Python-虚拟环境Pyenv环境安装
Python下载地址:https://www.python.org/ftp/python/
Pyenv安装
pyenv的安装方式
git安装
1、安装git
yum -y install git
2、安装Python编译依赖
yum -y install gcc make patch gdbm-devel openssl-devel sqlite-devel readline-devel zlib-devel bzip2-devel
3、创建python用户
[root@localhost ~]# useradd python [root@localhost ~]# echo "python" |passwd python --stdin Changing password for user python. passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully. [root@localhost ~]# su - python [python@localhost ~]$ ls
4、使用python用户登录后安装Pyenv
pyenv官网:https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv
pyenv-installer插件:https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv-installer
使用脚本安装:
#在国内可能被屏蔽 $ curl -L https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv-installer/raw/master/bin/pyenv-installer | bash #!/usr/bin/env bash set -e [ -n "$PYENV_DEBUG" ] && set -x if [ -z "$PYENV_ROOT" ]; then PYENV_ROOT="${HOME}/.pyenv" fi colorize() { if [ -t 1 ]; then printf "\e[%sm%s\e[m" "$1" "$2" else echo -n "$2" fi } # Checks for `.pyenv` file, and suggests to remove it for installing if [ -d "${PYENV_ROOT}" ]; then { echo colorize 1 "WARNING" echo ": Can not proceed with installation. Kindly remove the '${PYENV_ROOT}' directory first." echo } >&2 exit 1 fi shell="$1" if [ -z "$shell" ]; then shell="$(ps c -p "$PPID" -o 'ucomm=' 2>/dev/null || true)" shell="${shell##-}" shell="${shell%% *}" shell="$(basename "${shell:-$SHELL}")" fi failed_checkout() { echo "Failed to git clone $1" exit -1 } checkout() { [ -d "$2" ] || git clone --depth 1 "$1" "$2" || failed_checkout "$1" } if ! command -v git 1>/dev/null 2>&1; then echo "pyenv: Git is not installed, can't continue." >&2 exit 1 fi if [ -n "${USE_GIT_URI}" ]; then GITHUB="git://github.com" else GITHUB="https://github.com" fi checkout "${GITHUB}/pyenv/pyenv.git" "${PYENV_ROOT}" checkout "${GITHUB}/pyenv/pyenv-doctor.git" "${PYENV_ROOT}/plugins/pyenv-doctor" checkout "${GITHUB}/pyenv/pyenv-installer.git" "${PYENV_ROOT}/plugins/pyenv-installer" checkout "${GITHUB}/pyenv/pyenv-update.git" "${PYENV_ROOT}/plugins/pyenv-update" checkout "${GITHUB}/pyenv/pyenv-virtualenv.git" "${PYENV_ROOT}/plugins/pyenv-virtualenv" checkout "${GITHUB}/pyenv/pyenv-which-ext.git" "${PYENV_ROOT}/plugins/pyenv-which-ext" if ! command -v pyenv 1>/dev/null; then { echo colorize 1 "WARNING" echo ": seems you still have not added 'pyenv' to the load path." echo } >&2 case "$shell" in bash ) profile="~/.bashrc" ;; zsh ) profile="~/.zshrc" ;; ksh ) profile="~/.profile" ;; fish ) profile="~/.config/fish/config.fish" ;; * ) profile="your