Python-csv文件&ini文件
CSV文件简介
逗号分隔值Comma-Separated Values
CSV是一个被行分隔符、列分隔符划分成行和列的文本文件
CSV不指定字符编码
行分隔符为\r\n,最后一行可以没有换行符
列分隔符常为逗号或制表符
每一行称之为一条记录record
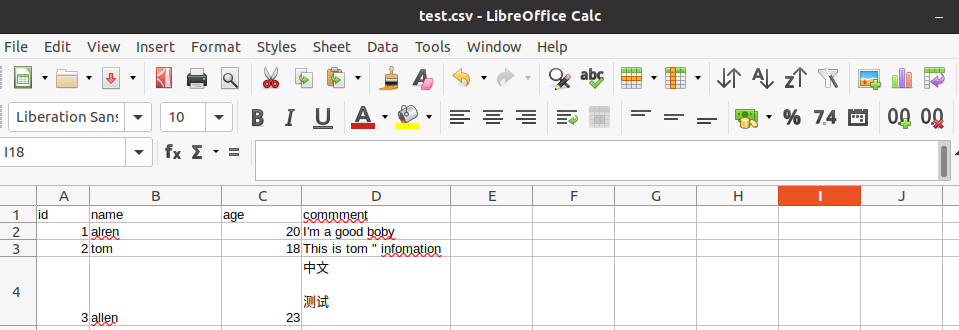
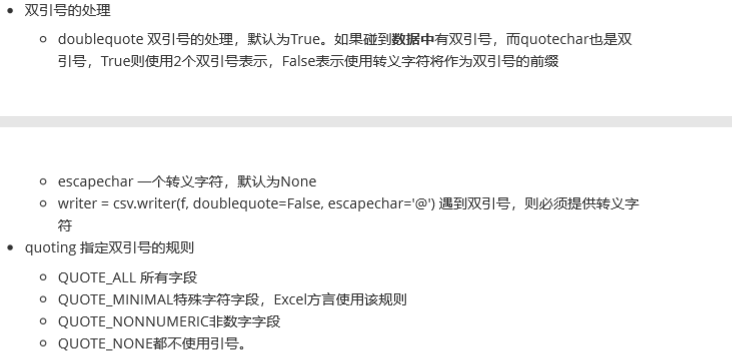
字段可以使用双引号括起来,也可以不使用,如果字段中出现了双引号、逗号、换行符必须使用双引号括起来,如果字段的值是双引号,使用两个双引号表示一个转义。
表头可选,和字段列对齐即可。
手动生成CSV文件
from pathlib import Path p = Path('/tmp/test/test.csv') # if not p.parent.exists(): # p.parent.mkdir(parents=True) p.parent.mkdir(parents=True,exist_ok=True) csv_body = '''\ id,name,age,commment 1,alren,20,"I'm a good boby" 2,tom,18,"This is tom "" infomation" 3,allen,23,"中文 测试 " ''' # with p.open('w',encoding='utf-8') as f: # f.write(csv_body) p.write_text(csv_body)
CSV模块
csv.reader(csvfile,dialect='execl',**fmtparams)
返回一个reader对象,是一个迭代器
默认使用execl方言 ,如下:
delimiter 列分隔符,号
lineterminator行分隔符\r\n
quotechar字段的引用符号,缺省为”双引号
csv.write(csvfile,dialect='execl',**fmtparams)
返回一个dictwrite的实例,主要方法有单行writerow和多行writerows
import csv rows = [ ('id','name','age','comment'), [1,'tom',20,'tom info'], (3,'jerry',18,'afdfdf\t"ing'), 'adfadfdfadf', ((1,),2,[3]) ] with open('/tmp/test/test.csv','w+',encoding='utf-8',newline='') as f: writer = csv.writer(f) writer.writerow(rows[0]) print('*' * 30) writer.writerows(rows[1:]) with open('/tmp/test/test.csv',encoding='utf-8',newline='') as f: reader = csv.reader(f) print(next(reader)) print('*' * 30) for line in reader: print(line) #输出 ****************************** ['id', 'name', 'age', 'comment'] ****************************** ['1', 'tom', '20', 'tom info'] ['3', 'jerry', '18', 'afdfdf\t"ing'] ['a', 'd', 'f', 'a', 'd', 'f', 'd', 'f', 'a', 'd', 'f'] ['(1,)', '2', '[3]']
ini文件处理
作为配置文件,ini文件格式非常流行
[DEFAULT] a = test [mysql] default-character-set=utf8 [mysqld] datadir =/data/mysql/data port = 3306 character-set-server=utf8 sql_mode=NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES
中括号里面的内容称之为section,译为节、段、区
每个section内,都是key=value形成的键值对,key称之为option选项
注意这里的DEFAULT是缺省配置段section,section名字必须大写
configparser
configparser模块的ConfigParser类就是用来操作,可以将section当成key,section存储着键值对组成的字典,可以把ini配置文件当做一个嵌套的字典,默认使用有序字典
read(filenames,encoding=None):读取ini配置文件,可以是单个文件,也可以是文件列表,可以指定文件编码
section()返回section列表,缺省section不包含在内
add_section(section_name)增加一个section
has_section(section_name)判断一个section是否存在
options(section)返回一个section的所有option,会追加缺省的option
has_option(section,option)判断section是否存在这个option
from configparser import ConfigParser filename = '/tmp/test.ini' newfilename = '/tmp/mysql.ini' cfg = ConfigParser() read_ok = cfg.read(filename) print(read_ok) #读取文件名绝对路径 print(cfg.sections()) #返回section列表,不包含default缺省section print(cfg.has_section('mysql'))#判断section是否存在 print(cfg.options('mysql')) #输出section mysql下的所有option,会追加DEFAULT段的option print(cfg.has_option('mysql','default-character-set')) #判断某section下是否有某option #输出如下 ['/tmp/test.ini'] ['mysql', 'mysqld'] True ['default-character-set', 'a'] True
get(section,option,*,raw=False,vars=None[,fallback]:从指定的section中取值,如果找到则返回,如果没有找到则就去DEFAULT段看看有没有。
