ARM v8 memory attribute
目录
1.Normal memory
1.1 位置
1.2 特性
1.3 属性
1.3.1 Cacheability
1.3.1.1 属性作用域
1.3.1.2 属性作用行为
1.3,2 Shareability
1.3.2.1 属性作用域
1.3.2.2 属性作用行为
2.Device memory
2.1 位置
2.2 特性
2.3 属性
ARM在架构中把全部memory空间定义为device memory和normal memory.
Normal memory
位置
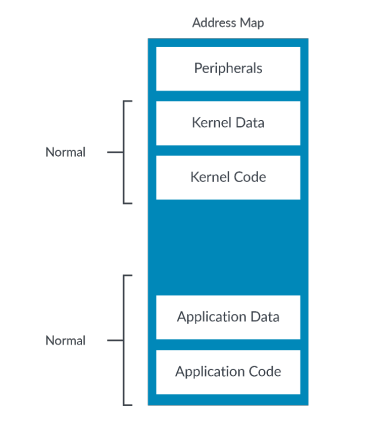
The Normal memory type is used for anything that behaves like a memory, including RAM,
Flash, or ROM. Code should only beplaced in locations marked as Normal.
Normal is usually the most common memory type in a system, as shown in this diagram:
Armv8-A memory model guide
Normal memory通常指的就是内存空间,即如上图所示包含除外设地址外的全部地址空间.
特性
针对normal memory的数据访问是没有side-effect的,这是和device memory的区别之一.
side-effect:即对某一地址的读取次数不会影响读取结果,也不会影响其他地址的数据,举一个反例就是对fifo的一次读操作会影响下一次读取的数据,这就是side effect.
对于针对normal memory的访问来说,处理器可能会做如下优化:
- 合并访问:访问一个地址多次,或访问多次连续的地址.
- 推测访问:当软件没有确切请求一个normal memory地址的时候,处理器会提前读这个地址,举例:prefetch based on previous accesses.
- 重排序访问: 关于重排序访问的限制指的是一些可能存在的数据依赖的问题.
属性
这两个属性是为了多核系统定义的,在单核系统shareability参数的设置没有实际作用.
Cacheability
属性作用域
该属性的作用域范围存在inner和outer的区分,即inner cache和outer cache,所以根据不同的对象也就有了各自独立的属性配置.
在参考资料中得知inner cache通常表示离PE更近的,集成在微架构之内的cache
通常来说,L1为inner cache,而L2依据soc的设计定义判断,L3/LLC则通常为outer cache,这个层级关系是由实现定义的
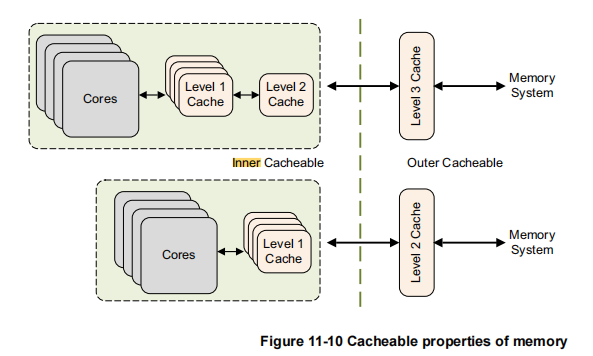
The cacheable properties of normal memory are specified separately as inner and outer attributes. The divide between inner and outer is IMPLEMENTATION DEFINED and is covered in greater detail in Chapter 13. Typically, inner attributes are used by the integrated caches, and outer attributes are made available on the processor memory bus for use by external caches.
DEN0024A_v8_architecture_PG
属性作用行为
| 属性分类 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| Non-cacheable | 不使用cache |
| Write-Through Cacheable | 依据对应策略操作cache |
| Write-Back Cacheable | 依据对应策略操作cache |
在DEN0024A_v8_architecture_PG中会把write-back和write-through叫做cache update行为,而write-allocate和read-allocate会被叫做cache-allocate行为.
| write | write | read | read | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hit | write-back,写入cache,后续flush回主存 | write-through,直接写入cache和主存(即每次hit的写操作都访问主存) | read,从cache中直接读出对应数据 | read,从cache中直接读出对应数据 |
| miss | write-allocate,把数据写入cache,后续flush回主存 | no write-allocate/write around,把数据直接写回主存 | Read-allocate,先从主存中读回到cache,在从cache中读回 | Read through,直接从主存中读回数据 |
根据上面表格可知访问时的hit和miss实际上是由各自的策略确定,且可以自由组合,执行allocate操作就会产生Linefill和eviction.表示当前访问导致的miss将会在cache中分配一个cacheline用于填充新的数据,为了存放新的数据可能需要对某些旧的cacheline执行eviction操作.