profile" ;; esac { echo "# Load pyenv automatically by adding" echo "# the following to ${profile}:" echo case "$shell" in fish ) echo "set -x PATH \"${PYENV_ROOT}/bin\" \$PATH" echo 'status --is-interactive; and . (pyenv init -|psub)' echo 'status --is-interactive; and . (pyenv virtualenv-init -|psub)' ;; * ) echo "export PATH=\"${PYENV_ROOT}/bin:\$PATH\"" echo "eval \"\$(pyenv init -)\"" echo "eval \"\$(pyenv virtualenv-init -)\"" ;; esac } >&2 fi
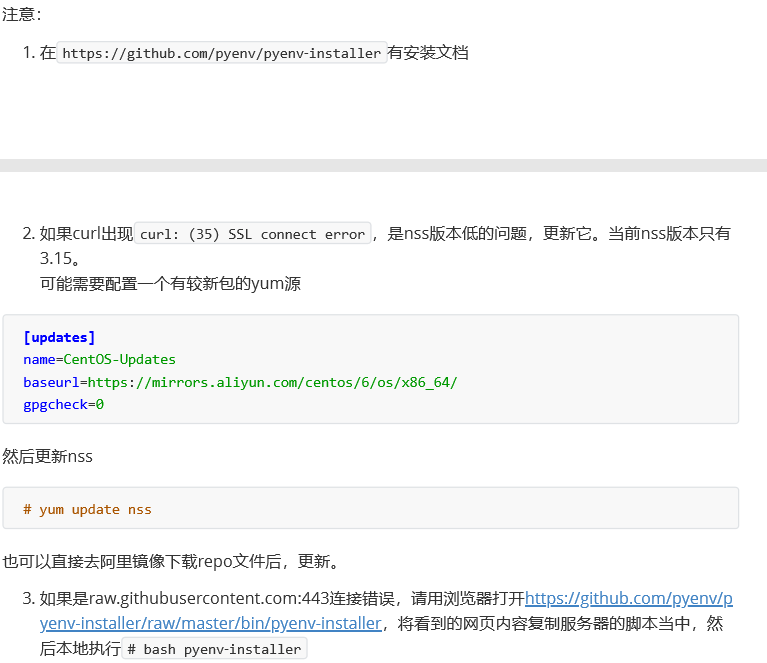
5、在python用户的~.bash_profile文件中追加,或在.bashrc中添加
$ curl -L https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv-installer/raw/master/bin/pyenv-installer | bash 从github克隆
export PATH="/home/python/.pyenv/bin:$PATH" eval "$(pyenv init -)" eval "$(pyenv virtualenv-init -)"
source ~/.bash_profile
如果后续需要更新pyenv,则使用pyenv update
$ pyenv update
pyenv的使用
Python版本即path路径
$ python --version $ python -V $ echo $PATH
#系统自带2.7.5 centos7+ [python@localhost .pyenv]$ python --version Python 2.7.5 [python@localhost .pyenv]$ python -V Python 2.7.5 [python@localhost .pyenv]$
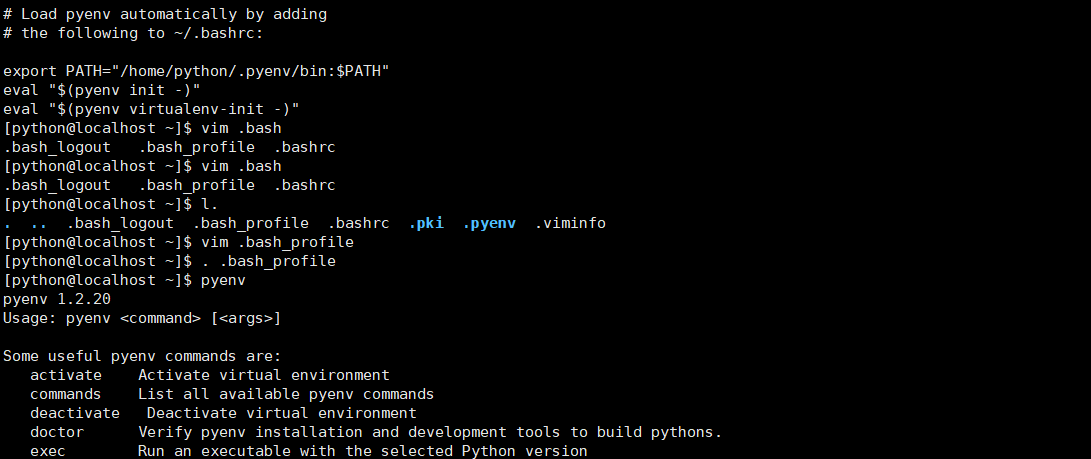
pyenv命令
[python@localhost .pyenv]$ pyenv pyenv 1.2.20 Usage: pyenv <command> [<args>] Some useful pyenv commands are: activate Activate virtual environment commands List all available pyenv commands deactivate Deactivate virtual environment doctor Verify pyenv installation and development tools to build pythons. exec Run an executable with the selected Python version global Set or show the global Python version(s) help Display help for a command hooks List hook scripts for a given pyenv command init Configure the shell environment for pyenv install Install a Python version using python-build local Set or show the local application-specific Python version(s) prefix Display prefix for a Python version rehash Rehash pyenv shims (run this after installing executables) root Display the root directory where versions and shims are kept shell Set or show the shell-specific Python version shims List existing pyenv shims uninstall Uninstall a specific Python version version Show the current Python version(s) and its origin --version Display the version of pyenv version-file Detect the file that sets the current pyenv version version-name Show the current Python version version-origin Explain how the current Python version is set versions List all Python versions available to pyenv virtualenv Create a Python virtualenv using the pyenv-virtualenv plugin
常用的有如下几个:
pyenv install pyenv local pyenv global pyenv shell pyenv versions pyenv version ....
