SpringBoot整合缓存笔记
一、几个重要概念&缓存注解
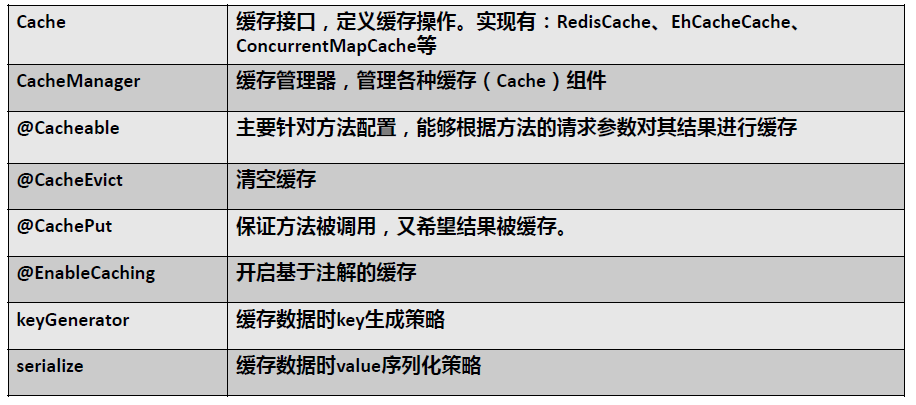
二、快速体验缓存
1.工程构建:POM文件
1 <dependency> 2 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 3 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> 4 </dependency> 5 6 <dependency> 7 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 8 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId> 9 </dependency> 10 11 <dependency> 12 <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> 13 <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> 14 <version>2.1.0</version> 15 </dependency> 16 17 <dependency> 18 <groupId>mysql</groupId> 19 <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> 20 </dependency> 21 22 <dependency> 23 <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> 24 <artifactId>druid</artifactId> 25 <version>1.1.20</version> 26 </dependency> 39 </dependencies>
2.整合MyBatis
1 spring: 2 datasource: 3 driverClassName: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver 4 username: root 5 password: root 6 url: jdbc:mysql://129.211.77.216:3307/jdbc 7 type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource 8 # 数据源其他配置 9 initialSize: 5 10 minIdle: 5 11 maxActive: 20 12 maxWait: 60000 13 timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000 14 minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000 15 validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL 16 testWhileIdle: true 17 testOnBorrow: false 18 testOnReturn: false 19 poolPreparedStatements: true 20 mybatis: 21 configuration: 22 map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
3.整合Druid连接池
1 @Configuration 2 public class DruidConfig { 3 4 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource") 5 @Bean 6 public DataSource druid(){ 7 return new DruidDataSource(); 8 } 9 10 //配置Druid的监控 11 //1.配置一个管理后台的Servlet 12 @Bean 13 public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet(){ 14 ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new StatViewServlet(), 15 "/druid/*"); 16 Map<String,String> initParams = new HashMap<>(); 17 initParams.put("loginUsername","admin"); 18 initParams.put("loginPassword","admin"); 19 initParams.put("allow",""); 20 21 bean.setInitParameters(initParams); 22 return bean; 23 } 24 25 //2、配置一个web监控的filter 26 @Bean 27 public FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter(){ 28 FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean(); 29 bean.setFilter(new WebStatFilter()); 30 31 Map<String,String> initParams = new HashMap<>(); 32 initParams.put("exclusions","*.js,*.css,/druid/*"); 33 34 bean.setInitParameters(initParams); 35 bean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/*")); 36 return bean; 37 } 38 }
4.SpringBootApplication
/**
* 一、搭建基本环境
* 1、导入数据库文件 创建出department和employee表
* 2、创建javaBean封装数据
* 3、整合MyBatis操作数据库
* 1.配置数据源信息
* 2.使用注解版的MyBatis;
* 1)、@MapperScan指定需要扫描的mapper接口所在的包
* 二、快速体验缓存
* 步骤:
* 1、开启基于注解的缓存 @EnableCaching
* 2、标注缓存注解即可
* @Cacheable
* @CacheEvict
* @CachePut
* 默认使用的是ConcurrentMapCacheManager==ConcurrentMapCache;将数据保存在 ConcurrentMap<Object, Object>中
* 开发中使用缓存中间件;redis、memcached、ehcache;
* 三、整合redis作为缓存
* Redis 是一个开源(BSD许可)的,内存中的数据结构存储系统,它可以用作数据库、缓存和消息中间件。
* 1、安装redis:使用docker;
* 2、引入redis的starter
* 3、配置redis
* 4、测试缓存
* 原理:CacheManager===Cache 缓存组件来实际给缓存中存取数据
* 1)、引入redis的starter,容器中保存的是 RedisCacheManager;
* 2)、RedisCacheManager 帮我们创建 RedisCache 来作为缓存组件;RedisCache通过操作redis缓存数据的
* 3)、默认保存数据 k-v 都是Object;利用序列化保存;如何保存为json
* 1、引入了redis的starter,cacheManager变为 RedisCacheManager;
* 2、默认创建的 RedisCacheManager 操作redis的时候使用的是 RedisTemplate<Object, Object>
* 3、RedisTemplate<Object, Object> 是 默认使用jdk的序列化机制
* 4)、自定义CacheManager;
*
*/
@MapperScan("com.amao.springboot.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class SpringbootCacheApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootCacheApplication.class, args);
}
}
5.Service
