知一定会被生成,执行是在事务之外。
工作流执行步骤
这里我们只考虑应用逻辑不考虑基础架构,下面只实现特殊的工作流步骤:
下订单之后创建支付命令
public class OrderPlacedDomainEventHandler : INotificationHandler<OrderPlacedEvent>
{
private readonly IPaymentRepository _paymentRepository;
public OrderPlacedDomainEventHandler(IPaymentRepository paymentRepository)
{
_paymentRepository = paymentRepository;
}
public async Task Handle(OrderPlacedEvent notification, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var newPayment = new Payment(notification.OrderId);
await this._paymentRepository.AddAsync(newPayment);
}
}
下订单后发送邮件
public class OrderPlacedNotification : DomainNotificationBase<OrderPlacedEvent>
{
public OrderId OrderId { get; }
public OrderPlacedNotification(OrderPlacedEvent domainEvent) : base(domainEvent)
{
this.OrderId = domainEvent.OrderId;
}
[JsonConstructor]
public OrderPlacedNotification(OrderId orderId) : base(null)
{
this.OrderId = orderId;
}
}
public class OrderPlacedNotificationHandler : INotificationHandler<OrderPlacedNotification>
{
public async Task Handle(OrderPlacedNotification request, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
// Send email.
}
}
支付命令创建后发送邮件
public class PaymentCreatedNotification : DomainNotificationBase<PaymentCreatedEvent>
{
public PaymentId PaymentId { get; }
public PaymentCreatedNotification(PaymentCreatedEvent domainEvent) : base(domainEvent)
{
this.PaymentId = domainEvent.PaymentId;
}
[JsonConstructor]
public PaymentCreatedNotification(PaymentId paymentId) : base(null)
{
this.PaymentId = paymentId;
}
}
public class PaymentCreatedNotificationHandler : INotificationHandler<PaymentCreatedNotification>
{
public async Task Handle(PaymentCreatedNotification request, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
// Send email.
}
}
下图展示了完整的工作流:
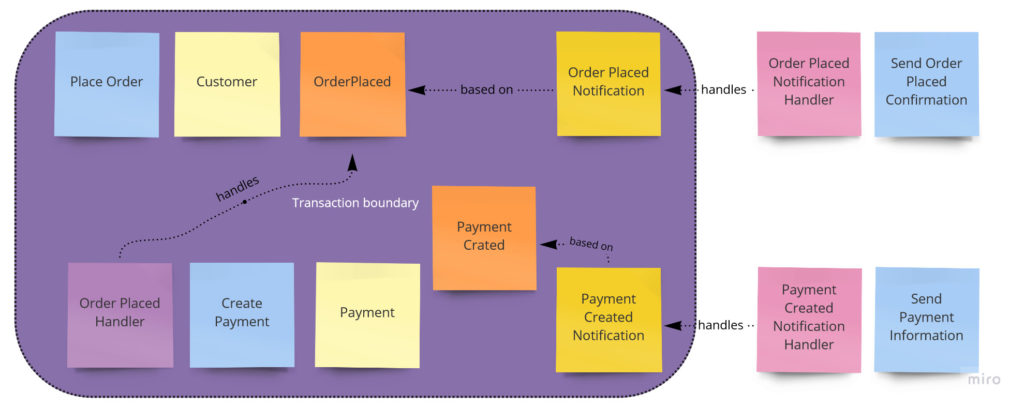
总结
这篇文章讲述了如何在一个深度系统里,采用响应式的方法来执行命令和领域事件:
- 装饰器模式用来处理事件的分发和事务边界的管理
- 盒子模式用来处理事务之外的逻辑
- Unit Of Work模式
- 领域事件通知保证盒子模式的实现
- 基础的DDD构建块-集成根和领域事件
- 事件一致性


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号