install
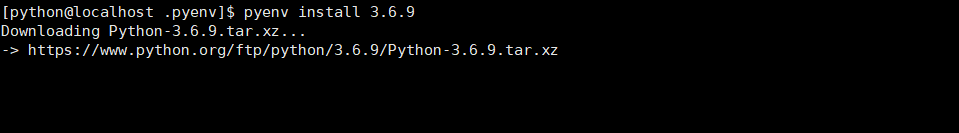
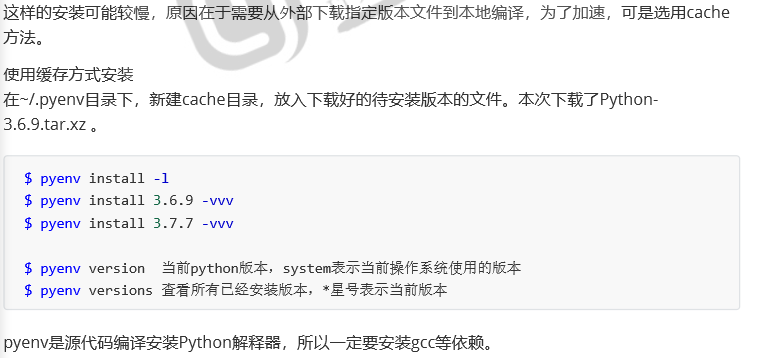
pyenv help install #安装Python版本 pyenv install --list pyenv install 3.6.9 pyenv versions
使用pyenv install 3.6.9非常慢,需要从Python的官网下载。
pyenv的python版本控制
global全局设置
pyenv global 3.6.9
可以看到所有受pyenv控制的窗口都是3.6.9的python版本,这里使用global是作用域非root用于的python用户上,如果是使用root用户安装,切记不要使用global,否则影响系统底层,CentOS7+系统默认使用的是Python2.7.5版本,使用了global就成了3.x,会带来很大的问题。
[python@localhost ~]$ pyenv global system [python@localhost ~]$ pyenv versions * system (set by /home/python/.pyenv/version) 3.6.9 3.7.8 [python@localhost ~]$ python -V Python 2.7.5 [python@localhost ~]$
shell会话设置
影响只作用于当前会话
pyenv shell 3.6.9
local本地设置
使用Python local设置从当前工作目录开始向下递归都继承这个设置,推荐
[python@localhost ~]$ mkdir a/b/c -pv mkdir: created directory ‘a’ mkdir: created directory ‘a/b’ mkdir: created directory ‘a/b/c’ [python@localhost ~]$ cd a/ [python@localhost a]$ pyenv local 3.6.9 [python@localhost a]$ [python@localhost a]$ [python@localhost a]$ [python@localhost a]$ pyenv versions system * 3.6.9 (set by /home/python/a/.python-version) 3.7.8 [python@localhost a]$ cd ../ [python@localhost ~]$ python -V Python 2.7.5 [python@localhost ~]$ cd a/ [python@localhost a]$ python -V Python 3.6.9 [python@localhost a]$
pyenv local --unset #取消local设置 [python@localhost a]$ pyenv local --unset [python@localhost a]$ python -V Python 2.7.5 [python@localhost a]$
Virtualenv虚拟环境设置
为什么需要虚拟环境?