1 package com.amao.springboot.service; 2 3 4 import com.amao.springboot.domain.Employee; 5 import com.amao.springboot.mapper.EmployeeMapper; 6 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; 7 import org.springframework.cache.annotation.*; 8 import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; 9 10 @Service 11 @CacheConfig(cacheNames="emp"/*,cacheManager = "employeeCacheManager"*/) //抽取缓存的公共配置 12 public class EmployeeService { 13 14 @Autowired 15 EmployeeMapper employeeMapper; 16 17 /** 18 * 将方法的运行结果进行缓存;以后再要相同的数据,直接从缓存中获取,不用调用方法; 19 * CacheManager管理多个Cache组件的,对缓存的真正CRUD操作在Cache组件中,每一个缓存组件有自己唯一一个名字; 20 * 21 22 * 23 * 原理: 24 * 1、自动配置类;CacheAutoConfiguration 25 * 2、缓存的配置类 26 * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GenericCacheConfiguration 27 * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.JCacheCacheConfiguration 28 * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.EhCacheCacheConfiguration 29 * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.HazelcastCacheConfiguration 30 * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.InfinispanCacheConfiguration 31 * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CouchbaseCacheConfiguration 32 * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration 33 * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CaffeineCacheConfiguration 34 * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GuavaCacheConfiguration 35 * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.SimpleCacheConfiguration【默认】 36 * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.NoOpCacheConfiguration 37 * 3、哪个配置类默认生效:SimpleCacheConfiguration; 38 * 39 * 4、给容器中注册了一个CacheManager:ConcurrentMapCacheManager 40 * 5、可以获取和创建ConcurrentMapCache类型的缓存组件;他的作用将数据保存在ConcurrentMap中; 41 * 42 * 运行流程: 43 * @Cacheable: 44 * 1、方法运行之前,先去查询Cache(缓存组件),按照cacheNames指定的名字获取; 45 * (CacheManager先获取相应的缓存),第一次获取缓存如果没有Cache组件会自动创建。 46 * 2、去Cache中查找缓存的内容,使用一个key,默认就是方法的参数; 47 * key是按照某种策略生成的;默认是使用keyGenerator生成的,默认使用SimpleKeyGenerator生成key; 48 * SimpleKeyGenerator生成key的默认策略; 49 * 如果没有参数;key=new SimpleKey(); 50 * 如果有一个参数:key=参数的值 51 * 如果有多个参数:key=new SimpleKey(params); 52 * 3、没有查到缓存就调用目标方法; 53 * 4、将目标方法返回的结果,放进缓存中 54 * 55 * @Cacheable标注的方法执行之前先来检查缓存中有没有这个数据,默认按照参数的值作为key去查询缓存, 56 * 如果没有就运行方法并将结果放入缓存;以后再来调用就可以直接使用缓存中的数据; 57 * 58 * 核心: 59 * 1)、使用CacheManager【ConcurrentMapCacheManager】按照名字得到Cache【ConcurrentMapCache】组件 60 * 2)、key使用keyGenerator生成的,默认是SimpleKeyGenerator 61 * 62 * 63 * 几个属性: 64 * cacheNames/value:指定缓存组件的名字;将方法的返回结果放在哪个缓存中,是数组的方式,可以指定多个缓存; 65 * 66 * key:缓存数据使用的key;可以用它来指定。默认是使用方法参数的值 1-方法的返回值 67 * 编写SpEL; #i d;参数id的值 #a0 #p0 #root.args[0] 68 * getEmp[2] 69 * 70 * keyGenerator:key的生成器;可以自己指定key的生成器的组件id 71 * key/keyGenerator:二选一使用; 72 * 73 * 74 * cacheManager:指定缓存管理器;或者cacheResolver指定获取解析器 75 * 76 * condition:指定符合条件的情况下才缓存; 77 * ,condition = "#id>0" 78 * condition = "#a0>1":第一个参数的值》1的时候才进行缓存 79 * 80 * unless:否定缓存;当unless指定的条件为true,方法的返回值就不会被缓存;可以获取到结果进行判断 81 * unless = "#result == null" 82 * unless = "#a0==2":如果第一个参数的值是2,结果不缓存; 83 * sync:是否使用异步模式 84 * @param id 85 * @return 86 * 87 */ 88 89 @Cacheable(value = {"emp"}/*,keyGenerator = "myKeyGenerator",unless="#a0==1",condition = "#p0==2"*/) 90 public Employee getEmp(Integer id){ 91 System.out.println("查询"+id+"号员工"); 92 Employee emp = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id); 93 return emp; 94 } 95 96 /** 97 * @CachePut:既调用方法,又更新缓存数据;同步更新缓存 98 * 修改了数据库的某个数据,同时更新缓存; 99 * 运行时机: 100 * 1、先调用目标方法 101 * 2、将目标方法的结果缓存起来 102 * 103 * 测试步骤: 104 * 1、查询1号员工;查到的结果会放在缓存中; 105 * key:1 value:lastName:张三 106 * 2、以后查询还是之前的结果 107 * 3、更新1号员工;【lastName:zhangsan;gender:0】 108 * 将方法的返回值也放进缓存了; 109 * key:传入的employee对象 值:返回的employee对象; 110 * 4、查询1号员工? 111 * 应该是更新后的员工; 112 * key = "#employee.id":使用传入的参数的员工id; 113 * key = "#result.id":使用返回后的id 114 * @Cacheable的key是不能用#result 115 * 为什么是没更新前的?