getint(section,option,*,raw=False,vars=None[,fallback]:
getfloat(section,option,*,raw=False,vars=None[,fallback]:
getboolean(section,option,*,raw=False,vars=None[,fallback]:
上面3个方法和get一样,返回指定类型数据
items(raw=False,vars=None)
items(section,raw=False,vars=None)
没有section,则返回所有的section名字及其对象,如果指定section则返回这个指定section的键值对组成的二元组
from configparser import ConfigParser filename = '/tmp/test.ini' newfilename = '/tmp/mysql.ini' cfg = ConfigParser() read_ok = cfg.read(filename) # print(read_ok) # print(cfg.sections()) # print(cfg.has_section('mysql')) # print(cfg.options('mysql')) # print(cfg.has_option('mysql','default-character-set')) for k,v in cfg.items(): print(k,type(k)) print(v,type(v)) print(cfg.items(k)) print()
# for k,v in cfg.items('mysqld'): #指定section
# print(k,type(k))
# print(v,type(v))
# print("~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~")
#
# print('-' * 30)
#输出如下 DEFAULT <class 'str'> <Section: DEFAULT> <class 'configparser.SectionProxy'> [('a', 'test')] mysql <class 'str'> <Section: mysql> <class 'configparser.SectionProxy'> [('a', 'test'), ('default-character-set', 'utf8')] mysqld <class 'str'> <Section: mysqld> <class 'configparser.SectionProxy'> [('a', 'test'), ('datadir', '/data/mysql/data'), ('port', '3306'), ('character-set-server', 'utf8'), ('sql_mode', 'NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES')] ******************************
from configparser import ConfigParser filename = '/tmp/test.ini' newfilename = '/tmp/mysql.ini' cfg = ConfigParser() read_ok = cfg.read(filename) tmp = cfg.get('mysqld','port') #返回3306 print(type(tmp),tmp) tmp = cfg.get('mysqld','a') #返回test,从DEFALUT配置段找 print(type(tmp),tmp) tmp = cfg.getint('mysqld','port') #默认返回的类型为str,如需要返回int型则需要在get后面声明int print(type(tmp),tmp) print(cfg.get('mysqld','alren',fallback='python')) #找不到则返回缺省值
#输出如下 <class 'str'> 3306 <class 'str'> test <class 'int'> 3306 python
set(section,option,value):section存在的情况下,写入option=value要求option、value必须是字符串
remove_section(section):移除section及其所有的option
write(fileobject,space_around_delimiters=True):将当前config的所有内容写入fileobject中,一般open函数使用w模式。
from configparser import ConfigParser filename = '/tmp/test.ini' newfilename = '/tmp/mysql.ini' cfg = ConfigParser() read_ok = cfg.read(filename) if cfg.has_section('test'): cfg.remove_section('test') #删除section cfg.add_section('test1') #添加section cfg.set('test1','HostPort','10081') #添加section下的option,key/value键值对 cfg.set('test1','HostNmae','dbserver') cfg.set('test1','Host','10.12.0.1') with open(newfilename,'w',encoding='utf-8') as f: #此处的w并不会覆盖原有内容 cfg.write(f)
#输出 [DEFAULT] a = test . . . . [test1] hostport = 10081 hostnmae = dbserver
cfg['test1']['x'] = '100' #section exists option and value not exists cfg['test2'] = {'test2':'1000'} # section is not exists with open(newfilename,'w',encoding='utf-8') as f: #修改后需要再次写入 cfg.write(f)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号