Linux利器:使用 gcc 编程C程序
文章更新于:2020-03-23
文章目录
一、手动编译链接单个C源文件
1、创建C源文件
注:此处创建名为 hello.c 的源文件。
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello,world!\n");
return 0;
}
2、编译源文件
gcc -c hello.c
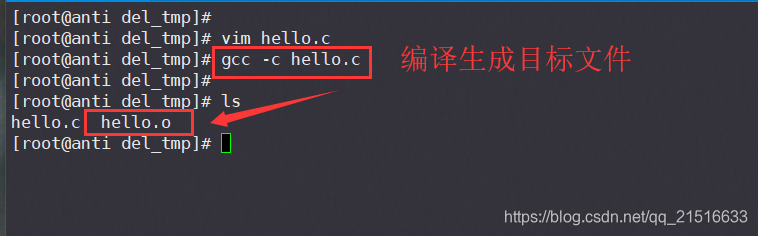
3、生成可执行文件
注:此处的 result 为你想要输出的可执行文件名。
gcc -o result hello.o
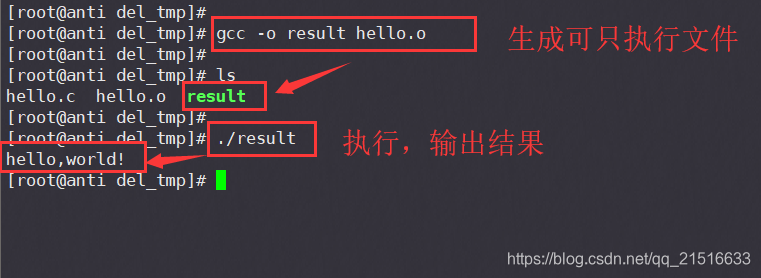
二、手动编译链接多个C源文件
1、创建两个C源文件
注:此处创建名为 hello.c 和 hello2.c 的两个源文件。
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello,world!\n");
testfun(); //调用另一个源文件中的函数
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
void testfun()
{
printf("\nThis is in hello2!\n");
}
2、编译两个源文件
注:此处也可使用 gcc -c *.c 来编译多个C源文件。
gcc -c hello.c hello2.c
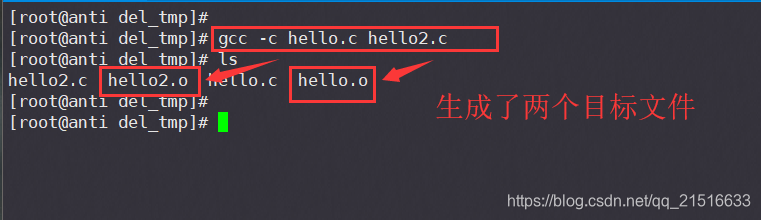
3、生成可执行文件
gcc -o result hello.o hello2.o
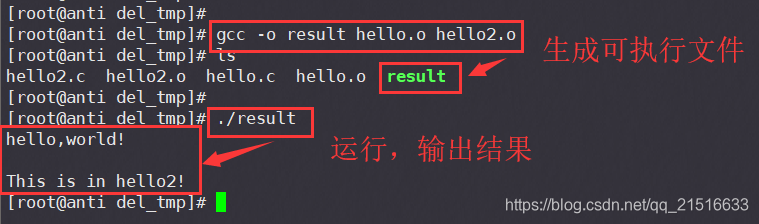
三、使用Makefile自动编译链接
1、创建C源文件
注1:此处延续使用上述例子的两个C源文件。
注2:创建名为 hello.c 和 hello2.c 的两个源文件。
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello,world!\n");
testfun(); //调用另一个源文件中的函数
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
void testfun()
{
printf("\nThis is in hello2!\n");
}
2、创建Makefile文件
注1:这里的hello.o 、hello2.o 是要创建的两个目标文件。
注2:result 为要输出的可执行文件名。
注3:gcc行前面的空白是Tab键生成的。
main: hello.o hello2.o
gcc -o result hello.o hello2.o -lm
3、执行make生成可执行文件
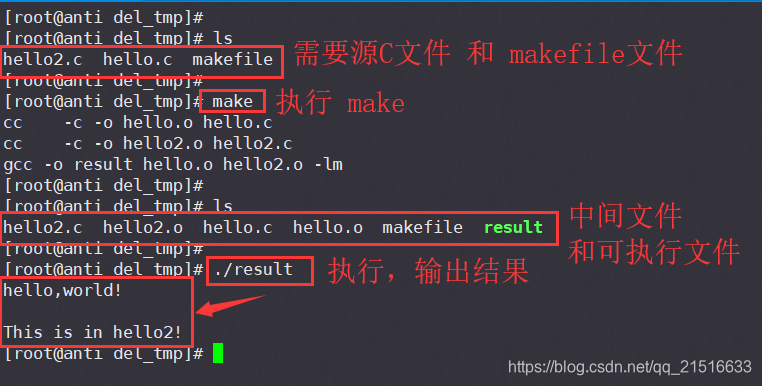
4、加上参数清理中间文件(可选)
注1:如果不想要中间产生的*.o文件,可在Makefile中加入清理参数。
注2:最后一行也可以写成 rm -f *.o。
main: hello.o hello2.o
gcc -o result hello.o hello2.o -lm
clean:
rm -f hello.o hello2.o
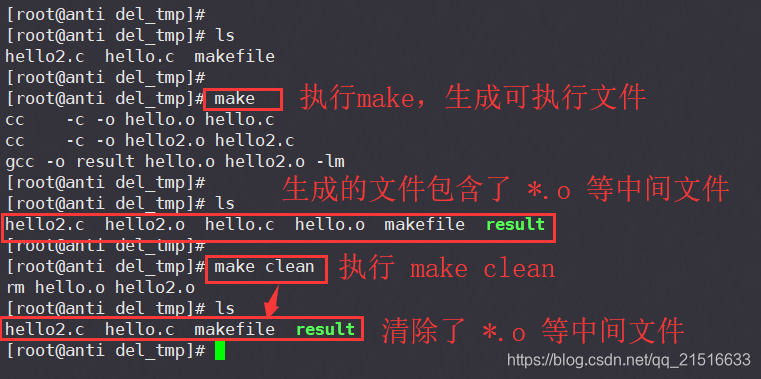
四、Enjoy!
有了计划记得推动,不要原地踏步。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号