【1号员工没有在缓存中更新】 116 * 117 */ 118 @CachePut(value = "emp",key = "#result.id") 119 public Employee updateEmp(Employee employee){ 120 System.out.println("updateEmp:"+employee); 121 employeeMapper.updateEmp(employee); 122 return employee; 123 } 124 125 126 /** 127 * @CacheEvict:缓存清除 128 * key:指定要清除的数据 129 * allEntries = true:指定清除这个缓存中所有的数据 130 * beforeInvocation = false:缓存的清除是否在方法之前执行 131 * 默认代表缓存清除操作是在方法执行之后执行;如果出现异常缓存就不会清除 132 * 133 * beforeInvocation = true: 134 * 代表清除缓存操作是在方法运行之前执行,无论方法是否出现异常,缓存都清除 135 * 136 * 137 */ 138 @CacheEvict(value="emp",beforeInvocation = true/*,key = "#id",*/) 139 public void deleteEmp(Integer id){ 140 System.out.println("deleteEmp:"+id); 141 //employeeMapper.deleteEmpById(id); 142 int i = 10/0; 143 } 144 145 // @Caching 定义复杂的缓存规则 146 @Caching( 147 cacheable = { 148 @Cacheable(/*value="emp",*/key = "#lastName") 149 }, 150 put = { 151 @CachePut(/*value="emp",*/key = "#result.id"), 152 @CachePut(/*value="emp",*/key = "#result.email") 153 } 154 ) 155 public Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName){ 156 return employeeMapper.getEmpByLastName(lastName); 157 } 159 }
6、配置缓存key自动生成器 :KeyGenerator
1 @Configuration 2 public class MyCacheConfig { 3 4 @Bean("myKeyGenerator") 5 public KeyGenerator keyGenerator(){ 6 return new KeyGenerator(){ 8 @Override 9 public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) { 10 return method.getName()+"["+ Arrays.asList(params).toString()+"]"; 11 } 12 }; 13 } 14 }
三、整合redis
1、pom加入坐标
1 <dependency> 2 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 3 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> 4 </dependency>
ymal配置redis
redis:
host: 129.211.77.216
2、MyRedisConfig配置类
1 @Configuration 2 public class MyRedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport { 3 4 @Bean 5 public RedisTemplate<Object, Department> deptRedisTemplate( 6 RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) 7 throws UnknownHostException { 8 RedisTemplate<Object, Department> template = new RedisTemplate<Object, Department>(); 9 template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); 10 Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Department> ser = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Department>(Department.class); 11 template.setDefaultSerializer(ser); 12 return template; 13 } 14 15 @Bean 16 public RedisTemplate<Object,Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory){ 17 RedisTemplate<Object, Object> objectObjectRedisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>(); 18 objectObjectRedisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); 19 Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> redisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class); 20 objectObjectRedisTemplate.setDefaultSerializer(redisSerializer); 21 return objectObjectRedisTemplate; 22 } 23 24 @Bean 25 public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) throws UnknownHostException { 26 StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate(); 27 Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> redisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class); 28 template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); 29 template.setDefaultSerializer(redisSerializer); 30 return template; 31 } 32 33 //CacheManagerCustomizers可以来定制缓存的一些规则 34 @Bean 35 public RedisCacheManager myRedisCacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) { 36 37 RedisCacheConfiguration cacheConfiguration = 38 RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig() 39 .entryTtl(Duration.ofDays(1)) 40 .disableCachingNullValues() 41 .serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(valueSerializer())); 42 return RedisCacheManager.builder(factory).cacheDefaults(cacheConfiguration).build(); 43 } 44 45 private RedisSerializer<Object> valueSerializer() { 46 return new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer(); 47 } 48 }
