mysql 锁
一、原理
MySQL InnoDB存储引擎,实现的是基于多版本的并发控制协议 —— MVCC
MVCC最大的好处,相信也是耳熟能详:读不加锁,读写不冲突
1. 快照读 和 当前读
快照读:简单的select操作,属于快照读,不加锁。
select * from table where ?;
当前读:特殊的读操作,插入/更新/删除操作,属于当前读,需要加锁
select * from table where ? lock in share mode; -- 共享锁(S) select * from table where ? for update; -- 排他锁(X) insert into table values (…); -- 排他锁(X) update table set ? where ?; -- 排他锁(X) delete from table where ?; -- 排他锁(X)
二、种类
1. 按锁的粒度分类:表锁 -----> 页锁 -----> 行锁
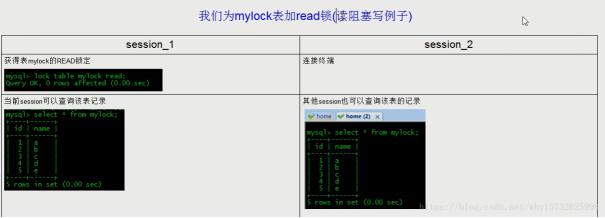
1)表锁:把整个表锁上,处理并发能力弱,但不会发生死锁(因为mysql不允许同一个session上锁期间去读写其他表)
2)行锁:把数据表的某一行上锁,处理并发能力强,可能发生死锁(因为在上锁期间,可能)
表锁演示
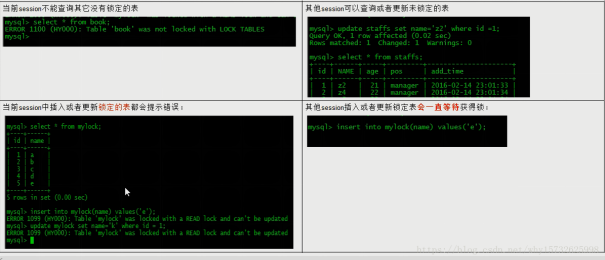
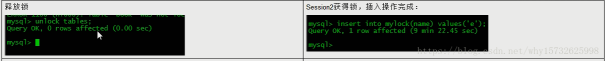
读锁演示
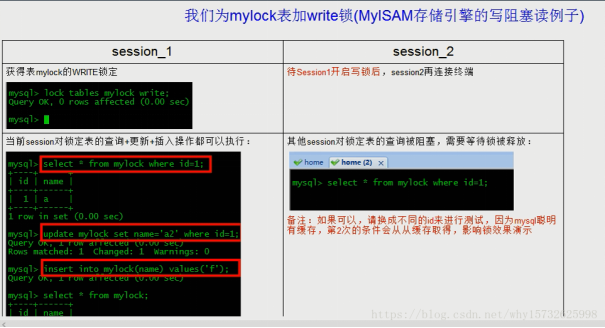
写锁演示
行锁演示
InnoDB行锁是通过给索引上的索引项加锁来实现的,因此InnoDB这种行锁实现特点意味着:只有通过第一索引(最左边第一位索引)条件检索数据,InnoDB才使用行级锁,否则,InnoDB将使用表锁!
|
Session a |
Session b |
|
mysql> set autocommit=0; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) |
mysql> set autocommit=0; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) |
|
mysql> update test_innodb_lock set b = '2' where b = 2000; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.02 sec) Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0 |
mysql> update test_innodb_lock set b = '3' where b = 3000; 被阻塞,等待 |
|
mysql> commit; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.10 sec) |
|
|
|
mysql> update test_innodb_lock set b = '3' where b = 3000; Query OK, 1 row affected (1 min 3.41 sec) Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0 阻塞解除,完成更新 |
间隙锁演示
值得注意的是间隙锁会把边接值也会锁上,例如where id>0 and id<=5,那么id=6也会被锁上;where id>0 and id<5,那么id=5也会被锁上
|
Session a |
Session b |
|
|
1 |
mysql> set autocommit=0; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) |
mysql> set autocommit=0; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) |
|
2 |
mysql> select * from test_innodb_lock; | a | b | | 1 | b2 | | 3 | 3 | | 4 | 4000 | | 5 | 5000 | | 6 | 6000 | | 7 | 7000 | | 8 | 8000 | | 9 | 9000 | | 1 | b1 | 9 rows in set (0.00 sec)
|
|
|
3 |
mysql> update test_innodb_lock set b = a * 100 where a < 4 and a > 1; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.02 sec) Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0 |
|
|
4 |
|
mysql> insert into test_innodb_lock values(2,'200'); 被阻塞,等待 |
|
5 |
mysql> commit; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec) |
|
|
6 |
|
mysql> insert into test_innodb_lock values(2,'200'); Query OK, 1 row affected (38.68 sec) 阻塞解除,完成插入
|
2. 按锁的机制分类:共享锁、排他锁
1)共享锁:就是多个线程共用一个锁(例如在sessionA,set autocommit=0,可以在sessionB commit提交)
2)排他锁:就是一个线程独享一个锁(例如在sessionA,set autocommit=0,只能在sessionA commit提交)
3.按锁的实现方式分类:乐观锁、悲观锁
1)乐观锁:想法很乐观,认为这次的操作不会导致冲突,不采用真实数据库的锁,自己加一个字段来处理
-- 1.查询出商品信息 select (status,status,version) from t_goods where id=1 -- 2.根据商品信息生成订单 -- 3.修改商品status为2 update t_goods set status=2,version=version+1 where id=1 and version='xxx';
2)悲观锁:想法很悲观,认为在操作数据时会出现数据冲突,所以在进行每次操作时都要通过获取锁才能进行对相同数据的操作



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号