我们日常编程过程中,特别是写功能库时,通常会产生一些疑问,比如,
问题1:是用静态方法好,还是实例方法好。
问题2:运行效率是x86高还是x64高。
...
在这里我们暂时抛开理论,来个实操对比,直接上代码:
using System; using System.Diagnostics; using System.Windows.Forms; namespace ClassPerformanceTest { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { double staticFuncTime = Calling("static"); double funcTime = Calling("aaaaaa"); Console.WriteLine("运行第{0}次", i + 1); Console.WriteLine("静态的执行时间:{0}", staticFuncTime); Console.WriteLine("实例的执行时间:{0}", funcTime); string compare = staticFuncTime > funcTime ? ">" : "<"; Console.WriteLine("静态的时间 {0} 实例的时间", compare); Console.WriteLine(); } } //实例化动作放在循环之外,避免循环调用时受申请内存的干扰 MyClass myClass = new MyClass(); public double Calling(string funcType) { string testStr = "synlitec";//定义测试字符串 Stopwatch watchTime = new Stopwatch();//实例化监视器 watchTime.Start(); //开始监视以下代码运行时间 //性能监测区 { int count = 10000000;//循环调用次数 if (funcType == "static") { for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { MyStaticClass.StaticFunc1(testStr); } } else { for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { myClass.Func1(testStr); } } } watchTime.Stop();//停止监视 double totalTime = watchTime.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds;//获取代码运行的总时间,单位是毫秒 return totalTime; } } public static class MyStaticClass { private static string staticStr = "synlitec"; public static void StaticFunc1(string str) { //随意做些运算,意义在放大执行时间,便于观察 string insideStr = staticStr + str; int insideInt = staticStr.Length + 1000; } } public class MyClass { private string Str = "synlitec"; public void Func1(string str) { //随意做些运算,意在放大执行时间,便于观察 string insideStr = Str + str; int insideInt = Str.Length + 1000; } } }
以上代码可以看出,在监测范围内避开了非静态方法的实例化时间,否则每次调用方法都实例化测试是不公平的。
循环10个回合进行对比,每个回合各调用10000000次,分别编译成x86、x64程序各测试一次,上结果:
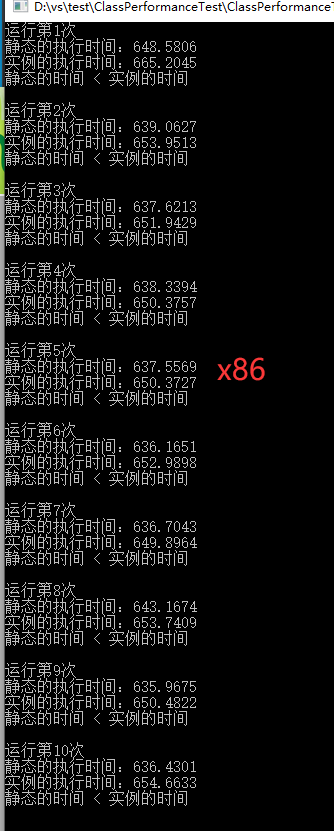

这种简单条件下的对比,从10个回合的测试结果可以得出以下总结
总结:
1、单从执行效率不考虑特性的情况下,使用静态方法还是有一点小优势的。
2、从x86和x64的对比数据上看,x64的执行效率比x86高出一大截。
建议:
具体还是要结合理论和实际来使用,静态方法写库和实例方法写库,都各有优缺点,比如
(1)从特性上考虑如果写调用频率很高的库就建议用静态库,因为静态库不用释放内存,不用每次申请开辟内存,调用简单,可以保障执行速度。
(2)实例库的优势是可以释放内存,可以申请多个实例进行传入不通属性处理,在一些经常需要处理占内存的活时,比如图片数据处理,大型数组处理,可以使用实例方法写库,用完就释放,避免长时间占用计算机内存。
(3)可以用x64尽量用x64。
在下不才,不能像太阳一样给你一片光明,但可以像星星一样献出一点光...



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号