3.Redis测试类
1 @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) 2 @SpringBootTest 3 class SpringbootCacheApplicationTests { 4 5 @Autowired 6 EmployeeMapper employeeMapper; 7 8 @Autowired 9 DepartmentMapper departmentMapper; 10 11 @Autowired 12 StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate; //操作k-v都是字符串的 13 14 @Autowired 15 RedisTemplate redisTemplate; //k-v都是对象的 16 17 @Autowired 18 RedisTemplate myRedisTemplate; 19 20 @Autowired 21 RedisTemplate deptRedisTemplate; 22 23 // @Autowired 24 // RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> employeeRedisTemplate; 25 26 /** 27 * Redis常见的五大数据类型 28 * String(字符串)、List(列表)、Set(集合)、Hash(散列)、ZSet(有序集合) 29 * stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue()[String(字符串)] 30 * stringRedisTemplate.opsForList()[List(列表)] 31 * stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet()[Set(集合)] 32 * stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash()[Hash(散列)] 33 * stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet()[ZSet(有序集合)] 34 */ 35 @Test 36 void contextLoads1() { 37 //给redis中保存数据 38 //stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().append("msg","helloo"); 39 // String msg = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("msg"); 40 // System.out.println(msg); 41 // stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush("mylist","你好"); 42 // stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush("mylist","张三"); 43 List<String> list = stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().range("mylist", 0, 7); 44 for (String s : list) { 45 System.out.println(s); 46 } 47 } 48 49 @Test 50 void contextLoads2() { 51 Employee employee = employeeMapper.getEmpById(1); 52 //默认如果保存对象,使用jdk序列化机制,序列化后的数据保存到redis中 53 //redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("emp",employee); 54 //1、将数据以json的方式保存 55 //(1)自己将对象转为json 56 //(2)redisTemplate默认的序列化规则;改变默认的序列化规则; 57 //System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("emp")); 58 // myRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("emp",employee); 59 Object emp = myRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("emp"); 60 System.out.println(emp); 61 } 62 63 @Test 64 void contextLoads3() { 65 Department deptartment = departmentMapper.getDeptById(1); 66 67 //myRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("dept",deptartment); 68 69 Object dept = myRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("dept"); 70 System.out.println(dept); 71 } 72 73 @Test 74 void contextLoads4() { 75 Department deptartment = departmentMapper.getDeptById(1); 76 77 // deptRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("dept",deptartment); 78 79 Department dept = (Department) deptRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("dept"); 80 System.out.println(dept); 81 } 82 83 }
4、RedisCache应用
1 @Service 2 public class DeptService { 3 4 @Autowired 5 DepartmentMapper departmentMapper; 6 7 @Autowired 8 RedisCacheManager myRedisCacheManager; 9 10 /** 11 * 缓存的数据能存入redis; 12 * 第二次从缓存中查询就不能反序列化回来; 13 * 存的是dept的json数据;CacheManager默认使用RedisTemplate<Object, Employee>操作Redis 14 * @param id 15 * @return 16 */ 17 // @Cacheable(cacheNames = "dept",cacheManager = "myRedisCacheManager") 18 // public Department getDeptById(Integer id){ 19 // System.out.println("查询部门"+id); 20 // Department department = departmentMapper.getDeptById(id); 21 // return department; 22 // } 23 24 // 使用缓存管理器得到缓存,进行api调用 25 public Department getDeptById(Integer id){ 26 System.out.println("查询部门"+id); 27 Department department = departmentMapper.getDeptById(id); 28 29 //获取某个缓存 30 Cache deptcache = myRedisCacheManager.getCache("dept"); 31 deptcache.put("1",department); 32 return department; 33 } 34 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号