通常来说write-back会和write-allocate搭配使用,而write-through会和no write-allocate搭配使用.
allocate属性可以和transient或non-transient组合,当一个地址空间被标记为transient,那表示其内的数据将不会被频繁使用
cache的设计则可以使用这种信息对cacheline的行为进行优化,比如当cache替换策略是可预测的时候,可以将这种数据分配到即将evict的位置优化访问.
Any cacheable Normal memory region is treated as Read-Allocate, No Write-Allocate unless it is explicitly assigned other cache allocation hints.
Applies to an implementation of the architecture Armv8.0-M onward
且任何cacheable的normal memory如无特殊说明都是read-allocate,no write-allocate的
A Cacheable Location with no Read-Allocate and no Write-Allocate hints is not the same as a Non-cacheable Location. A Non-cacheable Location has coherency guarantees for all Observers within the system that do not apply to a Location that is Cacheable, no Read-Allocate, no Write-Allocate.
Applies to an implementation of the architecture Armv8.0-M onward
Cache的填充实际上是依赖access miss时的allocate实现的,但cacheable的地址如果定义为no write-allocate和no read-allocate,该地址空间并不等效于non-cacheable的地址空间.因为non-cacheable的地址空间需要保证对系统中全部观察者的数据一致性,而这并不适用于cacheable的地址空间.
For read transactions, the Write-allocate bit is redefined to indicate that:
the location could have been previously allocated in the cache because of a write transaction (as the AXI3 definition)the location could have been previously allocated in the cache because of the actions of another master(additional AXI4 definition).
For write transactions, the Read-allocate bit is redefined to indicate that:
the location could have been previously allocated in the cache because of a read transaction (as the AXI3 definition)the location could have been previously allocated in the cache because of the actions of another master(additional AXI4 definition)
AXI4 spec
在AXI4中对write-allocate和read-allocate定义为当前操作的地址已经被之前的行为(可以是对应的读或者写,或者其他master导致的事务)被分配了一个cacheline.
Shareability
属性作用域
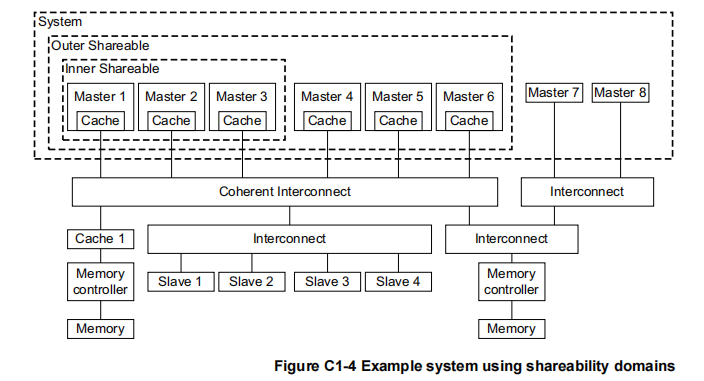
和cache属性类似,shareability的作用域范围也存在inner和outer的区分,如下图所示,其中观察者Observer表示能够主动发出数据访问的master.
In Figure C1-4, from the perspective of master 1:
the cache of master 1 is a local cache
the caches of masters 2-6 are peer caches
caches of masters 1-3 are in the Inner Shareable domain
caches of masters 1-6 are in the Outer Shareable domain
cache 1 is a downstream cache.
AMBA AXI and ACE Protocol Specification - IHI 0022E
关于作用域范围的定义:
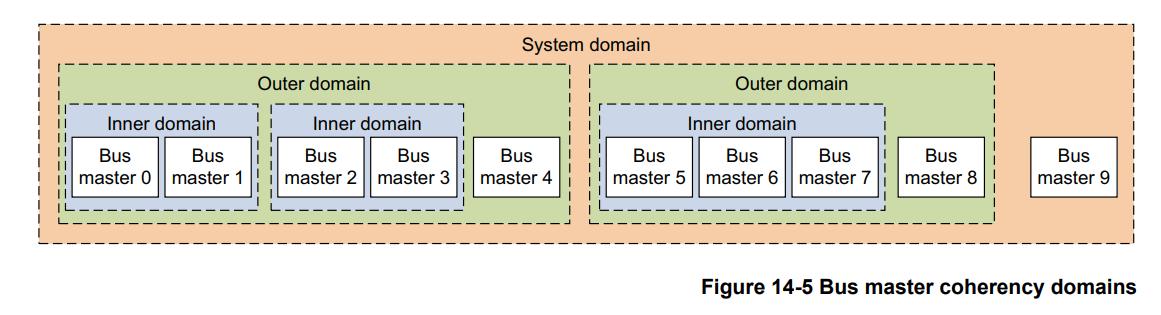
Typical system use is that masters running under the same operating system are in the same
Inner Shareable domain. Masters that are sharing cacheable data, but that are not so closely
coupled, are in the same Outer Shareable domain. Masters in the same inner domain must also
be in the same outer domain. Domain selection for memory accesses is controlled through
entries in the page tables.