因为刚才使用的python环境都是一个公共的空间,如果多个项目使用不同的Python版本开发,或者使用不同的python版本部署运行,或者使用相同的版本开发的但不同项目使用了不同版本的库,等等这些问题都会带来冲突,最好的解决方法就是每个项目独立运行自己的独立小环境。
[python@localhost ~]$ pyenv versions * system (set by /home/python/.pyenv/version) 3.6.9 3.6.9/envs/chen369 3.7.8 chen369 [python@localhost ~]$ mkdir projects/cmdb -pv mkdir: created directory ‘projects’ mkdir: created directory ‘projects/cmdb’ [python@localhost ~]$ cd projects/cmdb/ [python@localhost cmdb]$ pyenv local chen369 (chen369) [python@localhost cmdb]$ python -V Python 3.6.9 (chen369) [python@localhost cmdb]$ pip list Package Version ---------- ------- pip 18.1 setuptools 40.6.2 You are using pip version 18.1, however version 20.2b1 is available. You should consider upgrading via the 'pip install --upgrade pip' command. (chen369) [python@localhost cmdb]$
导出包
虚拟环境的好处在于和其他的项目环境进行隔离,每个独立的环境都可以使用pip命令导出已经安装的包,在另一个环境中安装这些包。
在开发工具中导出requirements文件,在虚拟环境中导入,能更好的还原环境到生成环境中,同时使用virtualenv,需要哪些个依赖就安装哪些。pip list列出依赖
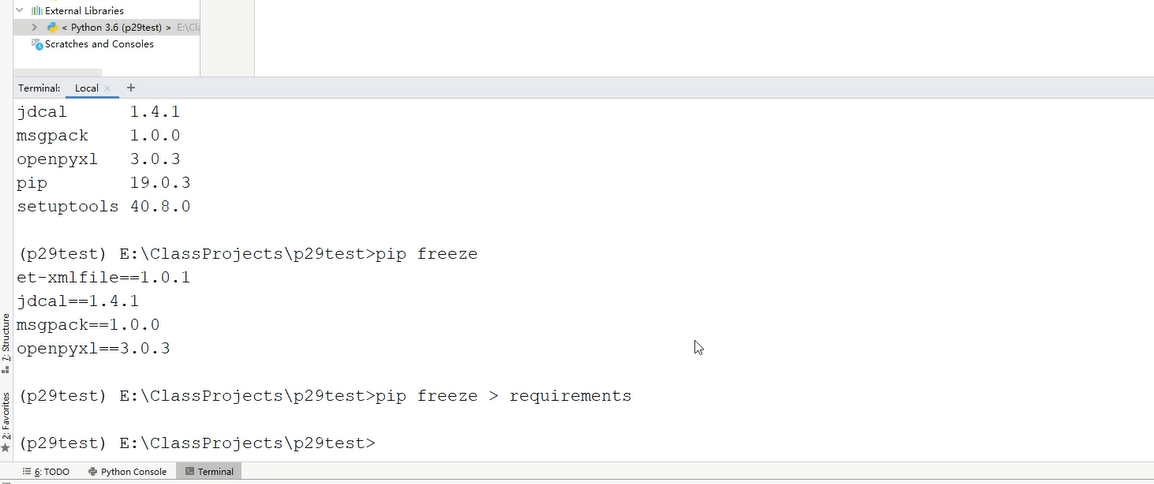
导入依赖:
pip install -r requirements 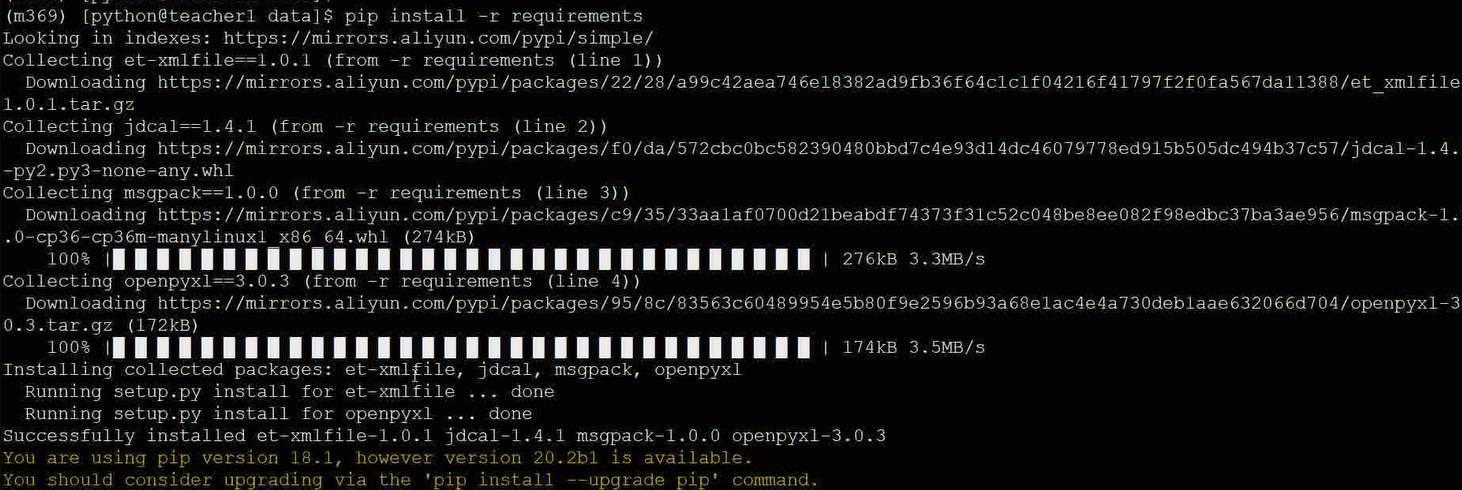
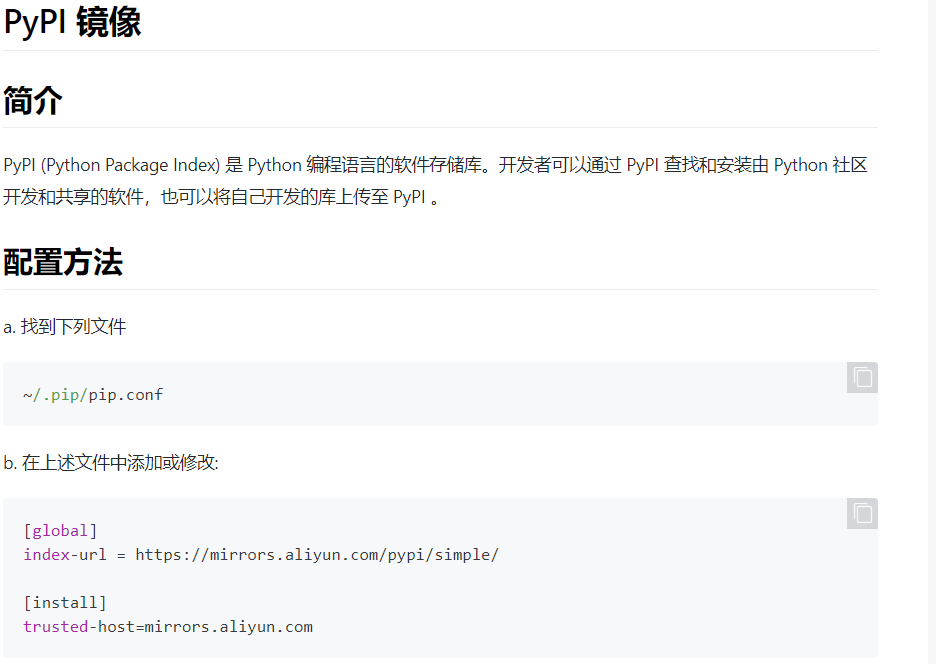
pip通用配置
[python@localhost ~]$ mkdir .pip [python@localhost ~]$ vim .pip/pip.conf [python@localhost ~]$ cat .pip/pip.conf [global] index-url = https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ [install] trusted-host=mirrors.aliyun.com [python@localhost ~]$




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号