属性作用行为
Shareable顾名思义是当前地址空间的数据访问和哪些部件共享,如下三种对应三种划分
| 属性名称 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| non-shareable | 当前区域只能由这个核使用,不与其他处理器共享 |
| inner-shareable | 观察者在对应inner共享域内访问数据一致,即一个处理器的操作会被这个共享域内其他处理器看到,但不会影响其他的inner域 |
| outer-shareable | 观察者在对应outer共享域内数据一致,其中outer域可由多个inner域组成,如果一个处理器的操作位于outer域,那么这个操作会被outer内的所有观察者(包括inner域内的观察者看到) |
| system | ACE总线中额外定义了system域,也就是整个系统的共享 |
整个共享是软件看见的层次,数据访问操作的广播实际上是通过对应的硬件机制实现的,比如ACE的snoop机制,所以如果处理器或者其他master不支持一致性,则他们会把共享域看作non-shareable的.
In the ARMv8-A Architecture, the term domain is used to refer to a set of primary bus masters.
Domains determine which of the masters are snooped, for coherent transactions. Snooping is the
checking of the master’s cache to see whether the requested location is stored there.
Device memory
位置
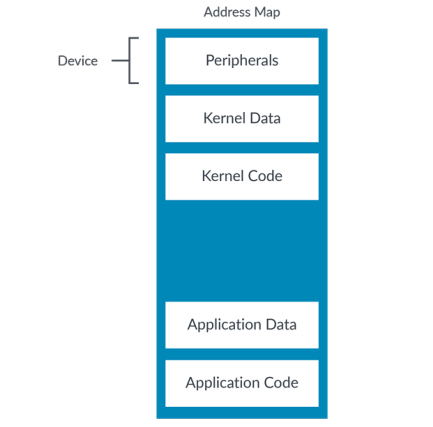
The Device memory type is used for describing peripherals. Peripheral registers are often referred to as Memory-Mapped I/O(MMIO). Here we can see what would be typically be marked as Device in our example address map
Armv8-A memory model guide
Device memory通常指的是外设的地址,这部分地址一般会被以MMIO的形式使用.
特性
Device memory默认是shareable,non-cacheable的,并且可能存在side-effect.
属性
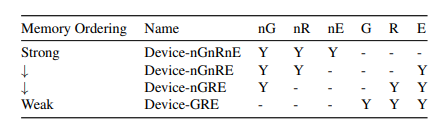
Device memory由下列属性定义
| attributes | flag | description |
|---|---|---|
| Gathering(合并) | G/nG | This specifies that accesses can be merged (G) or not (nG). This could be merging multiple accesses to thesame location into one access or merging multiple smaller accesses into one larger access. Armv8-A memory model guide |
| Reordering(重排序) | R/nR | This specifies that accesses to the same peripheral can be re-ordered (R) or not (nR). When re-orderingis permitted, the same restrictions apply in the same was as for the Normal type. Armv8-A memory model guide |
| Early Write Acknowledge hint(提前写响应) | E/nE | This determines when a write is considered complete. If Early Acknowledgement is allowed (E), an access can be shown as complete once it is visible to other observers, but before it reaches its destination. For example, a write might become visible once it reaches a write buffer in the interconnect. When Early Acknowledgement is not allowed (nE), the write must have reached the destination. Armv8-A memory model guide |
由上面的属性组合成了对应的内存域属性
Weaker memory can be accessed according to the rules specifified for stronger memory:
Memory with the:
– G attribute can be accessed according to the rules specifified for the nG attribute.
– nG attribute cannot be accessed according to the rules specifified for the G attribute.
Memory with the:
– R attribute can be accessed according to the rules specifified for the nR attribute.
– nR attribute cannot be accessed according to the rules specifified for the R attribute.
Because the nE attribute is a hint:
An implementation is permitted to perform an access with the E attribute in a manner consistent with there quirements specifified by the nE attribute.
An implementation is permitted to perform an access with the nE attribute in a manner consistent with the relaxations allowed by the E attribute.
Applies to an implementation of the architecture Armv8.0-M onward
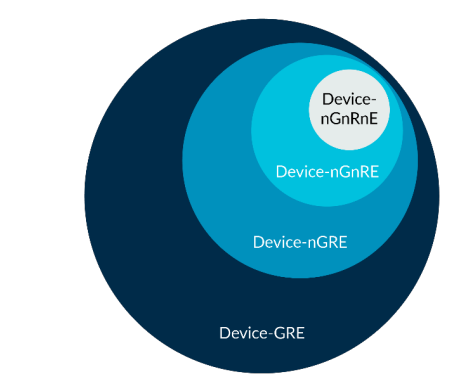
表中的memory ordering也可以用下图表示,其中最外层(weaker)的memory可以以更内层(stronger)的属性要求进行访问,可以理解成访问要求宽松的可以使用更严格的约束访问
Armv8-A memory model guide


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号